i.i paper 1 (ucm)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
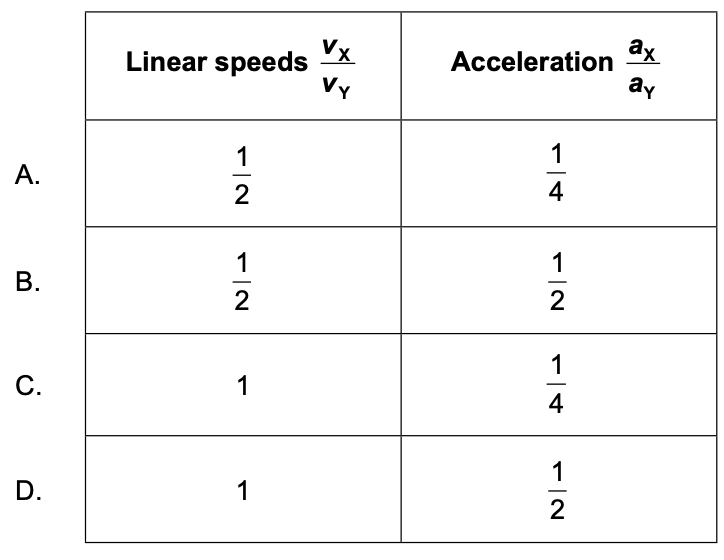
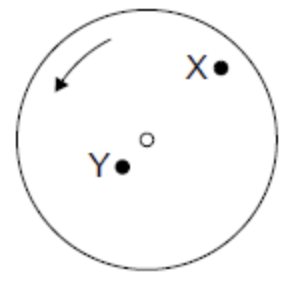
A disk of radius R rotates about its axis with angular speed ω . Point X is at a distance of R/2 from the centre and point Y is on the circumference.
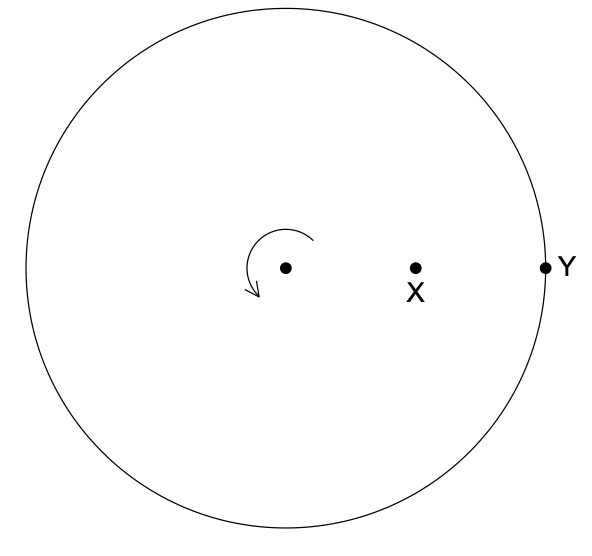 What are the ratios of the linear speeds and the centripetal acceleration of X to Y. The linear speed of X is vX and its acceleration is aX; the linear speed of Y is vY and its acceleration is aY
What are the ratios of the linear speeds and the centripetal acceleration of X to Y. The linear speed of X is vX and its acceleration is aX; the linear speed of Y is vY and its acceleration is aY

B
A particle of mass 0.02 kg moves in a horizontal circle of diameter 1 m with an angular velocity of 3π rad s-1.
What is the magnitude and direction of the force responsible for this motion?
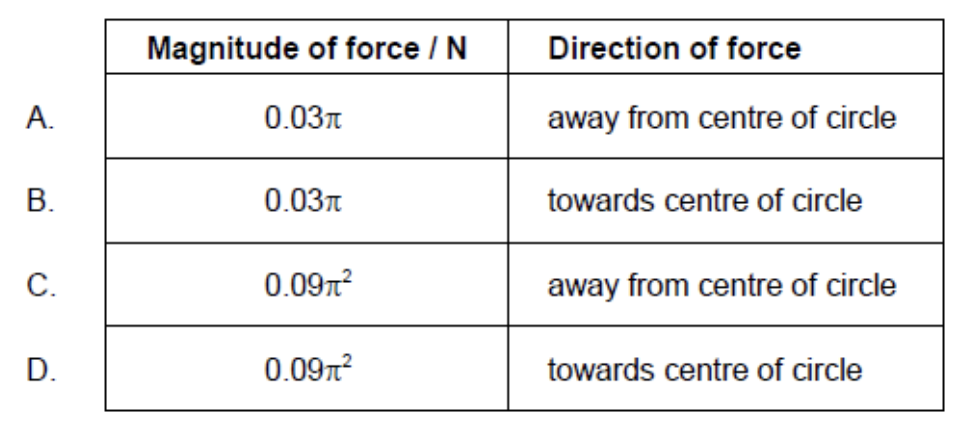
D
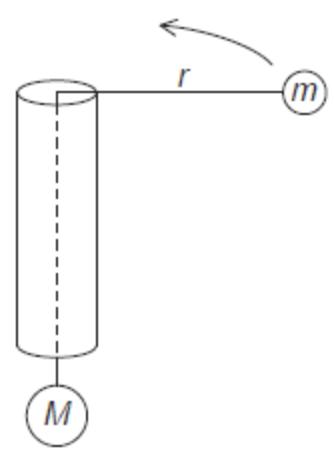
Mass M is attached to one end of a string. The string is passed through a hollow tube and mass m is attached to the other end. Friction between the tube and string is negligible.
Mass m travels at constant speed v in a horizontal circle of radius r. What is mass M?
A. mv²/r
B. mv²rg
C. mgv²/r
D. mv²/gr
D
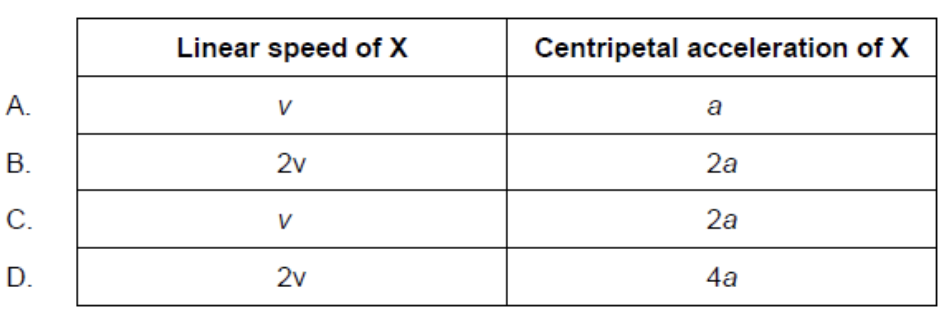
A horizontal disc rotates uniformly at a constant angular velocity about a central axis normal to the plane of the disc.
Point X is a distance 2L from the centre of the disc. Point Y is a distance L from the centre of the disc. Point Y has a linear speed v and a centripetal acceleration a.
What is the linear speed and centripetal acceleration of point X?
B
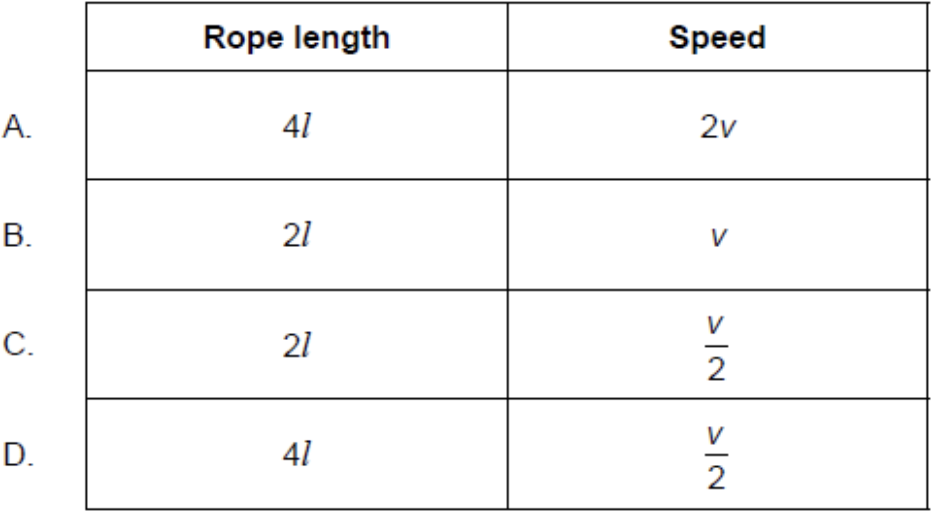
An object of constant mass is tied to the end of a rope of length l and made to move in a horizontal circle. The speed of the object is increased until the rope breaks at speed v. The length of the rope is then changed. At what other combination of rope length and speed will the rope break?
A
An object at the end of a wooden rod rotates in a vertical circle at a constant angular velocity. What is correct about the tension in the rod?
A. It is greatest when the object is at the bottom of the circle.
B. It is greatest when the object is halfway up the circle.
C. It is greatest when the object is at the top of the circle.
D. It is unchanged throughout the motion.
A
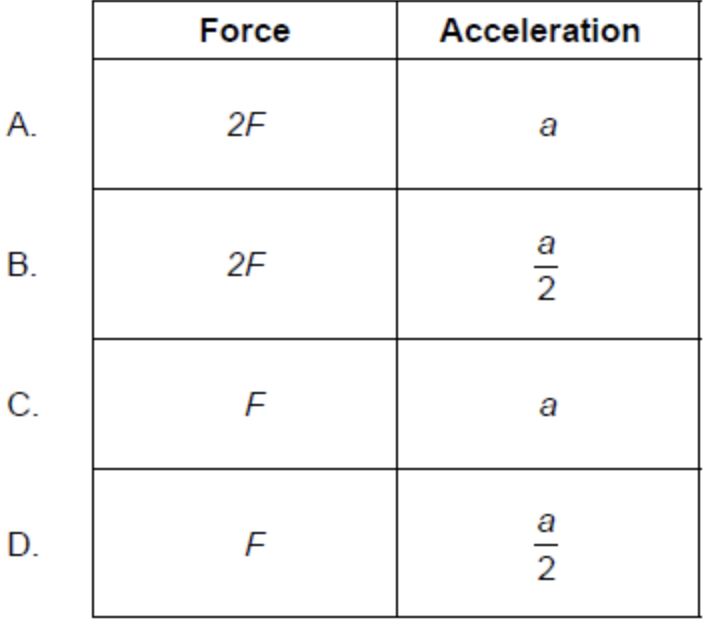
Two satellites of mass m and 2m orbit a planet at the same orbit radius. If F is the force exerted on the satellite of mass mby the planet and a is the centripetal acceleration of this satellite, what is the force and acceleration of the satellite with mass 2m?
A
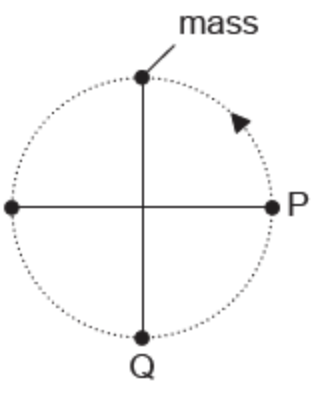
A mass attached to a string rotates in a gravitational field with a constant period in a vertical plane.
How do the tension in the string and the kinetic energy of the mass compare at P and Q?
B
An object of mass m at the end of a string of length r moves in a vertical circle at a constant angular speed ω.
What is the tension in the string when the object is at the bottom of the circle?
A. m(ω2r + g)
B. m(ω2r – g)
C. mg(ω2r + 1)
D. mg(ω2r – 1)
A
A satellite X of mass m orbits the Earth with a period T. What will be the orbital period of satellite Y of mass 2m occupying the same orbit as X?
A. T/2
B. T
C. √2T
D. 2T
B
A mass at the end of a string is swung in a horizontal circle at increasing speed until the string breaks.
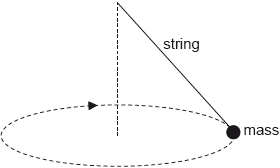
The subsequent path taken by the mass is a
A. line along a radius of the circle.
B. horizontal circle.
C. curve in a horizontal plane.
D. curve in a vertical plane.
D
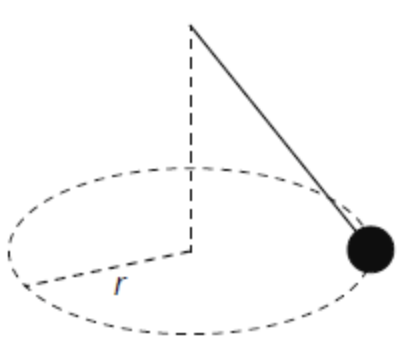
The mass at the end of a pendulum is made to move in a horizontal circle of radius r at constant speed. The magnitude of the net force on the mass is F.
What is the direction of F and the work done by F during half a revolution?
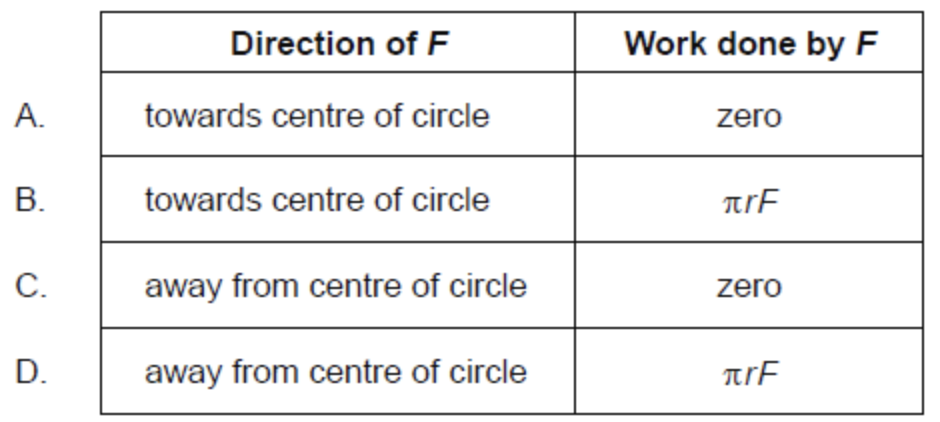
A
A motorcyclist is cornering on a curved race track.
Which combination of changes of banking angle θ and coefficient of friction μ between the tyres and road allows the motorcyclist to travel around the corner at greater speed?
A
Satellite X orbits a planet with orbital radius R. Satellite Y orbits the same planet with orbital radius 2R. Satellites X and Y have the same mass.
What is the ratio centripetal acceleration of X/centripetal acceleration of Y?
A. ¼
B. ½
C. 2
D. 4
D
A child stands on a horizontal rotating platform that is moving at constant angular speed. The centripetal force on the child is provided by
A. the gravitational force on the child.
B. the friction on the child’s feet.
C. the tension in the child’s muscles.
D. the normal reaction of the platform on the child.
B
Object P moves vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). Object Q moves in a vertical circle with a uniform speed. P and Q have the same time period T. When P is at the top of its motion, Q is at the bottom of its motion.
What is the interval between successive times when the acceleration of P is equal and opposite to the acceleration of Q?
A. T/4
B. T/2
C. 3T/4
D. T
B
A satellite is orbiting Earth in a circular path at constant speed. Three statements about the resultant force on the satellite are:
I. It is equal to the gravitational force of attraction on the satellite.
II. It is equal to the mass of the satellite multiplied by its acceleration.
III. It is equal to the centripetal force on the satellite.
Which combination of statements is correct?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
D
A mass at the end of a string is moving in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The string makes an angle θ to the vertical.
What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the mass?
A. g
B. g sin θ
C. g cos θ
D. g tan θ
D
An object moves in a circle of constant radius. Values of the centripetal force F are measured for different values of angular velocity ω. A graph is plotted with ω on the x-axis. Which quantity plotted on the y-axis will produce a straight-line graph?
A. √F
B. F
C. F²
D. 1/F
A
A sphere is suspended from the end of a string and rotates in a horizontal circle. Which freebody diagram, to the correct scale, shows the forces acting on the sphere?
D
A ball of mass 0.3 kg is attached to a light, inextensible string. It is rotated in a vertical circle. The length of the string is 0.6 m and the speed of rotation of the ball is 4 m s-1.
What is the tension when the string is horizontal?
A. 5 N
B. 8 N
C. 11 N
D. 13 N
B
An object hangs from a light string and moves in a horizontal circle of radius r.
The string makes an angle θ with the vertical. The angular speed of the object is ω. What is tan θ?
A. ω²r/g
B. g/ω²r
C. ωr²/g
D. g/ωr²
A
An object of mass m makes n revolutions per second around a circle of radius r at a constant speed. What is the kinetic energy of the object?
A. 0
B. ½π²mn²r²
C. 2π²mn²r²
D. 4π²mn²r²
C