APES - Unit 3 - Energy and Ecosystems
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
biogeochemical cycle
process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another
closed system
A system in which no matter is allowed to enter or leave
Geosphere
the solid part of the earth consisting of the crust and outer mantle
atmosphere
A thin layer of gases surrounding Earth
Hydrosphere
All the water at and near the surface of the earth, 97% of which is in oceans
Water Cycle (Hydrologic Cycle)
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
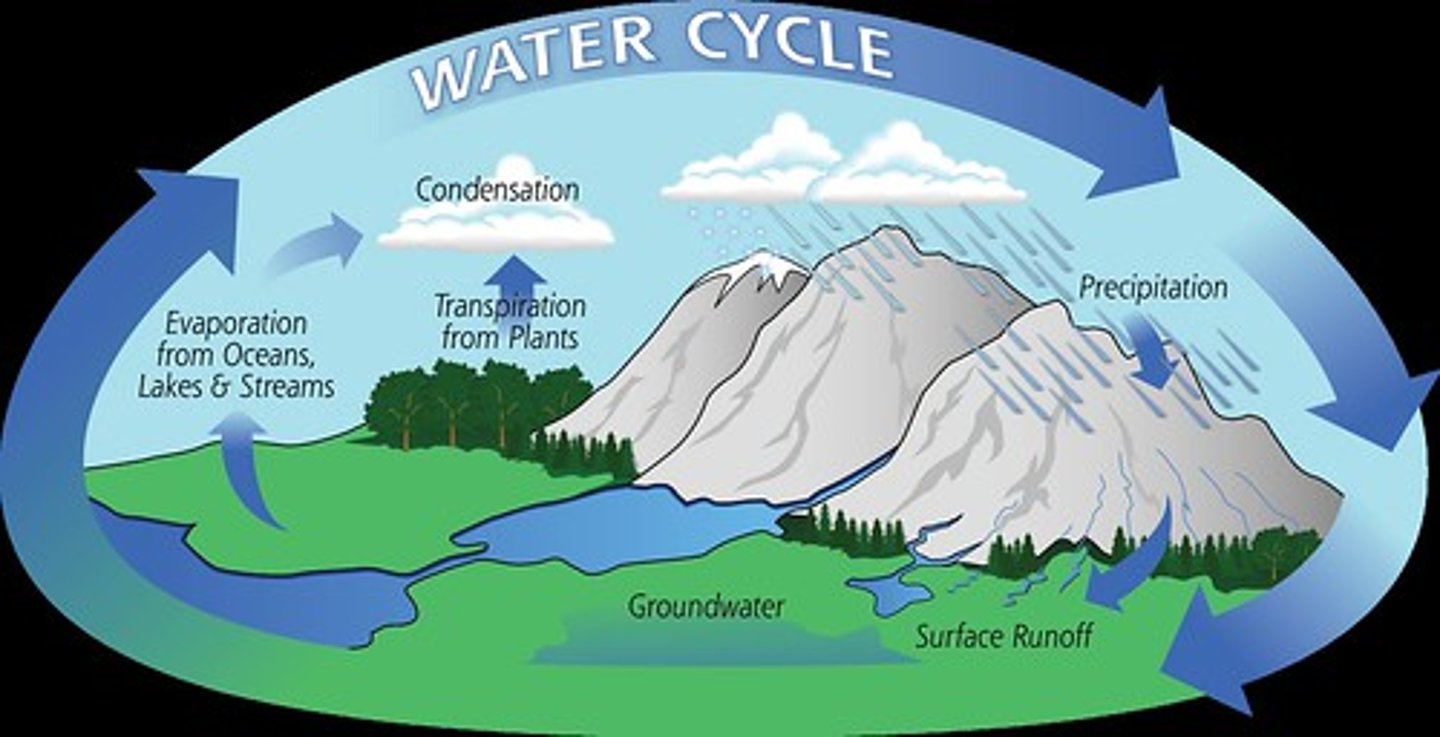
Evaporation (water cycle)
the process by which water changes from liquid form to an atmospheric gas
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
condensation
the cooling of water vapor that changes to water droplets that cling together -- CLOUDS form
Run-off
water leaves the soil and "runs" into bodies of water; sometimes this carries chemicals with it such as fertilizers
Infiltration
This is where water seeps through the ground and through the group and rocks to become groundwater
water cycle reservoirs
Ice/Snow/Lakes/ Groundwater/ Ocean
water cycle processes
precipitation, evaporation, condensation, transpiration
Human impact on water cycle most evident at ...?
rivers and aquifers
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
carbon cycle reservoirs
atmosphere, bodies of water, fossil fuels, peat, animals, plants
carbon cycle processes
photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion
nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
nitrogen fixation
process of converting nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds that plants can absorb and use
Nitrfication
The conversion of ammonia into nitrite and then into nitrate
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
bacteria that can use nitrogen in soil to make nitrogen compounds
Denitrification
process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas
nitrogen cycle - reservoirs
Atmosphere, organisms, sediments of aquatic biomes, soil
phosphorus cycle
The movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks.
Nutrient Cycle that doesn't cycle through the atmosphere
Phosphorous cycle
Phosphorus Cycle Process
Runoff, plate tectonics, erosion
phosphorus reservoirs
sedimentary rocks, soil, oceans, organisms
Sulfur Cycle Steps
As rocks are worn down by erosion they release sulfur that was once stored, becoming SO4 once it touches the air. Plants absorb this sulfur through photosynthesis and make this sulfur organic. Animals, specifically herbivores and omnivores consume the sulfur when they eat the plants. Sulfur moves through the food chain as secondary consumers and tertiary consumers eat the primary consumers. When animals and plants die, the sulfur dissipates into the atmosphere as sulfate and also through the body of the decomposers. The sulfur in the atmosphere is returned to the soil and water cycle when it rains
sulfer cycle
The chemical and physical reactions by which sulfur moves into or out of storage and through the environment.
human activity - sulfur cycle
burn sulfur, refine sulfur, convert sulfur
Air
n. the mixture of gases around the earth, mostly nitrogen and oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
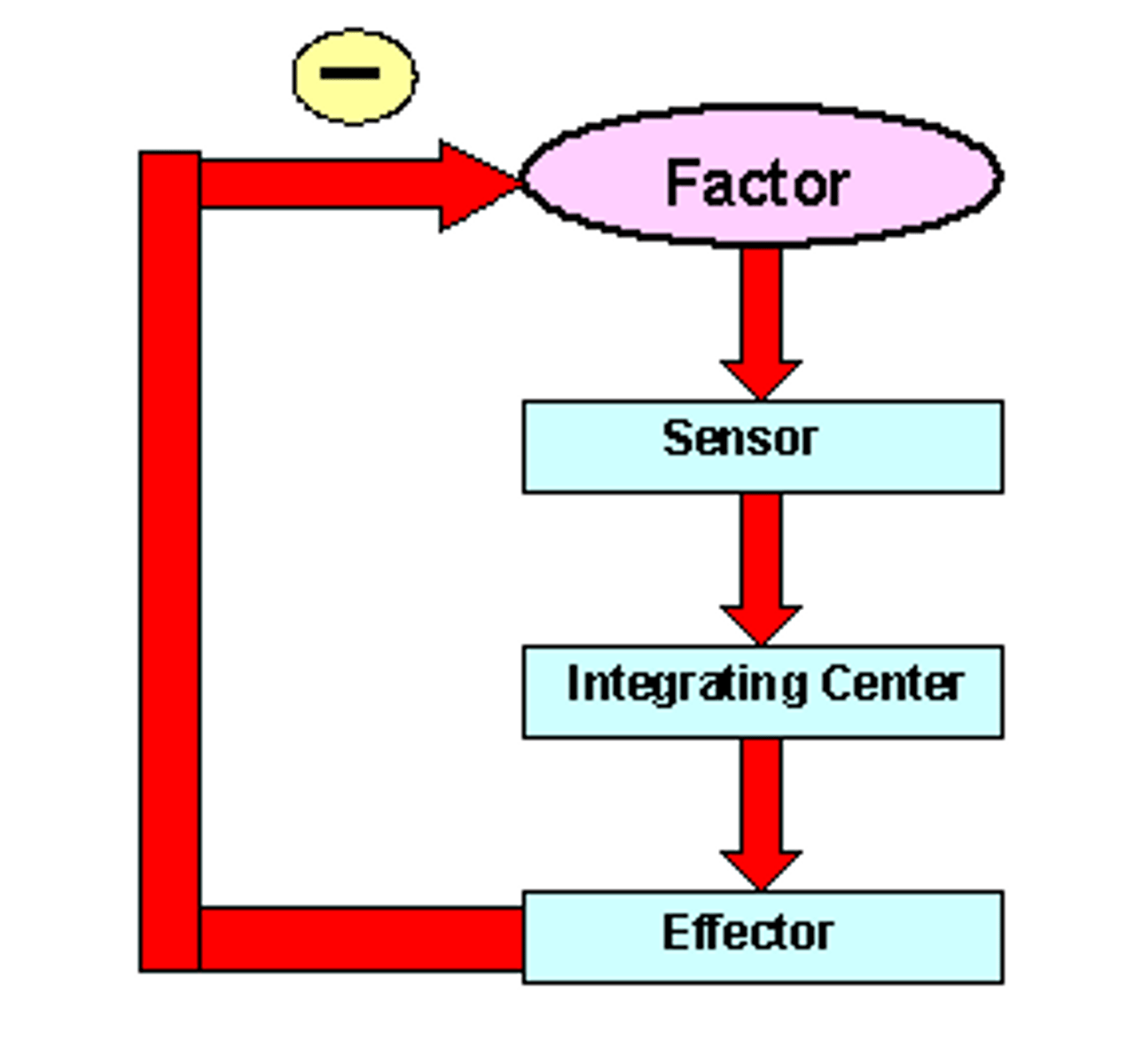
postivie feedback loop
A situation in which a factor or condition causes changes that further enhance that factor or condition.
potential energy
stored energy
kinetic energy
energy of motion
Forms of Potential Energy
chemical, nuclear, gravitational, or mechanical
Forms of Kinetic Energy
Radiant, thermal, motion, sound, electrical
chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
nuclear energy
Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
Stored Mechanical Energy
Energy stored in objects by the application of force
Gravitational energy
Potential energy that depends on the height of an object
radiant energy
energy carried by an electromagnetic wave
thermal energy
Heat energy
Motion Energy
the movement of objects and substances from one place to another
sound energy
energy carried by sound waves
electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
electromagnetic spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
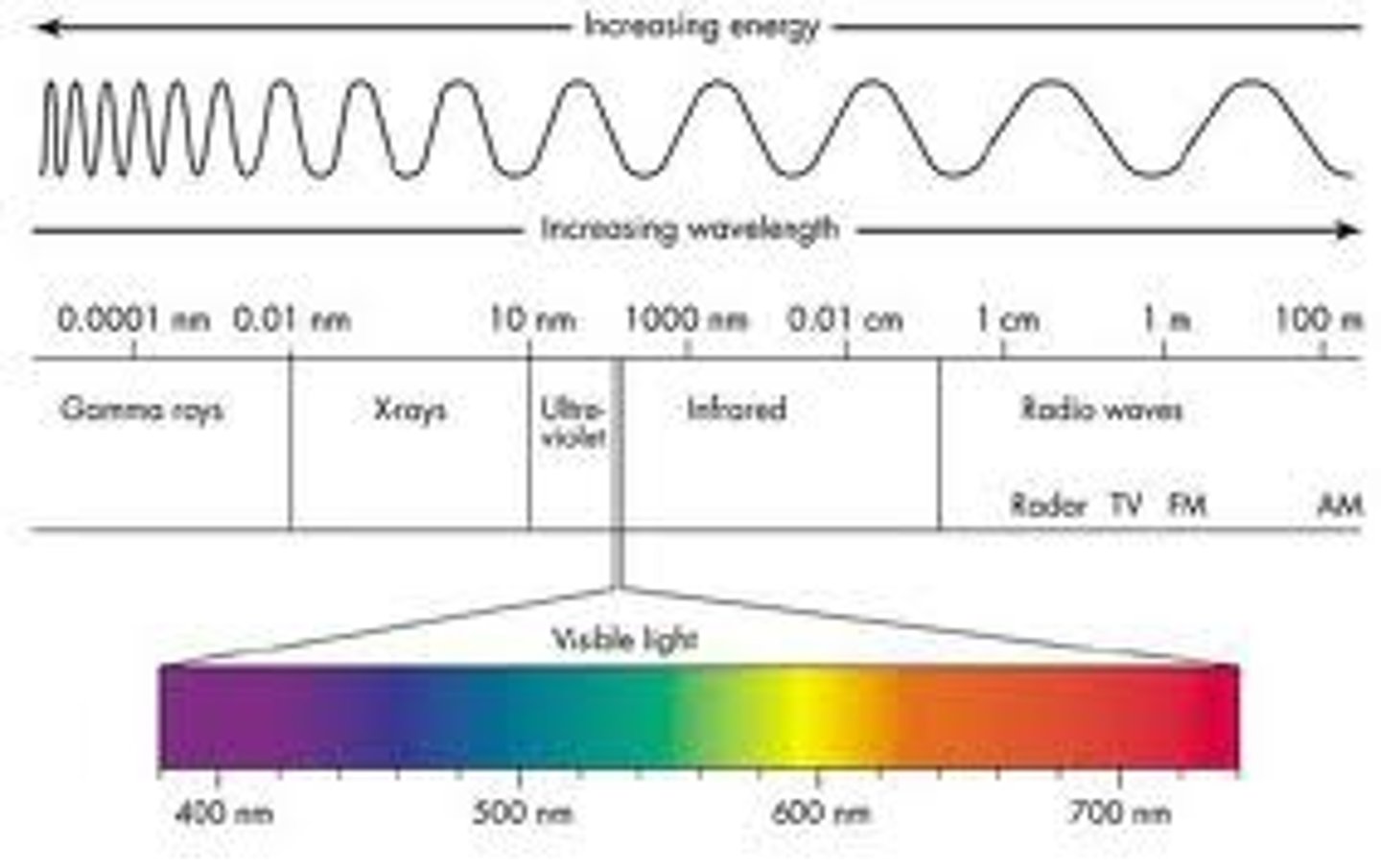
ultraviolet radiation
a type of energy that comes to Earth from the Sun, can damage skin and cause cancer, and is mostly absorbed by the ozone layer
Visible wavelength
range of wavelengths we can detect with our eyes
infrared
invisible short frequencies of light before red in the visible spectrum, heat energy
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6+6O2---> 6CO2+6H2O+ATP
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
trophic levels are
each step in a food chain or web
Producer
An organism that can make its own food.
Consumer
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
Detrivore
a scavenger, such as an earthworm, that feeds on dead plant and animal matter
energy pyramid
A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
10% rule of energy transfer
This rule specifically refers to energy transfer in a food chain.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
NPP formula
NPP = GPP - R
GPP formula
GPP = NPP + R
accessory pigments
energy absorbing plant pigments other than chlorophyll