Androgens
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the 6 facts about androgens?
Androgens are group names not single molecules
Synthesis of androgens and related steroid hormones are made from cholesterol
androgens have actions on multiple areas of the body including bone, muscle ,skin ,liver ,kidney, brain, immune system, bone marrow, and genital organs
Testosterone is the primary & most well known androgen
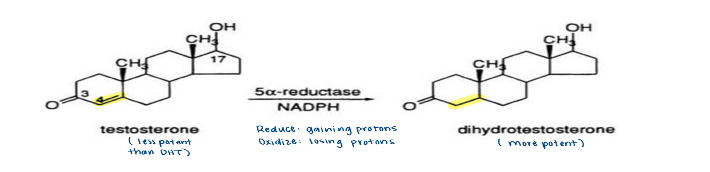
testosterone while active, is converted to more active form dihydrotestosterone
testosterone is made in testes(men) & ovaries(women) in adrenals (both genders)
Explain the steps in the synthesis of androgens
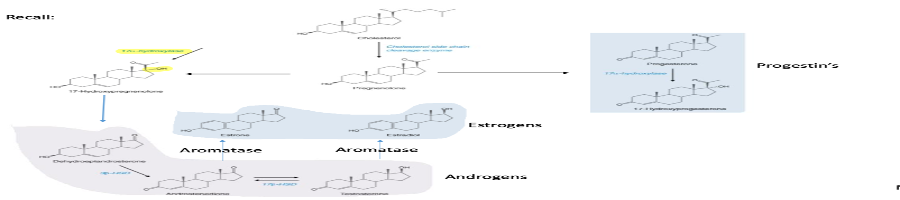
What is the 5 role of androgens in both genders?
helps with:
bone density
muscle development
puberty
red blood cell production
sexual desires & function
4 roles of androgens in women
regulate menstruation
aids conception & pregnancy
minimizes bone loss (osteoporosis)
stimulates pubic & underarm hair growth
3 roles of androgens in men
deep voice
hair growth on the face, scalp chest, underarm, genitals
sperm development
explain the steps & identify the hormones in androgen synthesis in the male reproduction system
LH stimulates testicular leydig cells to increase the synthesis of testosterone, which then diffuses into Sertoli cells
In the sertoli cells, FSH stimulation increases ABP, which is important for maintaining high testicular concentration of testosterone necessary for spermatogenesis
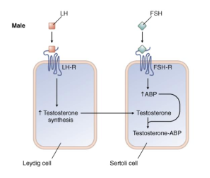
Testosterone has what 2 types of effects
androgenic effect
anabolic effects
explain androgenic effects
pertaining to the development of male characteristics
differentiation & growth of male reproductive organs
control of male sexual behavior, and the development & maintenance of male secondary characteristics that involve muscle, bone, larynx, hair
explain anabolic effects
Nitrogen retention by increasing the rate of protein synthesis & muscle mass while decreasing the rate of protein catabolism

MOA & regional effects of testosterone &DHT
Nuclear receptor located throughout the body. Testosterone & DHT have activity at these receptors
Testosterone: AR action in muscle, bone, brain, bone marrow; where anabolic effects are prevalent
DHT: AR action in genitalia, prostate, skin, and hair follicles due to higher expression of 5-alpha-reductase enzyme in these tissues
what enzyme converts testosterone to dihydrotesterone (DHT)?
5-Alpha-reductase
identify the hormones & explain the various steps in the testosterone control mechanism
Hypothalamic-pituitary testicular axis (HPTA)
hypothalamus makes LHRH (GnRH) and signals the pituitary to release LH/FSH
LH binds in the leydig cells & increases testosterone synthesis to fuse to the sertoli cells where FSH bins
Feedback control
Low concentration of testosterone or estradiol causes positive feedback and the body needs to make more (speed up the pulsatile to create more testosterone)
High concentrations causes negative feedback and the body needs to shut the pathway off (slows the pulsatile down, which its still producing GnRH but tells the pituitary not to do anything with it & not produce more testosterone)
male hypogonadism
testosterone deficiency
inability to produce sufficient testosterone to maintain sexual function, muscle strength,BMD, and fertility
What are the two basic types of male hypogonadism
primary: disorder of testes (LH & FSH elevated but testosterone is not produced by the testes)
secondary: caused by disorder of hypothalamus-pituitary axis
Klinefelter syndrome
primary hypogonadism
abnormality where two or more X chromosomes are present in addition to one Y chromosome
Hemochromatosis
primary hypogonadism
too much iron in blood producing testicular dysfunction
Injury or trauma to testicles
primary hypogonadism
not protected by body ,depends on extent of injury
Undescended testicles
primary hypogonadism
generally self-corrected or may require surgery
Kallmanns syndrome
secondary hypogonadism
hypothalamus can’t stimulate the release of hormone form the pituitary
loss of smell & red/green color blindness
Pituitary Disorders
secondary hypogonadism
tumor on or near the pituitary
radiation/chemotherapy
secondary hypogonadism
Describe the bioavailability of androgens
poor oral bioavailability
transdermal DHT has the most bioavailability
explain the structure activity relationship of androgens agonist when it comes to their potency
3-keto group
no 4,5 double bond
17-beta-alcohol
what does adding an alkyl chain do to agonist androgens ?
increases oral activity but decreases potency
what are the 3 types of androgen antagonist
androgen receptor inhibitors
5alpha reductase inhibitors
inhibitors of testosterone
what is the indications for androgen antagonist?
hormone treatment for prostate cancer (non-curative)
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
hair loss in males
excessive hair growth (hirsutism) in females
when is hormone therapy used for prostate cancer?
cancer has spread to far to be cured by surgery or radiation
reoccurrence of cancer
before (to shrink) or along with (for high risk reoccurence) radiation
How does hormone therapy work for prostate cancer?
prostate cancer needs androgens to grow
hormone therapies: decreases androgens levels or block androgen action
Androgen Antagonist; combine w/ luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist (Leuprolide & Goserelin) which results in medical castrations
what are the 4 SARs for androgen antagonist ?
ortho EWG groups on terminal benzene ring (cyano, trifluoro, chloro,nitro)