Skeleton study guide
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Support
Bearing the weight of the body
2
New cards
Protection
Encasing essential organs; ribcage protects heart and lungs
3
New cards
Movement
Joints provide movement for bones
4
New cards
Storage
Storage of minerals to be released into the bloodstream; Storage of fat in yellow bone marrow
5
New cards
Manufacturing
Of red and white blood cells from red bone marrow; called hematopoiesis
6
New cards
Bones are a solid 1) _____ of living 2) ____ and 3) ____ surrounded by 4) _____ deposits. Bones are classified by their 5) _____.
1) matrix, 2) cells, 3) fibers, 4) calcium, 5) shape
7
New cards
Flat bone
8
New cards
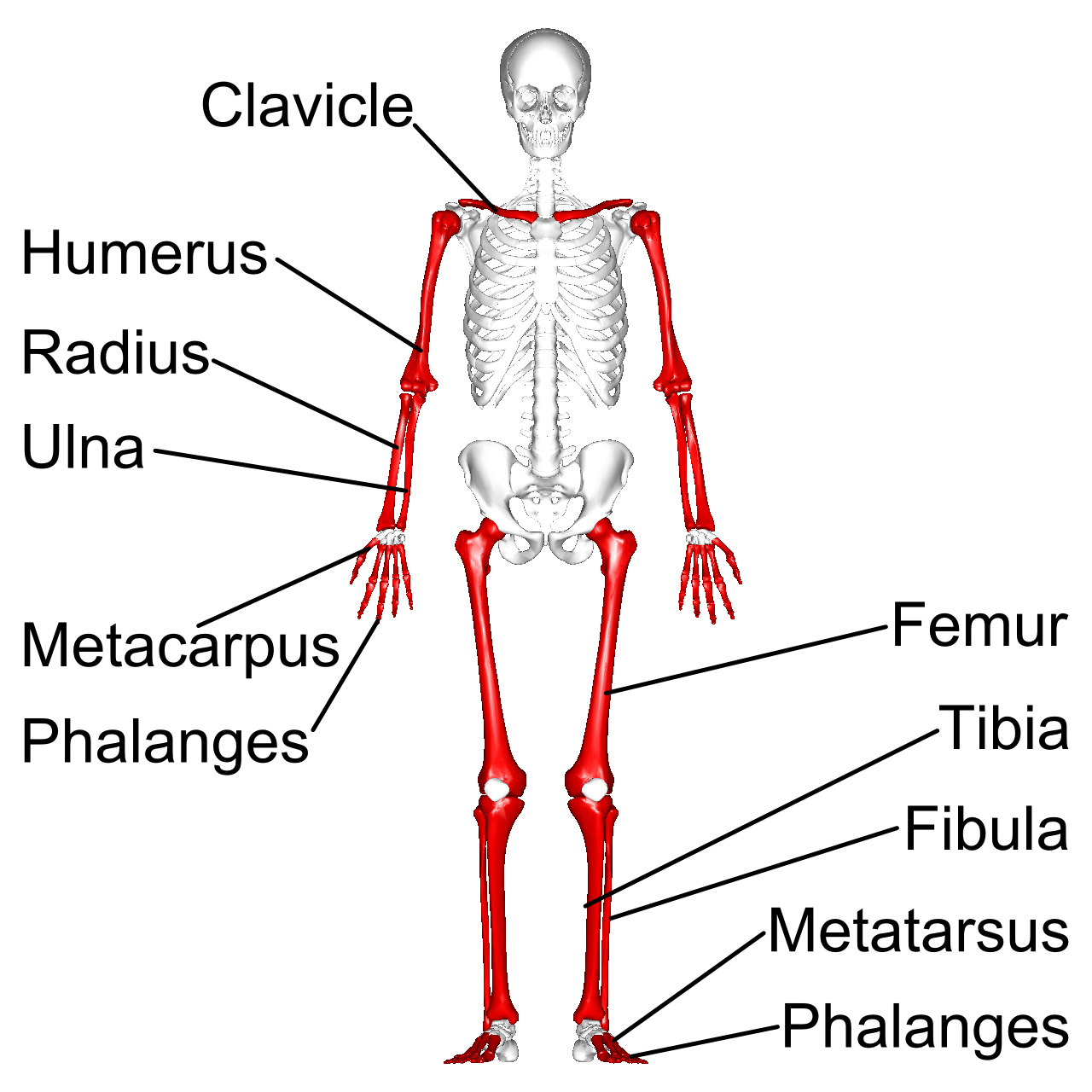
Long bones
9
New cards
Sesamoid bone
10
New cards
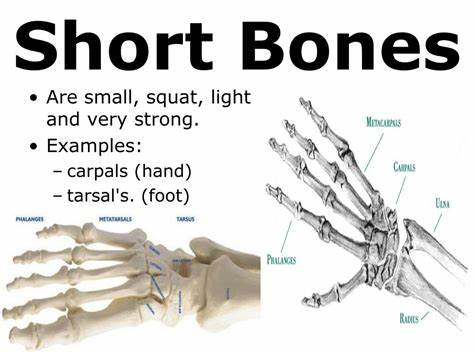
Short bone
11
New cards
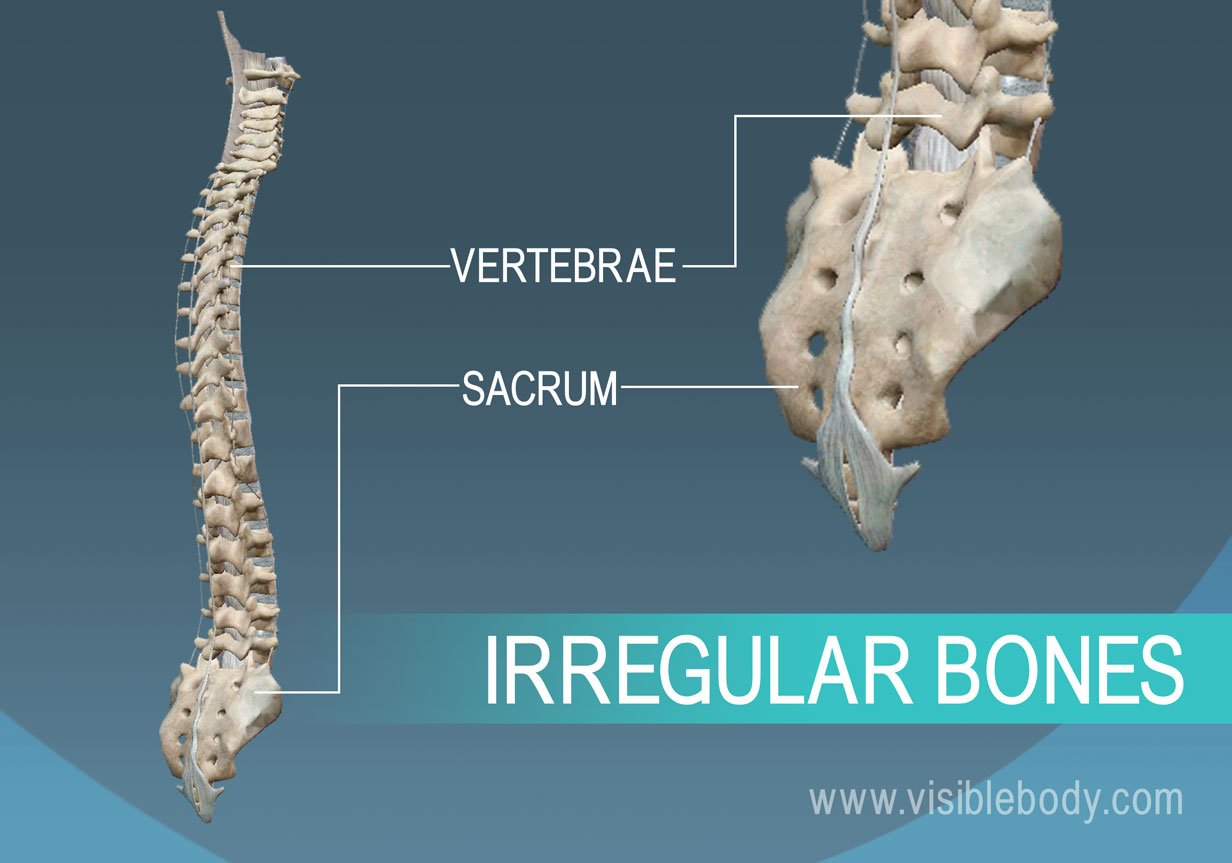
Irregular bone
12
New cards
Long bone 2 basic regions
Diaphysis: short, long part of the bone
Epiphyses: ends of the bone
Epiphyses: ends of the bone
13
New cards
also called the growth plate
Epiphyseal plate
14
New cards
- what the ends of the epiphyses are covered with
- which provides smooth 1)______ of joints and cushion from 2)_____
- which provides smooth 1)______ of joints and cushion from 2)_____
- an external layer of cartilage called articular cartilage
- 1) movement, 2) shock
- 1) movement, 2) shock
15
New cards
what is found in the diaphysis of the long bone
Medullary cavity
16
New cards
which bone marrow fills the cavity of young people
Red
17
New cards
Age causes red bone marrow to be replaced with 1) ______. it is within the bone marrow that new 2) ______ are produced. (called 3) _______.
1) fatty yellow bone marrow, 2) blood cells, 3) hematopoiesis
18
New cards
the outer layer of the bone made of tough connective tissue called 1) _______. It is the location of 2) ______ attachment and bone 3) ______.
1) periosteum, 2) muscle, 3) repair
19
New cards
A thick layer of what is beneath the periosteum
compact bone
20
New cards
what is beneath the compact bone at the ends of the long bones
the spongy bone layer
21
New cards
what is spongy bone a lattice of ("little beams") that are found along the 1) __________ for perfect resistance from 2) _______?
trabeculae, 1) lines of stress, 2) compression
22
New cards
what is compact bone arranged in
cylinders called osteons
23
New cards
osteons are arranged in concentric circles called 1) _______
1) lamellae
24
New cards
what does lamellae surround that contains blood vessels and nerves?
a central (or haversian) canal
25
New cards
what are central canals connected by that runs perpendicularly?
perforating (Volkmann's) canals
26
New cards
osteocytes
mature bone cells that make up majority of the bone structure
27
New cards
osteoclasts
break down bone
28
New cards
osteoblasts
produce new bone
29
New cards
what connects all bone cells, allowing them to receive nutrients and remove wastes?
Canaliculi
30
New cards
what is an embryo's skeleton made of?
cartilage
31
New cards
what happens near the third month f embryo development?
osteoblasts secrete mineral deposits that replace the cartilage. They then mature into osteocytes
32
New cards
ossification
the process of incorporating calcium and minerals into cartilage to become bone
33
New cards
as a child grows, tall columns of 1) _____ (cartilage cells) at the epiphyseal plate divide and then deteriorate as the matrix around them 2) ______. these cells are known as 3) ______, which form spongy bone.
1) chondrocytes, 2) calcifies, 3) osteoblasts
34
New cards
what do osteoblasts secret to enlarge the medullary cavity as the bone grows so that marrow is available for all cells?
Acid
35
New cards
Osteoid
35%, made of ground substance and collagen, provides flexibility and tensile required to keep bones from breaking, and lack of collagen causes brittle bone disease.
36
New cards
Mineral salts
65%, made of hydroxyapatites, provides bone strength and hardness, and lack of hydroxyapatite causes rickets.
37
New cards
two hormones that trigger bone formation and remodeling:
Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone
38
New cards
Calcitonin
deposits extra calcium from blood into bones
39
New cards
parathyroid hormone
stimulates osteoclasts to break down bone, adding calcium to blood
40
New cards
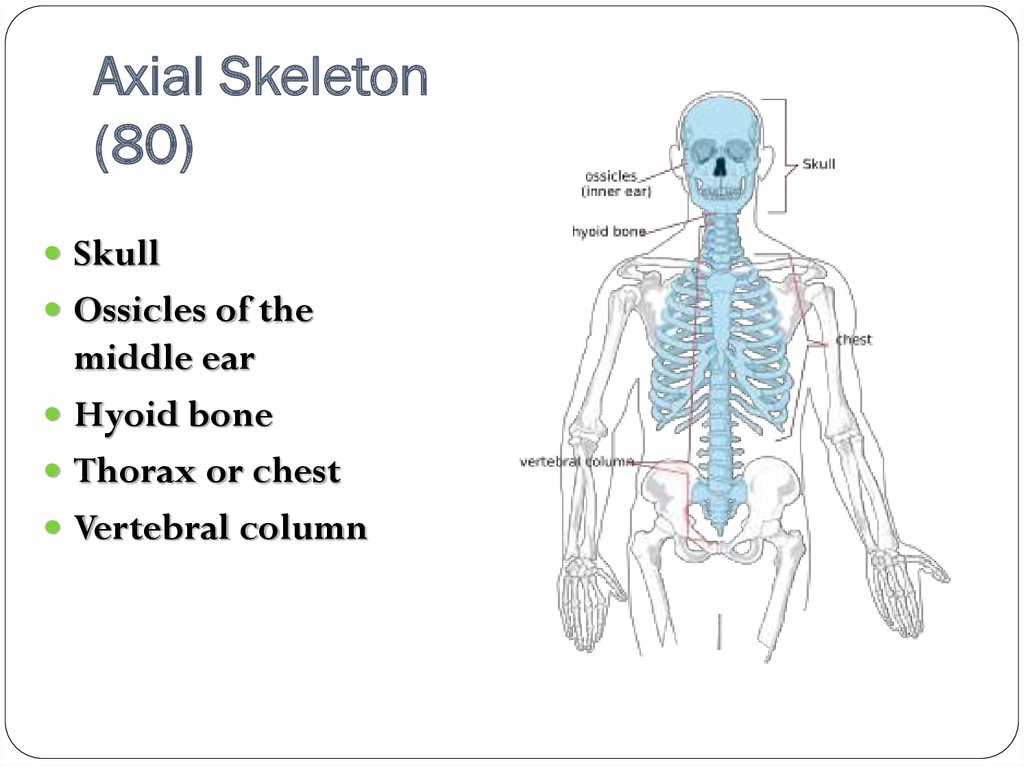
Axial skeleton (80 bones)
41
New cards
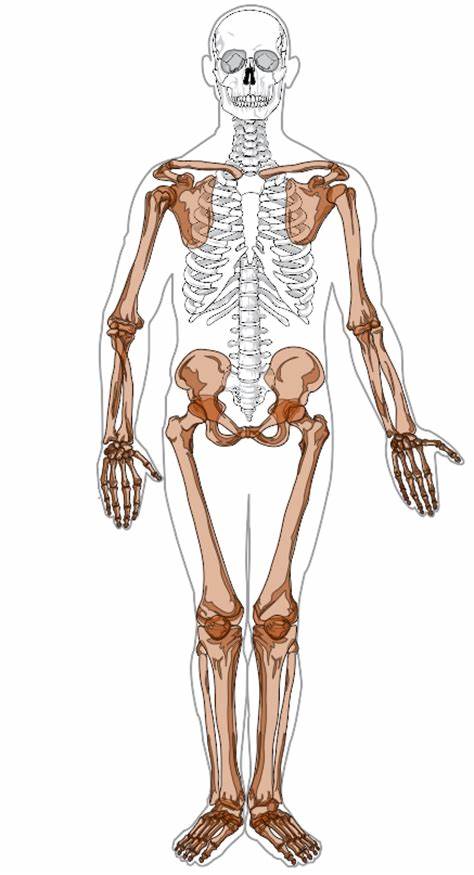
appendicular skeleton (126 bones)
42
New cards
where does the vertebral column extend from, provide, and protect?
from the skull to the pelvis, provides support, and protects the spinal cord.
43
New cards
how many vertebrae are there at birth?
33
44
New cards
which and how many vertebrae fuse together in adolescence?
5 sacral and 4 vertebrae of the coccyx
45
New cards
what are the remaining vertebrae separated by and what do they provide and absorb?
they are separated by intervertebral discs that provide cushioning and absorb shock
46
New cards
The spine is 1) ________ curved at birth, but two portions (in the cervical and lumbar vertebrae) develop 2) _______ curves later in life.
1) convexly, 2) concave
47
New cards
The 1) ________ (convex) and 2) ____________ (concave) curvatures of the spine allow for better 3) __________ and distribution of 4) ___________ throughout the body.
1) primary, 2) secondary, 3) balance, 4) weight
48
New cards
Fibrous
immovable or slightly, held together by fibrous connective tissue; ex: teeth
49
New cards
Cartilaginous
immovable or slightly, held together by cartilage; ex: lumbar vertebrate
50
New cards
Synovial
Highly movable, contains synovial fluid for frictionless movement
51
New cards
a joint capsule filled with what surrounds the end of the bones?
Synovial fluid
52
New cards
what lines the joint cavity?
a synovial membrane and articular cartilage
53
New cards
what surrounds the end of the bones?
a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid
54
New cards
ligaments
connect bone to bone
55
New cards
tendons
connect muscle to bone