Biology- Genes and Health
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 2 of A-level Biology (Salters Nuttfield)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are proteins’ fuctions and what do they make up?
Fuctions: antibodies, enzymes, hormones
Make up: muscles, ligaments, tendons and hair.
They also play a role in cell membranes.
Whats the general structure of an amino acid?
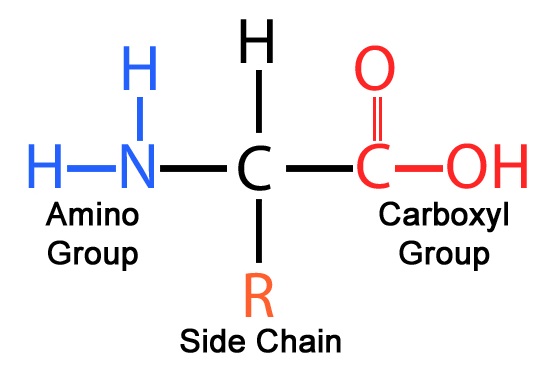
How/why do amino acids form ions in a solution?
They are soluble in water.
The hydrogen ion leaves the carboxylic acid group and another hydrogen ion joins the amino group.
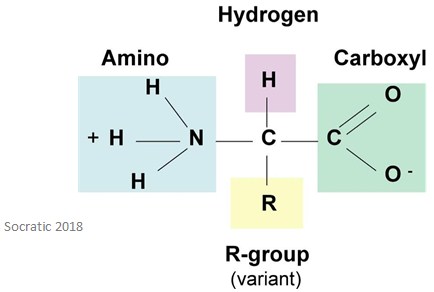
What is the structure of an amino acid dissolved in water?
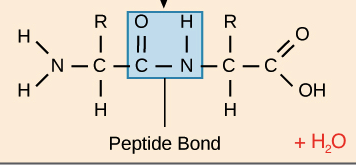
Explain what happens in a condensation reaction with amino acids
Two amino acids join and form a dipeptide, with a perptide bond forming between the two subunits. When many amino acids join together through a condensation reaction, they form a chain called a polypeptide.
How can peptide bonds between amino acids be broken?
Peptide bonds between amino acids can be broken by hydrolysis, which involves adding a water molecule to break the bond. This process can occur naturally in the body via enzymes like proteases or be induced in labs using acids or bases.
brief overview of cystic fibrosis. include symptoms, statistics and what type of gene
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder impacting the lungs and digestive system.
Persistent cough, Frequent lung infections, Difficulty breathing, Poor growth and weight gain, Digestive issues
Affects about 1 in 25 people.
CF is caused by a recessive gene.
What is the structure of amino acids with peptide bond?
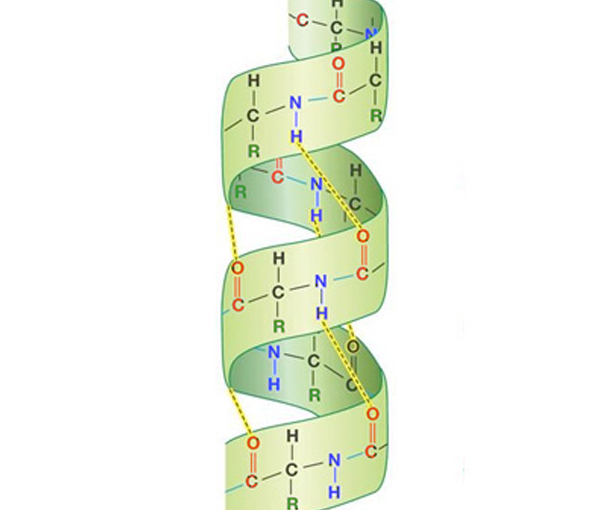
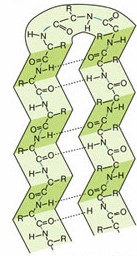
Explain the alpha helix structure
Hydrogen bonds form between the δ- C=O and the δ+ -NH of different amino acids that lie above and below each other
Hydrogen bonds form every 4th amino acid
Sections of alpha helix can be up to 35 amino acids long.
Explain beta-pleated sheet
Formed by amino acid chains folding back on themselves
Folds are linked together by hydrogen bonds.
Parallel chains held together in this way.
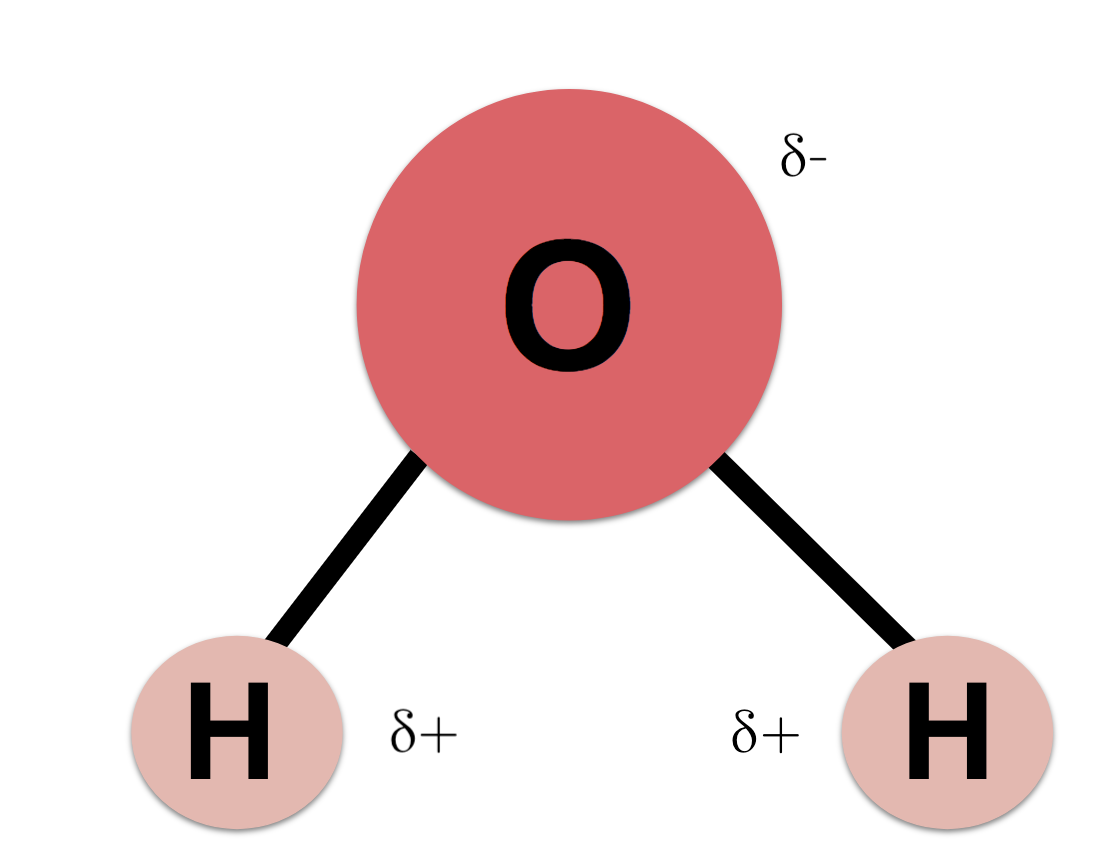
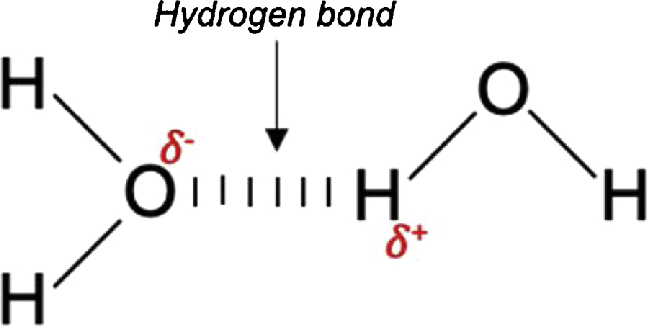
Explain Hydrogen bonding.
Water is polar (uneven distribution of charge)
The Hydrogen end is δ+ and the Oxygen end is δ-
Oxygen in water ha a greater affinity so ‘pulls’ the electrons closer making the oxygen slightly negative and the hydrogen slightly positive.
Explain tertiary protein structure
A polypeptide chain bends and folds further to produce a precise 3D shape.
Chemical bonds and hydrophobic interactions between R-groups maintain this final tertiary structure of the protein.
The three bonds resposible; hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds.
Explain Hydrogen bonds
Can be broken by high temperatures and altered pH.
Explain ionic bonds
Can be broken by changing the pH.
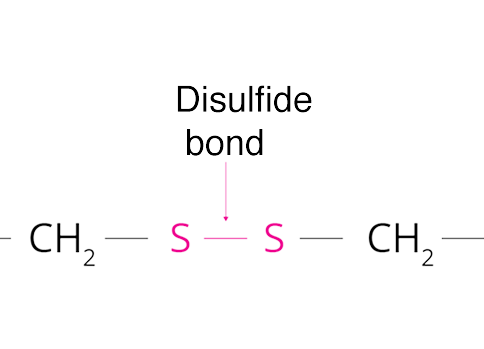
Explain dilsulphide bonds
Can be broken by reducing agents.
Explain Van der Waal’s forces
Weak forces of attraction between non-polar groups.
Water excluded from these hydrophobic side chains helps keep the side chains together.
These force can be split by a rise in temperature.
Explain hydrophilic interactions
An R-group is pola when the sharing of the electrons within it are not quite even.
Polar R-groups attract other polar molecules and are therefor hydrophilic.
Explain hydrophobic interactions
They are non-polar and are arranged so that they face the inside of a protein, excluding water from the centre of the molecule.
Explain quaternary protein structure
Quaternary protein structure refers to the assembly of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) into a single functional protein complex. These subunits can be identical or different and are held together by various interactions, including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions. This structure is crucial for the protein's functionality, as it can affect the protein's stability, activity, and regulation.
Explain globular proteins
Polypeptide chain folded into a compact spherical shape.
They are soluble
Hydrophilic side chains project out and they are therefore important in metabolic reactions
Examples; enzymes, transport of protein in membranes, antibodies and oxygen transport
Explain fibrous proteins
They remain a long chains and are often cross linked to increase strength
They are insoluble
They are important in structural molecules.
Examples; keratin, collagen, tendons, cartialge and blood vessel walls
Explain the movement of air through the respitory system.
Air enter through the nose/mouth and passes down the trachea → air travels down until it divides tnto the two bronchi → the bronchi divide into many smaller bronchioles, increaing surface area → the brochioles terminate with alveoi, where gas exchange with the bloodstream occurs
Explain why air is drawn in and out
In= via the trachea due to a low pressure in the lungs → increase in volume of the thorax, ribs move up, diaphragm moves down
Out= due to a rise in pressure in the lungs → diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, causes reduced volume and increased pressure.
Explain the role of mucus
Mucus lines the tubes of the gas excahnge system and removes dut debris and microorganisms.
Its produced continuously by globlet cells
Wave-like beating of cilia continuously remove mucus.
Pathogens trapped in the mucus usually get coughed out or swallowed.
Explain the difficulties for people with CF
Mucus contains less water and is stickier, making it harder to move → increases chance of lung infection and makes gas exchange less efficient.
The mucus is still produced so there is a large build up → low oxygen levels due to poor diffusion and epithelial cells creates anaerobic conditions
White blood cells fight the infections within the mucus but as they die, they break down and release DNA that makes the mucus stickier.
Why do gas exchange systems rely on a large surface area:volume ratio?
Gases cross the walls of the alveoli into the blood system by diffusion. They need a large surface area:volume ratio to supply enough oxygen to all the body’s respiring cells.
Define diffusion and give examples of things that effect the rate of diffusion
Movement of particles from a high to low concentration
Concentration gradient, temperature (in plants), surface area, length of diffusion pathway.
What’s Fick’s law
The rate of diffusion is proportional to both the surface area and concentration difference and is inversely proportional to the thickness of the membrane
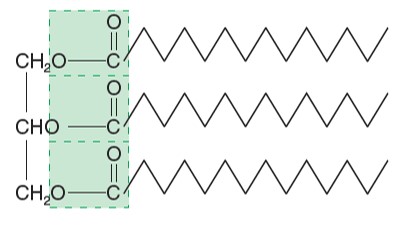
Explain what a triglyceride is
A glycerol that is made up of three fatty acids
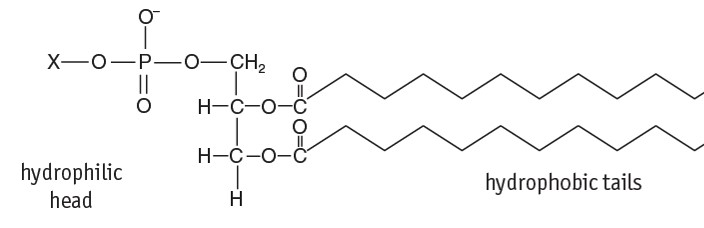
Explain what a phospholipid is
A glycerol with two fatty acids. A negatively charged phosphate group has replaced the third fatty acid and this makes it a polar molecule.
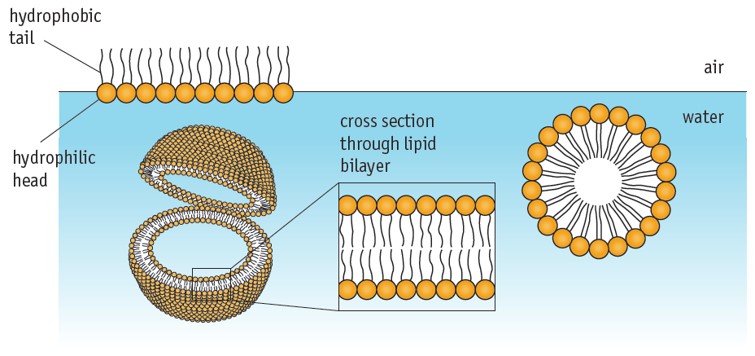
Ehen phospholipids are added to water…
They arrange so there no contact between the hydrophobic tails and the water.
What are the parts of the fluid mosaic model?
glucoproteins
glycolipids
integral membrane proteins
protein channels
phospholipid bilayer
cholesterol
peripheral membrane protein
cytoskeletal filaments
Explain diffusion
Particles are constantly moving in all directions. They move from a high to low concentration resulting in overall net movement. It only occurs when theres a concentration gradient and it continues until equilibrium.
Explain facilitated diffusion
Hydrophobic molecules and ions cannot simply diffuse through the bilayer because they’re insoluble in lipids so instead they cross the membrane with the aid of proteins.
What is a channel protein?
They are water filled pores that span the membrane. Theres a different channel protein for different molecules. Each has a specific shape so only one ion can be let through.
Explain gated channel proteins
Channel proteins that can be opened or closed depending on; presence/absence of a signal (ligand-gated) or a change in potential difference (voltage-gated)
Explain carrier proteins
Ions/molecule bind onto a specific site of the protein which causes the protein to change shape, allowing ions/molecules to cross.
Define osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a solution with a lower concentration of solute to a solution witha higher concentration of solute through a partially permeable membrane.
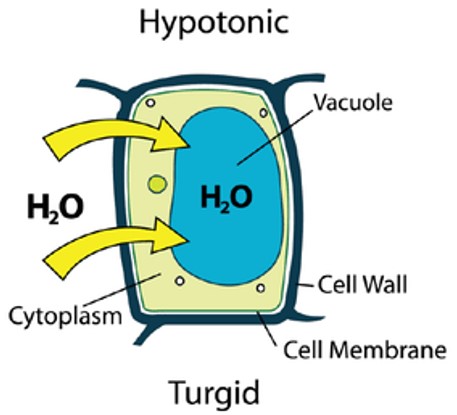
Explain hypotonic osmosis
less concentrated solution
water move into cell
plant cells swell and become turgid
the strong cell wall prevents bursting
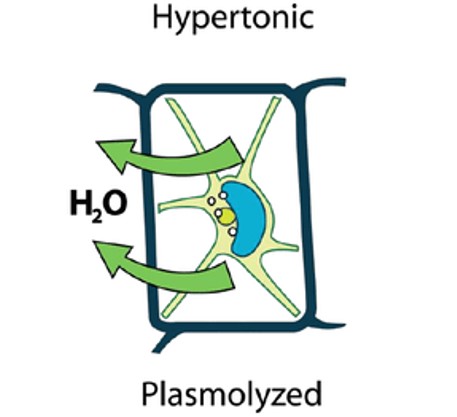
Explain hypertonic osmosis
a more concentrated solution
water moves out of the cell
plant cells become plasmolysed or falccid
membrane and cytoplasm shrink away
What are globlet cells?
Cells that line the airways and produce mucus
How is regulation of mucus achieved?
By the transport of sodium and chloride ions across epithelial cells.
What the lock and key theory?
only a complementary shaped substrte can fit into the active site of the enzyme
substrates and amino acids form temporary bonds in the active site (enzyme substrate complex)
the enyme holds the substrate so they react easily and it remains unchanged
Whats the induced fit theory?
the active ite is flexible and can be changed
when the subtrate enters the active site, the enzyme changes shape slightly which enables the substrates to react
How do enzymes reduce the activation energy?
attraction of the oppositely charged groups distorts the shape of the substrate
they assist in the breaking of bond or formation of new bonds
in some cases, the active site contains amino acids with acidic side chains
the acidic enviroment can provide favourable conditions for the reaction
What does intercellular and extracellular mean?
reactions within the cells
reactions outside the cells
What do catabolic and anabolic mean?
reactions that break down the substrate
reactions that build up the substrates
What are the factors that affect rate of reaction?
increasing temperature= speeds up reaction and more collisions
enzyme concentration
substrate concentration
pH
Summarise the simple info on DNA
forms the genome
the stands are diploids
its located in the nucleus (or cytoplasm) and found in many cells
a nucleic acid- deoxyribonucleic acid
a polymer with individual units called nucleotides- mononucleotides
What do nuceotide have?
a phosphate group
a pentose sugar
an organic base (C+G,T+A)