Geography 232 Test EVENTS
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:50 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Ethnicity
The equivalent of a language group and connects with a nation. (think of all the different kinds of these in India)
2
New cards
Nativism
A political outlook that immigrants are seen as a threat and are dangerous (think of the group “The Know Nothings”)
3
New cards
Geographic Connectivity
If you look at a map of the world and their transportation connections, some places are better than others. A place with lots of transportation connections would have a higher level of ______________
4
New cards
Chain Migration
Once you get a concentration of a certain ethnic group in a certain place, that place will start to draw more people from that ethnic group (ex. you have a cousin that lives in Chicago, so you move there to be close to them)
5
New cards
Quota System
The US would take a certain number of immigrants from each country (most countries were allowed none other than Denmark, Sweden, and other white countries)
6
New cards
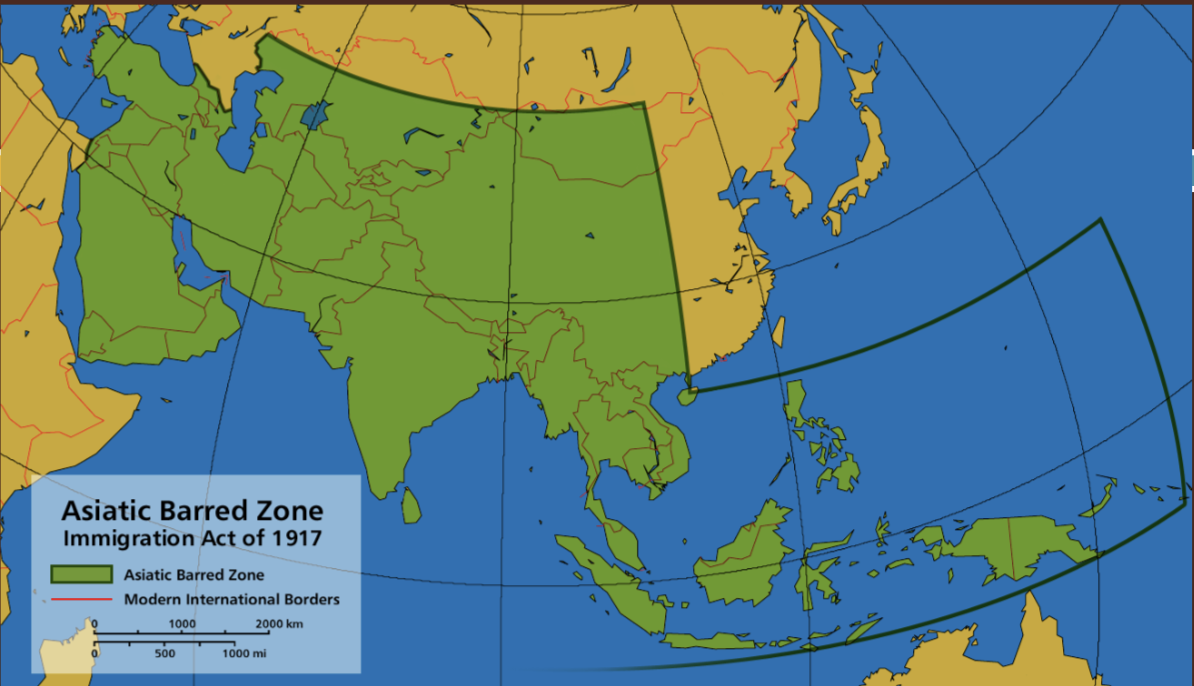
Asiatic Barred Zone - Immigration Act of 1917
Congress signed a law that said anything in the green part would not be allowed to immigrate to the US (From Turkey to halfway through China)
7
New cards
What countries immigrated to the US the most during Old Immigration?
Northern and Western Europe (England, Scotland)
8
New cards
What countries immigrated to the US the most during New Immigration?
Southern and Eastern Europe (Italy, Poland, Ukraine, Russia)
9
New cards
How did residents of the US feel about the shift in the demographics of immigrants during New Immigration?
A nativist backlash swept the nation, and many people saw this as a threat to democracy
10
New cards
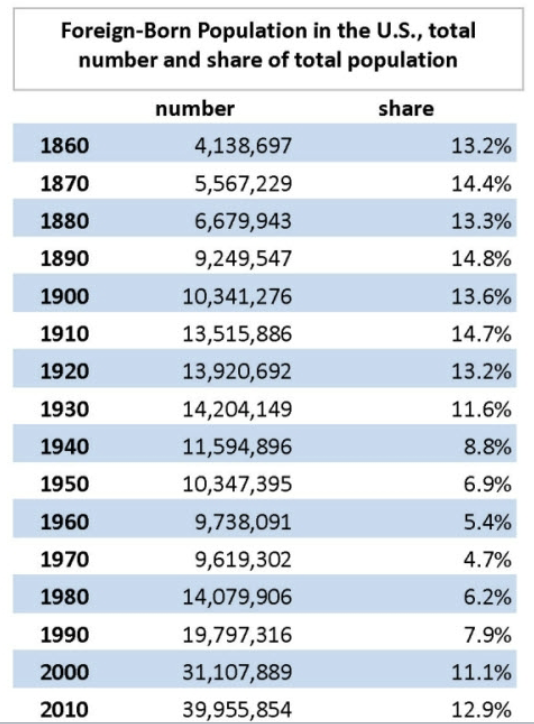
How does the % of foreign born citizens change throughout the Immigration period?
Just like the graph, there is a peak in the 1910’s, a trough in the 1960’s, and another expansion shortly after
11
New cards
What were some “Push” factors?
\-Massive surplus in European population
\-”Disruption” of the Industrial Revolution in Europe to small business owners
\-”Disruption” of the Industrial Revolution in Europe to small business owners
12
New cards
What were some “Pull” factors?
\-Huge demand for labor in the US due to industrial revolution
\-Cheap farming land to continue agricultural way of life
\-Cheap farming land to continue agricultural way of life
13
New cards
What was the time period in Wisconsin when Native American claims to land were extinguished?
1829-1842
14
New cards
What group began settling in Wisconsin first, and were did they settle?
Germans settled in the southern part of the state
15
New cards
What was the geography of settlement in Wisconsin?
South to North
16
New cards
What were some of the “Push” factors in the Wisconsin case study?
\-Population boom in Germany
\-Farmland consolidation
\-Industrialization in Germany
\-Religious freedom
\-Avoidance of the draft
\-Farmland consolidation
\-Industrialization in Germany
\-Religious freedom
\-Avoidance of the draft
17
New cards
What were some of the “Pull” factors in the Wisconsin case study?
\-Lots of cheap, good farmland
\-WI gave voting rights to immigrants after one year of being a citizen
\-Bankruptcy laws made homesteading less risky
\-State Immigration Commission
\-Feedback loop (they would tell family members how great Wisconsin was)
\-WI gave voting rights to immigrants after one year of being a citizen
\-Bankruptcy laws made homesteading less risky
\-State Immigration Commission
\-Feedback loop (they would tell family members how great Wisconsin was)
18
New cards
Where did earlier arriving groups settle?
In rural areas starting in the East, and moving towards the West
19
New cards
When did later arriving groups settle?
Urban areas
20
New cards
Were was German settlement primarily?
Midwest in rural cities (they had the most immigrants)
21
New cards
Where was Irish settlement primarily?
Highest concentration in the Northeast, but basically the whole country (they immigrated throughout all of Old Immigration and went where the opportunity was)
22
New cards
Where did the Russian’s settle primarily?
South and North Dakota because they arrived LATER
23
New cards
Racialized Slavery
Race and slavery overlap in a legal sense - slavery based on racial stereotypes
24
New cards
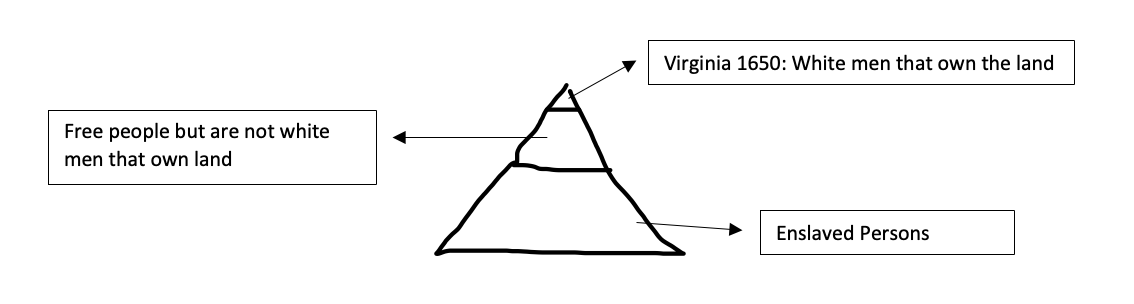
Racialized Hierarchy
A society that has stratifications based on power where racial identity figures are used
25
New cards
Chattel Slavery
Permanent and hereditary slavery
26
New cards
What were the regions of the US that chattel slavery was developed around?
Virginia down to Georgia
27
New cards
What are the four cultural hearths in terms of slavery?
The North, The Midland, Upper South, and Lower South
28
New cards
What was the anchor city for The North, and was there slavery?
Massachusetts, no
29
New cards
What was the anchor city for The Midland, and was there slavery?
Philadelphia, no
30
New cards
What was the anchor city for the Upper South, and was there slavery?
Virginia, yes
31
New cards
What was the anchor city for The Lower South, and was there slavery?
South Carolina, yes
32
New cards
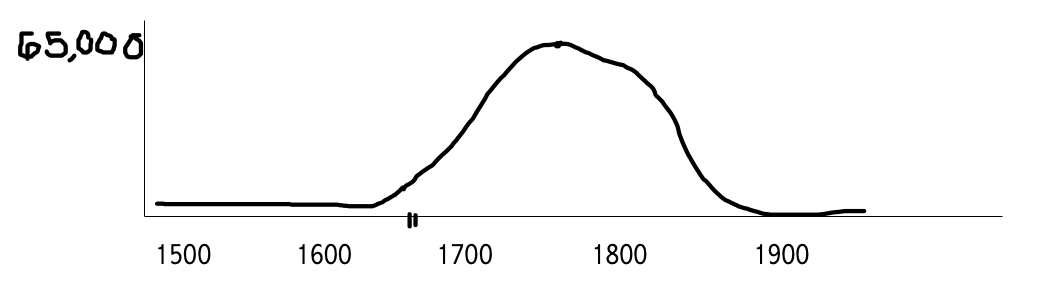
When was the peak of the Atlantic Slave Trade?
1760’s
33
New cards
When was the first Atlantic Slave Trade?
1500-1660’s/70’s
34
New cards
When was the second Atlantic Slave Trade?
1670’s-1900’s
35
New cards
How many slaves were being sent to the US per year during the peak of the slave trade?
\~65,000
36
New cards
What three continents were working together during the Atlantic Slave Trade?
Western Europe, Western Africa, Tropical and Subtropical parts of the Atlantic-facing American regions (Eastern US, Caribbeans, Eastern Mexico)
37
New cards
What was sent from Europe to Africa in the slave trade?
guns/manufactured goods
38
New cards
What was being sent from Africa to the Americas?
Slaves
39
New cards
What was being sent from the Americas to Europe?
Agricultural commodities (sugar, rice, lumber)
40
New cards
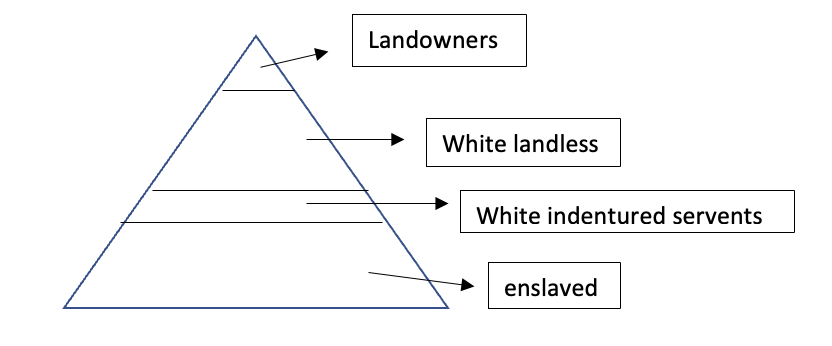
Bacon’s Rebellion
Militia of white landless people, indentured servants from Europe, and black enslaved people attempted to burn the capital of Virginia down. This resulted in the government giving white landless people more rights to avoid this in the future
41
New cards
Jim Crow Laws
Laws designed to make life harder for African Americans
42
New cards
De jure
“Of the law” - there is a law that says why this is how it is
43
New cards
de facto
“as a matter of fact” - happens organically because that is the way people are (ex. racial residential segregation in Milwaukee)
44
New cards
What were consequences of the slave trade for Europe?
\-Companies in Europe made lots of money that went into the European economy
\-Europe goes through the Industrial Revolution first and becomes very wealthy
\-Europe goes through the Industrial Revolution first and becomes very wealthy
45
New cards
What were consequences of the slave trade for Africa?
\-Underdeveloped
\-Human capital was taken away
\-Africa became dependent on EuropeW
\-Human capital was taken away
\-Africa became dependent on EuropeW
46
New cards
What were consequences of the slave trade for the Americas?
\-A racial hierarchy was developed
47
New cards
What is the significance of Bacon’s Rebellion in 1676?
This was the first time the terms “black” and “white” were used in the Americas, and racial categories were formed
48
New cards
What happened during Reconstruction from 1867-1877?
North tries to fix all the mistakes of the South by passing 3 reconstruction amendments
49
New cards
How did the Jim Crow Laws move in terms of de facto and de jure
Start as de jure, then de facto during reconstruction, then back to de jure after reconstruction
50
New cards
What were the Restrictive Covenants?
A document attached to the deed of your home. It stated you could never rent or sell your home to an ethnicity that was not yours. This was shot down in 1948.
51
New cards
What were the three events in the dismantling of Jim Crow Laws?
\-Abolishment of Restrictive Covenants (1948)
\-Brown v Board (1954)
\-Passage of Civil Rights Act (1964)
\-Brown v Board (1954)
\-Passage of Civil Rights Act (1964)
52
New cards
Sharecropping
Slaves could continue to work on the plantation lands, but they did not have political freedom, houses, or food
53
New cards
What was the system of Apartheid
Separation of race in Africa that separated whites from blacks (similar to Jim Crow)
54
New cards
How did voting work for African Americans during Jim Crow South?
Literacy tests had to be completed that were almost impossible
55
New cards
What was the Tulsa Race Massacre?
Homes of African Americans were set fire to in Greenwood, Oklahoma
56
New cards
What was the goal of the Tulsa Race Massacre?
To get African Americans back to their spot on the Racial Hierarchy