sex differences
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
sex
talks more about the biological aspects (gender = more cultural)
what is XX
WOMEN
what is XY
MALE
sex determination in mammals through the gene SRY involves
turning the fetal gonad into a testes - its the testes determining factor
in its absence the gonad becomes ovary
sex determination in mammals through hormones involves
early testes producing - anti-mullerian hormone (defeminising) and androgens (masculinising)
without these hormones the female sex organs will develop. the genitalia will develop female
what is the mullerian system
precursor to female system
what is the wolffian system
precursor to the male sex organs
what is the wolffian system maintained by
maintained by the androgens when androgens bind to their receptors and allow for the system to continue existing and become male internal genitalia
what happens to the wolffian system when there are no androgens
the wolffian system dissappears and the female internal sex organs are developed from the mullerian system
how is the mullarian system removed
if the testes is formed and the anti-mullarian hormone is produced then then mullarian system is disintergrated
sex determination in mammals through external sex organs
they start completely undifferentiated.
after the gonad is turned into either testes or ovaries the external genitalia are sensitive to androgens ( DHT) made by the testes.
DHT is required to turn the external anatomy into male specific like scrotum and penis.
if no DHT then we get female specific anatomy. what would be the scrotum becomes the labia.
what is persistent mullerian duct syndrome
person has external male genitalia, wolffian system is working fine but there is no anti-mullerian hormone so they have the start of a uterus.
they have both male and female internal genitalia
what are the organisational actions of hormones
effects remains after the hormone has been removed often occurs during a sensitive period. if you take the testosterone away from a boy they wont lose the internal and external genitalia these changes are permanent.
wide pelvis in women cannot be undone when they have occured
what are activational actions of hormones
effects if reversible depending on presence or absence of hormone. take hormone away the effect goes away.
when does puberty occur
at some point in teenage year
producing horomones and become sexually mature
what is the onset of puberty
during childhood - sex hormone levels are undetectably low
developmental timing mechanism starts puberty
sex differences in mechanism and timing
GnRH - during puberty
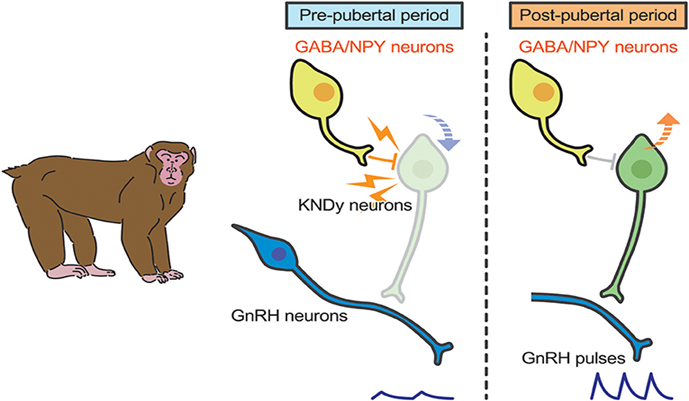
in the hypothalamus neurons called GnRH neurons that normally trigger a cascade of to release sex hormones. during childhood they dont release hormone called GnRH as these neurons are being inhibited by GABA.
during puberty you get activation of kisspeptin neurons and inhibition of GABA.
GnRH definition
Gonadotropin releasing hormone
hormone released into the blood. it effects the testes and ovaries production of hormones
hypothalamus, pituitary gland and GnRH
released into the small blood vessels which feeds into the anterior portion of the pituitary gland. where other cells have receptors for GnRH which will in turn start making their own hormones which goes to the gonads
gonadotropins are released.
what are gonadotropins
hormones whos target is the gonads
what does LH do
stimulates the production of testosterone from different set of cells in testes
in females LH causes ovulation
MALES - what occurs in the feedback system of the hypothalamus-pituitary gonadal axis
simple negative feedback system
HPG axis in males is a negative feedback system that keeps testosterone around a set point. if it is below in the blood then the hypothalamus GnRH will release to increase gonadotropins LH and release testosterone opposite if too much
if the male takes anabolic steroids the consequences on the HPG axis include the hypothalamus produces less GnRH testes make low amounts of testosterone and the testes will shrink.
FEMALES - the menstrual cycle and ovulation
at the end of the cycle there is an increase in FSH from the anterior pituitary gland in the bloodstream. this will bond to the follicles in the ovary one of those follicles will being to ripen.
from day 5-13ish the follicular phase occurs - producing oestradiol. when this reaches a certain level it crosses a threshold which will trigger GnRH in the hypothalamus to release LH and FSH.
peek of LH and FSH triggers ovulation - follicle is now called corpus luteum
this starts making oestradiol and progesterone which until now has been low. this stats building up the uterine lining ready to receive implantation of embryo.
variation in sexual differentiation - androgen insensitivity syndrome
the body isnt sensitive to androgens - the receptors dont work properly
gonads develop as testes - anti-mullairan hormones work fine
androgen receptors dont work - testosterone cant do its job
XY develop anatomically female but no female internal genitalia.
XX lack of public hair they have ovaries and female hormones - chances are they wont know they have it
puberty is typically late
people with it typically identify as female
variation in sexual differentiation - 5alpha - reductase deficiency
5 a reductase turns testosterone into DHT - DHT is crucial for prenatal external genital development
XY born with female external genitalia by male internal when they hit puberty they develop a penis
“guevedoces” - common in Dominican Republic call people penis at 12.
after puberty most identify as men
variation in sexual differentiation - congenital adrenal hyperplasia
21- hydroxylase deficiency
high levels of prenatal testosterone in girls - often treated when diagnosed.
XX assigned male at brith
5% of CAH girls assigned female at birth have gender dysphoria
12% of CAH “girls” assigned male at birth have gender dysphoria
hypothalamus-pituitary adrenal axis - CAH
the adrenal gald makes cortisol. 21-hydroxylase makes cortisol which is important as its involved in energy balance.
people with this struggle with symptoms of low cortisol as the precursor to cortisol become testosterone not cortisol. you get some of the primary sexual characteristics of males during embryonic development as a female
activational hormone effects on origins of sex differences in brain
variations with varying testosterone, oestradiol levels.
no differences detected in adulthood between sexual orientations
hormone fluctuations manipulation or treatments affect sexual motivations
hormone activation are the cause of many sex differences but not sexual orientation
gynophile
attraction to women
androphile
attraction to men
O.H - what are the r periods where testosterone is high in boys
8-24 weeks pregnant - early external genitalia, late - brain differentiation
first 3 months after birth - potential further brain differentiation
O.H correlates of embryonic testosterone - cognitive performance
verbal abilities are better in androphile men than gynophilic men
visuo-spatial performance is worse in androphile men than gynophile men
mental rotation is faster in gynophile women than in androphile women
all very tentative evidence
O.H - correlates of embryonic testosterone - ratio of 2nd and 4th finger lengths
sex differences in 2D/4D ratios = male - 0.95 female = 0.97
in females they are more similar lengths than that of men - on average men have shorter index fingers.
gynophile women - butch lesbians have more masculine 2d-4d ratios and are more masculine presenting suggesting more testosterone in development
no consistent findings in androphile men
O.H- correlates with embryonic testosterone - oto-acoustic emissions
when stimulated with a click the ears make a click back. this is louder and more frequent in women.
early t development in other species
gynophile women closer to gynophile men than androphile women
genetic effects for sex differences - twin studies
high concordance rates in mz than dz
estimates 30-100% - lower end more likely as there is more bias higher
possibly higher concordance for women than men.
genetic effects for sex differences - genetic mapping
androphile men more often have androphilic maternal uncles.
a region of the X chromosome has been identified as related to sexual orientation
genetic effects of sex differences - concerns from evolution standpoint
should homosexuals have less offspring?
how does a putatuve genetic basis not get selected out of the population.
possible mechanisms for maintaining such genes
heterozygotic advantage
kin selection
different effects in male and female.
genetic effects in sex differences - fraternal birth order effect
the odds of having a boy that is androphilic increases the more boys youve had as a mother - the more older brothers by the same mother the more likely the boy will be gay. sisters dont have an effect.
sexual orientation conclusions
clear biological developmental influences. no influences is absolute sexual orientation can be influence by several different factors
what is gender identity
has even larger sex differences than sexual orientation - doesnt seem to be binary
childhood gender dysphoria doesnt always continues after puberty - does for 40%
study looking at transgenders
genetic mapping was done and it was found that it seems like there are genes that are associated with gender dysphoria
for FTM having the long version of the oestrogen receptor alpha and the oestrogen receptor beta made more correlated with being trans.
there is enough of an association that there is something to connect them with effecting gender identity.
pre-transition brain differences
brain volume are in lines with natal sex
MTF individuals shown more feminine cortical thickness and white matter in some brain areas.