Mechanics I
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Displacement (definition)
The displacement of a particle from a fixed point is its distance from that point in a particular direction
Symbol + unit for displacement
[s], unit is metres (m)
Velocity (definition)
The rate of change of displacement w.r.t time
w.r.t meaning
With respect to
Velocity symbols + unit
Initial velocity [u], final velocity [v], unit is m/s or ms-1
Acceleration (definition)
The rate of change in velocity w.r.t time
Acceleration symbol + unit
[a] m/s squared or ms-2
Scalar (definition)
A scalar is a quantity which has a magnitude only. E.g. time
Quantity (definition)
Something you can measure
Vector (definition)
A vector is a quantity which has a magnitude and a direction. E.g. displacement, velocity, acceleration, momentum, force
Scalars and their Vector Equivalent
Distance-Displacement, Speed-Velocity
Mass/Inertia definition
The measure of an object's ability to resist changes in its velocity
1st Equation of Motion
v=u+at
2nd Equation of Motion
s=ut+1/2at2
3rd Equation of Motion
v2=u2+ 2as
what does v mean?
final velocity
what does u mean?
initial velocity
what does t mean?
time
what does s mean?
distance
what does a mean?
acceleration
Equation for momentum
p=mv
What is the symbol for momentum?
p
What is the unit for momentum?
kgms-1
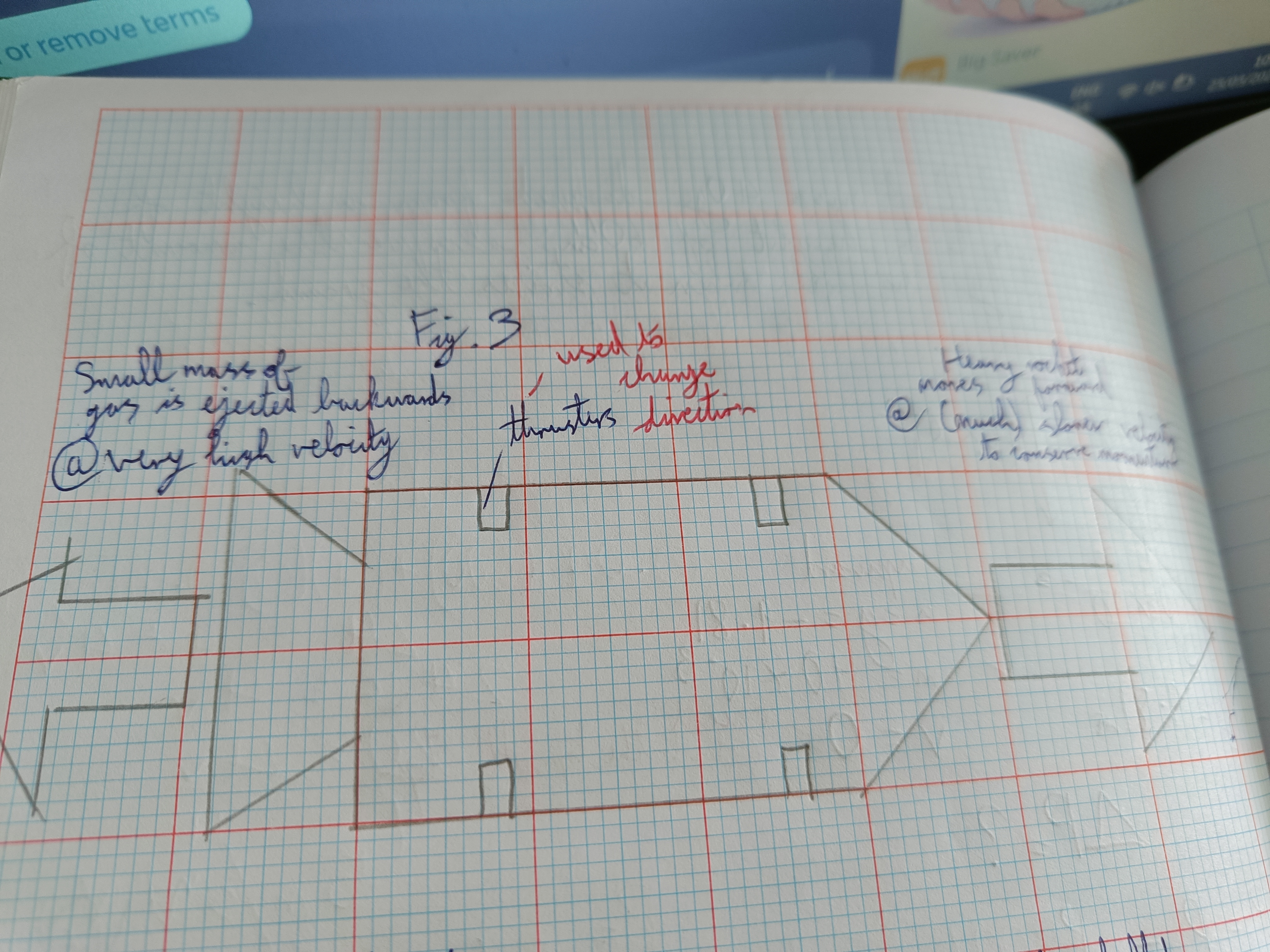
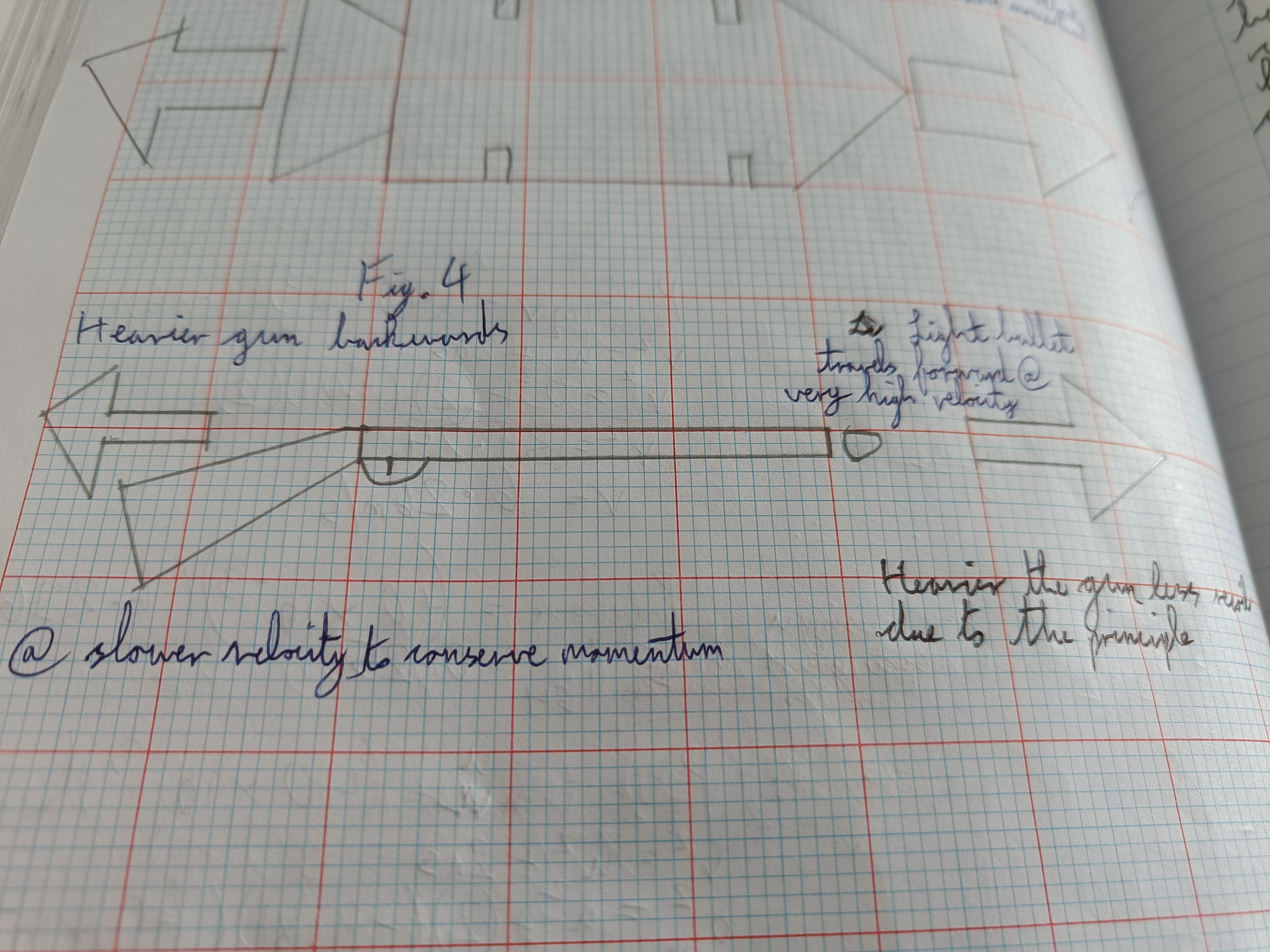
The principle of conservation of momentum
States that in any closed system the total momentum before an interaction is equal to the total momentum after an interaction
Equation for an elastic collision
(m1)(u1)+(m2)(u2)=(m1)(v1)+(m2)(v2)
Equation for an inelastic collision
(m1)(u1)+(m2)(u2)=(m1+m2)v
What is an elastic collision?
objects bounce off one another. e.g. emerges
What is an inelastic collision?
Objects join each other. e.g. embedded
What is a closed system?
One in which there is no interaction between objects inside the system and objects outside the system. For example, a tennis player hitting a ball with a tennis raquet is not a closed system because the player can add or subtract momentum to the collision. If the tennis player threw the raquet at the ball it would be a closed system and the principle of conservation of momentum would apply
Draw how the principle of conservation of momentum applied to rockets diagram
...
Draw how the principle of conservation of momentum applied to guns diagram
...
Newton's First Law of Motion
A force is something which causes an object to change its velocity. The velocity of an object does not change unless a resultant force acts on it. This law defines what a force is. Force is measured in Newtons
Force (definition)
A force is something which causes an object to change its velocity.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
When a resultant external force acts on an object, the rate of change of the object’s momentum is directly proportional to the force, and takes place in the same direction. This law tells you what size the force is.
Equation for Newton's Second Law of Motion
F=ma
Addition and Resolution of Vectors (Co-Linear and in the same direction)
Add them, stays in the same direction
What is the resultant force?
The total force acting on an object
Addition and Resolution of Vectors (Co-Linear and in the opposite directions)
Subtract them, direction of the bigger force
Addition and Resolution of Vectors (Perpendicular to each other and tail to tail)
complete the parallelogram, find the magnitude using Pythagoras' Theorem, use SOHCAHTOA for the direction which is in degrees
Addition and Resolution of Vectors (Perpendicular to each other and head to tail)
complete the triangle, find the magnitude using Pythagoras' Theorem, use SOHCAHTOA for the direction in degrees
Resolution of a Vector
find the horizonal and vertical components. Use SOHCAHTOA
Resolution of a Vector (meaning)
Means splitting one vector into its horizontal and vertical components
Note on the "F=ma" equation
The F is always the resultant force
Newton's Third Law of Motion
In any interaction between two objects, a and b, the force exerted by a on b is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted by b on a. This tells us that forces occur in pairs
Newton's Third Law of Motion is more commonly known as
Every action has an equal but opposite reaction
Friction (definition)
The force which opposes motion between two objects in contact
Disadvantages of friction
Causes wear and tear, wastes fuel
Advantages of Friction
makes movement possible
Reduction of Friction
using a lubricant e.g. oil, grease. By streamlining. Using ball bearings