Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Cosmology: Key Concepts for Physics Students
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is temperature a measure of?
Temperature is a measure of hotness or coldness.
How does temperature relate to kinetic energy?
Temperature is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance.
What determines the direction of heat flow?
Heat energy flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature until thermal equilibrium is reached.
What are the three common temperature scales?
Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin.
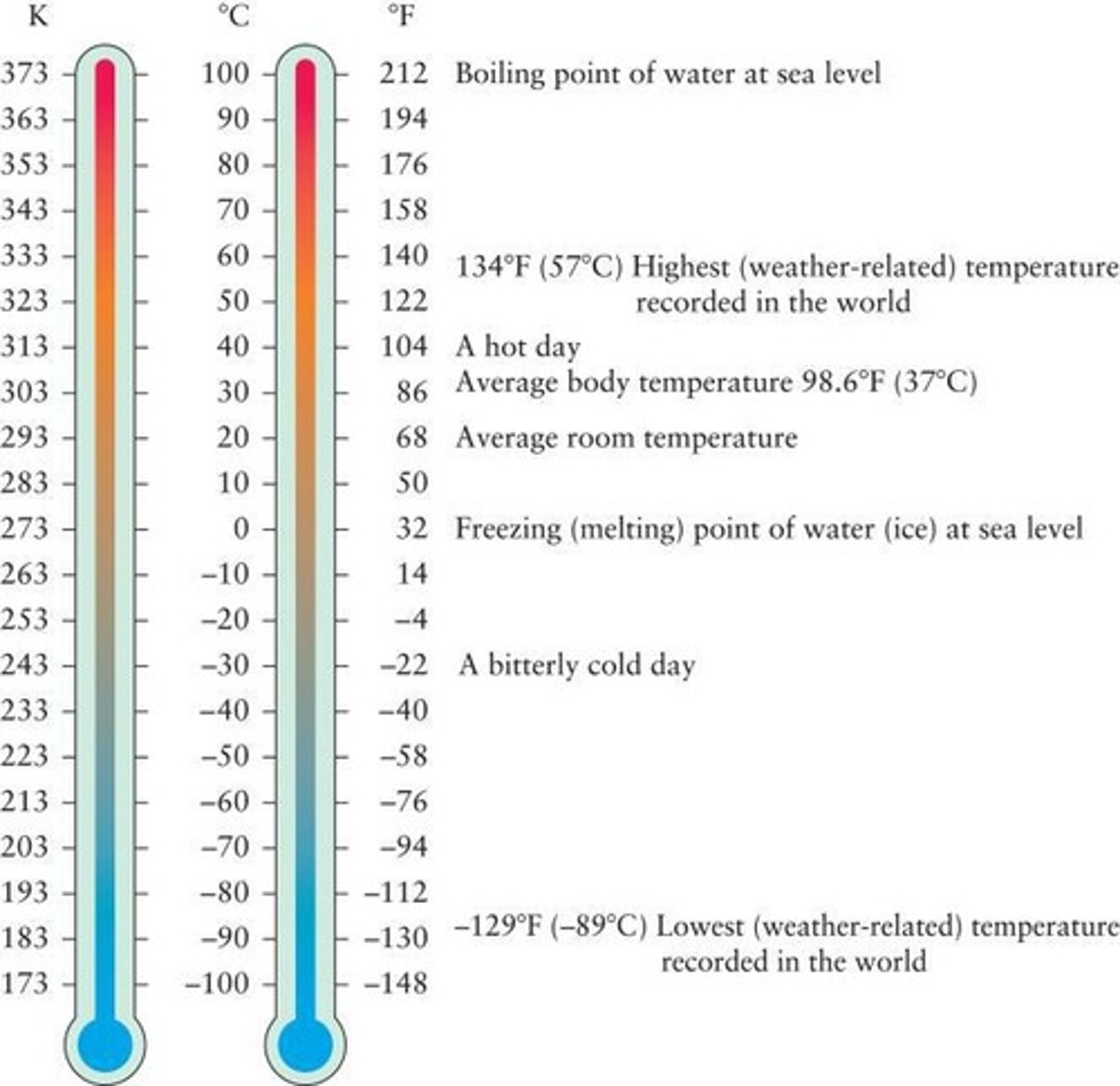
What is the freezing and boiling point of water in Fahrenheit?
Freezing point: 32°F, Boiling point: 212°F.
What is the freezing and boiling point of water in Celsius?
Freezing point: 0°C, Boiling point: 100°C.
What is absolute zero in Kelvin?
Absolute zero is 0 K, equivalent to -273.15°C.
How can the temperature of a substance be increased?
By exposing it to something with a higher temperature or by doing work on it.
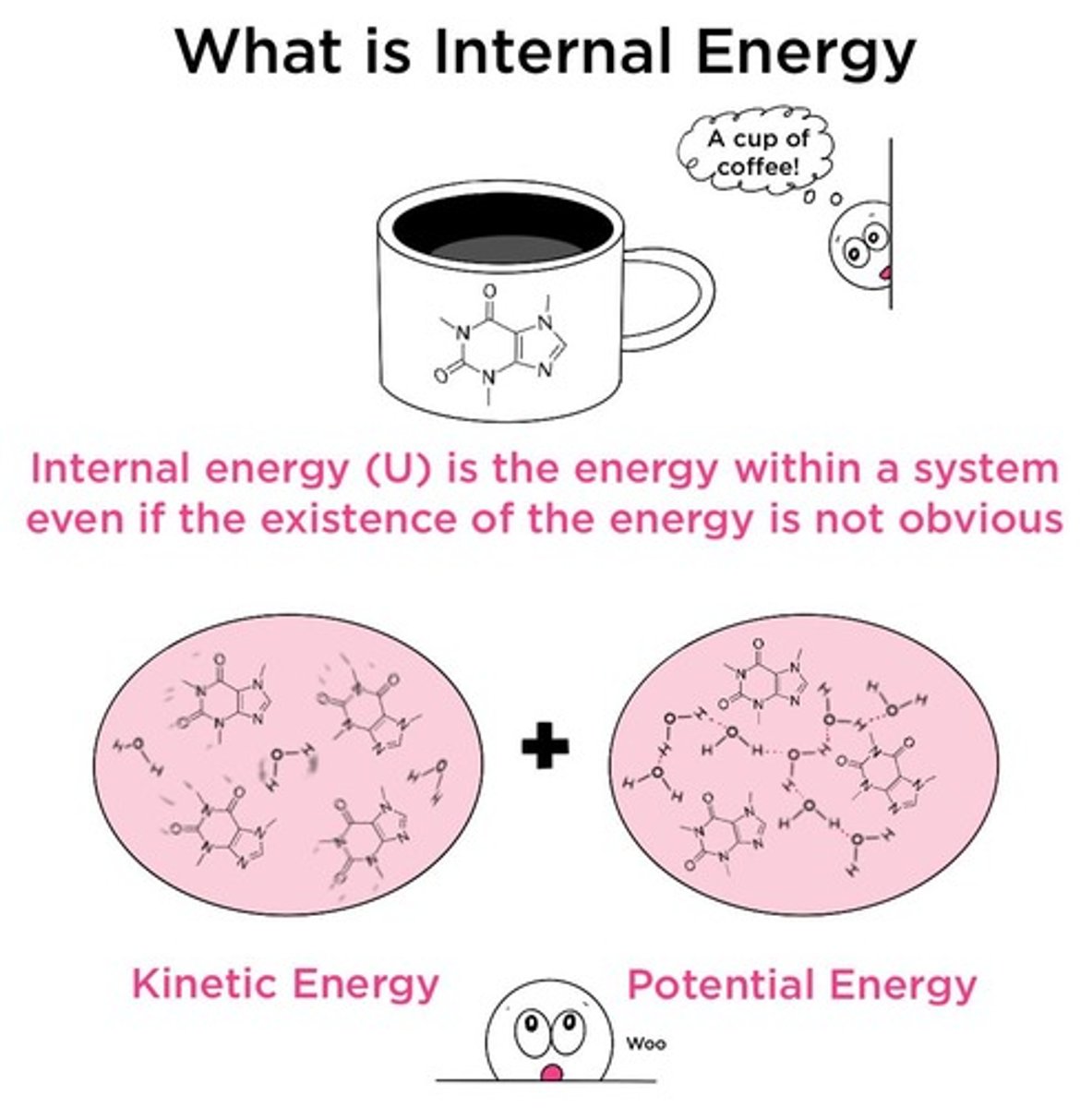
What is internal energy?
The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all the atoms and molecules in a substance.
What does the symbol U represent?
U represents internal energy.
What is heat in thermodynamics?
Heat is the form of energy transferred between two substances due to a temperature difference.
What does the symbol Q represent?
Q represents heat.
What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
The change in internal energy of a substance equals the work done on it plus the heat transferred to it (∆U = work + Q).
When is work considered positive in thermodynamics?
When work is done on the substance.
When is heat Q considered positive?
When heat flows into the substance.
What are the three mechanisms of heat transfer?
Conduction, convection, and radiation.

What occurs during a phase transition?
A substance changes from one phase of matter to another.
What is latent heat?
The specific amount of internal energy that must be added or removed for a phase transition.
How much heat is required to melt 1 kg of ice at 0°C?
334,000 joules.
How much heat is required to convert 1 kg of water at 100°C into steam?
2,260,000 joules.
What happens to internal energy during boiling?
Internal energy increases as the substance changes from liquid to gas.
What happens to internal energy during freezing?
Internal energy decreases as the substance changes from liquid to solid.
What is the effect of condensation on internal energy?
Internal energy decreases as the substance changes from gas to liquid.
What is the effect of melting on internal energy?
Internal energy increases as the substance changes from solid to liquid.
What does the Clausius Statement of the Second Law of Thermodynamics state?
Heat will not spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body without external work.
What is the Kelvin-Planck Statement regarding engine efficiency?
It is impossible to construct a device that converts heat completely into work without rejecting waste heat.
What is entropy in thermodynamics?
Entropy is a measure of the unavailability of a system's thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work.
What does the symbol 'S' represent in thermodynamics?
The symbol 'S' represents entropy.
What is the SI unit for measuring entropy?
The SI unit for entropy is joules per kelvin (J/K).
What does the Second Law of Thermodynamics state about total entropy?
The total entropy of a system and its environment either increases or remains constant and can never decrease.
Under what conditions do entropy changes become zero?
Entropy changes are zero only for reversible processes.
What is the implication of the Second Law of Thermodynamics for the universe's entropy over time?
The entropy of the universe is expected to increase over time.
How is time defined in classical physics?
Time is a fundamental quantity to measure the duration of events, constant for all frames of reference.
How does modern physics conceptualize time?
Time is a relative quantity that depends on the observer's motion and gravity, forming a four-dimensional continuum.
What is the consensus on backward time travel for macroscopic objects?
It is likely impossible due to fundamental laws and causality.
What is a Closed Timelike Curve (CTC)?
A CTC is a path in spacetime that loops back on itself, allowing for theoretical backward time travel.
What are wormholes in the context of time travel?
Wormholes are theoretical tunnels through spacetime that could allow for time travel if stabilized.
What is dark matter?
Dark matter is a mysterious form of matter that accounts for approximately 27% of the universe's total mass.
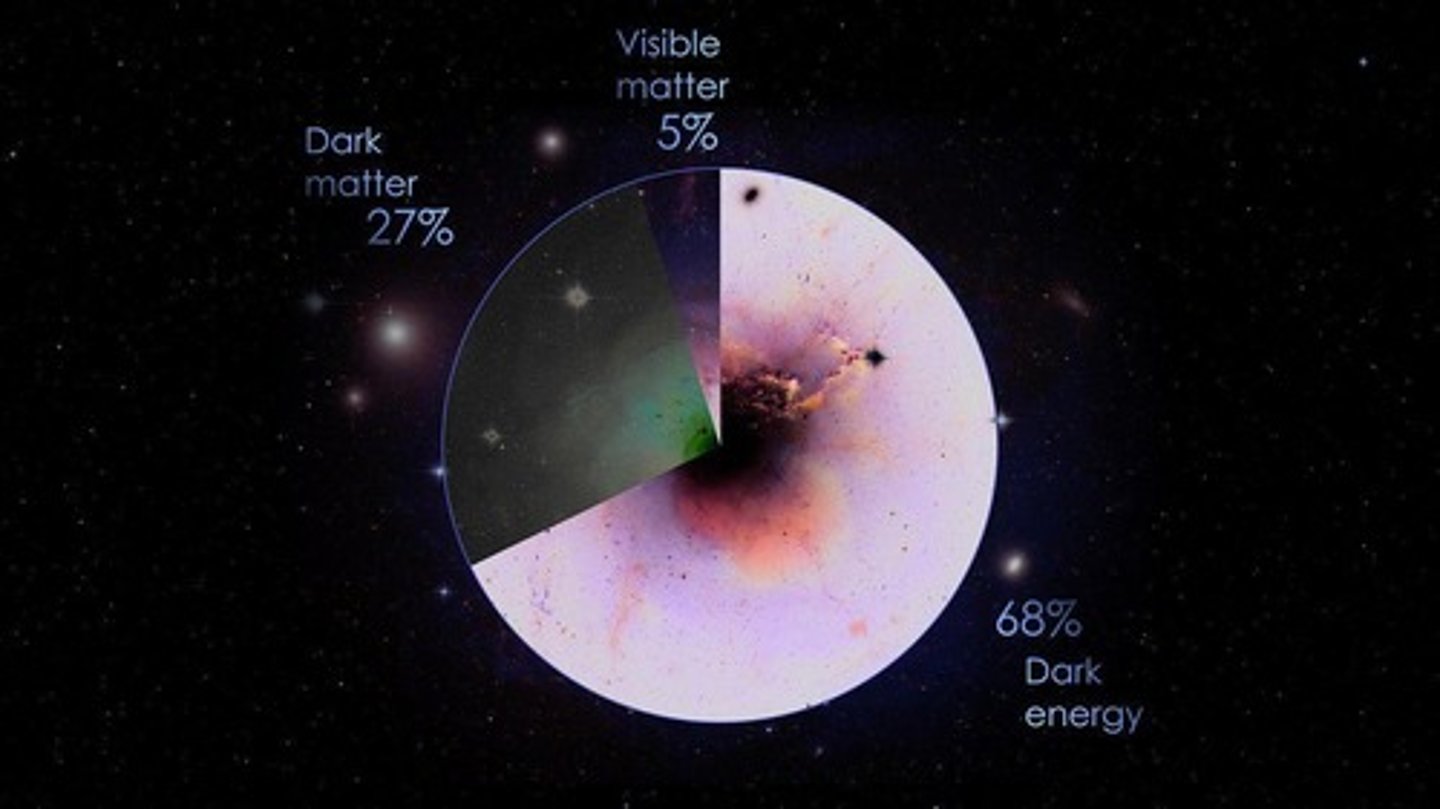
Why is dark matter referred to as 'dark'?
It does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it invisible to telescopes.
What evidence supports the existence of dark matter from galaxy clusters?
Galaxies in clusters move too fast to remain gravitationally bound unless more mass is present than can be seen.
What did Vera Rubin's observations of galaxy rotation curves indicate?
Stars in the outer regions of galaxies orbit faster than expected, suggesting the presence of dark matter.

What is dark energy?
Dark energy is a form of energy thought to exert negative pressure, acting as a repulsive force in the universe.
What was discovered about the expansion of the universe in 1998?
Observations of distant Type Ia supernovae showed that the universe's expansion is accelerating.