Gastrointestinal
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is stomatitis? What are three common causes?
- inflammation of the oral mucosa
- herpesvirus
- Candida albicans infection (thrush)
- Aphthous stomatitis (canker sores)
What causes mouth and genital herpes in the US?
- HSV1
- HSV2
Most oral cancers are what type of cancer? What are two common risk factors? How fast does oral cancer grow?
- squamous cell carcinoma
- tobacco smoking and chronic alcohol use
- grows very rapidly
What are two precancerous lesions of the mouth? Which is more likely to turn into cancer?
- leukoplakia (white plaque)
- erythroplakia (red plaque, more likely to turn into cancer)
What are 4 morphological presentations of oral cancer?
- plaque
- ulcer
- crater
- nodule
What is sialadenitis? What is the most common immunological cause? What are the symptoms?
- Inflammation of the salivary gland
- infections or autoimmune:
Bacterial Infection - Staphylococcus Aureus or Strep. Viridans
Viral Infection - Mumps (common in children)
Sjorgren's syndrome (autoimmune, antibodies attack salivary and lacrimal glands)
Infection is most common cause of sialadenitis
Symptoms:
swelling of glands, xerostomia (dry mouth + bad breathe), sialorrhea (overproduction of saliva)
How common are salivary gland neoplasms? What percentage is benign? What is the most common salivary tumor?
- very rare and slow growing
- over 60% are benign
- pleomorphic adenoma
[Adenoma b/c it’s benign]
What are three general presentations of esophageal disease?
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- esophageal (retrosternal) pain
- aspiration or regurgitation
What is esophageal atresia? How prevalent is it?
- Congenital condition in which the esophagus ends in a blind pouch
Can also result in an esophagotracheal fistula (Esophagus connects to trachea → GI contents enter trachea)
- most common developmental issue of the esophagus
What are the two types of hiatal hernia? Which is more common? Which is more serious? Hiatal hernias are the most common cause of what condition?
- Sliding [More Common]
Displacement of esophagus above hiatus
- Paraesophageal [More Serious]
Displacement of stomach above hiatus
Sx: Heart burn, chest pain, nausea, belching
Severe Sx: Necrosis, rupture → infection, and strangulation
Most common cause of gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
What is achalasia? What does it result in?
Motor disorder of the esophagus characterized by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), stenosis of the sphincter
Fluid accumulation and dilation of esophagus proximal to the sphincter
What is esophageal varices?
What is a common cause of esophageal varices?
What can it cause (3)?
- Dilated veins in esophagus
- Diseases that produce portal HTN
- upper GI bleed (melena & hematemesis) and iron-deficiency anemia
What are four causes of esophagitis?
- reflux of gastric juice (peptic esopagitis)
- infection (viruses, fungi [immunosupressed pt], bacterial infection)
- chemical irritants (exogenous chemicals or drugs)
- mechanical irritants (feeding tube)
Carcinoma of the esophagus accounts for what percentage of all cancers?
- 4%
What places have higher incidence of esophageal cancer?
Asia and Africa
What are 3 risk factors for esophageal cancer? What is the prognosis?
- alcohol and tobacco use
- more common in men than women
- race: more common in black people than white people
- poor prognosis: 2 yr avg survival rate
Symptoms of Stomach and Duodenum Diseases (5)?
- pain: midline/upper abdomen
- vomiting
- bleeding
- dyspepsia (reccurent abdominal pain or discomfort)
- systemic symptoms: iron def. anemia, vit B12 malabsorption (megaloblastic anemia)
What is the most common and rare developmental abnormality of the stomach? What group is most affected?
- Congenital Stenosis of the pyloric sphincter (thickening of the pyloris)
“Olive-like” palpable mass in the epigastric region
Prevents emptying of pyloris → Vomit nonbilious white/yellow
4x more common in males
- Duodenal Atresia (Rare)
Failure to duodenum to fully develop resulting in a blockage
Vomit bilious blue/green
What are three causes of acute (erosive) gastritis? What two things result?
Causes:
circulatory disturbances
food
exogenous chemicals and drugs
Results:
erosions
ulcerations
What are the causes of chronic atrophic gastritis?
- Mainly idiopathic but have relations to:
Helicobacter pylori
autoimmune (with pernicious anemia)
What are three things that contribute to peptic ulceration?
- gastric juice: HCl, pepsin
- mucosal barrier defects: stress, shock, NSAIDs, smoking
- Infection from Helicobacter pylori: found in most pts with ulcers
What is the first and second most common sites for peptic ulcers?
- #1 duodenum
- #2 stomach
What are 4 possible complications of peptic ulcer disease?
- hemorrhage (most common): hematemesis, melena, iron def. anemia
- penetration into pancreas (2nd most common) -> acute pancreatitis
- perforation -> peritonitis
- cicatrization (hardening) -> stenosis, decreases peristalsis
What are polyps? And how common are they?
benign epithelial gastric tumors, 5%
What is a leiomyoma?
benign stromal gastric tumor
What are two malignant tumors of the stomach and which is most common?
- adenocarcinoma (most common 90%)
- lymphoma
Carcinoma of the stomach is 8 x more common in which countries?
Japan and Chile
How has the incidence of gastric cancer changed in the US over the past 70 years? What are possible etiologies for gastric cancer?
- decreased
- nitrosamines in food and maybe H. pylori
- Smoking and Alcohol consumption
What are two developmental diseases of the intestines?
- Hirschsprung's disease (missing nerve cells in colon → affected segment stays tonically contracted (can’t relax), so stool can’t pass)
- Meckel's: congenital diverticula
What is diverticulosis? How can you get it? What is diverticulitis?
- out-pouchings of the haustra, diverticula
- congenital or acquired
Meckel’s (congenital)
Age + Constipation (acquired)
- when the out-pouchings (diverticula) get inflammed
What are hemorrhoids?
varicose veins in rectum
What is angiodysplasia?
localized vascular lesion in the colon caused by HTN -> bleeding
Dilated + thin-walled blood vessels in mucosa & submucosa
What are the different types of ischemic bowel diseases
- Chronic (Artherosclerosis)
- Acute (Emboli)
- Occlusive (blood flow ceases → infarction)
- Non-occlusive (blood flow can still occur)
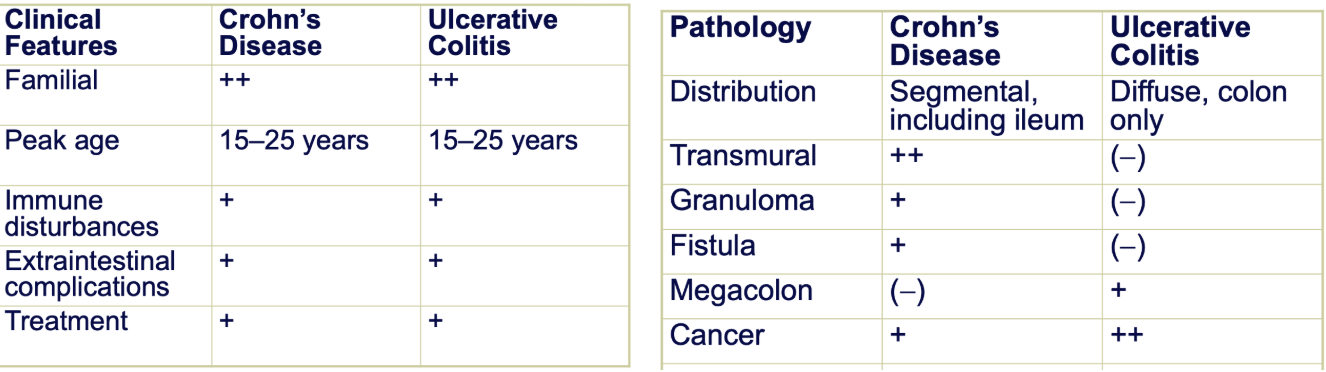
What are the two types of inflammatory bowel diseases?
What are the causes?
Crohn’s Disease
Ulcerative Colitis
Unknown causes - may be familial related
Similarities and Differences between Crohns and Ulcerative Colitis
Differences:
Transmural = Inflammation across all layers → allowing for granulomas and fistulas
Megacolon = enlarged colon (UC effects diffused across entire mucosal layer → issues with integrity of the colon)
Higher risk of colon cancer if you have UC
What are three GI infections that cause bacterial diarrhea?
- food poisoning (bacterial toxins)
- travelers diarrhea (E. coli)
- salmonella
How does viral gastroenteritis compare to bacterial?
more mild
What is the most common cause of viral gastroenteritis and the demographics
Rotovirus more common in unvax’d young children and infants
Norovirus more common in adults and children
What causes acute appendicitis?
The opening of the appendix is obstructed leading to stagnation of contents and inflammation. Bacteria may colonize the appendix and infection occurs that may cause rupture.
What are 4 causes of acute infectious peritonitis?
- rupture of stomach (peptic ulcers)
- spread of infection from fallopian tubes
- rupture of abscess (diverticuli)
- infection of preexisting ascites
What are three causes of acute sterile peritonitis?
- acute pancreatitis
- rupture of gallbladder
- postsurgical peritonitis by talc or chemicals used during surgery
What are two general causes of intestinal obstruction?
- paralytic ileus (dynamic ileus)
Neuromuscular paralysis (inflammation or distruption of nervous innervation to intestine)
- mechanical ileus
What are causes of mechanical ileus?
- atresia/stenosis
- stricture (narrowing of lumen)
- intussusception (folds on self → invaginations)
- volvulus (twisting/wrapping around itself)
- hernia
- adhesions
- neoplasms
Malabsorption results from abnormalities involving what three processes?
- intraluminal digestion of food
- uptake and processing of nutrients within intestinal cells
- transport of the nutrients from intestine to liver
What are 4 ways defective intraluminal digestions can cause malabsorption?
- deficiency of gastric juices:
postgastrectomy conditions, atrophic gastritis
- deficiency of bile or brush border enzymes:
biliary obstruction, liver disease, Crohn's disease, short bowel syndrome
- deficiency of pancreatic juices:
chronic pancreatitis, CF
- overgrowth of microorganisms:
Giardia lamblia
What are 5 conditions that damage the absorptive surface of the intestine?
- Celiac sprue
- Tropical sprue
- infectious enteritis (ex: E. coli)
- Crohn's
- Whipple's (rare, bacterial, similar symptoms to Crohn's)
Can The Intestine Carry Water?
What is short bowel syndrome?
malabsorption and diarrhea resulting from extensive bowel resection
What are three ways malabsorption can result from defective transport of nutrients?
- Lymphatic obstruction (gastrointestinal lymphoma)
- Intestinal ischemia (congestive heart failure)
- inadequate lipoprotein synthesis (congenital abetalipoproteinemia)
What part of the GI is most commonly affected by intestinal neoplasms?
colon
What proportion of intestinal neoplasms are benign and malignant?
What propotion of intestinal neoplasms are familial related or sporadic
Is primary or secondary more common?
3 Benign : 1 malignant
8 sporadic : 2 familial
Primary is more common
What is the most common type of intestinal neoplasm?
What are the least common?
90% - Epithelial (adenomos and carcinomas)
Least common - Soft tissue (Lyphomas and mesenchymal tumors)
What are three classes of intestinal tumors?
- non-neoplastic polyps (hyperplastic polyp, inflammatory polyp etc)
- benign neoplasms (adenomas, benign stromal tumors)
- malignant neoplasma (carcinomas and sarcoma)
What is the third most common cancer of internal organs? How can you prevent it?
- large intestine
- regular colonoscopies and getting benign polyps removed
What are three genetic colon cancers and how are they inherited?
- familial polyposis coli (AR)
- Gardner's syndrome (AD)
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (AD)
What about the Western diet contributes to colon cancer?
- low fiber, high carb and fat
Gastrointestinal carcinoids occur where?
Where do you usually find multiple?
Which type tend to metastasize?
What are they composed of?
- 90% in intestines, appendix most common site
- terminal ileum and stomach
- large ones can metastasize
- neuroendocrine cells that contain granules visible by electron microscopy
How do gastrointestinal carcinoids compare to carcinomas in terms of malignancy? What do they secrete? What can these secretions cause? Tumors that metastasize to the liver cause what?
- Not as malignant as carcinoma
- Polypeptide hormones that are locally active (secrete hormones)
diarrhea and hypermotility of intestines
- Metastasize to Liver
carcinoid syndrome: facial blushing, bronchial wheezing, heart valve damage
What are the two types of Esophagus Carcinoma? What do they primarly affect?
Squamos Cell Carincoma: Most common effecting 2/3 of upper esophagus
Adenocarcinoma: Effects lower 1/3 esophagus
[Oral cavity is also squamos cell, so remember oral cavity and upper part of esophagus are squamos cell]
What is pseudomembranous colitis and it’s symptoms?
nonfoodborne acute bacterial infection
Causing an Overgrowth of C. difficile
Symp: acute bloody diarrhea
Common L. Intest. Infections
SEEN:
Shigella
E. Coli
Entamoeba
Norovirus
Common S. Intest. Infections
VERG: Very Evil Rotten Guts
Vibrio Cholerae
E. Coli
Rotovirus
Giardia lamblia