Automation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Define automation in molecular diagnostic laboratories
Automation = the use of various control systems for operating equipment such as machinery in a factory, or processes such as network switching requiring no, minimal, or reduced human intervention
Results in reduced technician time and cost, faster testing turnaround times, and in many cases improved accuracy and reliability of highly complex molecular diagnostic testing
Provide examples of the earliest uses of automation in the molecular laboratory
Earliest use of automation...
Invention of thermal cycler (thermocycler)
Device responsible for controlling temp during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of gene targets
Invention of first automated thermal cycler (Mr. Cycle)
Controlled cycling temp by placing each sample in the appropriate water bath and replenish the nonstable polymerase after each successive temp cycle, allowing for dramatically less human intervention
First published application, using these processes, to test for diagnosing sickle cell disease
Taq polymerase allowed for further advancements in automation and the creation of the first fully automated commercially available PECI (DNA thermal cycler 480 system)
Explain three reasons why automation of nucleic acid extraction can be beneficial
Automation benefits:
Increase throughput by reducing manual manipulation
Reducing turnaround times by increasing capacity
Improving and standardizing extraction efficiency and quality from a growing number of biological samples
Increased throughput by reducing manual manipulation
Automated nucleic acid extraction systems can process many samples simultaneously with minimal hands-on time. By eliminating repetitive manual steps (pipetting, transfers, centrifugation), laboratories can handle a higher number of samples in a shorter period while also reducing labor demands and human error.Reduced turnaround time by increasing capacity
Automation allows continuous or batch processing of large sample volumes, which speeds up workflow compared to manual extraction methods. This increased processing capacity enables faster completion of tests, leading to shorter turnaround times—especially important in clinical and high-volume testing settings.Improved and standardized extraction efficiency and quality
Automated systems use predefined protocols that apply consistent reagent volumes, incubation times, and processing conditions. This standardization improves reproducibility, extraction efficiency, and nucleic acid quality across samples, even as the number and diversity of biological specimens increase.
What is a closed system
Closed system = instruments that require manufacturer-provided reagents to perform preprogramed extraction protocols
Allows for minimal additional training in order to produce high-quality and consistent results for a variety of additional sample types for both DNA and RNA extractions
Many are used to extract nucleic acids as part of a testing platform for screening and diagnosis of infectious disease
What is an open system
Open system = instruments that provide the greatest flexibility in high-volume testing
High capacity
Are a completely customizable automated workstation
Results in the capability to adapt a wide variety of extraction methods and kits to suit the laboratory’s needs
Drawback = require a high level of instrument and workflow expertise
Results in this system being better suited for automating either complex molecular workflows (NGS nucleic acid extraction and library preparation) or novel techniques or methods where no commercially available high-throughput technology is available
Categorize the following automated instruments according to low-volume vs. high-volume testing:
a. Biofire Filmarray
b. Cepheid GeneXpert
c. GenmarkDx ESensor XT8
d. Luminex
e. Cobas instruments
f. Hologic Tigris/Panther
g. Abbott m2000/Alinity
Highest volume
Hologic Tigris/Panther (120-182 samples)
Cobas instruments (48-96 samples)
Abbott m2000/Alinity (96 samples)
Cepheid GeneXpert (80 samples)
Luminex (12 Samples)
GenmarkDx ESensor XT8 (8 samples)
Biofire Filmarray (1 sample)
Lowest volume
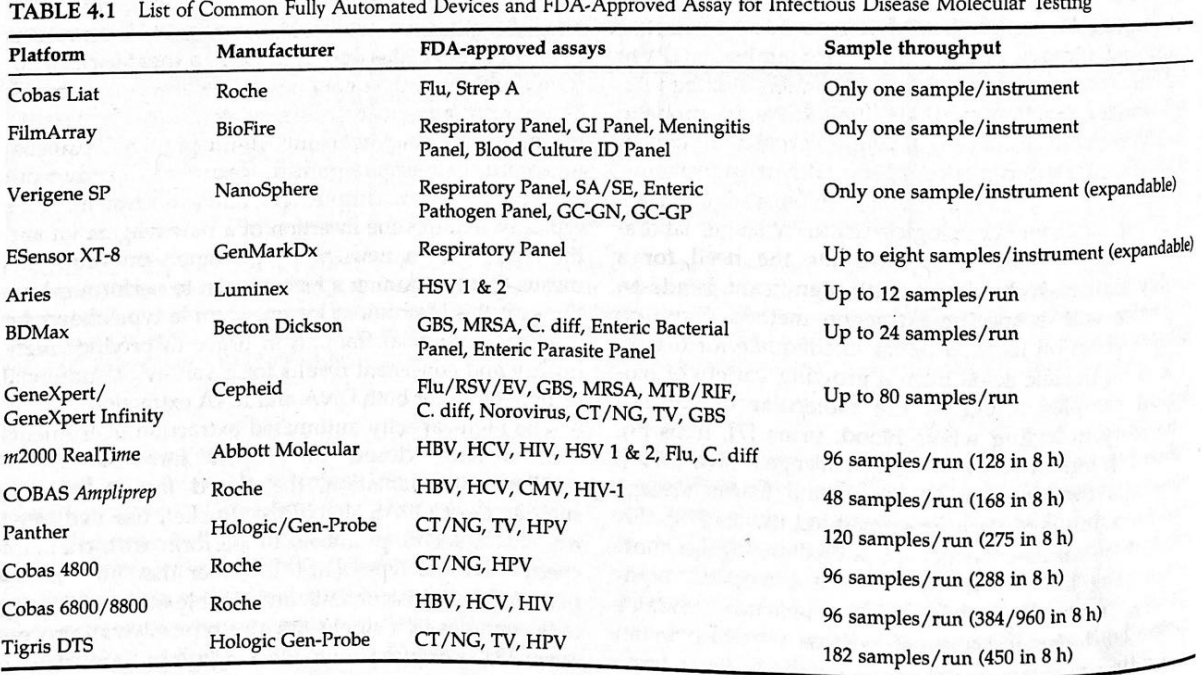
Describe advantages of automated instrument regarding sample and reagent tracking and direct sample tube input
Advantages of automated instruments in...
Sample and reagent tracking:
Automated instruments use barcodes or RFID to uniquely identify samples and reagents.
This ensures accurate sample-to-result traceability, reducing the risk of mix-ups or misidentification.
Reagent tracking allows the instrument to monitor lot numbers, expiration dates, and remaining volumes, helping ensure reagents are valid and sufficient for testing.
Improves quality control, regulatory compliance, and audit readiness, since all actions are electronically documented
Direct sample tube input:
Eliminates the laborious process of transferring samples into platform-specific disposables
Allows labs to process up to 960 tests in 8hrs and over 3,000 in 24hrs without having to drastically increase the amount of technologist time required to achieve testing requirements
Justify the advantages of using multiplexed techniques such as qPCR and ddPCR
Both: result in a reduction in technologist workload per sample and an increase in sensitivity and accuracy of PCR-based diagnostics
qPCR: Provides the ability to detect the relative quantity of specific PCR products during the PCR reaction through the use of fluorometry
Can detect 2-3 (up to 7) targets per reaction... reducing the variation introduced by manually pipetting one sample into numerous separate reactions, allowing for more precise target quantification and normalization across the assay
The use of fluorophore-labeled oligonucleotide probes designed to pair only with a single variant, allow for the rapid detection of multiple variants in a single PCR run
Increases the lab’s ability to detect all kinds of SNVs, including those used to determine which drug treatments are best suited for a particular patient
ddPCR: uses various technologies to isolate each individual target reaction, resulting in thousands of discrete measurements, allowing for more accurate and quantitative analysis of initial target amounts
Allows for accurate detection of CNVs for diagnosis of genetic disease, identification of low frequencies variants in heterogeneous tumor samples, as well as allows for a higher level of multiplexing due to the elimination of competing primers within a reaction
Give examples of clinical applications of automation in genetics and molecular oncology with capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis = allows for accurate determination of fragments differing by as little as a single base pair
Commonly used for a variety of diagnostic assays, including the detection of microsatellites to monitor bone marrow engraftment after transplantation and the diagnosis of expansion repeat diseases such as FXS and Huntington’s disease
Used to identify actionable hotspot mutations, defined as common cancer mutations which have identified therapeutics for a given tumor type
Give examples of clinical applications of automation in genetics and molecular oncology with Chromosomal microarray analysis
Chromosomal microarray analysis
Detection of CNVs can result in diagnosis of various genetic disorders or alter the treatment selection for certain tumor types
Allows for automated molecular analysis of chromosomes resulting in a virtual karyotype with higher sensitivity and increased diagnostic yield
Resulted in higher resolution detection of CNVs
Give examples of clinical applications of automation in genetics and molecular oncology with next generation sequencing
Next generation sequencing
Instead of running dozens of Sanger sequencing assays to identify breast cancer associated variants in BRCA1, with NGS you can now examine all variations across a number of different genes with known breast cancer associations
Targeted sequencing panels/whole exome sequencing help narrow the scope of the diagnostic assay allowing for easier adoption into a clinical setting