bio 108 topic 31: Clade Amniotes
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Clade amniotes characteristics
tetrapods
Living members are reptiles ( and birds, mammals)
Adaptions for terrestrial life
Amniotic egg
Amniotes shared derived traits
amniotic egg
Internal fertilization via specialized intromittent organs
Direct development
Explain the amniotic egg
4 extra-embryonic membranes
Enable reproduction on land
gas exchange done by chorion and allantois
Nutrient supply (provided by yolk sac and albumen
Protection
from desiccation (amnion, chorion, external shell)
Mechanical shock (cushioned by amniotic fluid)
Waste removal (allantois)
Eggs lay in land
Reproduction not in water
Explain internal fertilization via intromittent organs
external genitalia of males specialized for sperm delivery during copulation
Intromittent organs are traits of internal fertilization
What is direct development
amniotes dev directly into terrestrial adults without aquatic larvae stage
Amniotes adaptations for land life
relatively impermeable skin
Use rib cage to ventilate lungs
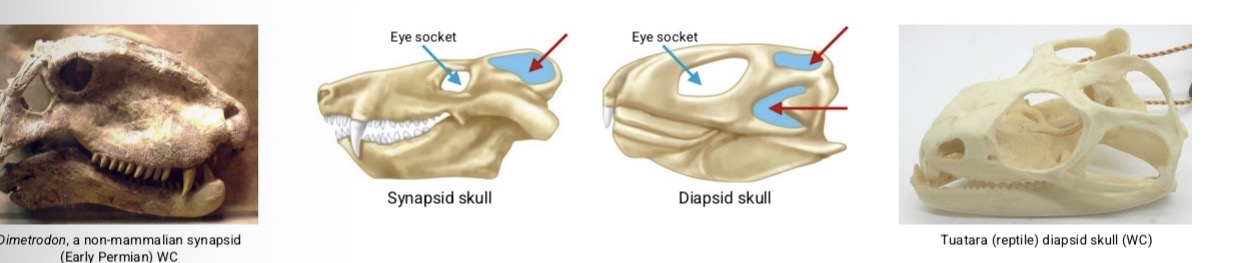
Temporal fenestrae
Classification of amniotes partially based on major skull openings
Three types of temporal fenestrae
Anapsid: lack temporal fenestrae (ex: turtles)
Synapsid: one pair of temporal fenestra (mammals)
Diapsid: 2 pairs of temporal fenestrae behind eye sockets (reptiles)