Topic 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the mass of an electron?
1/2000
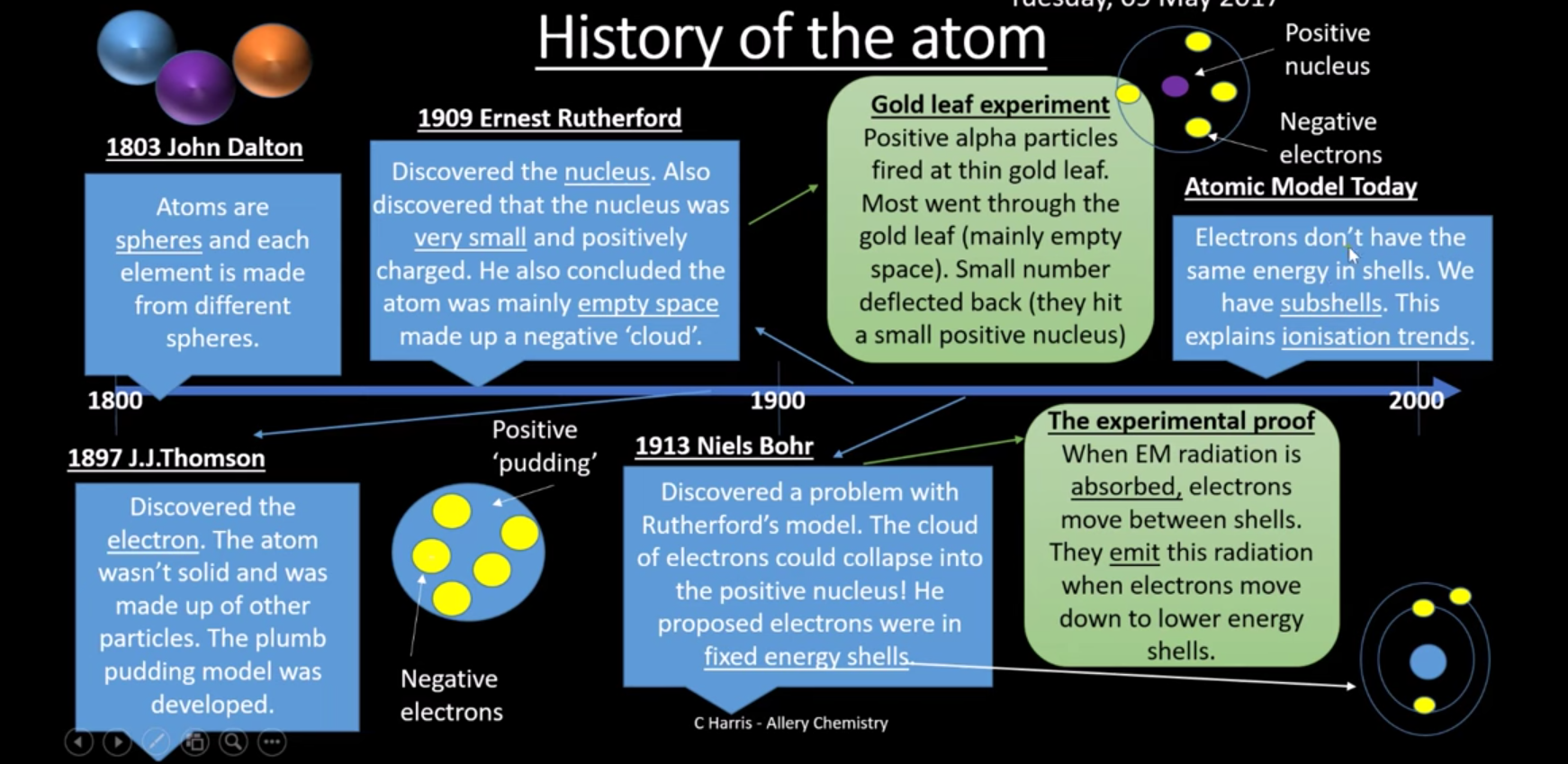
what was the year John dalton discovered the first thing about the atom and what did he discover?
1803 all atoms are spheres
What was the second thinhg about the atom discovered by J.J Thompson and what was it?
1897 - Plum pudding model
What did Ernest Rutherford discover about the atom and when?
1909 - discovered nucleus, (very small + atom has empty space - electrons negative clouds) - gold leaf experiment
What discovery did Niels Bohr make about the atom and when?
1913 - electrons exist in energy levels (Experiment - EM radiation absorbed, electrons move between shells, energy emitted when electrons move down lower shells)
What was the last discovery about the atom and when?
2000s - subshells
What is the history of the atom?
What do subshells tell us about an atom?
ionisation energies
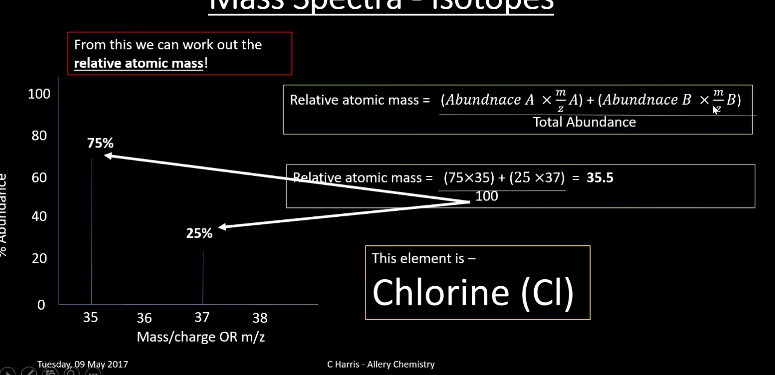
What is relative atomic mass?
the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon 12
What is relative isotopic mass?
The mass of an atom of an isotope compared to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon 12
what is the equation for relative atomic mass?
What are the molecular ions?
OH- = hydroxide
NO3- = Nitrate
NH4+ = Ammonium
SO42- = Sulfate
CO32- = Carbonate
What is the charge of a zinc ion?
Zn2+
What is the experiment for calculating water of crystallisation?
heat hydrated salts until you have a constant mass. = anhydrous salt
How do you calculate water of crystallisation?
write out the 2 molecules involved
write the masses of each molecule
divide these by relative molecular mass to get number of moles
divide all the number by the smallest number of moles
Why might % yield not be 100%?
you may lose product when transfering beaker to beaker
not all product may have reacted
products such as gases can escape
there may be impurities
What is atom economy?
How efficient a reaction is
Why is atom economy important?
companies try to use reactions that tend towards 100% atom economy
high atom economies produce less waste = benefit environment
less by products = less time + money spent separating these form desirable products
high atom economies mean raw materials used more efficiently = more sustainable
What is a polyprotic acid?
an acid that donates more than one proton
How does ammonia produce OH- ions?
reacts with water first and accepts a proton to produce ammonium ions (NH4+) and OH- ions

What happens when ammonia reacts with acids?

What is the colour of phenolphthalein in acids and alkali?
acid - colourless
alkali - pink
What is the colours of methyl orange in acid and alkali?
acid - red
alkali - yellow
neutral - orange
What is a reducing agent?
something which loses electrons but is oxidised itself

What is an oxidising agent?
something which gains electrons and is reduced itself
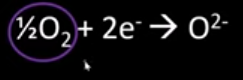
What is the oxidation number of aluminium?
+3
What is the oxidation number of hydrogen
+1 - except in hydrides - it is -1 (NaH)
What is the oxidation number of chlorine?
-1 except in a compound with F and O - positive value
What is the oxidation number of oxygen?
-2 except in peroxides (-1 H2O2) and +2 in OF2
how many orbitals can the f subshell have and therefore how many electrons can it hold?
7 orbitals so 14 electrons
How many electrons are there in the third subshell?
18
What is the principle quantum number?
the shell number
Do the shells further away form the nucleus have a higher or lower energy level?
higher
Where can the 2 electrons move in the s subshell?
anywhere in the sphere
What does the p subshell look like?
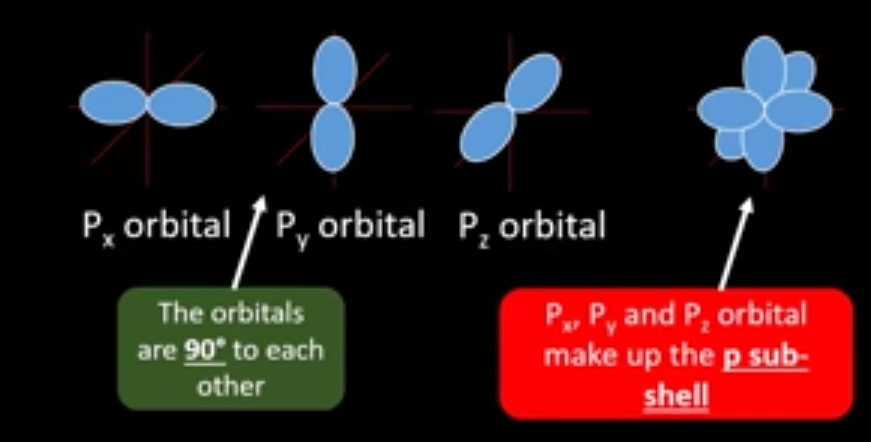
What happens when 2 electrons occupy 1 orbital?
they spin in opposite directions
Are the subshells with the highest energy the most stable?
no they are the least stable
What can you do for a short hand of electron configuration?
put a noble gas in brackets - then add the extra bit
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
there are many strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions - lots of energy is needed to overcome these forces
Where is the electrostatic attraction in covalent bonds?
between the shared electrons and the positive nucleus
What is a covalent bond?
the strong electrostatic attraction between the positive nuclei of two non-metal atoms and the shared pair of negative electrons between them
What is a dative covalent bond?
when one atom donates 2 electrons to an atom to form one bond
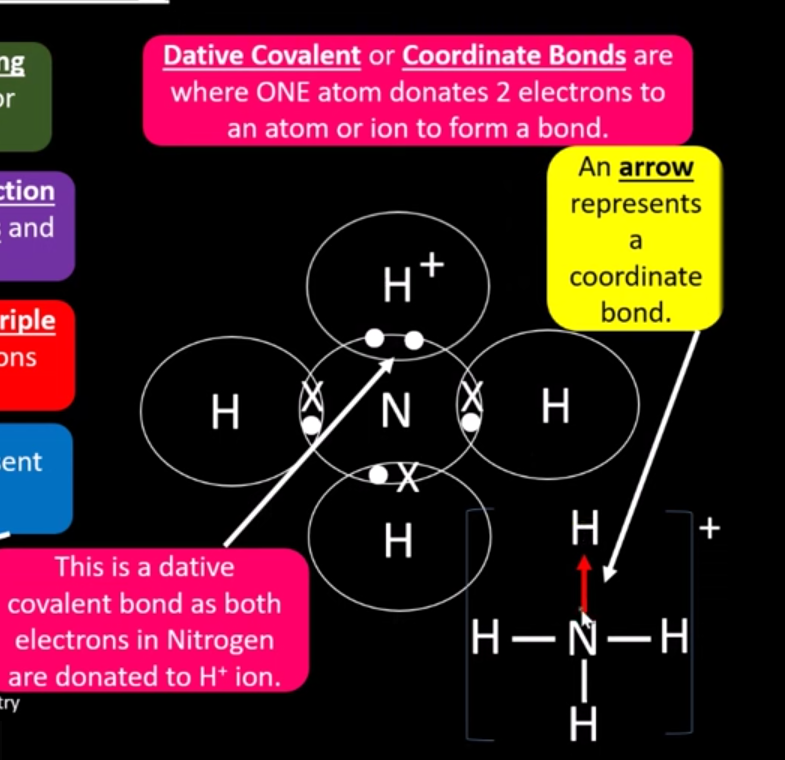
What is another word for dative bond?
coordinate bond
What are the shape and bonding angles for shapes of molecules with bonding pairs
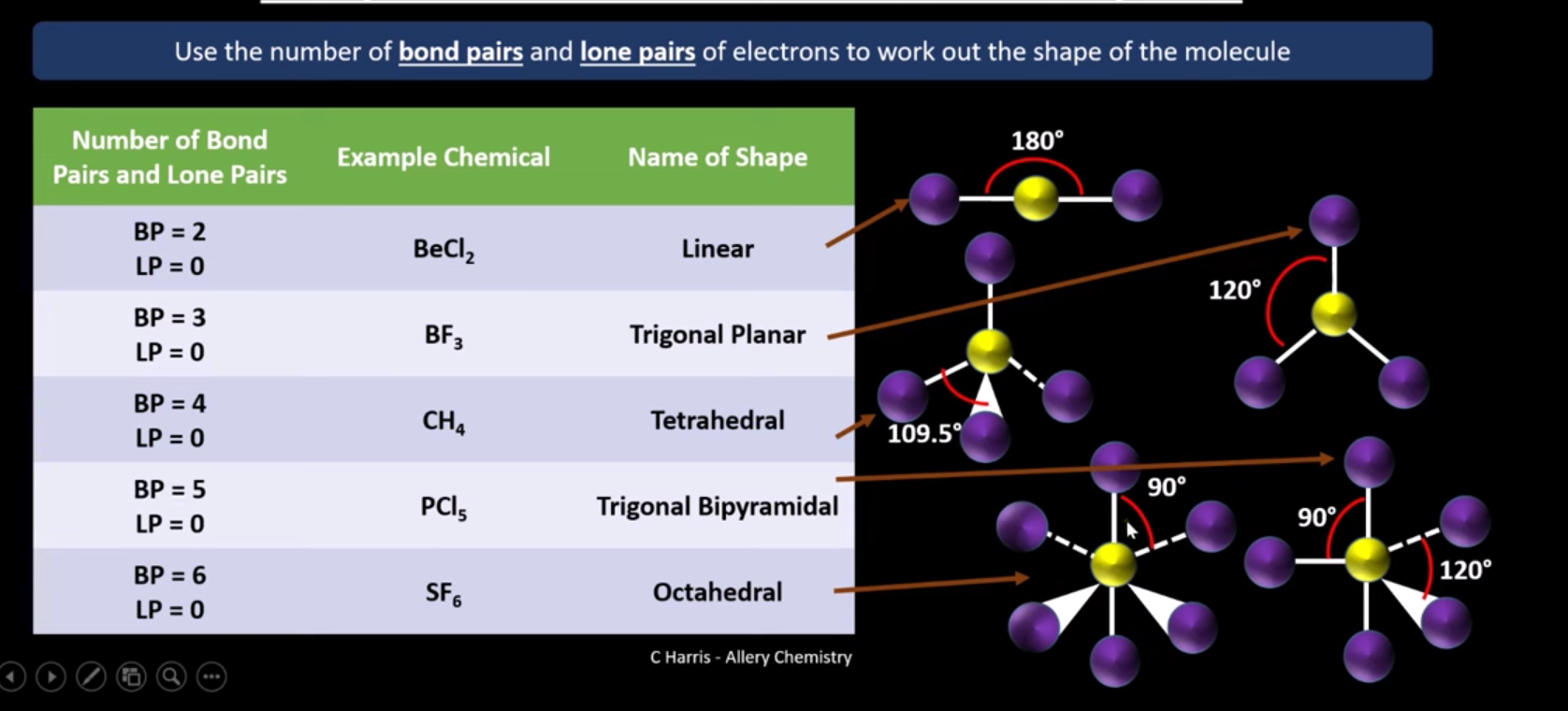
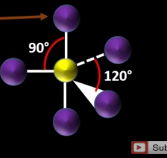
What is the name and angle of a shape with 5 bonding pairs?
Trigonal bipyramidal (90 and 120) degrees
What is the name and angle of a shape with 6 bonding pairs?
Octahedral (90 degrees)
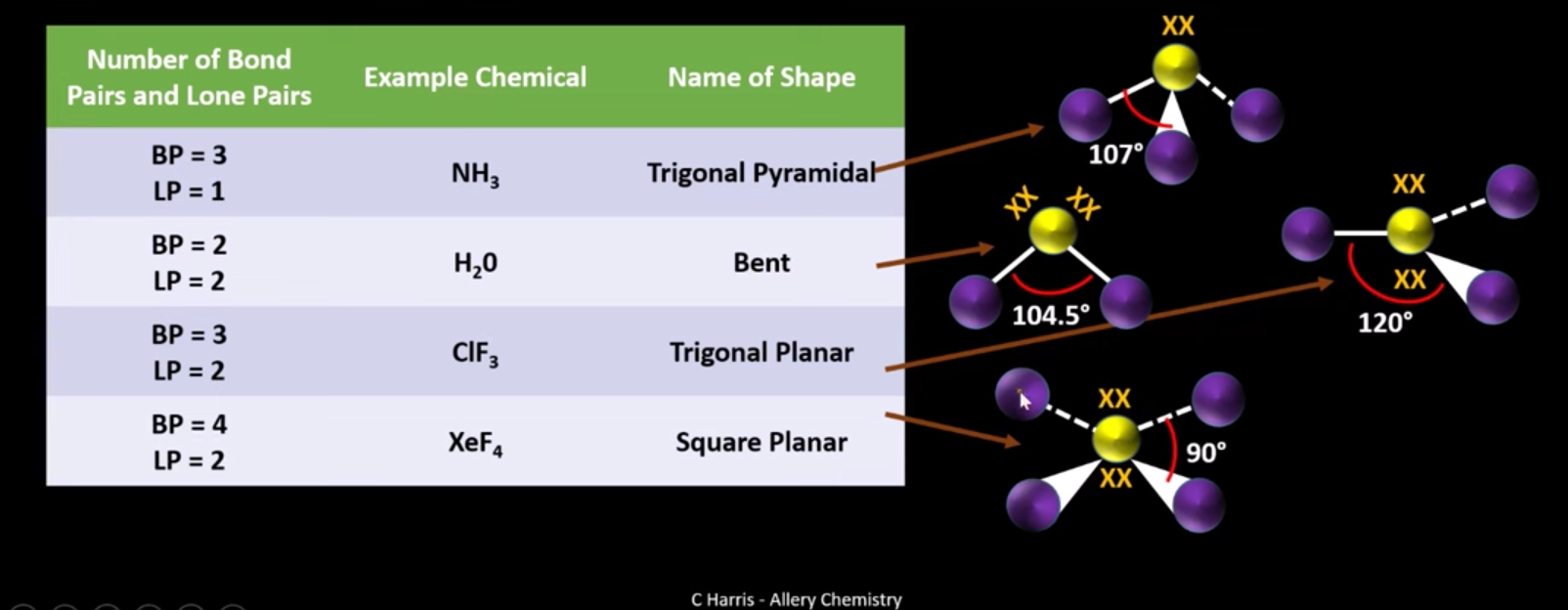
why is a molecule with 3 bonding regions and 2 lone pairs called trigonal planar?
because one set of lone pairs squash down, and another set push back up so its the same overall angle
What are the names and bond angles of molecules with lone pairs
What is electronegativity?
the ability for an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond
where do you go for electronegativity in the periodic table?
the further up and right you go in the periodic table (excluding the noble gases) the more electronegative the element is
The bigger the difference in electronegativity the more …………… the compound
ionic
What is a compound with a difference of 0 in electronegativity?
purely covalent
When can covalent bonds be polar?
if the atoms attached to them have a difference in electronegativty
When do london forces arise?
when molecules are nearby
when we boil a liquid what bonds are we breaking?
the intermolecular forces NOT the covalent bonds
when do permanent dipoles exist?
in molecules with a polarity
What are permanent dipole dipole forces?
weak electrostatic forces that exist between molecules with a polarity e.g. HCl
How can you test for polar molecules?
place a charged rod near a steady stream of polar liquid and it will bend towards the rod as the molecules align to face the oppositely charged rod
Why is ice less dense than water?
it forms a regular lattice structure held by hydrogen bonds and the molecules are further apart - makes ice less dense than water
in terms of bonding what does it mean to have a bigger molecule?
more london forces
are simple molecular molecules soluble in wateR?
depends on their polarity
What is the usual state of giant ionic molecules?
solid
what do polar molecules dissolve in?
polar solvents