Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Names + Rxns
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
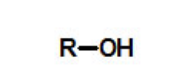
functional group, prefix, suffix
alcohol
prefix: hydroxy-
suffix: -ol
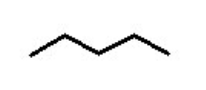
functional group, prefix, suffix
Alkane
prefix: alkyl-
suffix: -ane
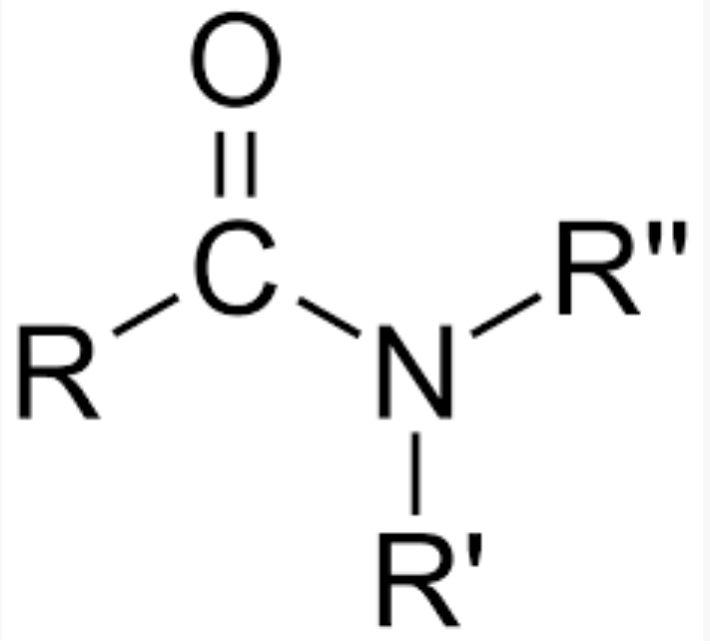
functional group, prefix, suffix
amide
prefix: carboxyl, amido-
suffix: -amide
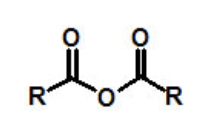
functional group, prefix, suffix
anhydride
prefix: alkanoyloxycarbonyl-
suffix: anhydride
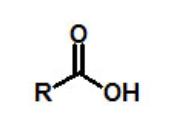
functional group, prefix, suffix
carboxylic acid
prefix: carbox-
suffix: -oic acid
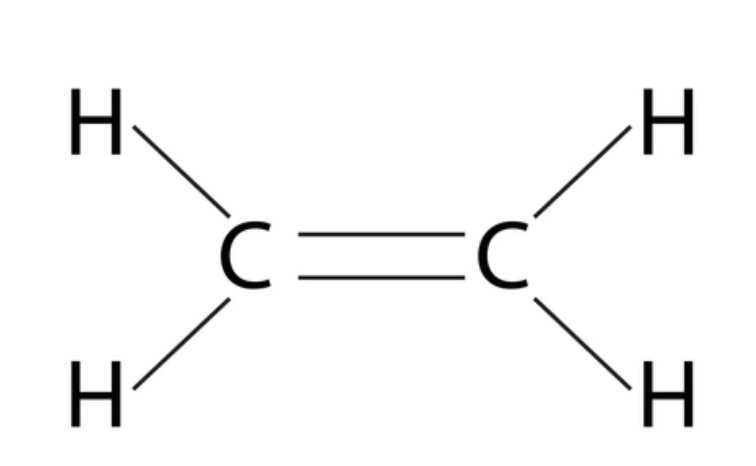
functional group, prefix, suffix
alkene
prefix: alkenyl-
suffix: -ene
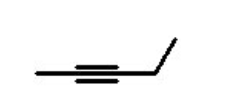
functional group, prefix, suffix
alkyne
prefix: alkynyl-
suffix: -yne
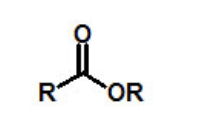
functional group, prefix, suffix
ester
prefix: alkoxycarbonyl-
suffix: -oate
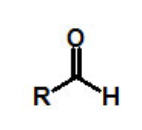
functional group, prefix, suffix
aldehyde
prefix: -oxo
suffix: -al
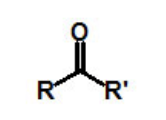
functional group, prefix, suffix
ketone
prefix: oxo-, keto-
suffix: -one
steps to naming
ID highest priority functional group by ox state (total bonds to O or N); compound will be named by suffix of this group
# the longest consecutive carbon chain that contain’s highest priority group. highest priority group should receive lowest # possible
name the carbon chain
name constituents (non- priority functional groups) that are part of carbon chain with prefix
name compound by listing #’s in alphabetical order
rank reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives (highest to lowest). what determines this order?
acid halides > anhydrides > carboxylic acid > esters > amides
based on leaving group stability and charge
naming carbon chains based on # of carbons (1-8)
1 = meth-
2 = eth-
3 = prop-
4 = but-
5 = pent-
6 = hex-
7 = hept-
8 = oct-
REDOX
oxidation = increase in oxidation state = loss of e-
increase in # of bonds to O, N, halides, + C
decrease in # of bonds to H
reduction = decrease in oxidation state = gain of e-
increase in # of bonds to H
decrease in # of bonds O, N, halides, + C
ox or red: primary alcohol to aldehyde using PCC
oxidation
ox or red: secondary alcohol to ketone using CrO3/pryamidine
oxidation
ox or red: aldehyde to carboxylic acid using H2CrO4
oxidation
ox or red: aldehyde to primary alcohol using LiAlH4/NaBH4
reduction
ox or red: ketone to secondary alcohol using LiAlH4/NaBH4
reduction
ox or red: carboxylic acid to primary alcohol using 1.LiAlH4, ether/2. H2O
reduction
adding one equivalent of alcohol to an aldehyde produces? two equivalents?
1 equiv: hemiacetal
2 equiv: acetal
adding one equivalent of alcohol to a ketone produces? two equivalents?
1 equiv: hemiketal
2 equiv: ketal