Diencephalon, internal capsule & limbic system
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Diencephalon
Thalamus
Epithalamus
Subthalamus
Hypothalamus
Mammilary bodies
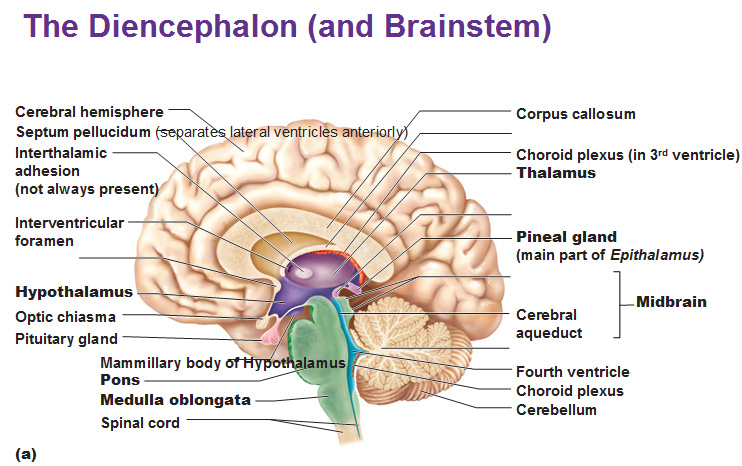
Boundaries of the diencephalon
Dorsal: Lateral ventricles
Laterally: Internal capsule
Medially: 3rd ventricle
Ventrally: Midbrain
Rosterally: Anterior commissure
Cadually: Posterior commissure
Papez Circuit
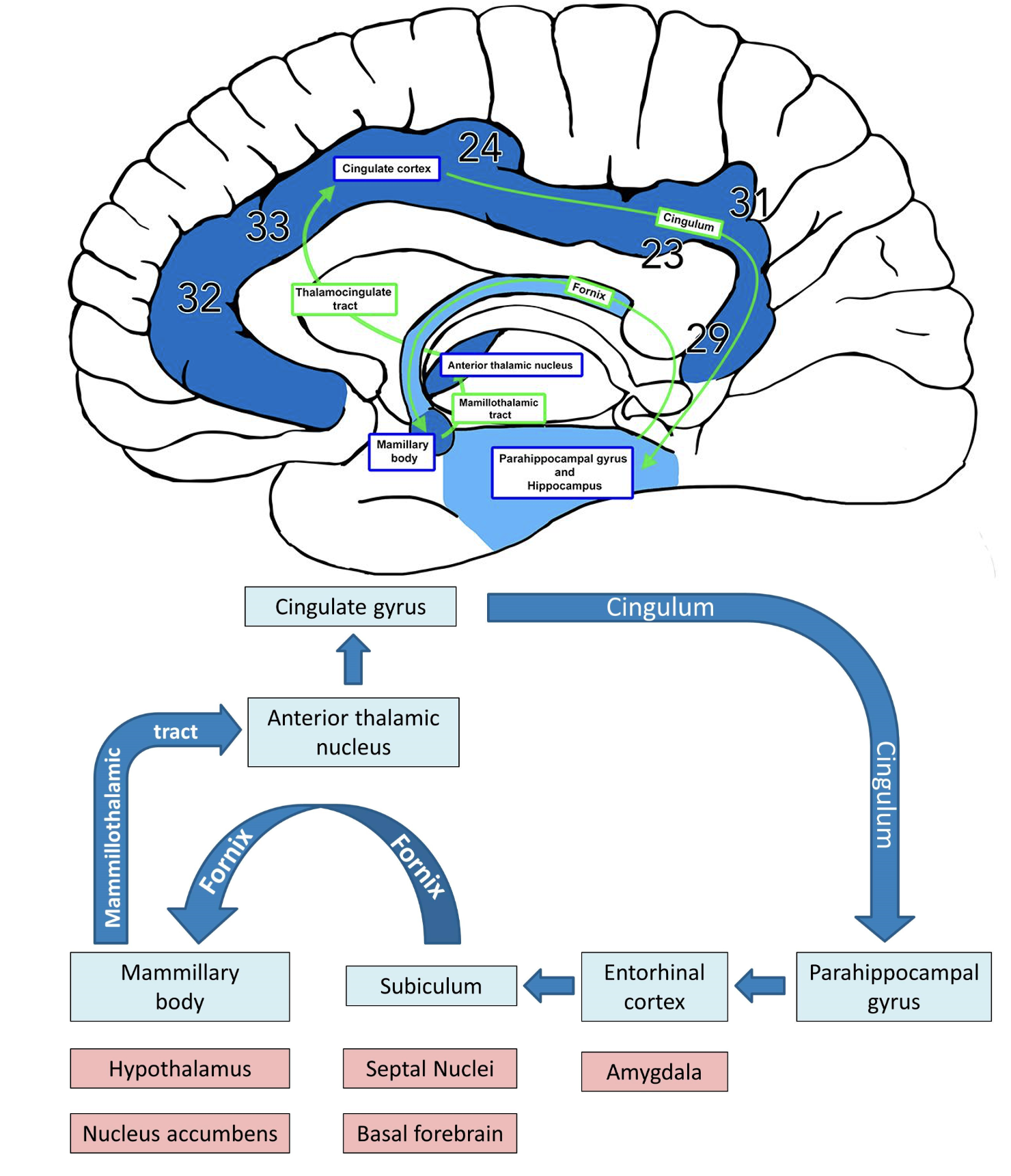
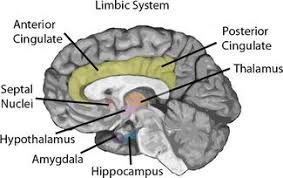
Limbic System
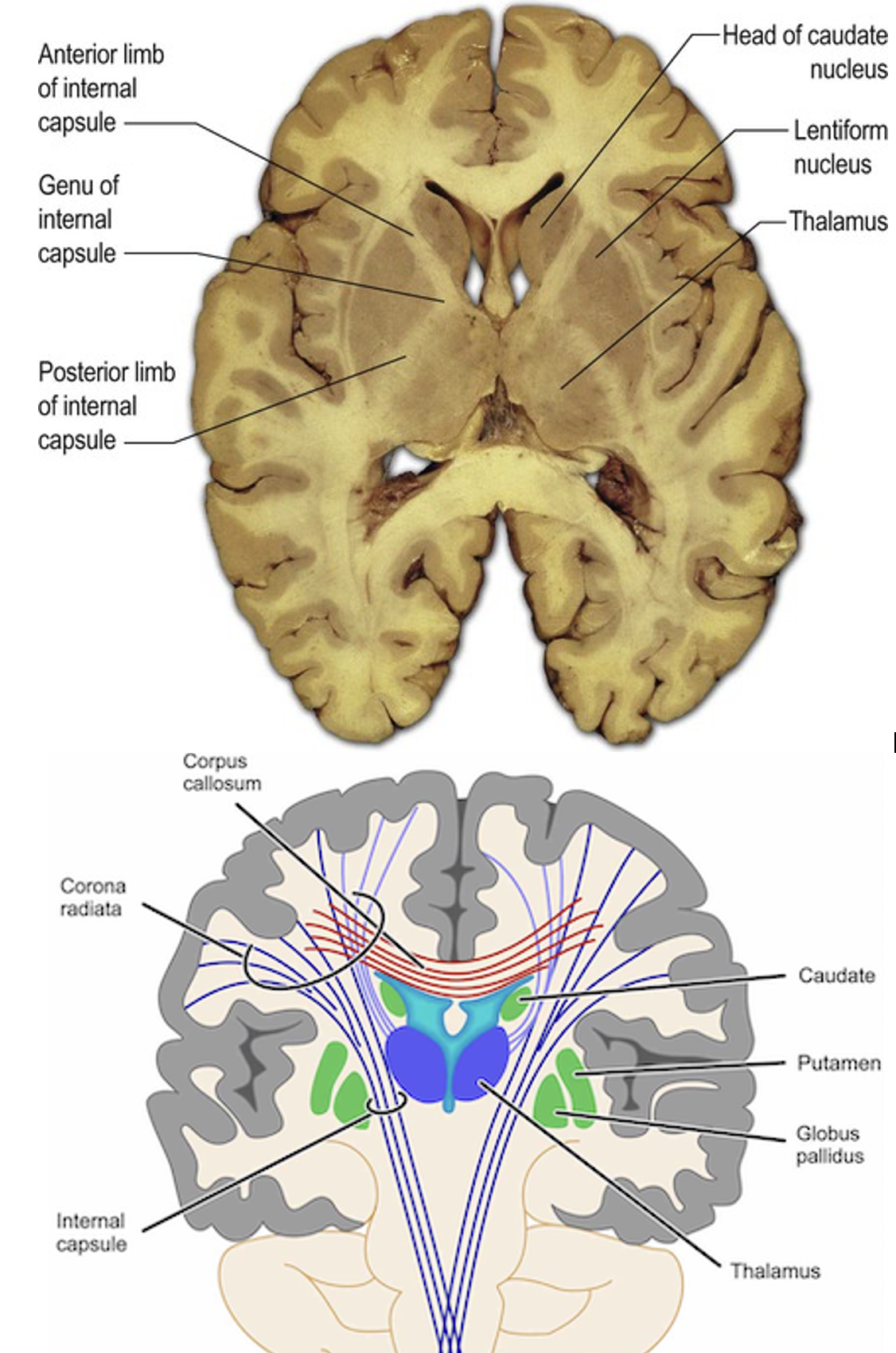
Fibres of the Internal Capsule
Projection fibre tract (white matter axons)
Both sensory (ascending) and motor (descending) neuron axons
Anterior limb:
Corticopontine (motor)
Thalamocortical (sensory)
Genu limb:
Corticobulbar (motor)
Posterior limb:
Corticospinal (motor)
Corticobulbar (motor)
Thalamocortical (sensory)
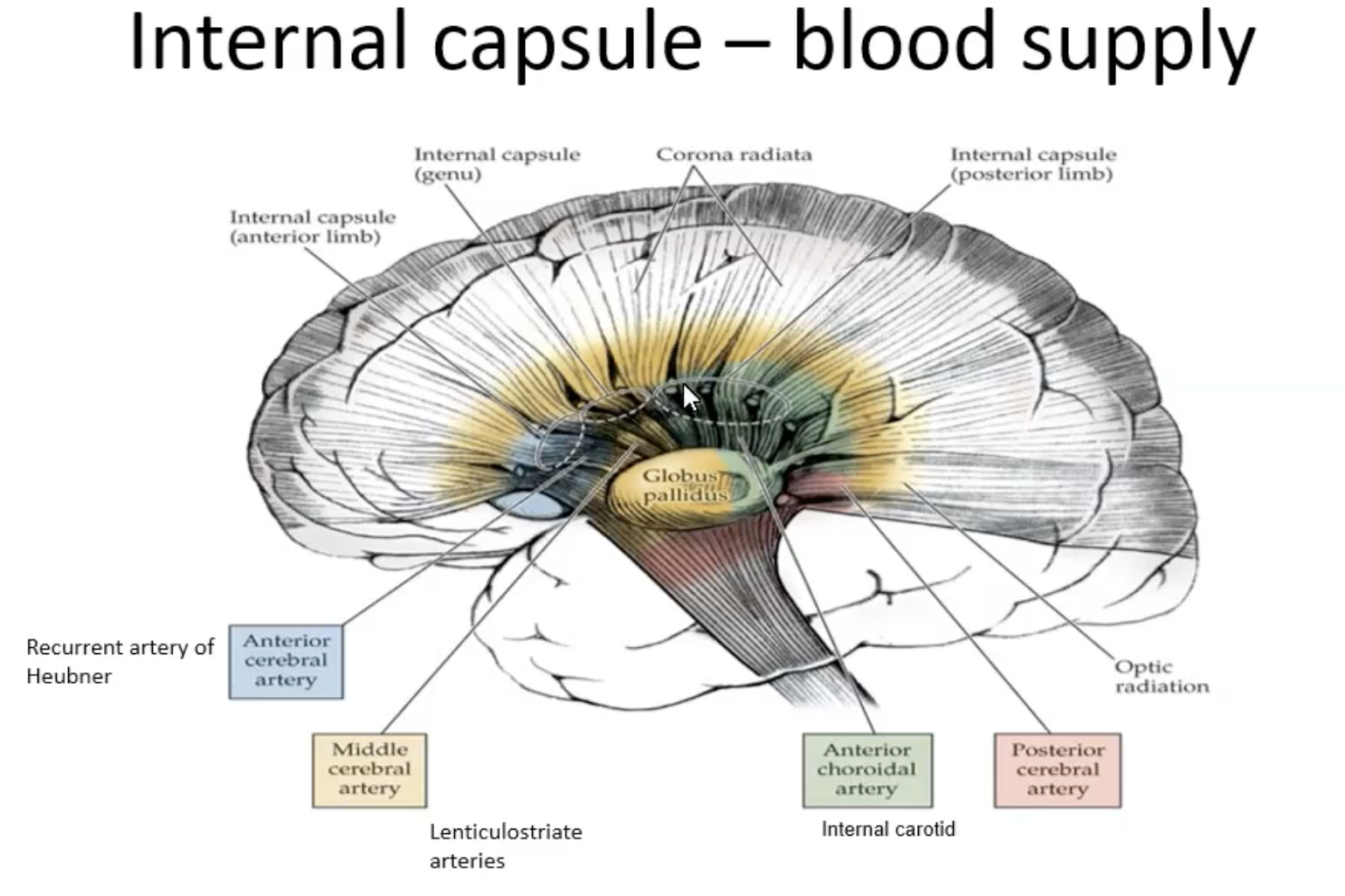
Blood Supply of the Internal Capsule
Anterior Limb
Anterior cerebral artery
Genu Limb
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior Limb
Anterior choroidal artery supply by internal carotids
Amygdala
Fear and fear conditioning
Emotional reactions such as fear, aggression or anger.
Learning that a neutral stimulus predicts the appearance of an aversive event.
Experimental stimulation most often elicits an anger or a fear response.
Emotional learning and memory
Anterior superior to hippocampus to add emotional response to a visual, auditory, olfactory etc inputs going into memory
Reward processing: Processing of information that leads to positive emotions, and this affects our thinking and preferences
Epithalamus
Pineal gland (size of a pea) and habenular nuclei
The pineal gland is part of the endocrine system because it secretes
Melatonin in high concentrations in the darkness for sleepiness.
Pineal gland is also regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Explicit Memory
Memory of facts
Declarative memory
inferomedial aspects of the temporal lobes — in the hippocampus.
Bilateral removal of medial portion of the temporal lobe (treat epilepsy) resulted in devastating declarative memory deficits
Recent and remote memory.
Could still learn certain tasks and retain this. (implicit/procedural memory)
Conscious memory that can be classified as episodic (events and personal experience) or semantic (memory of facts e.g. learnt at school, and recognition of people)
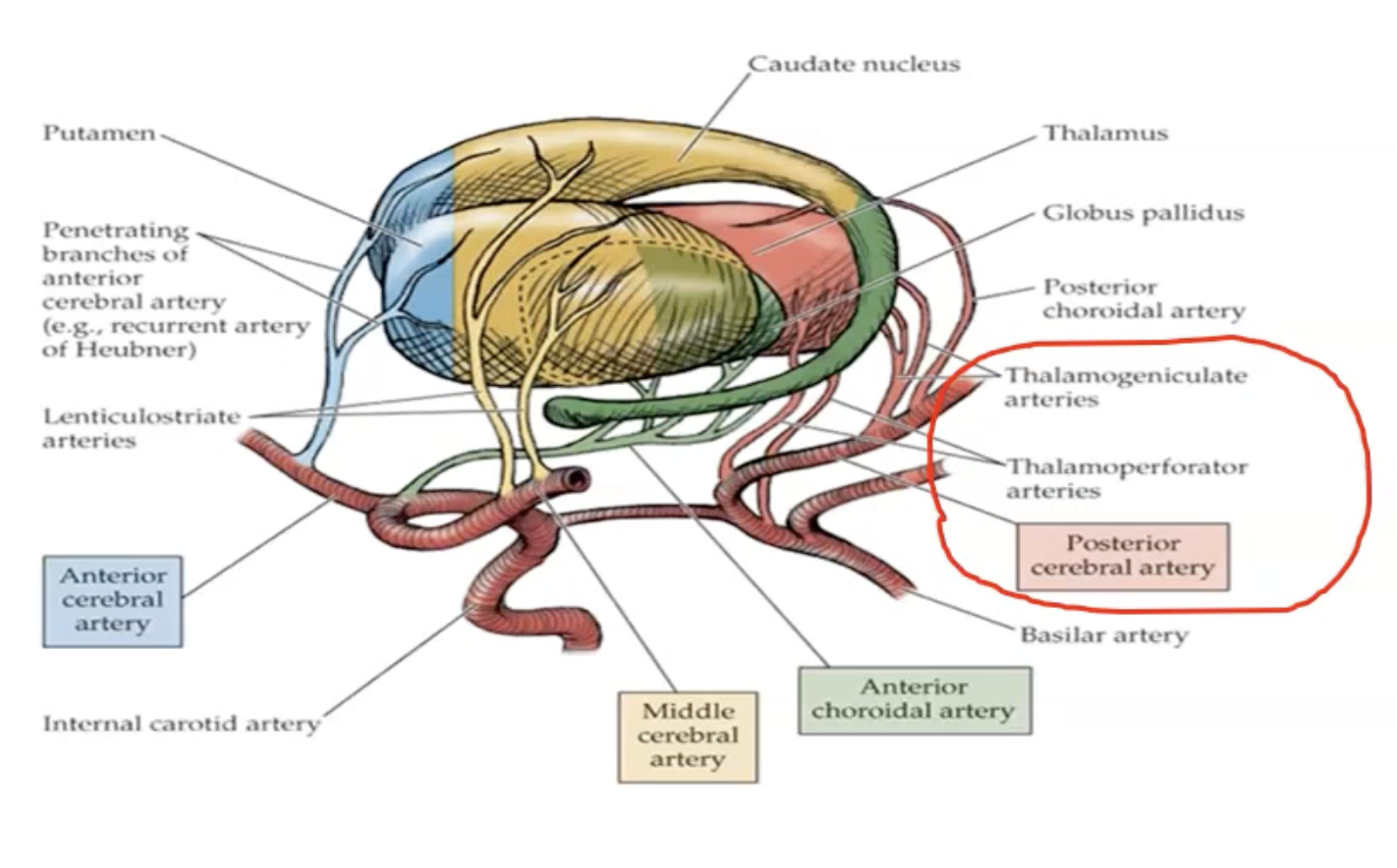
Blood Supply of the Thalamus
Branching of posterior cerebral
Thalamogeniculate Arteries
Thalamoperforator Arteries
Posterior communicating to connect it to the internal carotids
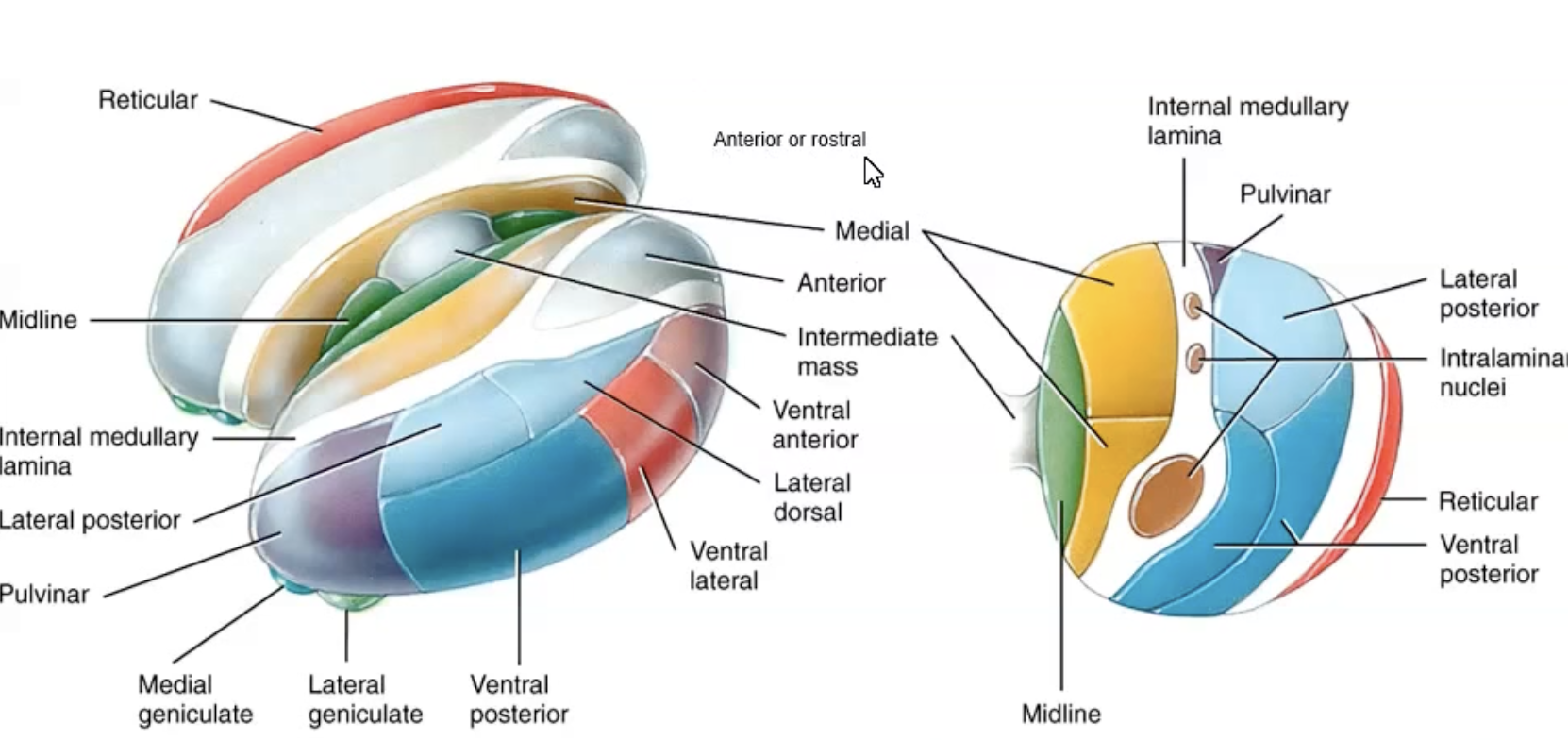
Lateral Division of the Thalamus
Lateral dorsal: Expression
Lateral posterior: Sensory
Pulvinar: Sensory.
Lateral ventral anterior: Basal ganglia cerebellum
Lateral Ventral lateral: Basal ganglia, cerebellum
Ventral posterolateral (body) + posteromedial (head)
Internal medullary lamina of fibres divides
Medial geniculate (auditory)
Lateral geniculate (visual)
Midline = olfaction and memory
Encloses splits and closes anterior division
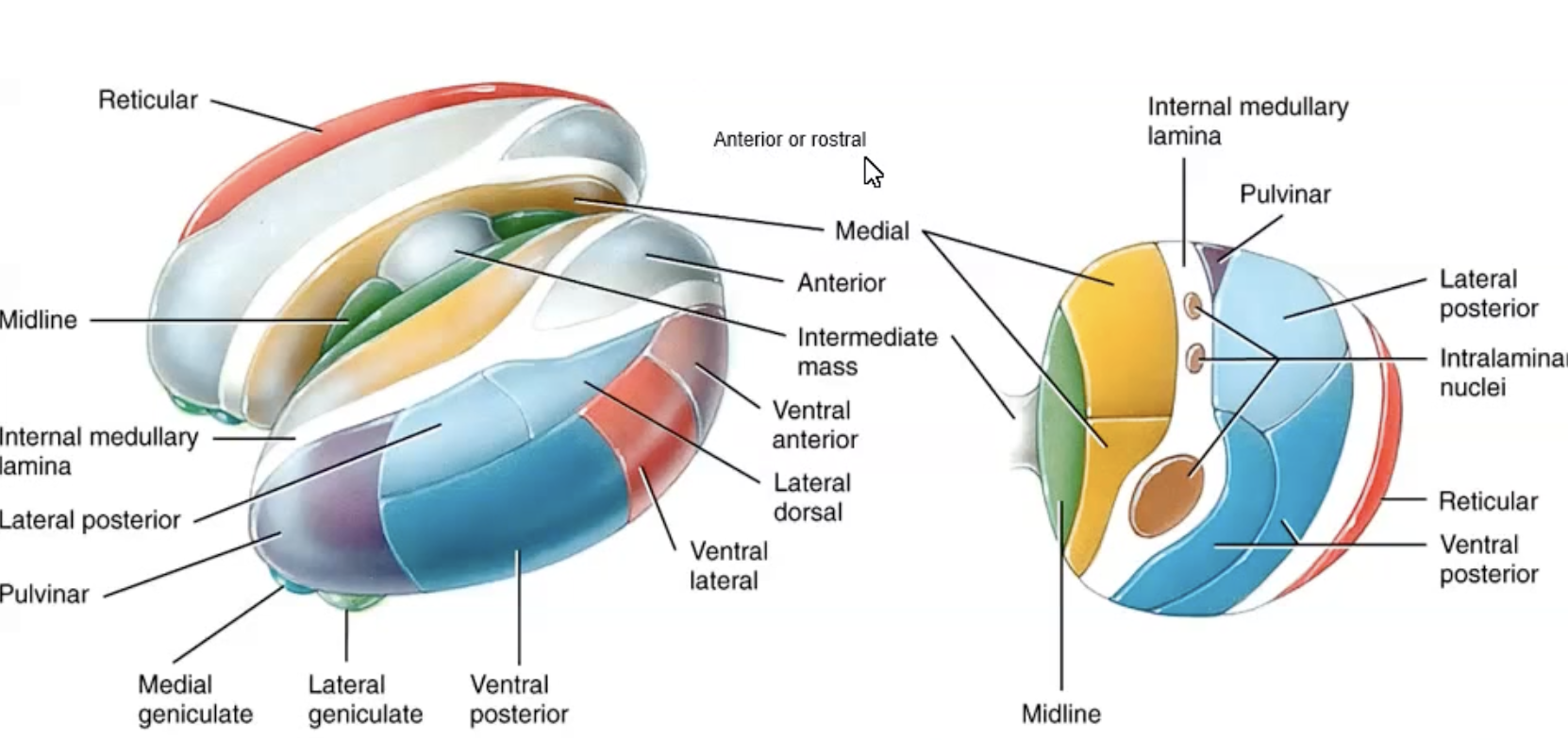
Other divisions of the thalamus (anterior, medial, intralaminar and reticular)
Anterior division = anterior nucleus = emotion memory
Medial division = Dorsomedial nucleus = learning memory cognition
External medullary lamina
Reticular division inhibits other thalamic nuclei
Intralaminar nuclei are within the internal medullary lamina connecting reticular formation, cerebellum, basal ganglia, cortex pain perception
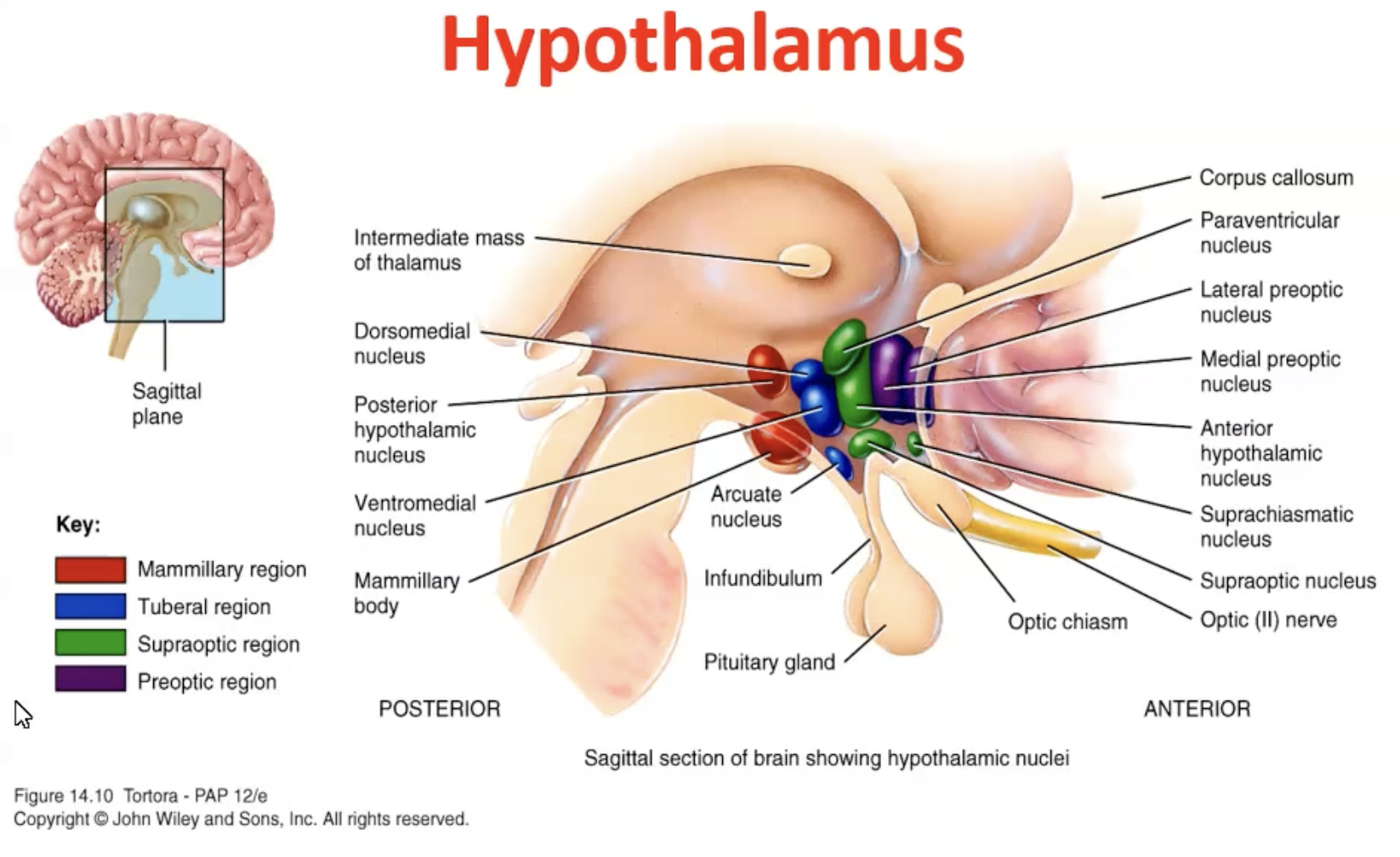
Hypothalamus
Regulates 6 basic physiological needs (homeostasis)
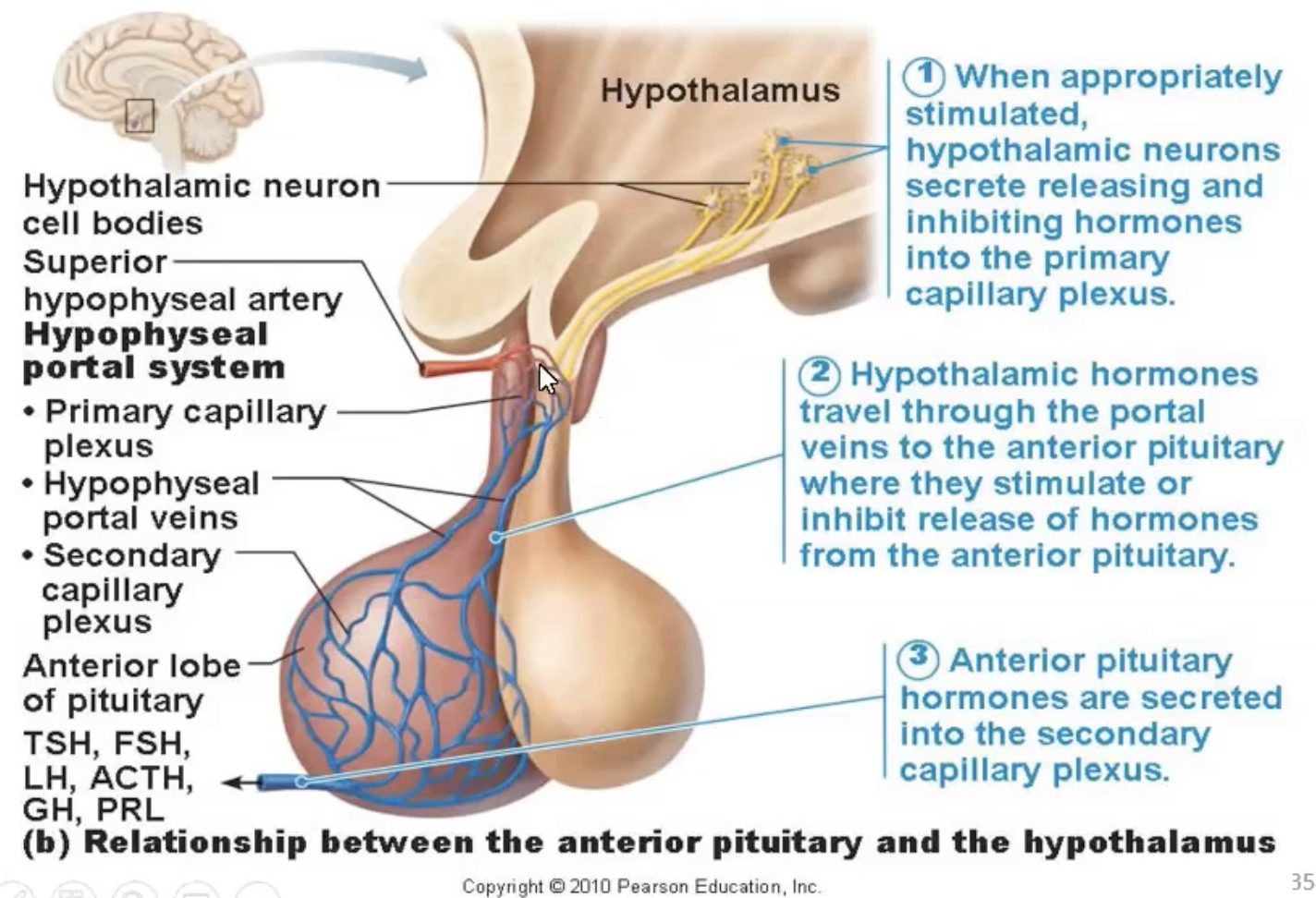
Releases tropic hormones to regulate the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis - produces hormones)
Synthesises hormones that are stored in the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis).
Output along the hypothalamospinal fibre tracts to control autonomic motor output - autonomic control
Somatic motor output (behavioural responses)
4g
Tropic hormone
Secreted by one endocrine gland
Travels in the blood to another endocrine gland
Affects hormone release of that gland
Relationship between the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus - ADD
Divisions of the hypothalamus
Lateral and medial zones: extensive connections
with the brainstem and telencephalonThe periventricular zone: lies next to the 3rd
ventricle and receives much of its inputs from
the medial and lateral zones
Septal area
A group of nuclei for pleasurable states and reward mechanisms.
Experimental animals press a lever repeatedly to obtain electrical stimulation of the septal area to the point of neglecting to eat.
Lesions of the septal area in animals cause "sham rage," sudden outbursts of aggressive behaviour.
Nucleus Accumbens
Processing emotion and reward/addiction.
When something is rewarding or pleasurable, dopamine is released and sends signals to the nucleus accumbens, reinforcing the behaviour
Large inputs from brainstem dopaminergic neurons, the hippocampus, and the amygdala.