Maxillary Injection Techniques
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture that was supposed to be given 10/2/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
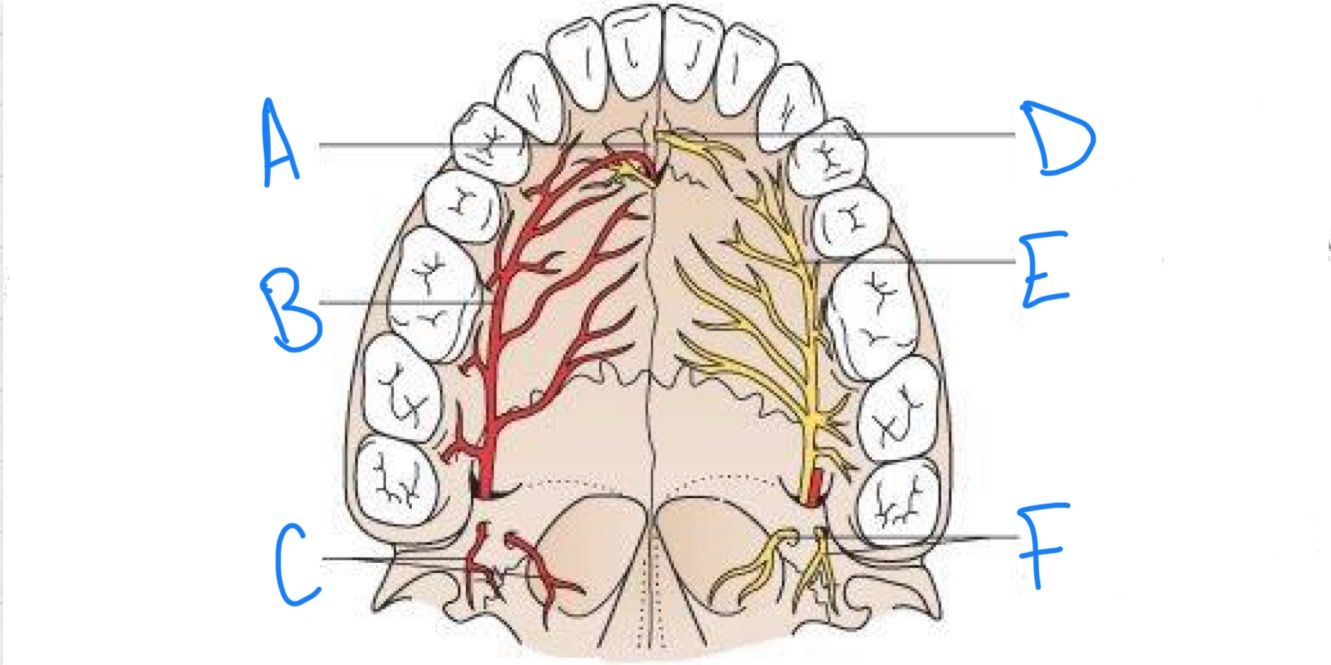
what structure is labeled A?
incisive fossa
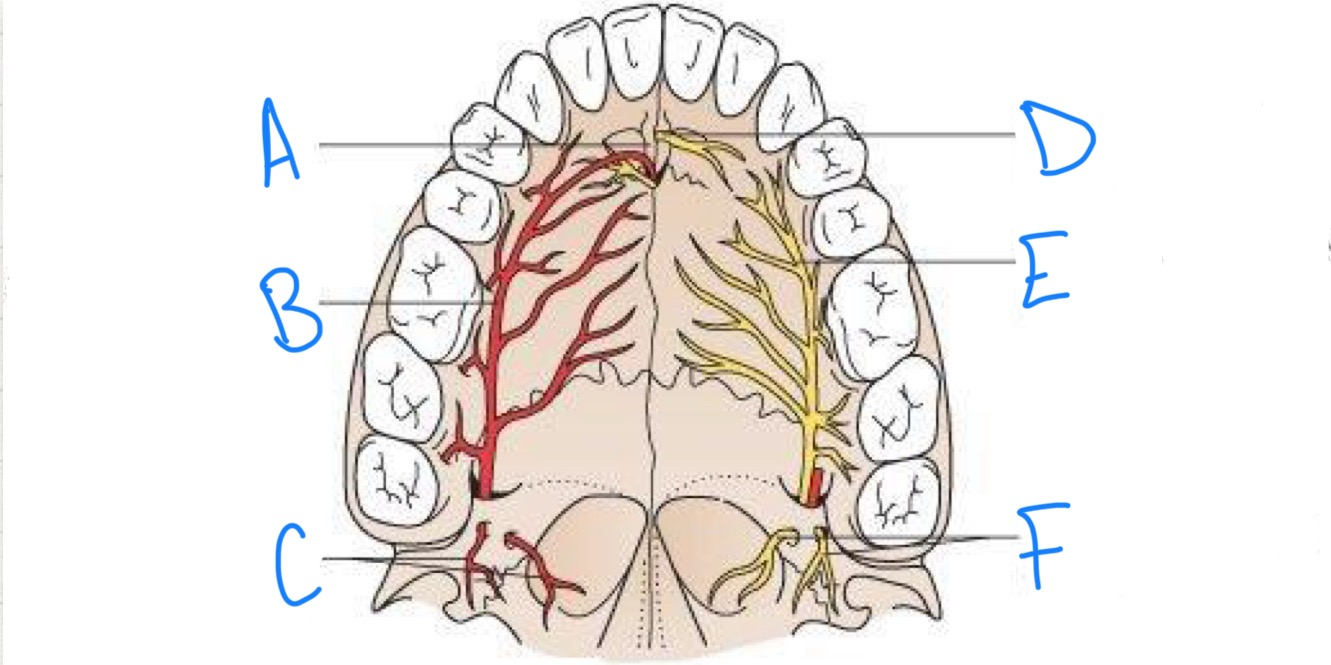
what structure is labeled B?
greater palatine artery
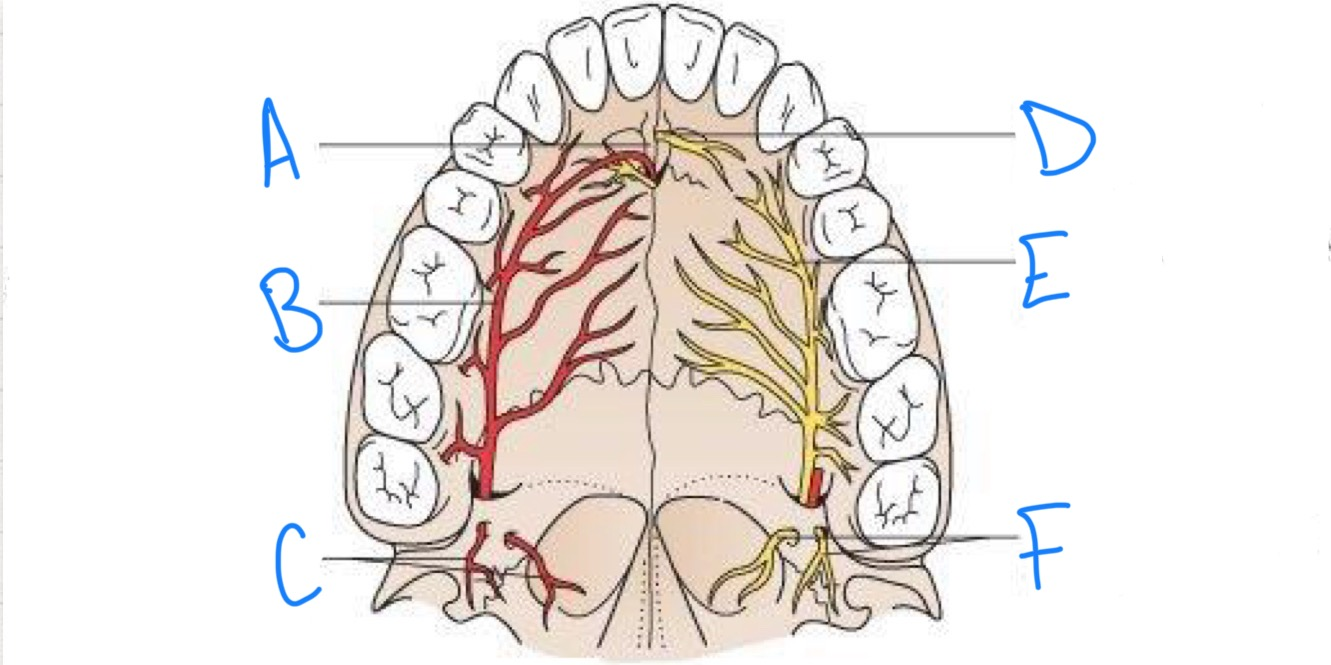
what structure is labeled C?
lesser palatine arteries
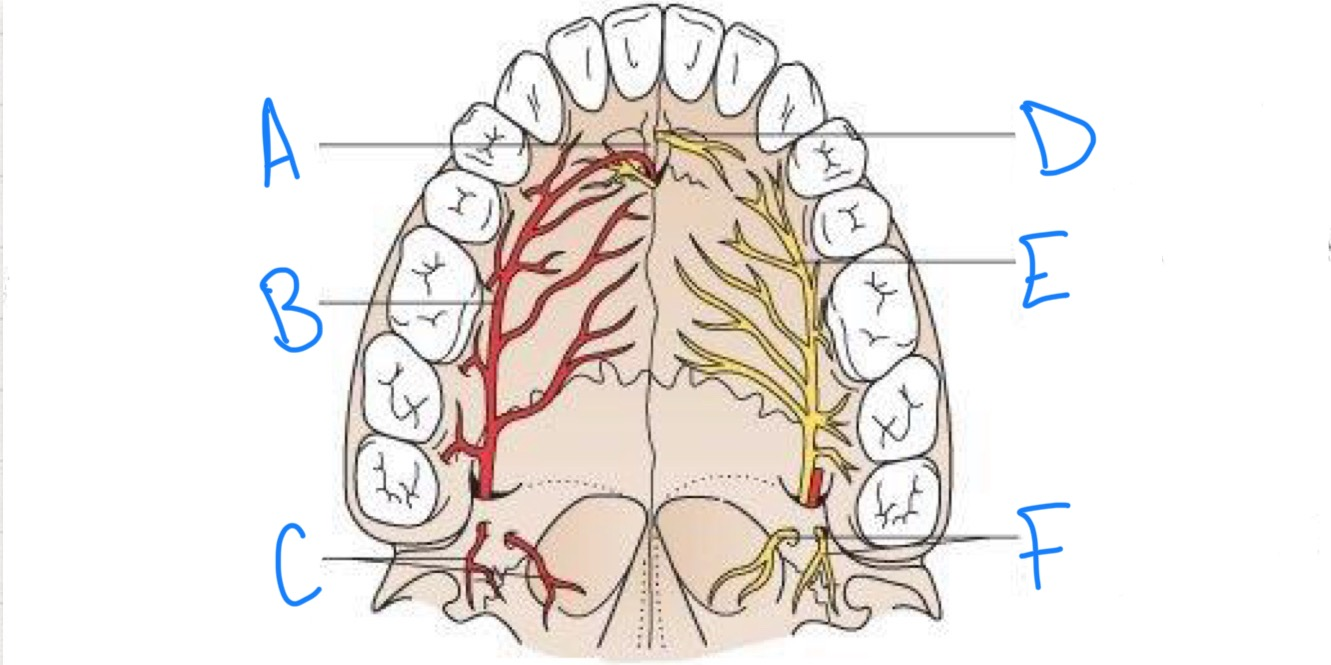
what structure is labeled D?
nasopalatine nerve
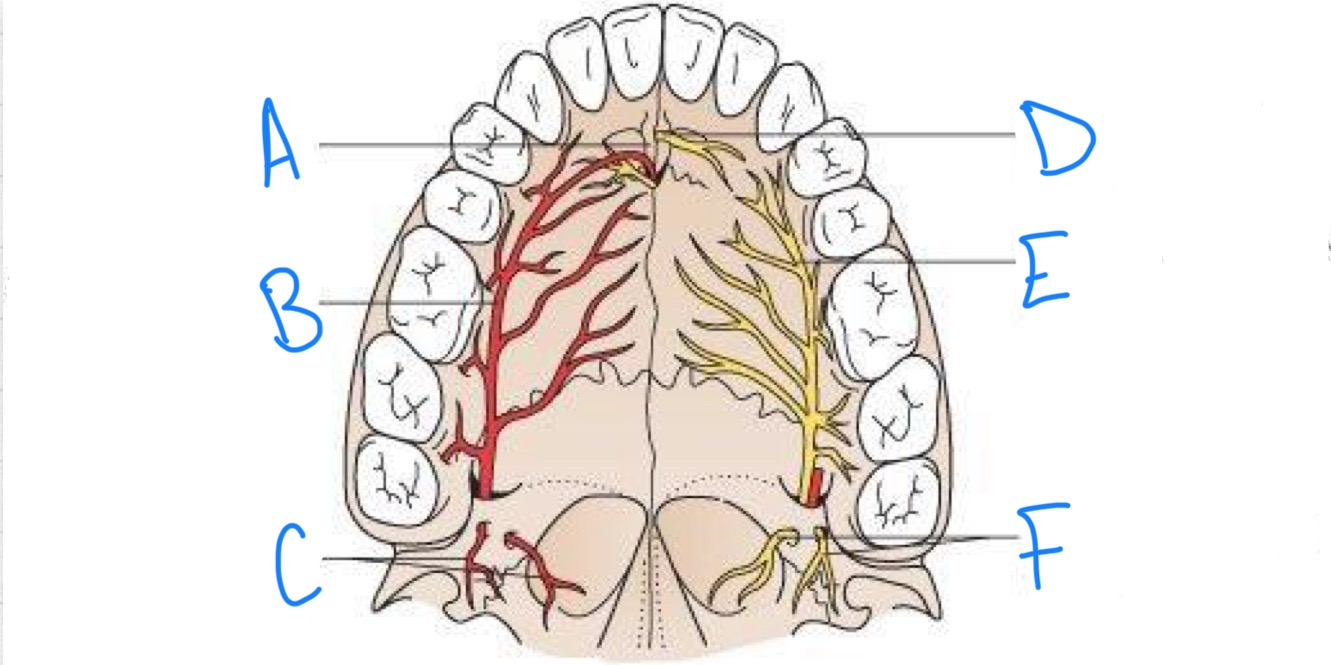
what structure is labeled E?
greater palatine nerve
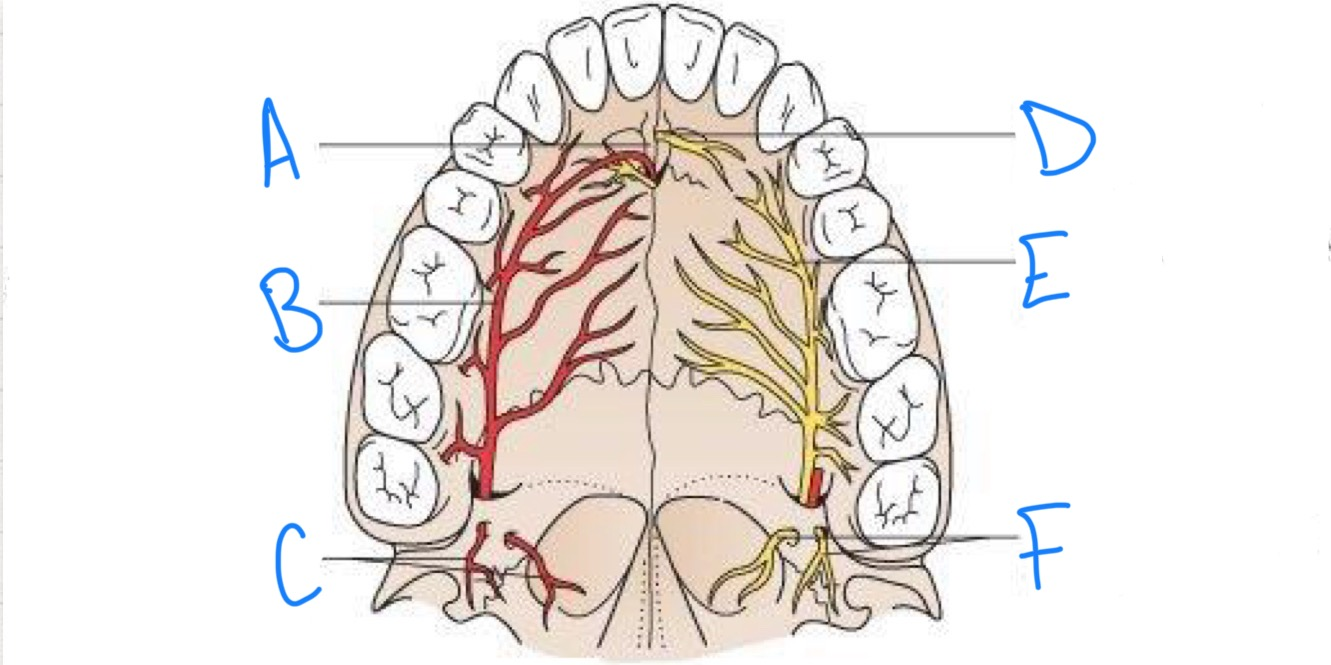
what structure is labeled F?
lesser palatine nerves
what type of tissue does topical anesthesia work well on?
non-keratinized tissue
what is the depth of penetration of topical anesthesia?
2-3mm
how long should topical lidocaine be left on for maximum efficiency?
2 minutes
t/f the alveolar bone is thinner on the maxilla than the mandible?
true
t/f local anesthetics cannot diffuse through the bony plate of the maxilla to reach apical nerves
false- they can diffuse
t/f in the mandible, the cortical plate is thick so solution cannot diffuse to apical nerves hence regional blocks are preferred
true
what is the aim for infiltration/supraperiosteal injections?
just above the bone, not in the bone
which way should the bevel face in infiltration injections?
toward the bone
do you use a short or long needle for infiltration injections?
short
t/f you should strech the tissue that you will be going through for the injection because it makes landmarks more clear
false- you should stretch tissue but it is to make patients more comfortable
what should you do if you make bony contact when doing an infiltration injection?
withdraw and deposit solution
how much solution should you inject in an infiltration injection?
about 1/3 of the carpule but it depends on your sources
regardless of the amount of solution used, the effect of pulpal anesthesia starts to decline after 35-45 minutes so it is good practice to supplement local anesthesia around 35 minutes if needed
what is anesthetized in an infiltration injection?
buccal bone, gingiva, buccal periodontium, cheek mucosa adjacent to injection
what should you do if the site of an infiltration injection is bleeding?
apply pressure for 2 minutes
how long does it take for the effects of an infiltration injection to take place?
4-5 minutes
slow injections
more comfortable for the patient as the tissue space expands more slowly
solution is more likely to remain at the intended site
why are palatal infiltrations much more uncomfortable?
the palatal mucosa is tightly adhered
how much solution should you deposit during a palatal infiltration?
0.2 ml because of the lack of space between the tissue and underlying bone
where is the foramen for the greater palatine nerve located?
distal to the second molar
what is anesthetized during a greater palatine nerve block?
soft tissue and hard tissue on one side of the midline from molars to premolar
what is anesthetized during a nasopalatine nerve block?
soft tissue and hard tissue of the anterior hard palate adjacent to six anterior teeth
where is there overlap in a greater palatine nerve block and nasopalatine nerve block?
canine region
is a short or long needle used for infraorbital/anterior superior alveolar nerve block?
long needle
what is the entry point for an infraorbital/anterior superior alveolar nerve block?
buccal sulcus in the mid pre-molar region
what is anesthetized during an infraorbital/anterior superior alveolar nerve block?
pulps of maxillary lateral incisors, canines, and first premolars
mucosa of upper lip, lateral nose, and lower eyelid are also anesthetized
t/f in an infraorbital/anterior superior alveolar nerve block, the maxillary central may not be fully anesthetized
true- due to cross innervation from the other side
are second premolars anesthetized during an infraorbital/anterior superior alveolar nerve block?
maybe? depends on the presence or lack of middle superior alveolar nerve
how can you anesthetize the middle superior alveolar nerve?
infiltration injection at the apex of the 2nd premolar (#4 or #13)
when is a middle superior alveolar nerve block useful?
when we intend to work on premolars only or when the infraorbital/posterior superior alveolar nerve block fails to provide adequate anesthesia for premolars or 1st maxillary molar
what is the ideal location for injection if you need to block the posterior superior alveolar nerve?
behind the maxillary tuberosity
needle is inserted at the height of buccal sulcus in plane of distal surface of 2nd molar
how should you do a posterior superior alveolar nerve injection?
needle is inserted at the height of buccal sulcus in plane of distal surface of 2nd molar
the needle is advanced close to bony surface at an angle of 45 degrees superiorly, posteriorly, and medially to a depth of about 20 mm
use shorter needle to minimize risk of nicking the maxillary artery!
what areas are anesthetized during a posterior superior alveolar nerve block?
buccal gingiva, periodontium, buccal bone adjacent to molars
pulps of all molars except the mesiobuccal pulp/root of 1st molar
what are the potential complications from a posterior superior alveolar nerve block?
risk of hematoma formation if needle penetrates the pterygoid plexus of veins
bleeding due to nicking of maxillary artery by the needle
what should you do if a hematoma occurs after a posterior superior alveolar nerve block?
apply pressure in the pterygoid region for 5 minutes
what are the indications for a maxillary nerve block?
pain control for extensive procedures requiring anesthesia of the entire maxillary division
when tissue inflammation or infection precludes the use of other regional nerve blocks or supraperiosteal injection
diagnostic or therapeutic procedures for neuralgias of V2
what areas are anesthetized during a maxillary nerve block?
pulpal anesthesia of the maxillary teeth on the side of the block, buccal periodontium and bone overlying these teeth, soft tissues and bone of the hard palate and part of the soft palate medially to the midline, skin of the lower eyelid, side of the nose, cheek, and upper lip
what are the 2 approaches you can take for a maxillary nerve block?
high tuberosity approach or greater palatine approach
what are some things you can do to make anesthesia more comfortable?
wait 2 minutes for topical to be fully effective, stretch mucosa to distract the patient, apply pressure on the palate at the site of injection just before/during injection, inject slowly, avoid multiple injections with the same needle (becomes blunted)