VCE Unit 3 Biomechanics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
force
the push or pull acting on an object. F= m x a
friction
Force that acts in the opposite direction to motion when 2 surfaces are in contact with one another.
inertia
Tendency of a body to resist change in its state of motion
momentum
measure of the amount of motion an object has and its resistance to change
momentum=
mass (kg)x velocity (m/s)
conservation of momentum
whenever two bodies collide, the combined momentum of the two bodies is conserved
Summation of Momentum
sequential movement of each body segment to generate more momentum
angular momentum
Quantity of angular motion of an object
angular momentum=
moment of inertia x angular velocity
Moment of inertia=
mass x radius
impulse
the change of momentum of an object when the object is acted upon by a force for over time
impulse=
force x time
newtons first law-
Inertia - A body will remain at rest or continue in a state of constant motion unless acted upon by an external force/torque
newtons second law-
Acceleration of an object depends on its mass and on the force applied to it
torque
a twisting force
newtons third law-
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
linear motion
Movement of a body along a straight line or curved path where all body parts move in the same direction at the same speed.
distance
The path travelled by a body from point A to B
displacement
A change in the position of a body in relation to its starting position
speed
time taken to cover distance- speed= distance/ time (m/s)
velocity
The time taken change position- velocity= displacement/ time (m/s)
acceleration
A change in velocity in a given period of time- can be speeding up/ down or remaining constant
acceleration=
Change in velocity / Change in time (m/s)
angular motion
Rotation around a central axis or fixed point, measured in degrees
angular distance
The distance an object travels (measured in degrees) around an axis
angular displacement
difference between the initial and final position of an object that has travelled around an axis (measured in degrees)
projectile motion
Horizontal component: relates to the horizontal distance covered
Vertical component: relates to the height reached
Factors influencing path of a projectile
angle of release, speed of release, height of release
Equilibrium
When all forces and torques are balanced
stability
The ability of a body to resist change in its current state of equilibrium
base of support
The area of an object that is in contact with the surface supporting it
Centre of gravity
The central point of an object, about which all of its weight is evenly distributed and balanced
Line of Gravity
An imaginary line that passes through the centre of gravity in the direction that gravity acts
lever
A simple machine consisting of a rigid bar that can be made to rotate around an axis.
Have an axis (fulcrum), resistance (load) and a force (effort).
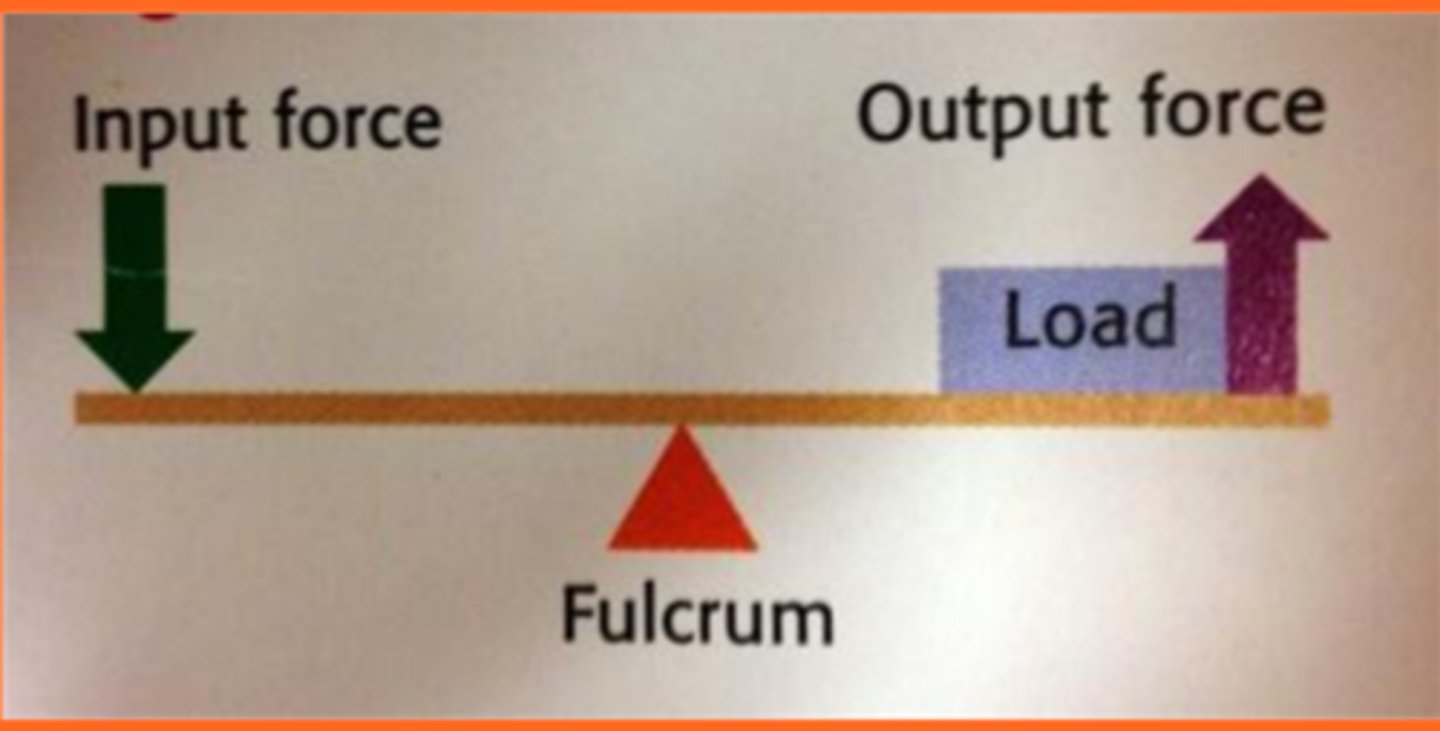
1st class lever
FAR
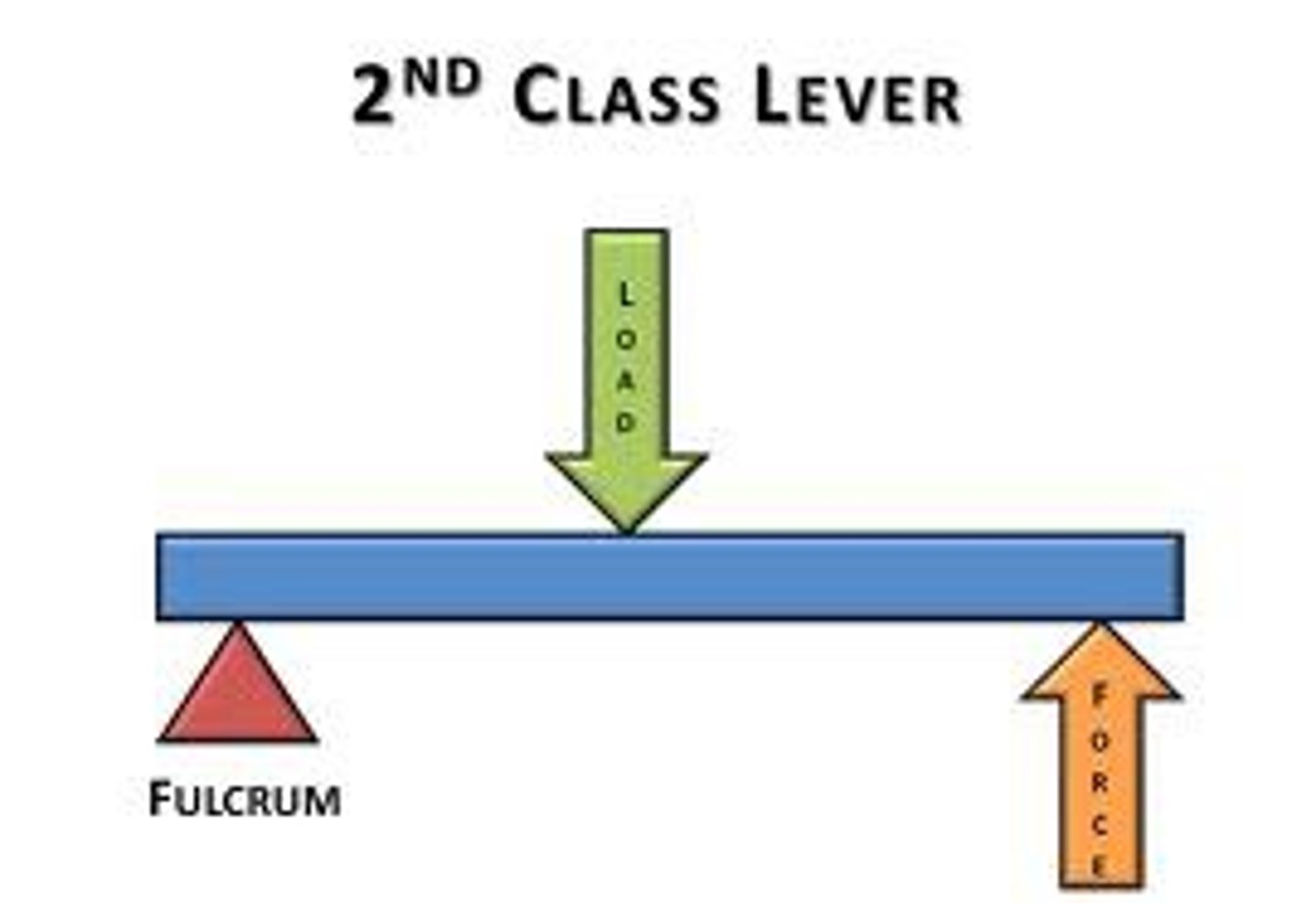
2nd class levers
ARF
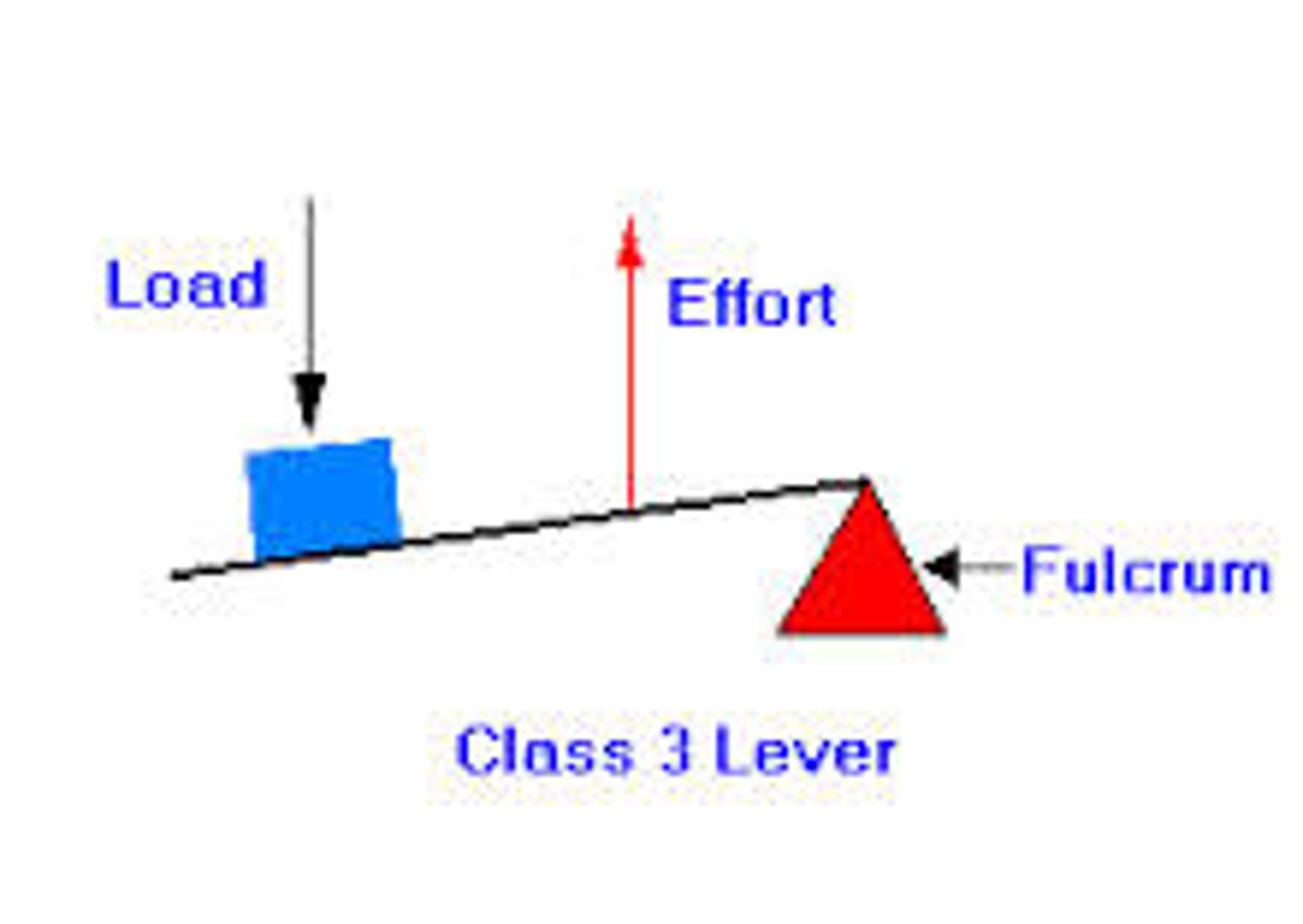
3rd class levers
AFR