The determination of equilibrium market prices
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is the market system
The interaction of supply and demand through negotiations between buyers and sellers, who meet an agreed upon price that works for both parties
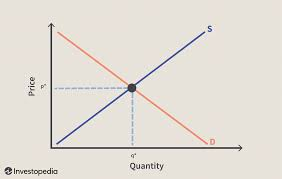
Equilibrium price - definition
When demand = supply
Also known as market-clearing price
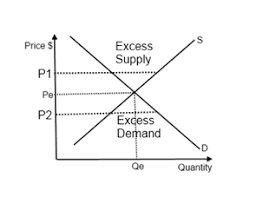
Disequilibrium - definition
Any price above or below the equilibrium price creates this, occuring when there’s excess supply or demand
Excess demand and supply - definitions and graph
Excess demand: when demand> supply - caused by low prices
Excess supply: when supply> demand - caused by high prices
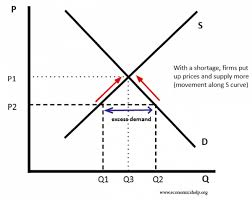
How do markets respond to excess demand?
There’s a shortage in the market, more is demanded than suppliers can produce.
This pushes prices up and causes firms to supply more (expands), since prices increase, demand will contract causing the price to return to the equilibrium price
How do markets respond to excess supply?
There is a surplus of supply, so prices will fall as firms try to sell more goods. This leads to supply contracting and demand expanding at the lower price, returning price to equilibrium
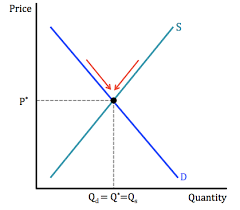
What causes new market equilibriums?
When the demand or supply curves shift due to PIRATES or PINTSWC reasons, forming a new equilibrium price
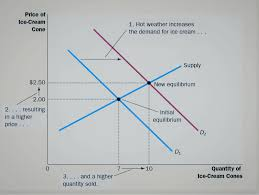
Example of a new market equilibrium (shifting)
E.g. population increases, causing demand to shift outwards, this leads to a new higher equilibrium price, as more QD, but same supply.