science Cells
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
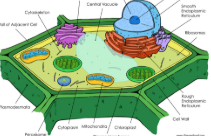
Nucleus
Contains DNA
Ribosomes
Synthesize Proteins
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Making and transporting proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Lipid synthesis; helps create fats, oils
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for storage or transport out of the cell
Vacuoles and vesicles
Stores materials
Lysosomes
Break down and recycle macromolecules
Cytoskeleton
Maintains cell shape; like a whip moves cell parts; helps cells move
Centrioles
Organize cell divisions
Chloroplasts
Converts solar energy to chemical energy stored in food; ex: photosynthesis
Mitochondria
convert chemical energy in food to useable compounds
Cell Wall
Shapes, supports, protects the cell
Cell membrane
Regulates materials entering and leaving the cell; protects and supports the cell
Cillian
hair on the eukaryotic cell
Organelles
parts that are within the cell
Unicellular
an organism made up of a single cell
Multicellular
an organism made up of more than one cell
Three principles of Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things
New cells are produced from existing cells
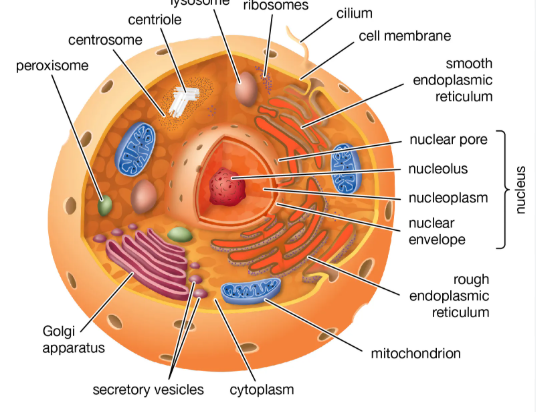
What is this?
Eukaryotic Animal
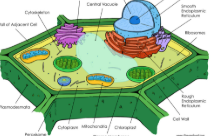
What is this?
Eukaryotic Plant
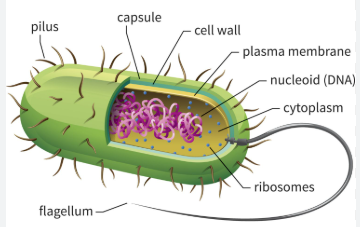
What is this?
Prokaryotic (ex: bacteria)
Structural Organelles Examples
Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton, Centrioles, Spindle Fibers
Structural Organelles….
provides structure and shape of the cell
Produce the macromolecule organelles
Ribosomes, Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, Smooth ER, Golgi Apparatus, Chloroplast, Mitochondria
Transport, store, recycle, macromolecules
Lysosomes Vesicles Vacuoles
Protect the cells and its parts harm
Nucleus, Cell membrane, Cell Wall, Capsule, Peroxisome
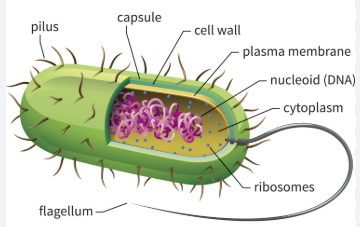
No membrane
No Nucleus
Divides by nucleus
Unicellular
Prokaryote
Membrane= = bound organelles, wider variety and complexity
DNA held and protected in nucleus
Divides by mitosis
Uni- and multicellular organisms
Eukaryote
Cell
Small
endless variety of shapes and sizes
well organized and complex
Osmosis
Movement diffusion of water molecules
Low solute concentration
High water concentration
High solution concentration
High water water concentration
Cell Membrane
controlling the movement of things in and out of the cell
What is the structure of Cell Membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer
Membrane Proteins
Carbohydrates
Cholesterol
What is the function of Cell membrane
Provides protection for the cell by keeping harmful substances out and keeping the components of the cell inside