Human Reflex Physiology and Reflex Arcs
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What are reflexes?
Rapid, predictable, involuntary motor responses to stimuli mediated over neural pathways called reflex arcs.
How can reflexes be categorized?
Into two large groups: autonomic reflexes and somatic reflexes.
What are autonomic reflexes?
Reflexes mediated through the autonomic nervous system, usually not consciously perceived, regulating functions like digestion and blood pressure.
What do somatic reflexes involve?
The stimulation of skeletal muscles by the somatic division of the nervous system.
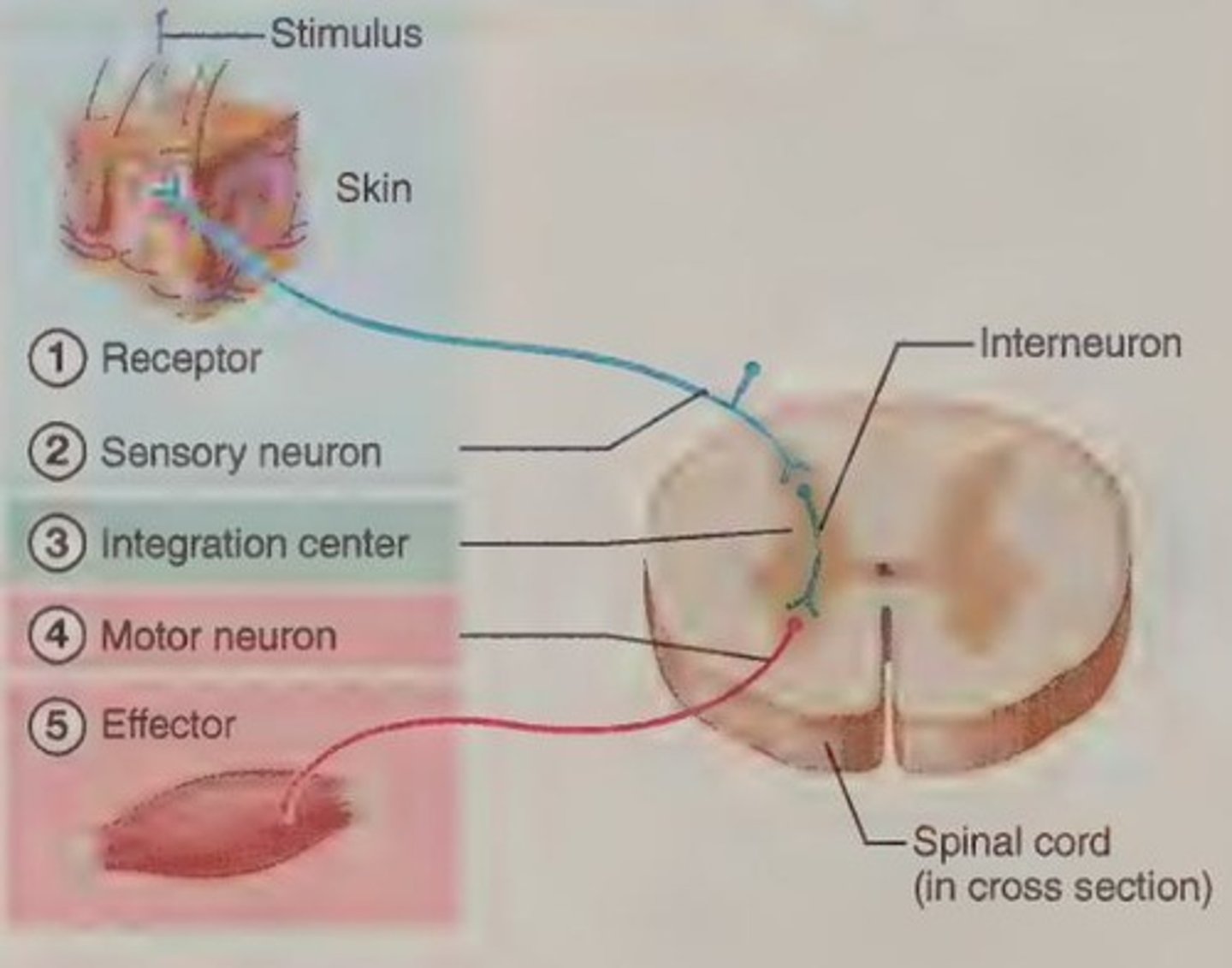
What are the five basic components of a reflex arc?
1. Receptor, 2. Sensory neuron, 3. Integration center, 4. Motor neuron, 5. Effector.
What is a monosynaptic reflex?
A reflex integration center with a single sensory neuron and a motor neuron, such as the patellar reflex.
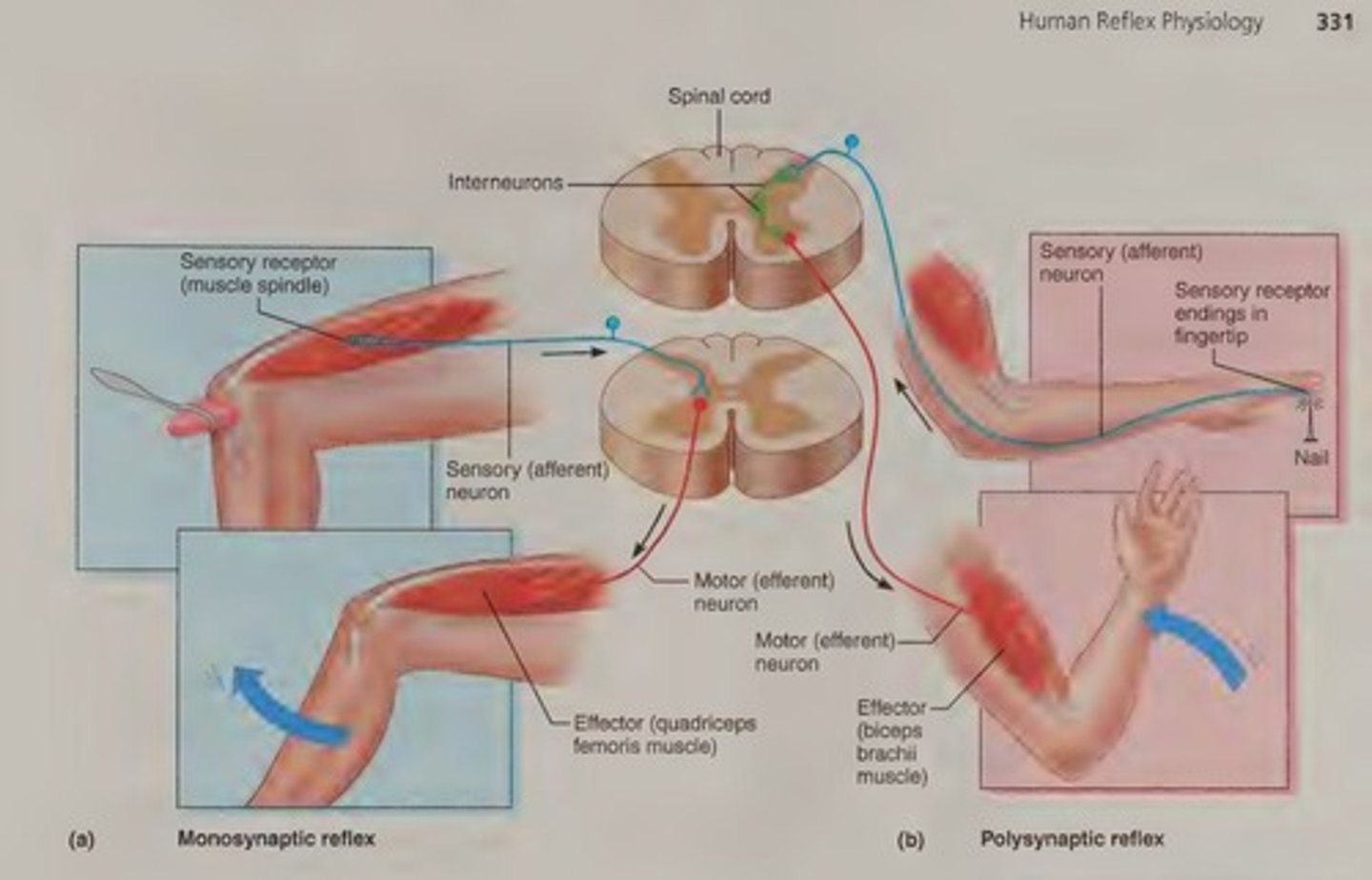
What is a polysynaptic reflex?
A reflex involving one or more interneurons in the integration center, such as the flexor reflex.
What is the role of the motor neuron in a reflex arc?
To conduct efferent impulses from the integration center to an effector organ.
What is the effector in a reflex arc?
A muscle fiber or gland cell that responds to efferent impulses by contracting or secreting.
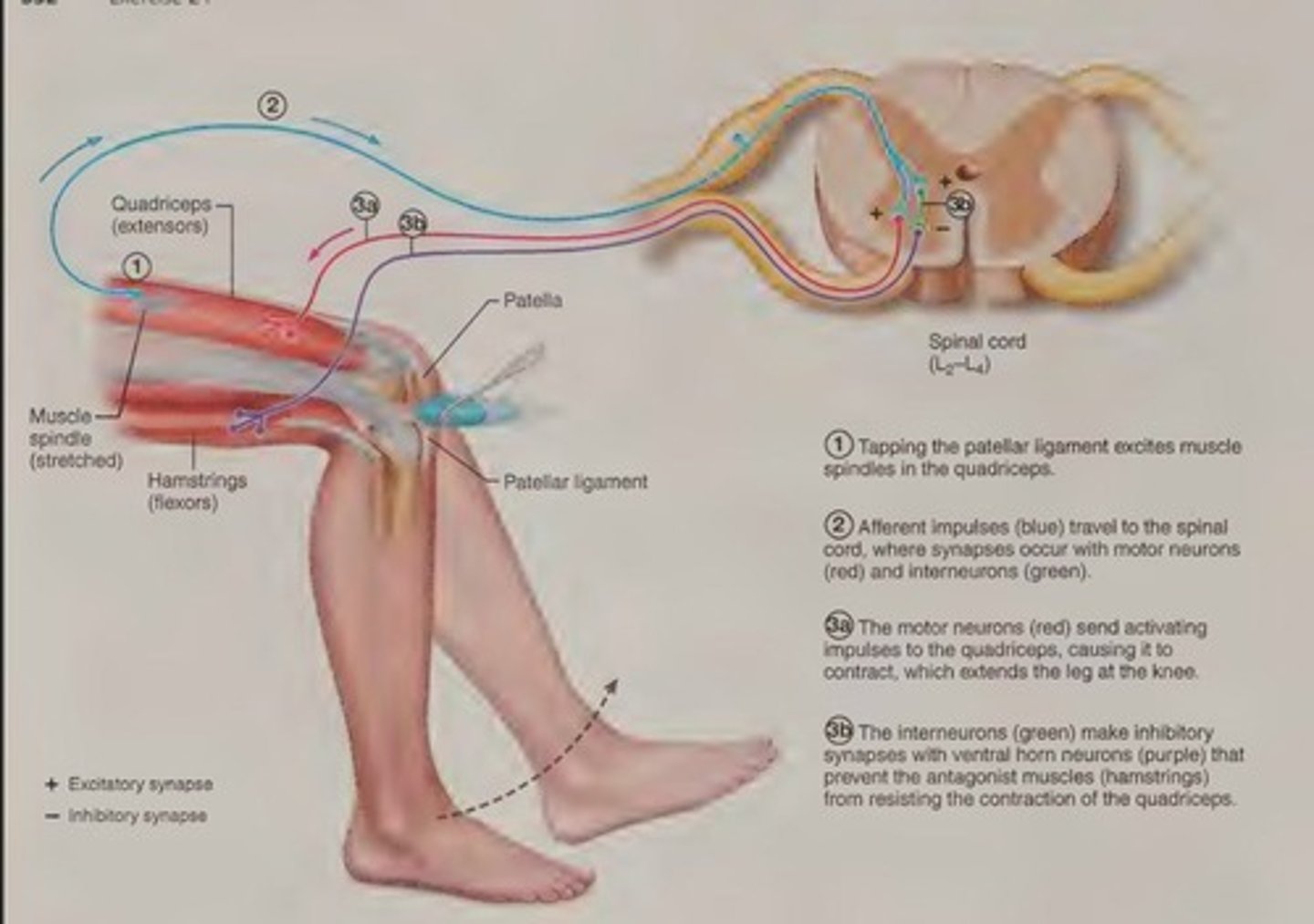
What is reciprocal inhibition in the context of reflexes?
The inhibition of antagonist muscles to prevent them from resisting the contraction of the stretched muscle.
What is the purpose of stretch reflexes?
To maintain and adjust muscle tone for posture, balance, and locomotion.
How are stretch reflexes initiated?
By tapping a tendon or ligament, which stretches the attached muscle.
What is the patellar reflex?
A specific example of a stretch reflex assessed by tapping the patellar ligament.
What does the calcaneal tendon reflex assess?
The first two sacral segments of the spinal cord.
What is the crossed-extensor reflex?
A more complex reflex than the stretch reflex, involving multiple pathways.
What is the role of interneurons in reflex arcs?
To connect sensory and motor neurons, especially in polysynaptic reflexes.
What is the significance of spinal reflexes?
They are mediated by the spinal cord without direct involvement of higher brain centers.
How can reflex activity be modified?
It can be inhibited or facilitated depending on circumstances.
What types of reflexes are mediated by cranial nerves?
Some somatic reflexes.
What is the function of muscle spindles in stretch reflexes?
To detect stretch in muscles and initiate a reflex contraction.
What information do impulses relayed to higher brain centers provide?
Information needed to maintain muscle tone and posture.
How does the body respond to a stretch reflex?
By contracting the stretched muscle and relaxing the antagonist muscle.
What is the role of the dorsal white columns in reflexes?
To relay information about muscle length and speed of shortening to higher brain centers.
What is the significance of the knee-jerk response?
It assesses the L2-L3 level of the spinal cord.
What is the initial response when a stranger grips one's arm?
The immediate response is to withdraw the clutched arm and push the intruder away with the other arm.
What are superficial reflexes and how are they initiated?
Superficial reflexes (abdominal, cremasteric, and plantar) are initiated by stimulation of receptors in the skin and mucosae.
What is the significance of the plantar reflex in adults?
In adults, stimulation of the sole of the foot causes the toes to flex and move closer together.
What does Babinski's sign indicate in adults?
Damage to the primary motor cortex or the corticospinal tract, resulting in an upward direction of the toes and fanning out.
Why is Babinski's sign normal in newborn infants?
It is normal because myelination of the nervous system is incomplete.
How is the plantar reflex tested?
By stroking the lateral border of the subject's sole with a moderately sharp object, starting at the heel and moving toward the great toe.
What cranial nerve mediates the corneal reflex?
The trigeminal nerve.
What does the absence of the corneal reflex indicate?
It often indicates damage to the brain stem resulting from compression or trauma.
How is the corneal reflex tested?
By gently touching the subject's cornea with a wisp of absorbent cotton while they look away.
What cranial nerves are involved in the gag reflex?
Cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal) and X (vagus).
What happens when the oral mucosa on the sides of the uvula are stroked?
Each side of the mucosa should rise, and the amount of elevation should be equal.
What are the autonomic reflexes mentioned in the notes?
The autonomic reflexes include the papillary, ciliospinal, and salivary reflexes.
What are the two types of pupillary reflexes examined?
The Pupillary Light reflex and the Consensual reflex.
What is the receptor in the pupillary reflexes?
The retina of the eye.
What nerve contains the afferent fibers for pupillary reflexes?
The optic nerve.
What nerve contains the efferent fibers for pupillary reflexes?
The oculomotor nerve.
What is the effector in the pupillary reflexes?
The smooth muscle of the iris.
What does the absence of normal pupillary reflexes indicate?
It is generally a late indication of severe trauma or deterioration of vital brain stem tissue due to metabolic imbalance.
What is a contralateral response?
A reflex observed on one side of the body when the other side has been stimulated.
What is an ipsilateral response?
A reflex occurring on the same side that is stimulated.
What type of effectors are involved in the salivary reflex?
Glands.
What is the ciliospinal reflex?
A reflex activity where pupillary responses can be observed.
What are somatic reflexes?
Reflexes that include abdominal reflex, calcaneal tendon reflex, corneal reflex, crossed-extensor reflex, gag reflex, patellar reflex, and plantar reflex.
Which reflexes are classified as stretch reflexes?
Calcaneal and Patellar reflex.
What are superficial reflexes?
Reflexes such as Abdominal Reflex and Plantar Reflex.
Can the stretch reflex be elicited in a singly pithed animal?
Yes, it can be elicited in an animal where the brain is destroyed but the spinal cord is intact.
What is the reflex arc for the Patellar Reflex?
Proprioceptors in the quadriceps muscle → afferent fibers of femoral nerve → spinal cord → efferent fibers of femoral nerve → quadriceps muscle.
What is the reflex arc for the Calcaneal Tendon Reflex?
Proprioceptors in the gastrocnemius muscle → afferent fibers of sciatic nerve → spinal cord → efferent fibers of sciatic nerve → gastrocnemius muscle.
What factors influence the speed and effectiveness of reflex arcs?
Mental distraction, simultaneous muscle activity in another body area, and fatigue.
Which factors increase the excitatory level of the spinal cord?
Simultaneous muscle activity and mental distraction.
Which factor decreases the excitatory level of the muscles?
Muscle fatigue.
Do brain activities modify the patellar reflex?
Yes, they may modify it, but the reflex will occur regardless.
What activities do autonomic reflexes involve?
Activation of smooth or cardiac muscle and glands.
What activities do somatic reflexes involve?
Activation of skeletal muscles.
What is a gyrus?
An elevated ridge of cerebral tissue.
What is the significance of convolutions in the cerebrum?
They increase the surface area.
What is gray matter composed of?
Neuron cell bodies.
What is white matter composed of?
Myelinated fibers.
What is an association tract?
A fiber tract that provides communication between different parts of the same cerebral hemisphere.
What is a projection tract?
A fiber tract that carries impulses from the cerebrum to lower CNS areas.
What is the hypothalamus responsible for?
Regulation of body temperature and water balance; it is the most important autonomic center.
Where do the medial fibers of the optic nerves cross?
At the optic chiasma.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Regulation of posture and coordination of complex muscular movements.
What is the role of the thalamus?
It is an important synapse site for afferent fibers traveling to the sensory cortex.
What does the medulla oblongata regulate?
Blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rhythm, coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.
What connects the cerebral hemispheres?
The corpus callosum.
What is the cerebral aqueduct?
A canal that connects the third and fourth ventricles.