Anatomy of Spinal cord
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
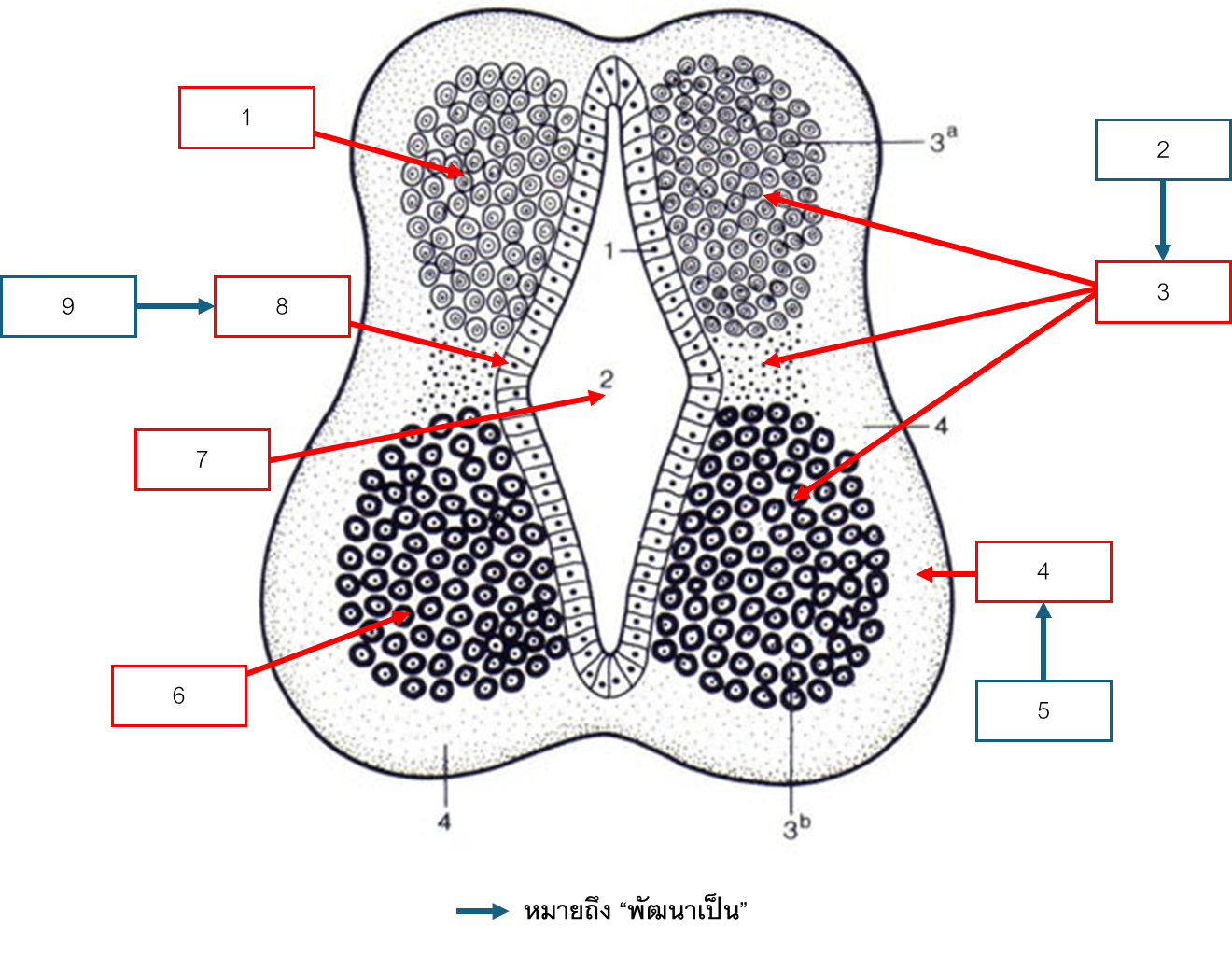
การพัฒนาของ Neural tube
Alar plate
Mantle zone
Gray matter
White matter
Marginal zone
Basal plate
Central canal
Ependymal cell
Epidermal zone
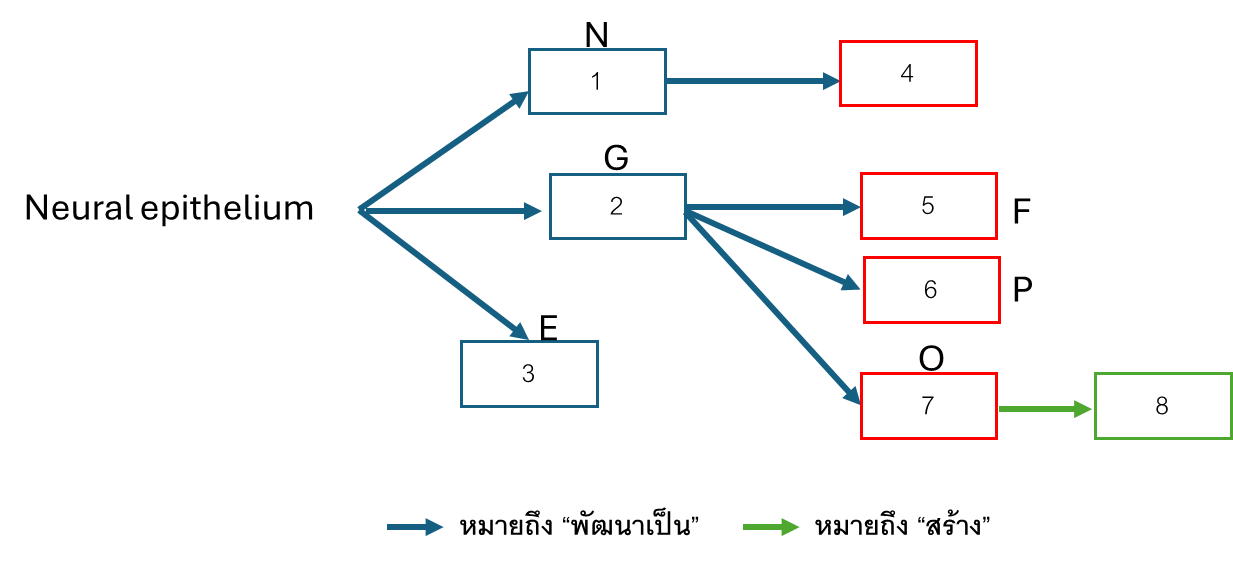
Neural epithelium พัฒนาเป็นอะไร
Neuroblast
Glioblast
Ependymal epithelium
Neuron
Fibrous astrocyte
Protoplasmic astrocyte
Oligodendrocyte
Myelin sheath
Neural crest cells พัฒนาเป็น 8 อย่าง คือ
Dorsal root ganglion
Ganglion of Cranial nerve
Satellite cell
Schwann cell
Ganglion of Autonomic nervous system
Chromaffin cell
Melanoblast
Cartilage cell
Chromaffin cell สร้างฮอร์โมนอะไร
Catecholamine
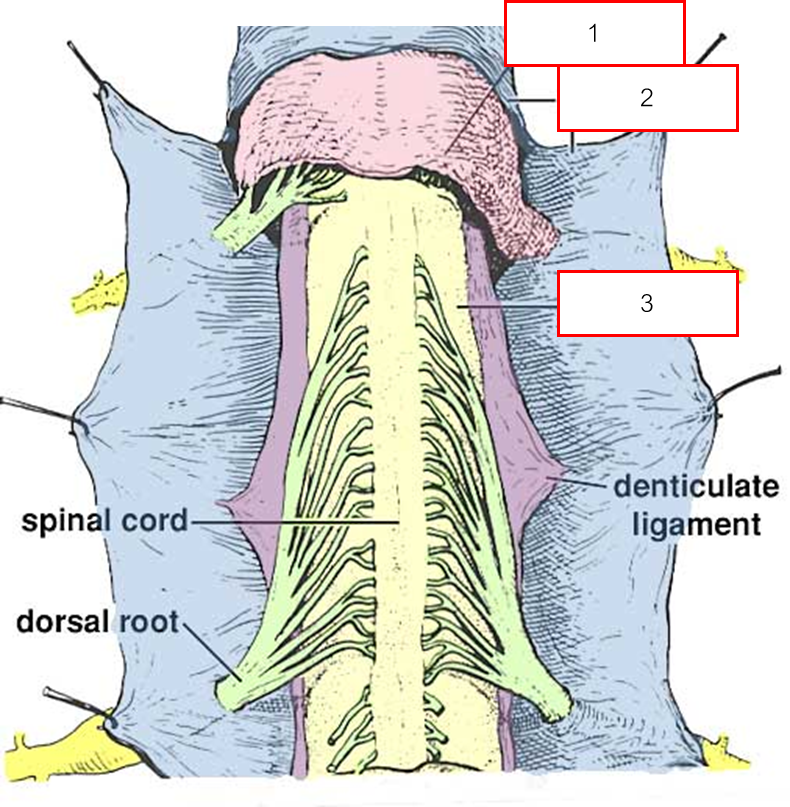
Spinal meninges มี 3 ชั้น อะไรบ้าง
Arachnoid mater
Dura mater
Pia mater
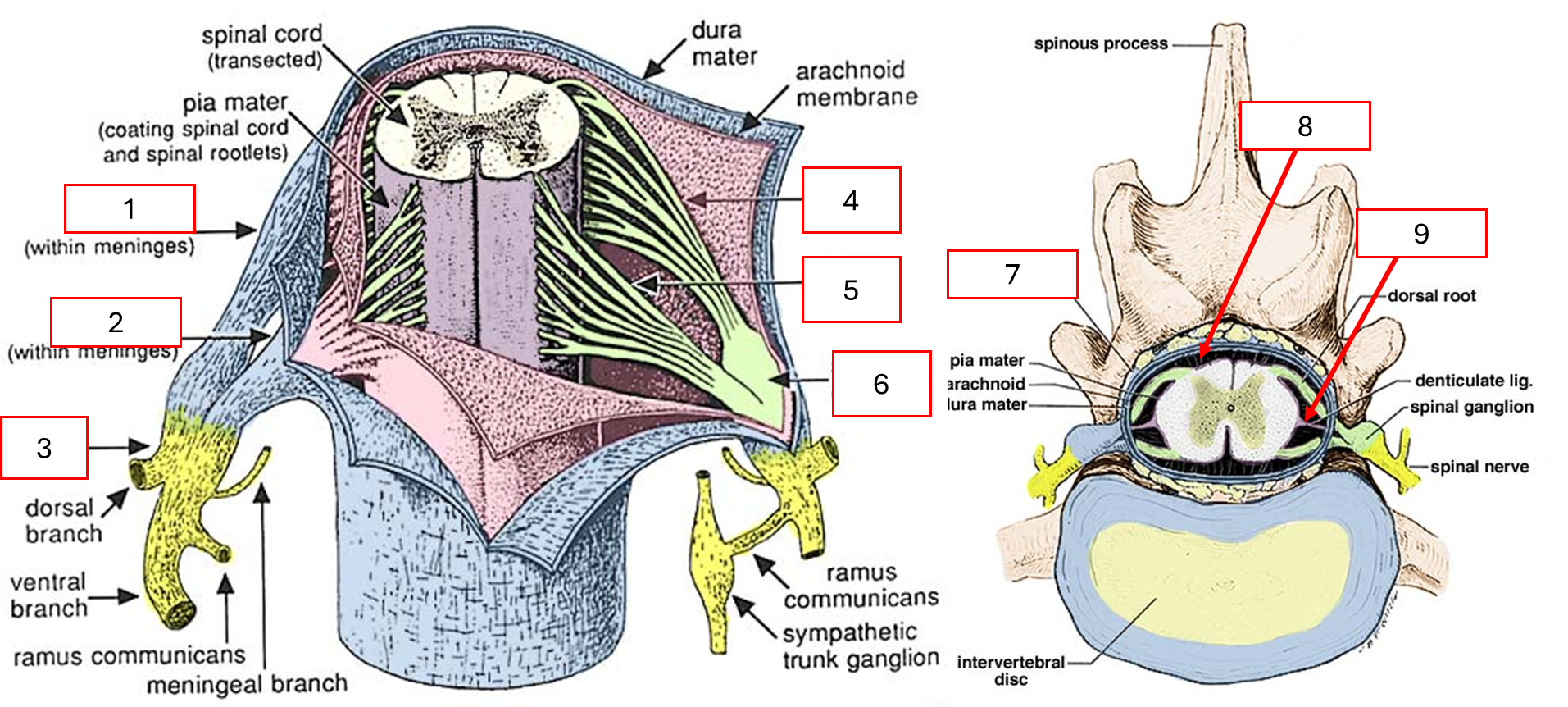
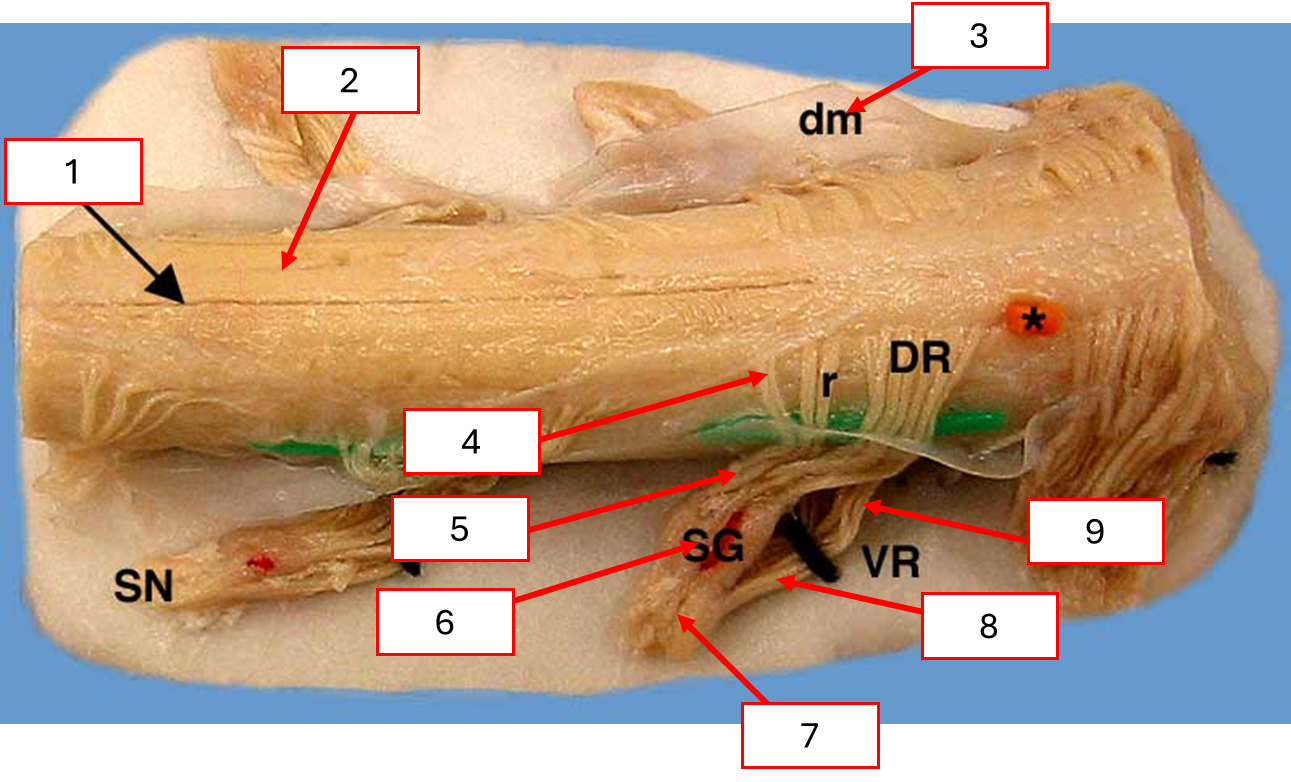
สิ่งที่อยู่ข้างนอก Spinal cord
Dorsal root
Ventral root
Spinal nerve
Dorsal rootlet
Ventral rootlet
Spinal ganglion
Epidural space
Subarachnoid space
Denticulate ligament
ส่วนปลายของ Spinal cord
Conus medullaris (บริเวณ L6-L7)
Caudal equina
Filum terminale
ส่วนป่องของ spinal cord เรียกว่าอะไร
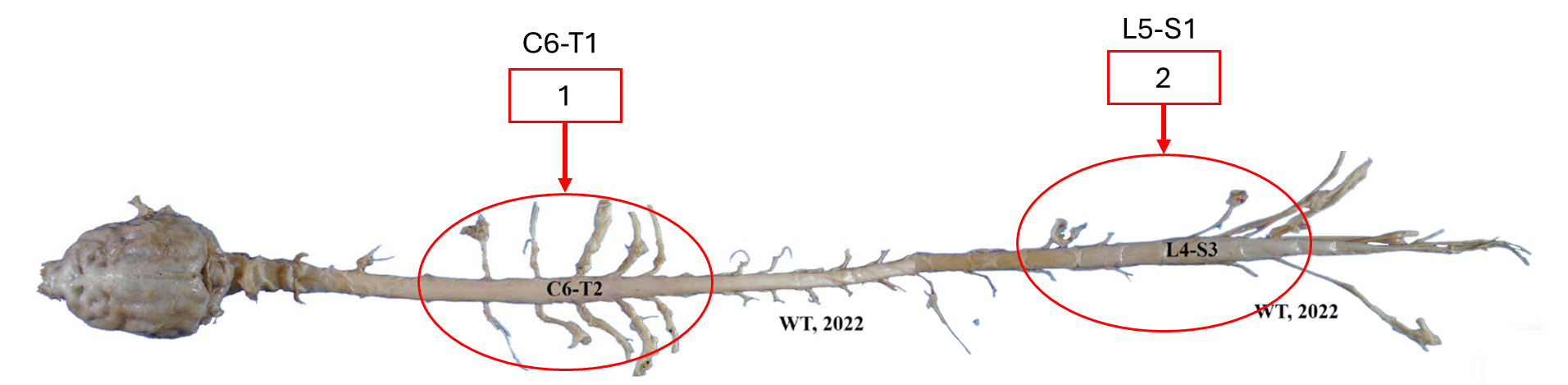
Cervical enlargement
Lumbosacral enlargement
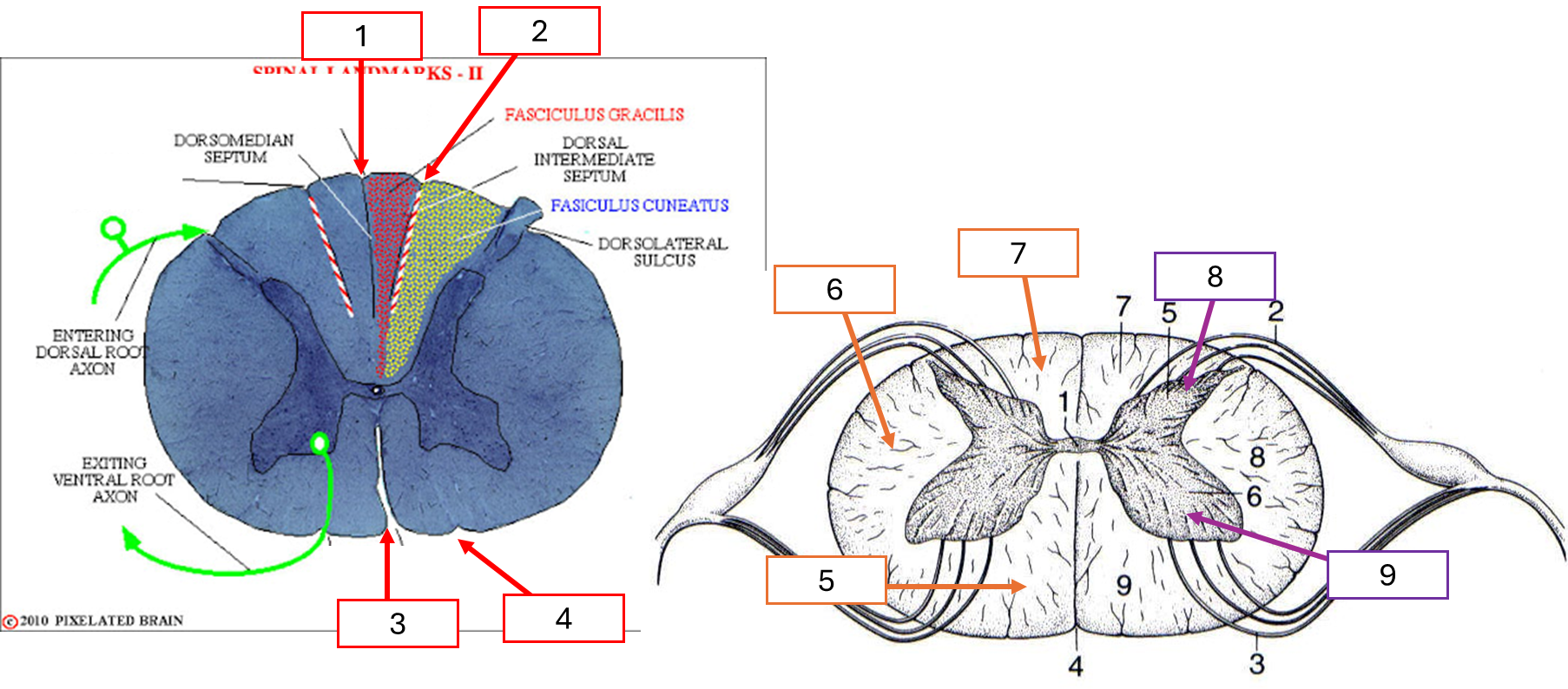
โครงสร้างด้านใน spinal cord (โครสร้างรอยหยัก, white matter, gray matter)
Dorsal median fissure
Dorsolateral sulcus
Ventral median fissure
Ventrolateral sulcus
Ventral funiculus
Lateral funiculus
Dorsal funiculus
Dorsal horn
Ventral horn
สาเหตุที่กระดูก Vertebra เจริญเร็วกว่า Spinal cord
การหดตัวของ spinal cord 2/3 ของ Vertebral bone → Segment ของ SC. กับ VB. ไม่ตรงกัน → เกิดการเหลื่อมกันบางบริเวณ ดังนี้
ตรงกัน → C1-C3, T11-L2
ต่างกัน 1 ระดับ → C4-T10
ต่างกันหลายระดับ → L4-S (ส่วนท้ายๆ)
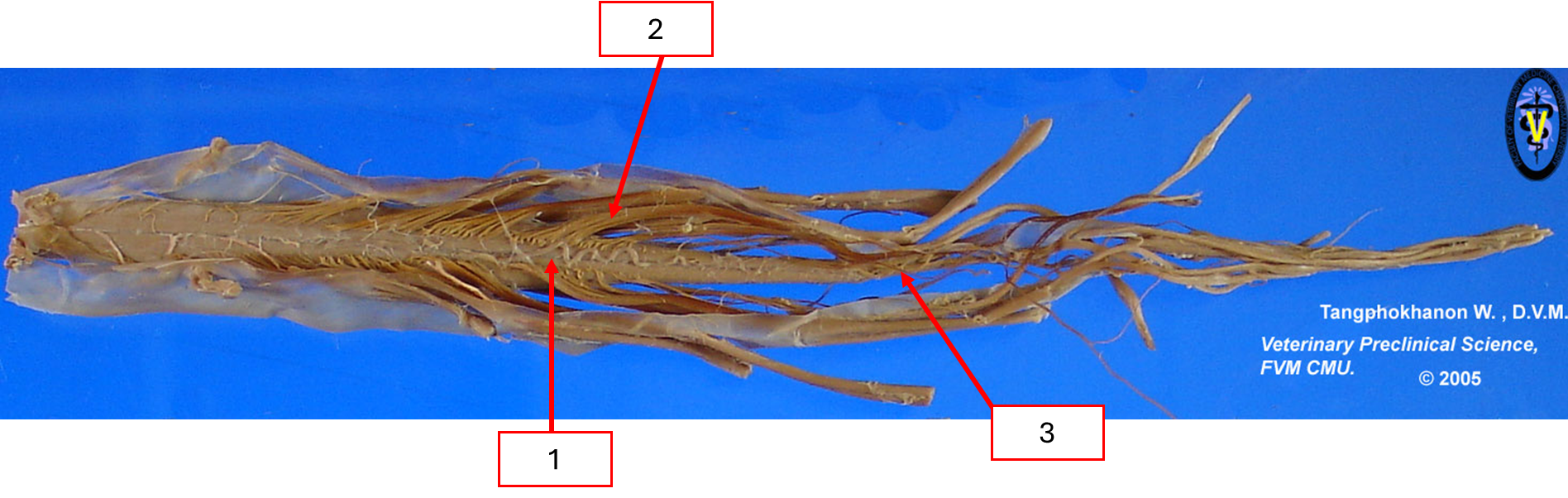
สิ่งที่อยู่ภายนอกของ spinal cord
Dorsal median fissure
Dorsolateral sulcus
Dura mater
Dorsal rootlet
Dorsal root
Spinal ganglion
Spinal nerve
Ventral root
Ventral rootlet
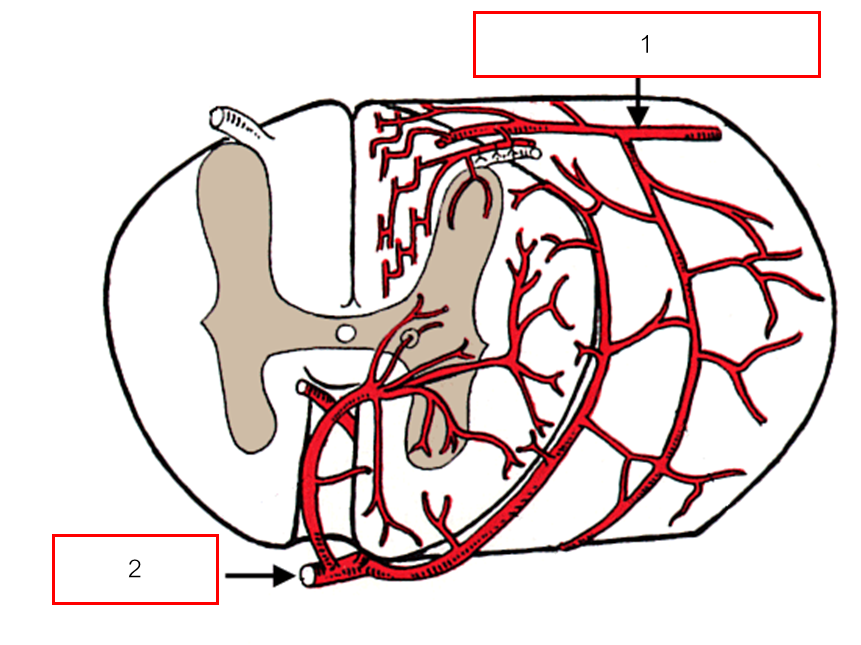
เลือดที่เลี้ยง spinal cord มี 2 เส้น แตกแขนงมาจาก Radicular a.
Dorsal spinal a.
Ventral spinal a.
Neuron ใน gray matter มี 3 กลุ่ม
Spinal interneuron เกี่ยวกับ Reflex (ถูกเข็มจิ้ม -> Sensory neuron -> Interneuron -> Spinal efferent neuron -> กล้ามเนื้อ)
Spinal projection neuron รับสัญญาณไปยังสมอง (Pain/T. → Sensory neuron → Projection neuron → Brain)
Spinal efferent neuron ส่งคำสั่งจากสมอง (Brain → Descending tract → Spinal efferent neuron → Muscle)
Gray matter แบ่งพื้นที่ได้เป็น 3 ส่วน
Dorsal horn
Lateral horn
Ventral horn
Intermediate horn
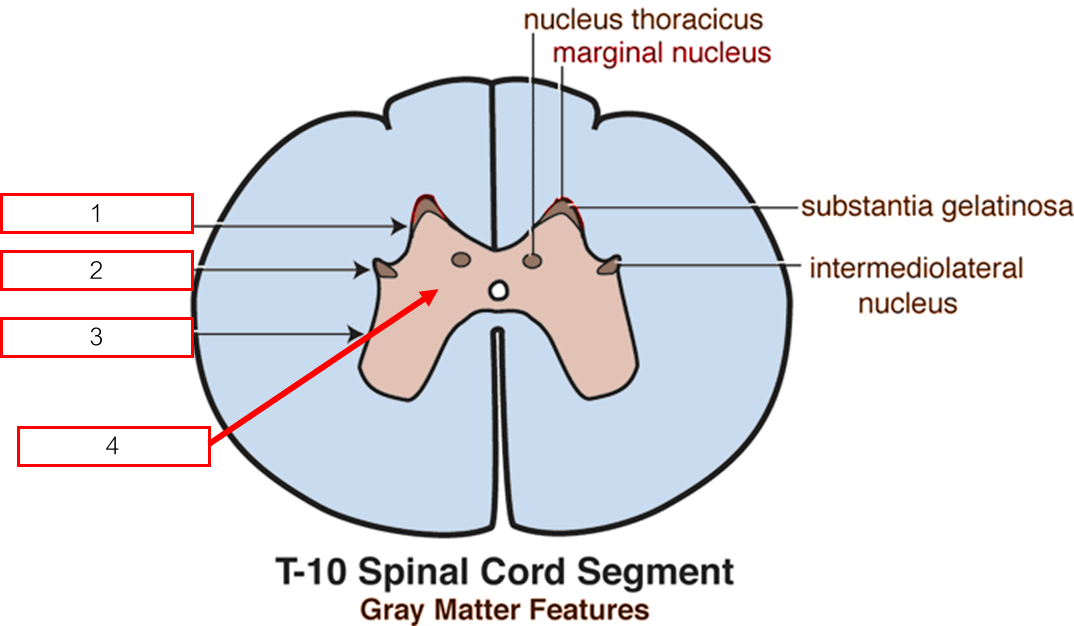
Nucleus บริเวณ Dorsal horn
Substantia gelatinosa ปรับแต่งความเจ็บปวด
Nucleus proprius รับความรู้สึก เจ็บ อุณหภูมิ สัมผัส
Dorsal nucleus/Nucleus thoracicus (T1-L2) รับข้อมูลการทรงตัวที่ไม่ได้ตั้งใจ
Lateral cervical nucleus(C1-C2) รับข้อมูลการทรงตัวที่ไม่ได้ตั้งใจ (รับ unconscious proprioception (spinocervicothalamic))
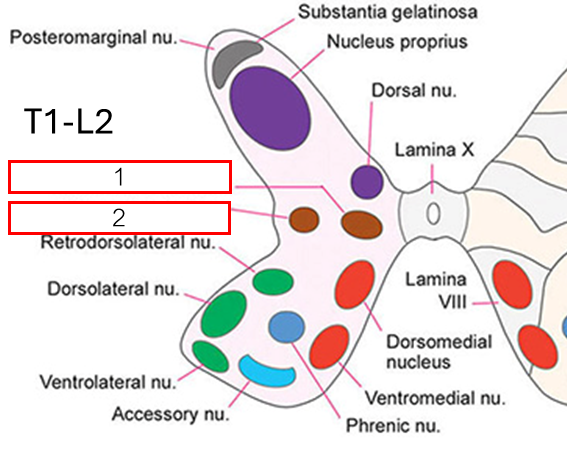
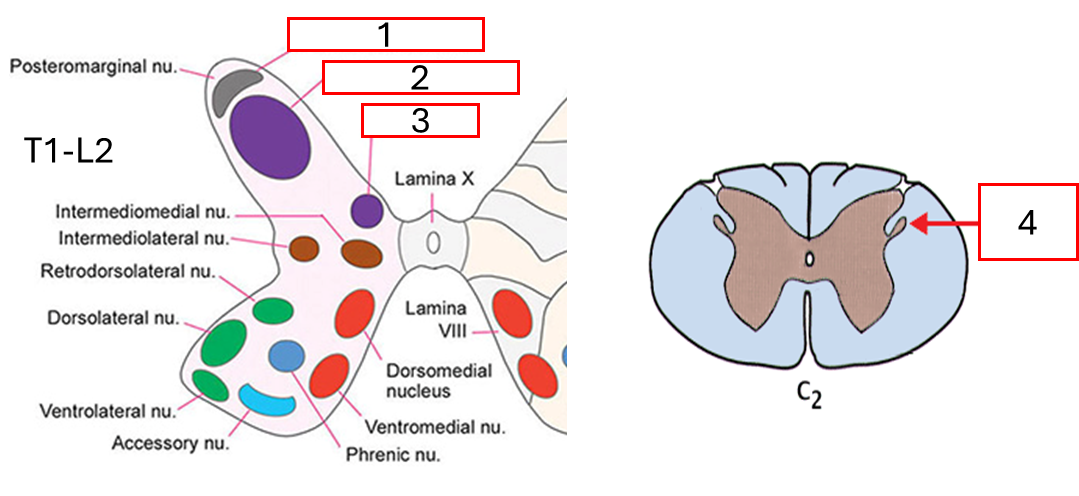
Nucleus บริเวณ Intermediate horn
Intermediomedial nucleus รับสัญญาณจากอวัยวะภายใน
Intermediolateral nucleus (Brain → IML → Ganglion → Visceral Organ)
ที่ T1-L4 เป็นส่วนของ Lateral horn หน้าที่ Preganglionic sympathetic neuron
ที่ S2-S3 หน้าที่ Preganglionic parasympathetic neuron
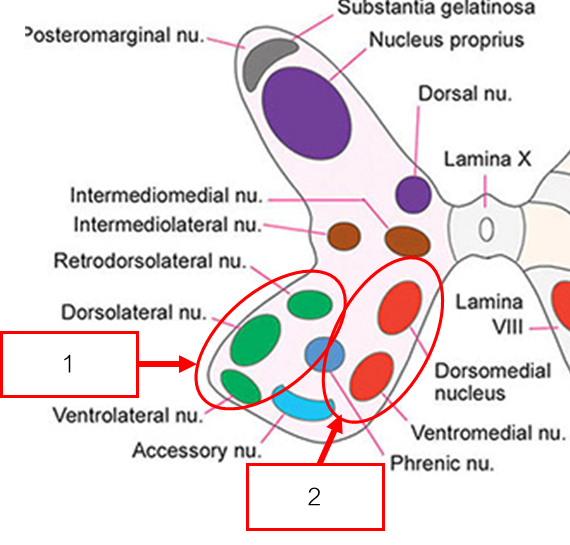
Nucleus บริเวณ Ventral horn แบ่งเป็น 2 กลุ่ม
Medial group สั่งการ axial muscle
Lateral group สั่งการ limb muscle พบมากในตำแหน่ง Enlargement
ทั้งสองเป็น Motor neuron
Tract คืออะไร
กลุ่ม Axon ที่ทีต้นกำเนิดเดียวกัน ทำหน้าที่เดียวกัน
Funiculus คืออะไร มี 2 กลุ่ม คือ
กลุ่มของ Tract
Ascending tract (Sensory/Afferent n.)
Descending tract (Motor/Efferent n.)
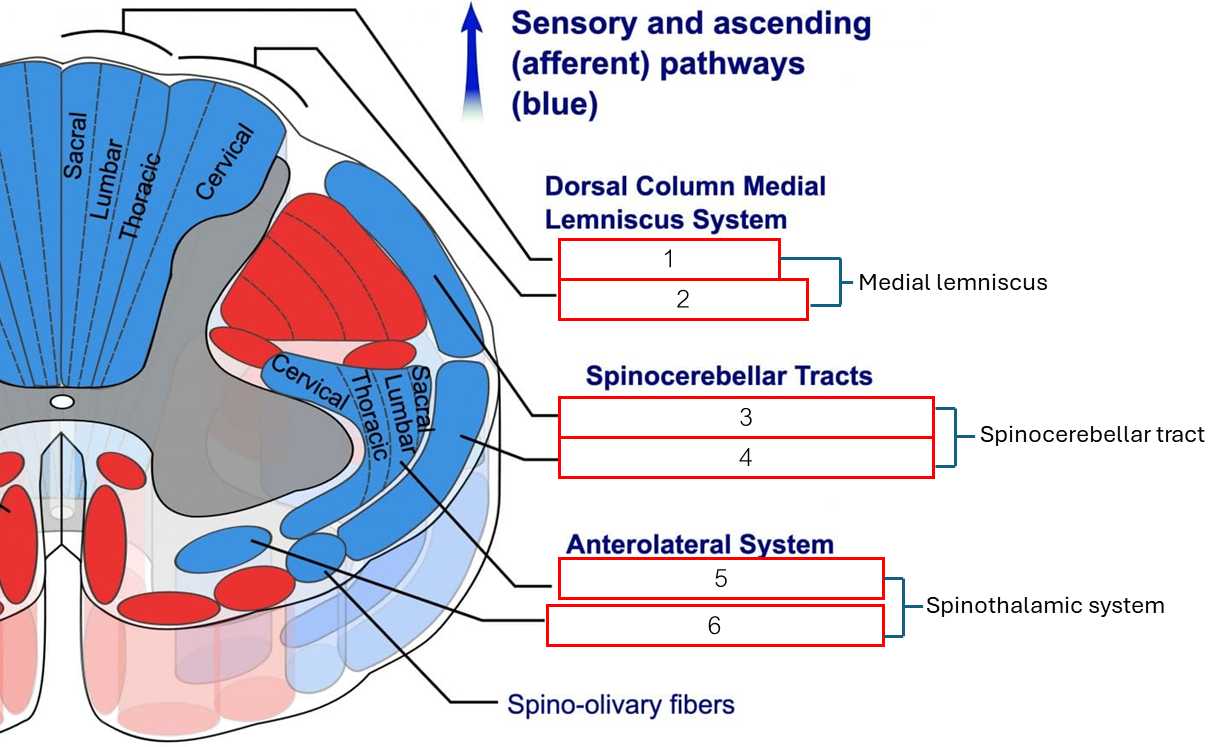
Ascending tract มี 6 สาย
Fasciculus gracilis รับรู้ตำแหน่ง(ขาหลัง) กด สัมผัสละเอียด
Fasciculus cuneatus รับรู้ตำแหน่ง(ขาหน้า) กด สัมผัสละเอียด
Dorsal spinocerebellar การทรงตัว
Ventral spinocerebellar การทรงตัว
Lateral spinothalamic รับรู้ เจ็บ อุณหภูมิ
Ventral spinothalamic สัมผัสหยาบ
Propriospinal เป็น Tract ที่มีหน้าที่อะไร
ประกอบด้วย ascending และ descending tract สั้น ๆ เป็น axon ของ interneuron มีหน้าที่ เชื่อม spinal cord ระหว่าง segment
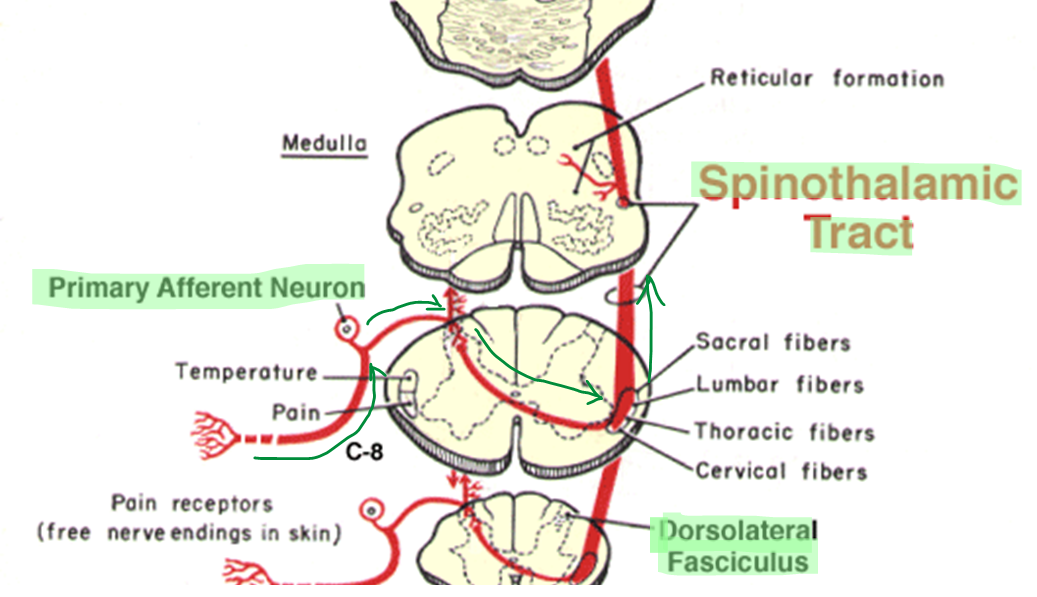
อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Spinothalamic tract (pain & temperature)
รับเจ็บ/อุณหภูมิ → Primary afferent neuron → เข้า dorsolateral fasciculus → synapse กับ marginal nucleus / nucleus proprius → Spinal projection neuron(GM.) → ไขว้ข้าง → ขึ้นไปใน Spinothalamic tract → thalamus → somesthetic area of cerebral cortex
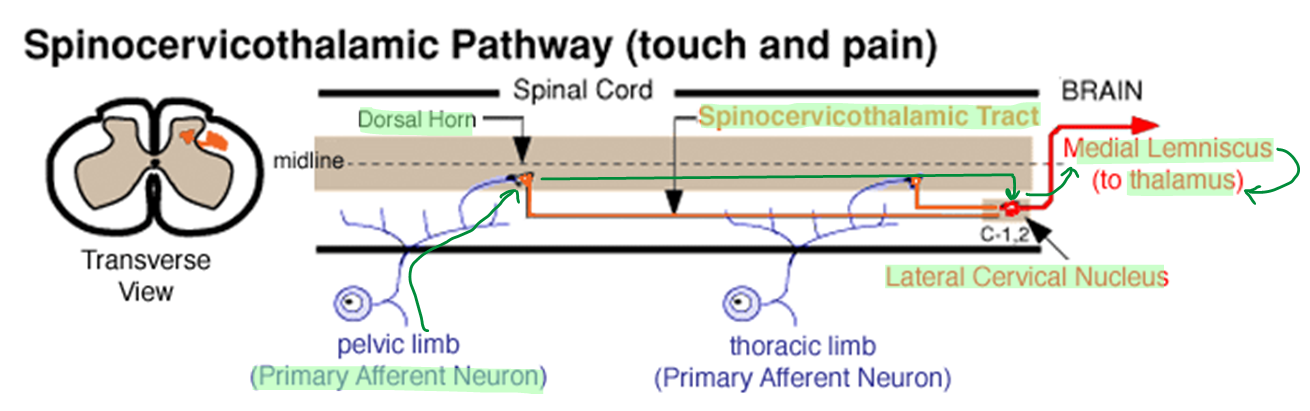
อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Spinocervicothalamic pathway (pain ใน Carnivore)
รับเจ็บ → Primary afferent neuron → เข้า dorsal horn → เข้า spinocervicothalamic pathway → lateral cervical nucleus(C1-C2) → ไปยัง projection neuron และ ไขว้ข้าง → เข้า thalamus → somesthetic area of cerebral cortex

อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Discriminative touch and Kinesthesia pathway (การรับรู้จำแนกสัมผัส, การเคลื่อนไหวร่างกาย)
encapsulated mechanoreceptors → ไปยัง primary afferent neurons(มี myelin) → เข้า dorsal funiculus → fasciculus gracilis/fasciculus cuneatus → ไปยัง brainstem → synapse กับ nucleus gracilis / medial cuneate nucleus → projection neurons ของ NG./MCN → ไขว้ข้าง → วิ่งขึ้นไปใน medial lemniscus → ไปยัง thalamus → internal capsule → somesthetic area of cerebral cortex
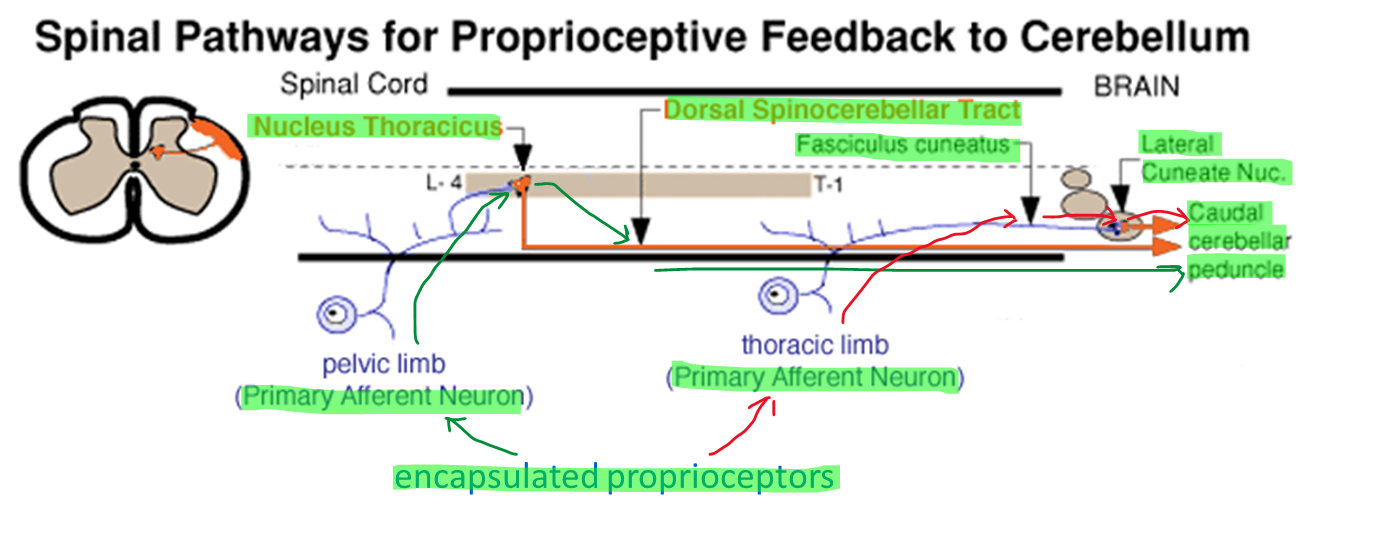
อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Spinocerebellar subconscious pathway (รับข้อมูลความตึงตัวของกล้ามเนื้อ → ทรงตัว)
เข้าไป 2 ทาง ไม่มีการไขว้ข้าง
Pelvic limb : encapsulated proprioceptors -> primary afferent neuron(myelinใหญ่) -> เข้าไป nucleus thoracicus(GM.) -> axon ของ projection neuron วิ่งใน white matter → ส่งขึ้นไปผ่าน dorsal spinocerebellar tract -> caudal cerebellar peduncle -> cerebellum
Thoracic limb : encapsulated proprioceptors -> primary afferent neurons(myelinใหญ่) -> เข้าบริเวณ fasciculus cuneatus(WM.) -> ส่งขึ้นไปยัง lateral cuneate nucleus ที่ brain stem -> axon ของ projection neuron วิ่งใน white matter → caudal cerebellar peduncle -> cerebellum
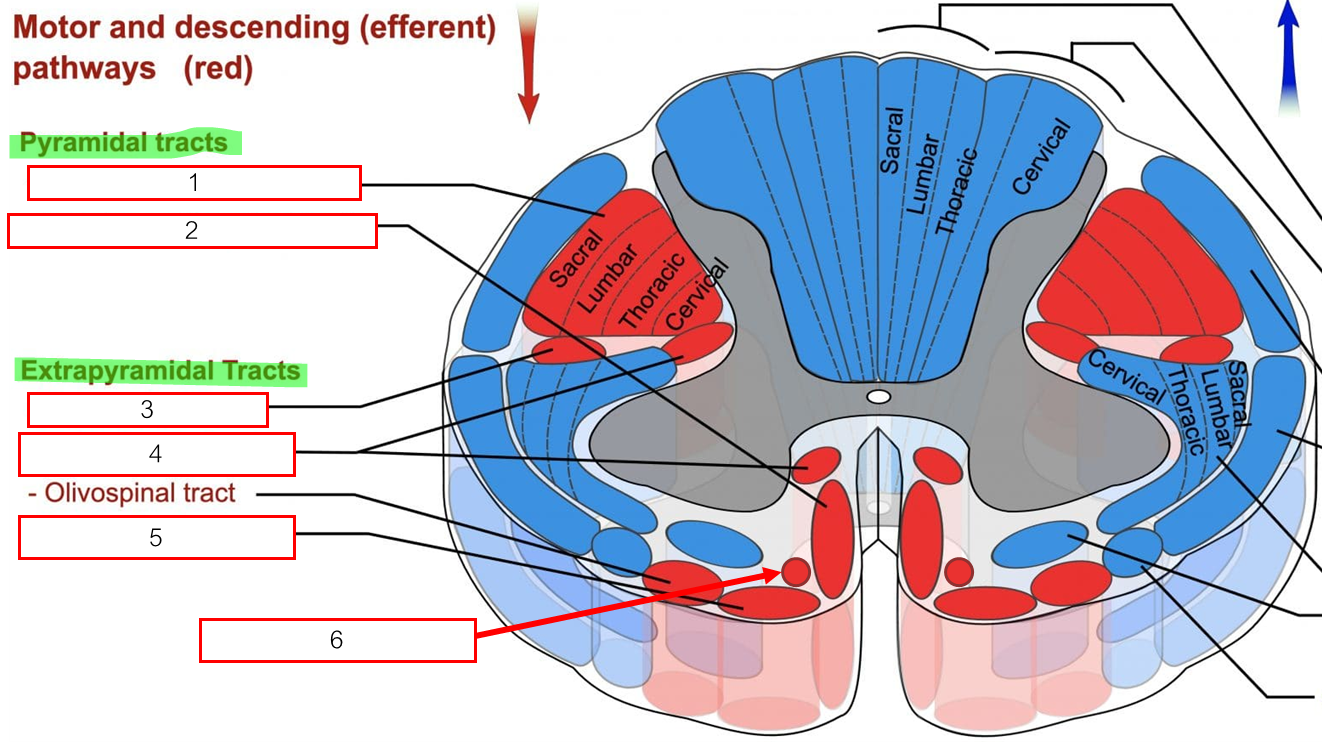
Descending tract มี 6 สาย
Lateral corticospinal tract
Ventral corticospinal tract
Rubrospinal tract
Reticulospinal tract origin จาก red nucleus ใน midbrain ความคุมกล้ามเนื้อฝั่งตรงข้ามของมัน
Vestibulospinal tract
Tectospinal tract ควบคุม reflex การหันหัวไปตามเสียง/ภาพ
Tectobulbar (ไม่ได้ลงไป spinal cord) ควบคุม reflex การหันดวงตา และใบหู ตามเสียง/ภาพ
Pyramidal tracts : ควบคุมการเคลื่อนไหวที่ตั้งใจ (กล้ามเนื้อลาย)
Extrapyramidal tracts : ควบคุมการเคลื่อนไหวอัตโนมัติ
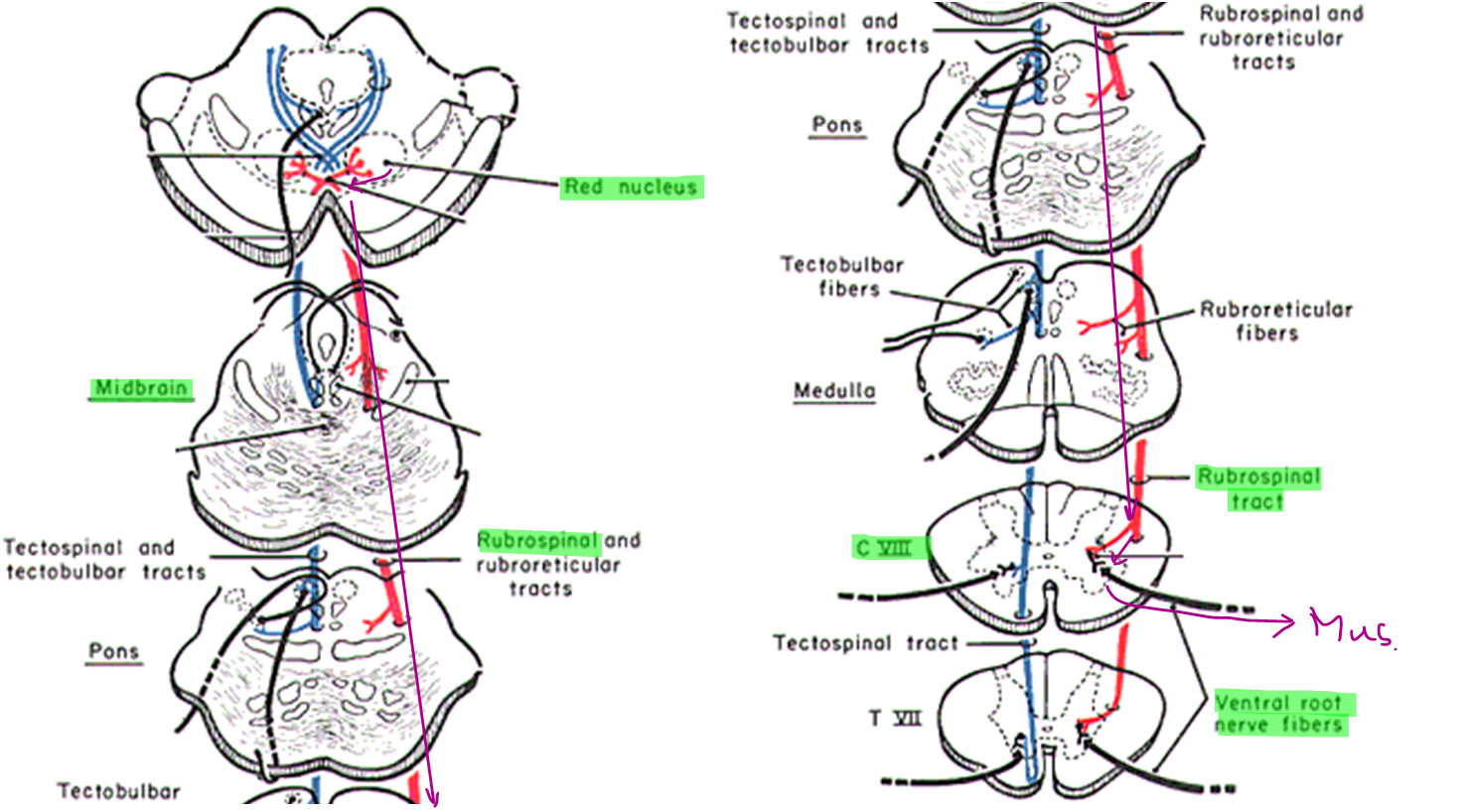
อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Rubrospinal tract (ควบคุมการเคลื่อนไหวที่ตั้งใจ) เริ่มจาก Red nucleus
เส้นทางของ : projection neurons ใน red nucleus -> รวมกันเป็น Rubrospinal tract -> เกิด ไขว้ข้างทันทีที่ midbrain -> วิ่งลงไปยัง lateral funiculus(WM.) คู่กับ lateral corticospinal tract -> rubrobulbar fibers ที่แยกจาก RST. -> เชื่อมกับ motor nuclei of cranial nerves -> ความคุมกล้ามเนื้อรยางค์ (สำคัญใน domestic mammals)
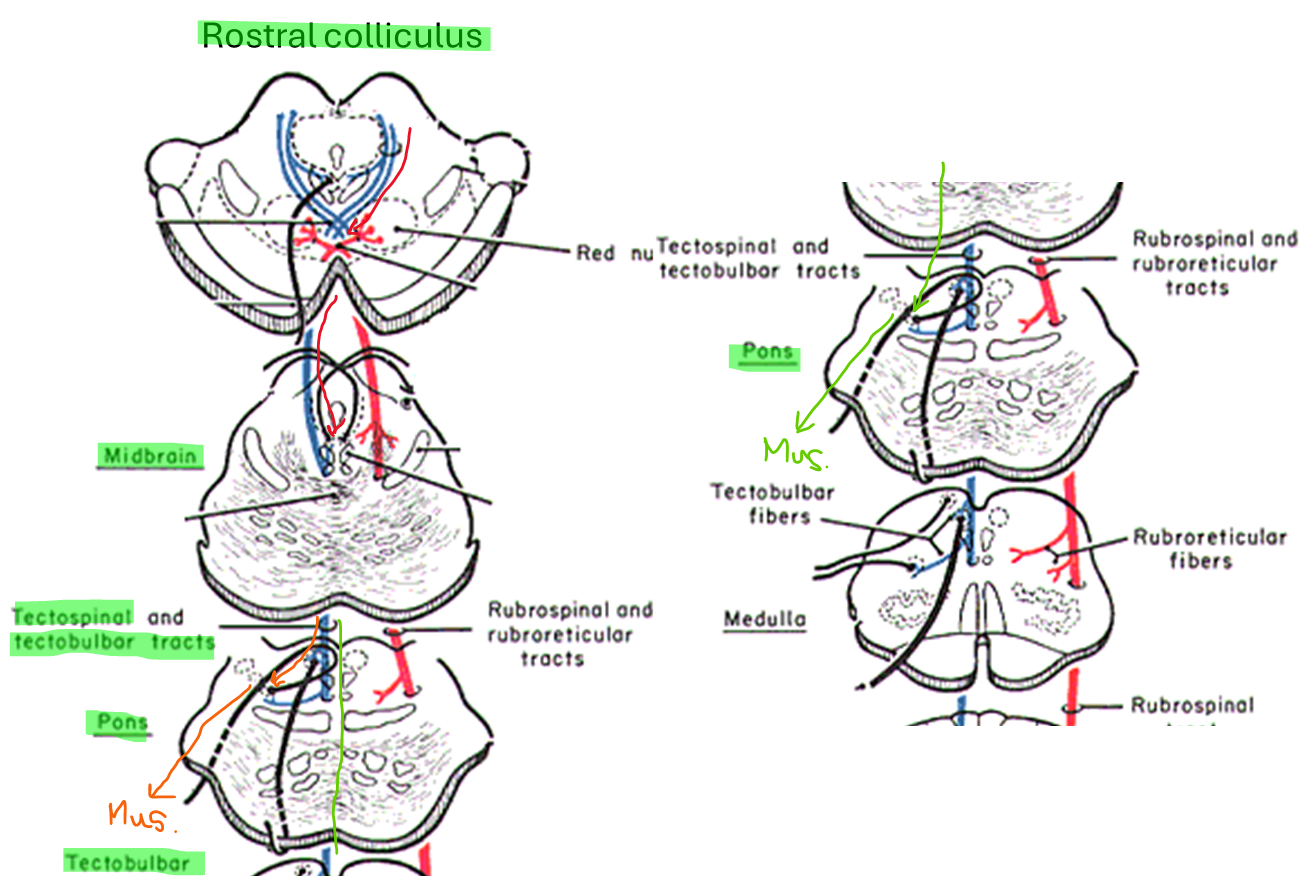
อธิบาย ลำดับการทำงานของ Tectospinal tract และ tectobulbar tract (รีเฟล็กซ์ ในการหัน ศีรษะ ดวงตา และใบหู เข้าหา แสงวาบหรือเสียงดังที่เกิดขึ้นอย่างฉับพลัน)
Tectospinal tract เส้นทาง : ส่งมาจาก Rostral colliculus -> เกิด ไขว้ข้างทันทีที่ midbrain -> วิ่งลงสู่ ventral funiculus -> ไปบริเวณ Cervical spinal cord -> ควมคุมกล้ามเนื้อ คอ/ไหล่ -> reflex หันหัว
Tectobulbar tract เส้นทาง : ส่งมาจาก Rostral colliculus -> เกิด ไขว้ข้างทันทีที่ midbrain -> สิ้นสุดที่ Brainstem nuclei -> Cranial nerve III, IV, VI(Reticular formation) -> ควบคุมกล้ามเนื้อ ลูกตา/หู -> reflex หันตา/หู
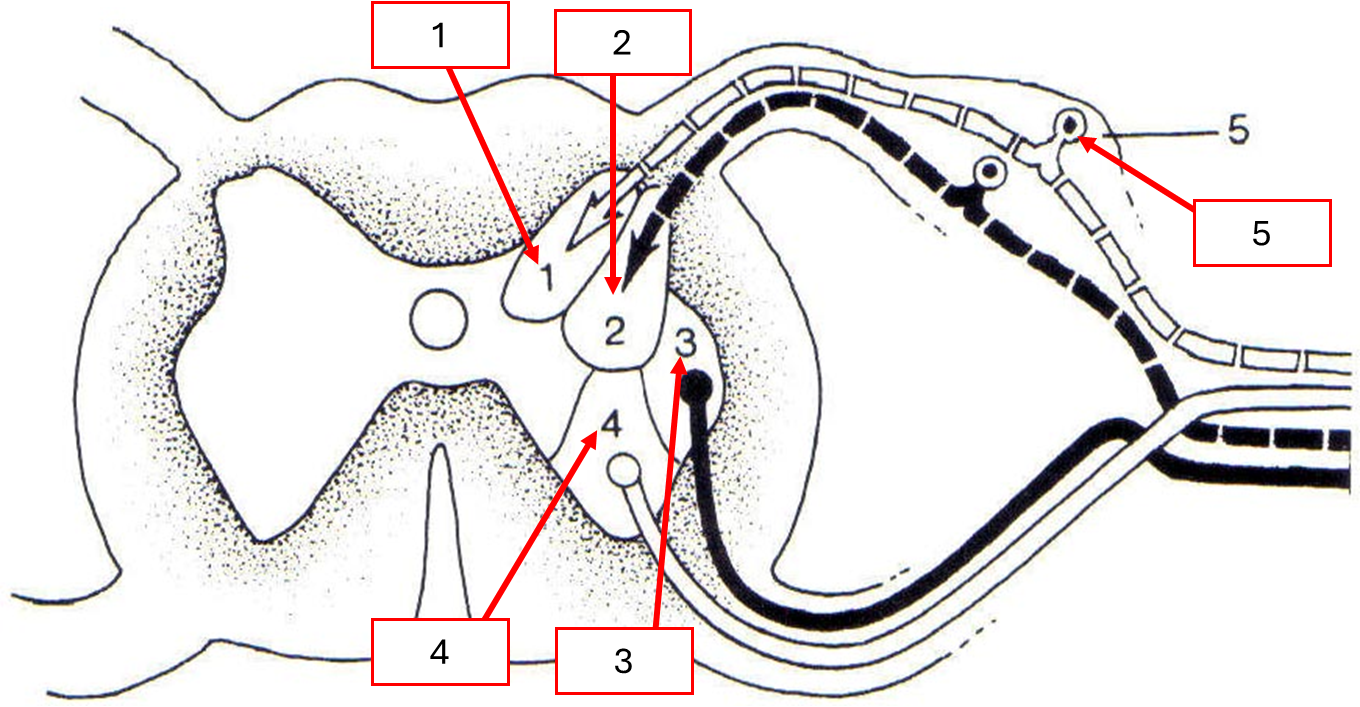
การแบ่งส่วนของ Neuron ใน GM. ตามการทำงาน
General Somatic Afferent: GSA
General Visceral Afferent: GVA
General Visceral Efferent: GVE
General Somatic Efferent: GSE
Dorsal Root Ganglion
ด้าน Dorsal horn : กลุ่มรับข้อมูล(A)
ด้าน Ventral horn : กลุ่มควบคุม(E)
ด้าน Lateral : กลุ่ม visceral(อวัยวะภายใน)
ด้าน Medial : กลุ่ม somatic(กล้ามเนื้อลาย)
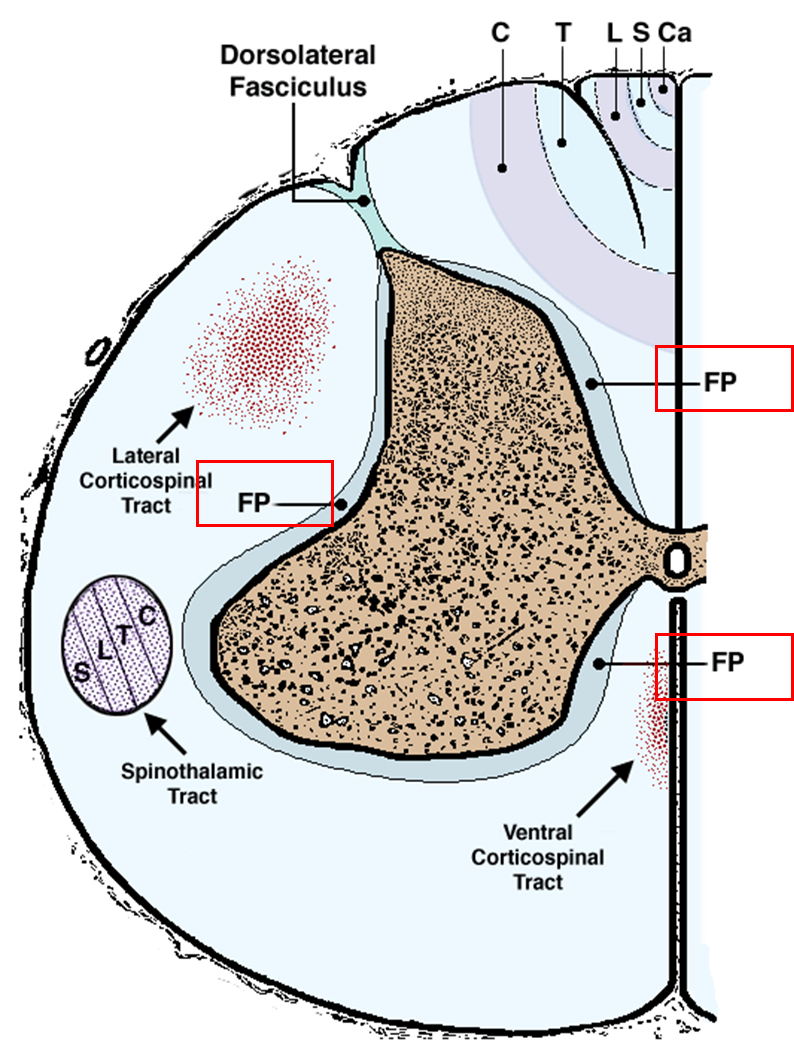
Fasciculus proprius มีหน้าที่อะไร
อยู่ติดกับ GM. เป็นที่อยู่ของ propriospinal tract ที่มีหน้าที่ เชื่อม spinal cord segment หนึ่งกับอีก segment หนึ่ง
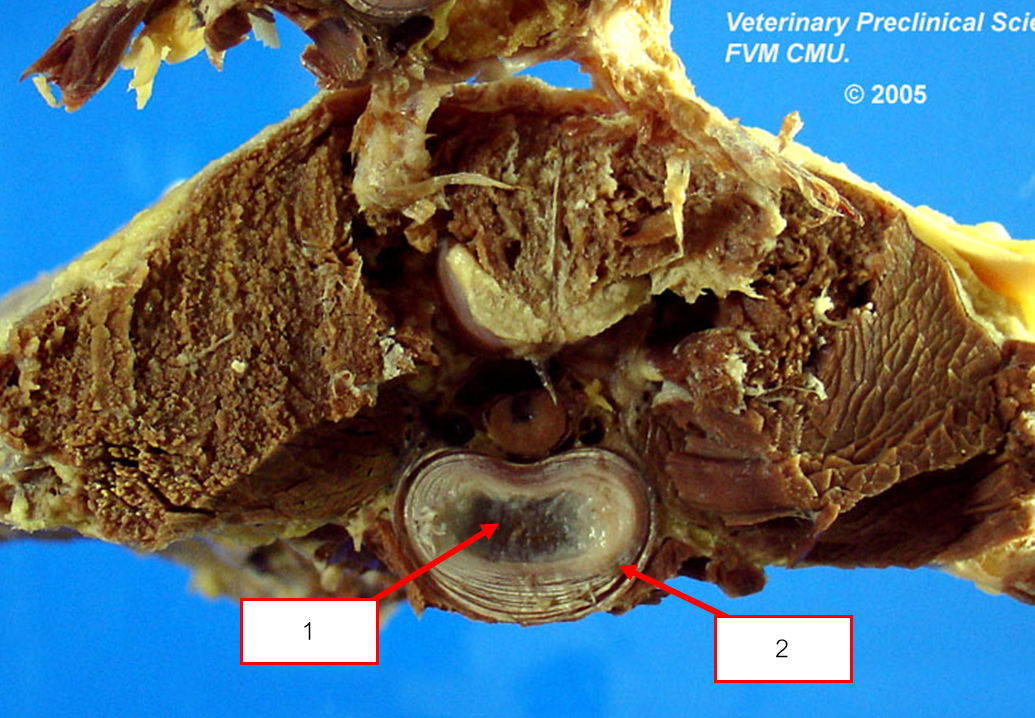
Intervertebral disc ประกอบด้วย
Nucleus pulposus เนื้อเยื่อเจลลี่ รับแรง ยืดหยุ่น
Annulus fibrosus รับแรงบิด ยึดกระดูก
เมื่อ AF. ฉีกขาด → NP. จะเปลี่ยนเป็น fibrocartilage → FC. จะทะลุ AF. ออกไป → กด spinal cord → เกิดอาการชา(พบในวัยชรา)