Types of Light Microscopes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
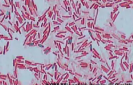
Bright-field
Commonly used in laboratory applications as the standard microscope; produces images on a bright background
Example of Bright-field
Bacillus (rod-shaped) showing endospores
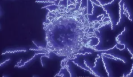
Dark-field
Increases contrast without staining by producing an image with a DARKER background; viewing LIVE specimen
Example of dark-field
Borrella burgdorferi
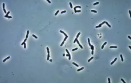
Phase Contrast
uses refraction (bending of light) and interference to create high contrast images WITHOUT staining; useful for seeing LIVE specimen
Example of Phase Contrast
Pseudomonas sp.

Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)
uses interference to produce high-contrast images with a three-dimensional appearance; useless to view STRUCTURES within living and unstained specimen
Example of Differential Interference contrast (DIC)
Escherichia Coli
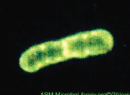
Fluroescence
uses fluorescent stains to produce an image; used to identify pathogens and to distinguish between living and dead cells; used for immunofluorescence
Example of Fluorescence
P. Putida
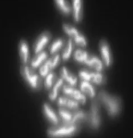
Confocal
uses laser to produce 2-dimensional that can construct into 3-dimensional images; used to examine thick specimens like biofilm
Example of Confocal
Escherichia coli
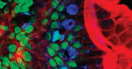
Two-photon
uses scanning technique (fluorochrome) and long wavelength to penetrate deep specimen, like biofilm
Example of two-photon
mouse intestine cells