EXS 420 Midterm Study Notes
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
50 Question test (25 multiple choice, 25 T/F)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
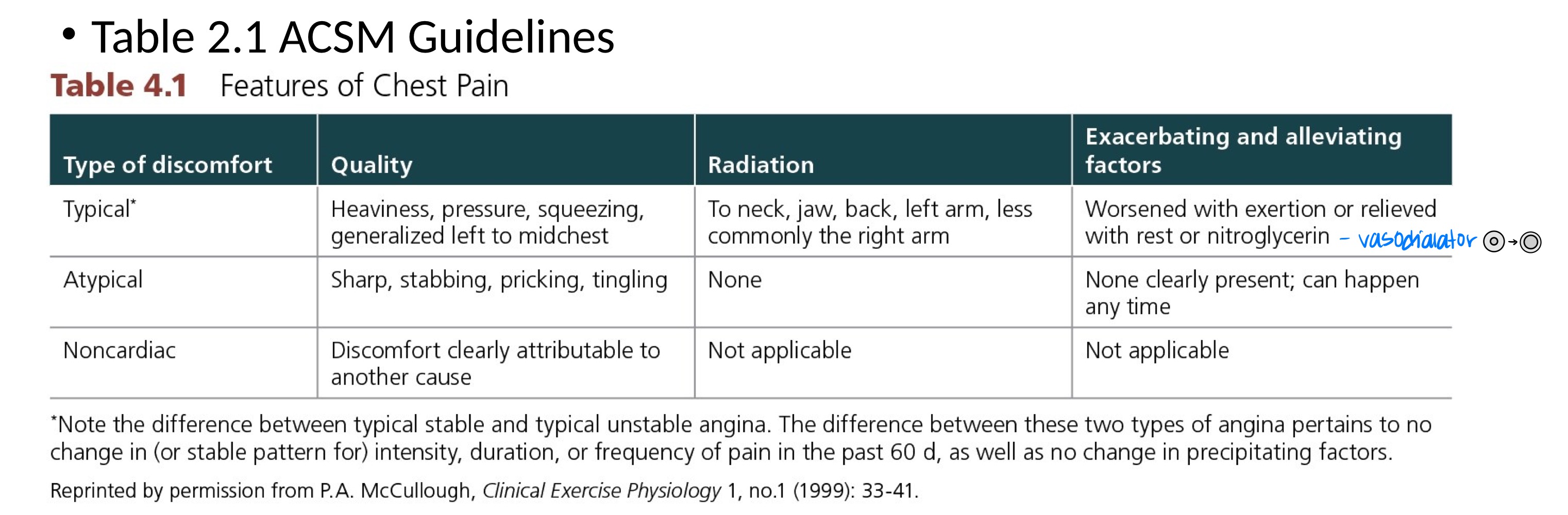
Why should one perform an EKG?
Diagnosis or evaluation of symptoms
To monitor heart’s electrical activity (pacemakers, ICD’s)
Assess medical side effects
To detect exercise-induced abnormalities
What are signs/symptoms an EKG is used to diagnose/evaluate?
angina
MI (myocardial Infarction)
palpitations
faintness
dyspnea (shortness of breathe)
arrhythmias (abnormal rhythm of heart)
hypertrophy (enlarged heart)
pericarditis (swelling & sharp chest pain)
What is an exercise EKG called? How are the electrodes different?
GTX (Graded Exercise Test); more sticker & different limb placements
when sodium (Na+) enters cells, leading to ventricular contraction
Depolarization of the heart
when myocytes return to their resting negative charge (polarized), preparing for the next depolarization
Repolarization of the heart
The Sympathetic Nervous System innervates _______
SA, AV, and ventricular myocardium (His bundle, Purkinje fibers)
The Parasympathetic Nervous System innervates _______
SA and AV node only
(Sympathetic/Parasympathetic) Increases HR and contraction strength via norepinephrine; excitatory
(Sympathetic/Parasympathetic) Decreases HR via acetylcholine; inhibitory
Sympathetic; Parasympathetic
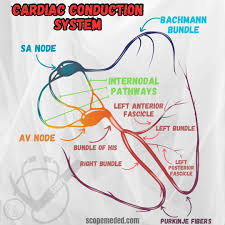
Match the term to the definition pertaining to the Cardiac Conduction System:
SA Node
AV Node
AV Bundle (bundle of His)
Right & Left Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
A. Continue down both sides of ventricular septum; bundles of rapidly conducting Purkinje Fibers
B. Upper part of the interventricular septum; start of ventricular conduction system
C. Pacemaker of the heart; located on superior wall of right atria
D. Relays impulses from atria to ventricles with a delay for atrial contraction; only pathway thru AV valves
E. Continuation of bundle branches; rapidly distribution depolarization to ventricular myocytes
C
D
B
A
E
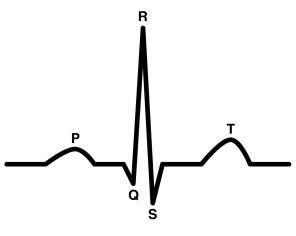
Match the EKG Complex term with its respective definition:
P wave
QRS Complex
T wave
A. Atrial depolarization; leads to atrial contraction via the SA Node (*after isoelectric baseline)
B. Ventricular depolarization; leads to ventricular contraction; atrial repolarization also happens but is not visible
C. Ventricular Repolarization (rapid pulse)
A
B
C
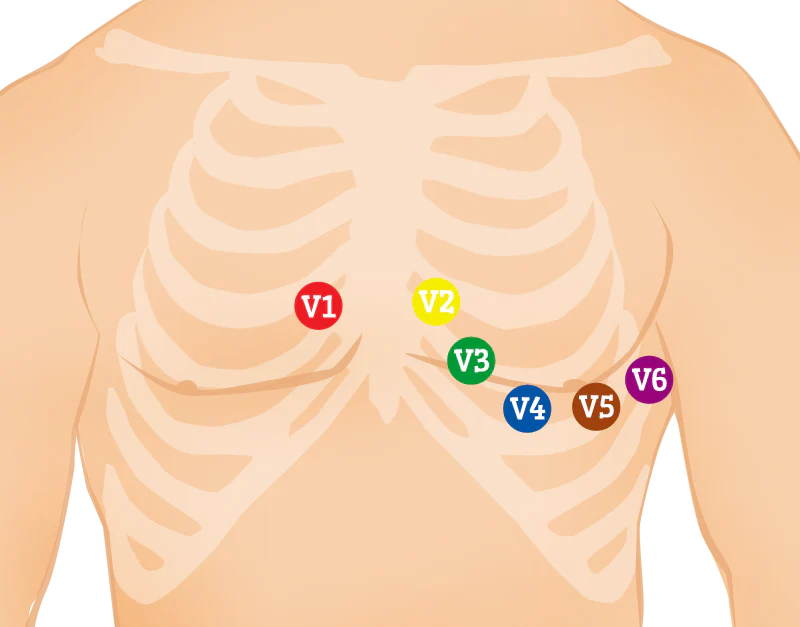
What are the 5 steps to an 12-Lead EKG Electrode Placement?
Identify anatomical landmarks
Clean skin with an alcohol-saturated pad
abrade skin with abrasion paper to remove dead skin
Shave chest hair if necessary
Apply electrodes
Name the proper placement and landmarks of V1-V6:
V1: Right 4th intercostal space, next to the sternum.
V2: Left 4th intercostal space, next to the sternum.
V3: Midway between V2 and V4.
V4: Left 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line.
V5: Horizontal to V4, anterior axillary line.
V6: Horizontal to V5, mid-axillary line.
T/F: Focus=one; Foci=many
True
Atrial foci rate =
60-80 per min
Junctional foci rate =
40-60 per min
Ventricular foci rate =
20-40 per min
How much squares is in one bold box on an EKG recording?
5 across, 5 down = 25 total
How much time is one square of a EKG reading? One bold box?
0.04 secs; 0.20 secs
What is the amplitude of one square in a bold box of an EKG reading? One bold box?
1mm = 0.1 mV; 5mm = 0.5 mV
Match the EKG intervals w/ their respective times:
PR Interval (PRI)
QRS interval
QT interval
ST segment
A. 0.35-0.45 sec (Rate Dependent)
B. up to 0.10 sec
C. 0.12 – 0.20 sec
D. isoelectric or within 1
C
B
A
D
Represents length of ventricular systole
QT interval
What three thing will knowing the EKG leads well help to do?
Determine axis deviation
Atrial / Ventricular Hypertrophy
Location of Infarction
General interview & examination skills
What does the general patient interview establish?
• Patient database
• Demographic information
• History of present illness (HPI)
• Signs & Symptoms
• Current medications
• Allergies
• Past medical history
• Family history
• Social history
**continously update treatment thru rehabilitation program (quiz question)
The Independent predictor of survival in almost every cardiopulmonary condition
Age
Why should one incorporate the patient’s own words as spoken to you
and gather information from medical records?
to check the two for consistency
What are the symptoms of History of Present Illness (HPI)? *OPQRSTA
• O = onset
• P = provocation and palliation
• Q = quality
• R = region and radiation
• S = severity
• T = timing
• A = associated signs and symptoms
🤠
🤠
1MET =
3.5mL/kg/min
Auscultation of the anterior and posterior chest surfaces for breath sounds are characterized as:
• Normal
• Decreased or absent
• Coarse
• Wheezing
• Crackling (i.e., rales)
Match the term to its respective definition:
Tachypnea
Bradypnea
Hypoxia
A. Respiratory rate less than 8 breaths per minute
B. Respiratory rate greater than 20 breaths per minute
C. Blood oxygen saturation below 95%
B
A
C
turbulent flow in artery
Bruits
What are the different types of physical examinations?
General
Pulmonary
Cardiovascular
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Metabolic
Infection
the determination of the presence of a disease or condition
Diagnosis
an assessment of the probable future course and outcome of a disease
Prognosis
T/F: If someone has a myocardial infarction and is back healthy w/ treatment and medication, they have a low chance of getting it again
False; they have a higher chance of getting it again compared to someone who has not had one
For Contraindications to Exercise Testing Absolute, when should u NOT conduct a GTX?
• Acute myocardial infarction within 2 days
• Ongoing unstable angina
• Uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmia with hemodynamic compromise
• Active endocarditis
• Symptomatic severe aortic stenosis
• Decompensated heart failure
• Acute pulmonary embolus, pulmonary infarction, or deep venous thrombosis
• Acute myocarditis or pericarditis
• Acute aortic dissection
• Physical disability that precludes safe and adequate testing
For Contraindications to Exercise Testing Relative, when should u NOT conduct a GTX?
• Known obstructive left main coronary artery stenosis
• Moderate to severe aortic stenosis with uncertain relationship to symptoms
• Tachyarrhythmias with uncontrolled ventricular rates
• Acquired advanced or complete heart block
• Recent stroke or transient ischemia attack
• Mental impairment with limited ability to cooperate
• Resting hypertension
• SBP > 200 mmHG or DBP > 110 mmHg
• Uncorrected medical conditions
• Significant anemia, important electrolyte imbalance (K+ and Ca++), hyperthyroidism
What two equipment are most commonly used modalities
Treadmill & cycle ergometer
What is the difference between relative and absolute contraindication to exercise prescription?
Absolute contraindication means a condition where exercise should never be prescribed under any circumstances
Relative contraindication means a condition where exercise may be risky, but can be considered on a case-by-case basis depending on the individual's situation and if the benefits outweigh the risks
Cycle tests permit what?
Easier EKG recording and BP measurement
Principles for selecting a GXT protocol:
Initial level of exertion should be clearly _______
Increments between stages should be comparatively (small/large) and of consistent size
Protocol should allow easy estimation of _______
Test should be efficient of patient and physician ______
submaximal
Small
exercise capacity
Time
For treadmill tests, protocol selection should consider what 3 things?
Test purpose
Desired outcomes of test
Individual being tested
T/F: ≤ 5 METS and lower is low exercise capacity
True
________ protocol is low level and is better for individuals with low exertion levels
-gradual changes, lower speed
-3.5% every 2 mins; speed= 2.0mph after first 2 mins
-more fit individuals may not experience enough exertion to produce symptoms
Naughton TM GTX
What does the left bundle branch block (BBB) create?
Wide QRS’s
What does left ventricular hypertrophy create?
Abnormal ST segment
What is the difference in absolute and relative indications for terminating a clincal GXT pertaining to ischemia?
Drop in BP & increase of exercise intensity w/ evidence of ischemia = absolute
Drop in BP & increase of exercise intensity w/ NO evidence of ischemia = relative
For a pretest, when should an EKG & BP be taken? *take 4 ways
take BP laying down then take EKG
take BP sitting then take EKG
take BP standing up then take EKG
sitting, make patient hyperventilate for 30s then take EKG
During test:
-one should take 2-lead EKG during last ___ secs of every stage and at peak exercise
-BP during last ____ of each stage
15, minute
For Posttest:
-Take 12-lead EKG & BP ______ post exercise & every ____ minutes until stabilized near baseline level
immediately, 1-2
What are conditions that prevent reliable EKG analysis during GXTs?
Left bundle branch block (BBB)
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Extensive anterior wall MI
Resting ST and/or T wave abnormalities
Drug effects (digoxin)
Electrolyte abnormalities
What are normal EKG changes during exercise?
• PR interval shortens (rate-related)
• QT interval shortens (rate-related)
• Minimal shortening of QRS duration
• Superposition of P and T waves
• R wave amplitude decreases
• T wave amplitude increases
• ST segment has a progressively positive upsloping beginning from J point (J point may be slightly depressed)
What is the most common manifestation of exercise-induced myocardial ischemia?
ST-segment depression
T/F: ST-segment depression does NOT localize the area of ischemia nor indicate which coronary artery is involved
True
Significant ST-segment depression occurring only in recovery likely represents a (True/False) positive response and should be considered an important diagnostic finding
True
What are the 3 types of ST depressions associated with ischemia?
Upsloping, Horizontal, Downsloping
Match the ST depressions associated with ischemia to their respective definitions:
Upsloping
Horizontal
Downsloping
A. Most indicative of myocardial ischemia.
ST segment slopes downward from the baseline.
Often suggests severe coronary artery disease (CAD) and significant ischemia.
B. Least specific for ischemia
ST segment slopes upward toward baseline.
Can be seen in healthy individuals during exercise and may not always indicate ischemia.
C. Strongly associated with ischemia.
ST segment remains flat and depressed below baseline.
Often seen during exercise stress tests and suggests subendocardial ischemia.
B
C
A
What is the threshold for ST segment depression?
≥1mm (0.1mV) measured 0.08 secs past J point
What are preexisting conditions which can result in “false positive” responses during GXTs?
intense exercise
metabolic disturbances
Baseline EKG abnormalities
Drugs
Failure of HR to increase commensurate w/ the bodies demands w/ increased exercise intensity
chronotropic incompetence
one-minute HR recovery =
active recovery
during exercise, SBP should increase about ____ mmmHg/MET
5-10
What are normal clinical responses to maximal exercise?
• Skin flushed and wet with perspiration
• Shortness of breath
• Generalized or local muscular fatigue
• Achieve appropriate max MET level
• No abnormal EKG changes
• Normal hemodynamic responses
What are the criteria for an adequate GXT?
• Attaining stage 4 standard Bruce (13 METs)
• Achieving a double product (*RPP= HR x BP) or MVO2 of 20,000 or more
*Healthy individuals: >20,000
Ischemic threshold: <20,000
• Reaching at least 85% of maximum predicted heart rate (220-age)
• Achieving > 80% of chronotropic reserve
• RPE > 17 (6-20 Borg scale)
• Normal EKG response
During the general interview, a patient reports that they have been experiencing anginal pain that occurs with less physical exertion and at times anginal pain at rest. They have been taking nitroglycerin to relieve the anginal pain more frequently over the past few days prior to coming in for their current appointment. The patient appears to be experiencing?
Stable Angina
Unstable Angina
Anxiety attack
Heart Failure
None of the above
Unstable Angina
A blockage in which coronary artery will have the greatest impact on blood flow to the heart?
A. Great cardiac vein
B. Distal right coronary artery
C. Coronary sinus
D. Proximal left main coronary artery
E. None of the above
Proximal left main coronary artery
How is the heart rate response, blood pressure response and exercise capacity impacted when a patient is taking Tenormin as prescribed.
A. Increase in HR and BP with an increase in exercise capacity in patients with angina
B. Decrease in HR with an increase in BP and no change in exercise capacity for patients with angina
C. Decrease in HR and BP with an increase in exercise capacity in patients without angina
D. Increase in HR with a decrease in BP with no change in exercise capacity in patients with angina
E. Decrease in HR and BP with and increase in exercise capacity in patients with angina
F. None of the above
Decrease in HR and BP with and increase in exercise capacity in patients with angina
-
*Tenormin = Atenolol = Beta Blocker = Decrease HR & BP
A patient has been referred by their Physician to the Cardiovascular lab for a Graded Exercise Test
(GXT) for evaluation of chest pain over the last few days. Upon the initial evaluation of the patient, it is determined that they are not capable of walking on the treadmill. What is the diagnostic test that will likely be recommended in place of the GXT?
Coronary Angiogram
Exercise Imaging Study
Pharmacologic Imaging Study
Coronary Artery Bypass
Pharmacologic Imaging Study
Which of the following are clinically accepted reasons for performing a graded exercise test (GXT).
A. Extension of the history and physical exam
B. Evaluate exertional discomfort in the legs
C. Evaluate presence of occult coronary artery disease (CAD)
D. Risk stratification in patients with known CAD
E. All of the above are clinically accepted reasons for performing a GXT
All of the above are clinically accepted reasons for performing a GXT
Which of the following listed below would be considered an Absolute Contraindication to performing a Graded Exercise Test on the treadmill (GXT)?
A. Acute myocardial ischemia within 7 days
B. Stable angina
C. Uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmia
D. Orthopedic limitation limiting the patient's ability to safely walk on the treadmill
E. None of the above
Orthopedic limitation limiting the patient's ability to safely walk on the treadmill
Most complications during Graded Exercise Testing occur:
A. Prior to the test during the prep period
B. Below 85% age-predicted HRmax
C. Above 85% of VO 2max
D. None of the above
None of the above
*Above 85% age-predicted HRmax
A patient completes a GXT and has a normal increase in heart rate and blood pressure, no significant changes in the EKG, and there are no symptoms reported during are after the GXT.
Patient continued until volitional fatigue and requested to stop. The estimated MET level based on the time on the TM using the Bruce Protocol was 13 METs. Based on the information provided, choose the one best answer.
A. Based on GXT results there is a good 5 year survival rate and a low risk of annual mortality
B. Based on GXT results there is a poor 5 year survival rate and a low risk of annual mortality
C. Based on GXT results there is a good 5 year survival rate and a high risk of annual mortality
D. None of the above
Based on GXT results there is a good 5 year survival rate and a low risk of annual mortality
A cardinal manifestation of cardiac disease is chest, neck, jaw, or arm pain/discomfort or angina equivalent. Which of the following is a key feature against an ischemic origin:
A. Constricting
B. Heaviness
C. Burning
D. Sharp, stabbing aggravated by respiration
E. None of the above
Sharp, stabbing aggravated by respiration
-
*Unlikely to be ischemic; more commonly associated with pleuritic (lung-related) pain, musculoskeletal pain, or pericarditis
A 42 year old patient with a resting HR of 82 bpm discontinued a GXT at 6 minutes and 30 seconds with a peak heart rate of 182 bpm, RPE 17 and Blood Pressure of 168/92. Based on the information provided how would you classify the chronotropic reserve?
(Peak HR - rest HR)/ (220 - age - rest HR).
A. Normal
B. Abnormal
C. Borderline
D. None of the above
*(182 - 82) / (220 - 42 - 82) = 1.04 = 104%
Normal = >80%
A 40 year old female patient completed a GXT on the treadmill using the Bruce protocol. She discontinued the test at 6:00 due to fatigue reported an RPE of 19. No other signs or symptoms were reported. Her resting heart rate was 84 bpm and resting Blood pressure was 130/80. Her peak heart rate was 148 bpm and peak blood pressure was 150/78. Based on the information provided, what percentage of her estimated VOmax/peak did she achieve? Choose the one best answer that best estimates the percentage of estimated VOmax/peak.
Women: 41.2 - (0.343 x Age)
VO 2max = 14.8 - 1.379 x Time + 0.451 x Time2 - 0.012 x Time3
A. 73%
B. 80%
C. 65%
D. 85%
*VO2Max / Women x 100
*VO2max= 14.8 − (1.379 × 6) + (0.451 × 62) − (0.012 × 63)
= 20.17mL/kg/min
Women = 41.2 − (0.343 × 40)
= 27.48 mL/kg/min
.
( 20.17) / (27.48) × 100 = 73.4% = 73%
A patient completed a Clinical GXT it was determined that it was a positive for CAD. However, when they went on for further testing (Angiogram), it was determined that there was no evidence of CAD. How would you classify the results of the the GXT?
A. False Positive
B. False Negative
C. True Positive
D. True Negative
False Positive
The patient discontinued exercise at stage 2 of the Bruce Protocol with peak heart rate at 170 bpm due to volitional fatigue. During the cool-down phase, as they walk on the treadmill, their heart rate is 167 bpm at 1 minute post exercise. Based on their recover HR response select the best answer from below.
A. A normal recovery response following a GXT
B. An abnormal recovery response following a GXT
C. A strong predictor of morbidity
D. None of the above
An abnormal recovery response following a GXT
How is the heart rate response, blood pressure response and exercise capacity impacted when a patient is taking Lisinopril (Vasodilator) as prescribed.
A. Increase in HR with no change in BP and an increase in exercise capacity with those with chronic heart failure.
B. No change of HR and a possible decrease in BP along with possibly increasing exercise capacity in those with chronic heart failure.
C. Possible decrease in HR and BP with no change in exercise capacity in those with chronic heart failure.
D. Decrease in HR along with an increase in BP along with a possible increase in exercise capacity in those with chronic heart failure.
No change of HR and a possible decrease in BP along with possibly increasing exercise capacity in those with chronic heart failure.
Assume you are conducting a clinical GXT with a physician present. Which of the following is an absolute indication for terminating the test?
A. Drop in systolic blood pressure > 10 mm Hg with an increase in workload and evidence of ischemia
B. < 2 mm horizontal ST-segment depression
C. Hypertensive BP response (SP=250 mmg and/or DBP > 115 mmHg)
D. Shortness of breath and/or wheezing
E. None of the above is an absolute indication
Drop in systolic blood pressure > 10 mm Hg with an increase in workload and evidence of ischemia
You are preparing to perform a GXT on a severely deconditioned patient that is currently asymptomatic and has complained of exertional chest pain at low levels of activity in the past week. When deciding on a GXT protocol, which of the protocols listed below has the lowest starting MET level would be most appropriate for the patient?
A. Bruce
B. Naughton
C. Modified Bruce Protocol
D. None of the above
Naughton
Which of the following statements is accurate about a graded exercise test?
A. With EKG, it is the first choice for evaluating myocardial ischemia in individuals with a normal resting EKG and the ability to exercise.
B. It is considered an invasive procedure.
C. It should be performed in individuals with a low risk of CAD.
D. All of the above are accurate regarding a GXT.
With EKG, it is the first choice for evaluating myocardial ischemia in individuals with a normal resting EKG and the ability to exercise.
Which of the following is true of a 12 lead EKG specifically regarding ST segment changes during exercise?
A. ST segment elevation during stage 3 of the Bruce protocol with a patient reporting level 4 anginal symptoms, may suggests a minimal narrowing of one of the major coronary arteries.
B. ST depression during stage 2 of the Bruce protocol with a patient reporting level 3 anginal symptoms may suggest of a total occlusion of one or more of the coronary arteries.
C. ST segment depression during stage 3 of the Bruce protocol with a patient reporting level 3 anginal symptoms, may suggests narrowing of one or more of the major coronary arteries.
D. All of the above are true regarding ST segment changes are true
ST segment depression during stage 3 of the Bruce protocol with a patient reporting level 3 anginal symptoms, may suggests narrowing of one or more of the major coronary arteries.
Which of the following medications can be taken to relieve an acute angina attack?
A. Lanoxin
B. Isordil
C. Tenormin
D. Diovan
E. None of the above
Isordil
Which of the following is the defining criteria for Blood Glucose to be a Positive Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factor?
A. Fasting glucose ≥ 60 mg/d| OR a 2 hour Plasma glucose in OGTT ≥ 130 mg/dI OR HbA1c ≥ 4.7%
B. Non fasting glucose > 60 mg/d| OR a 2 hour Plasma glucose in OGTT > 100 mg/dI OR HbA1c > 3.7%
C. Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/d| OR a 2 hour Plasma glucose in OGTT ≥ 140 mg/di OR HbA1c ≥ 5.7%
D. None of the above are
Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/d| OR a 2 hour Plasma glucose in OGTT ≥ 140 mg/di OR HbA1c ≥ 5.7%
T/F: When performing a 12 Lead EKG, you begin with identifying the anatomical landmarks, followed by abrading the skin, and then wiping the skin with an alcohol prep pad, and then placing the electrode on the skin according to the Lead/electrode and appropriate anatomical landmarks.
False; wipe the skin w/ alcohol before abrading
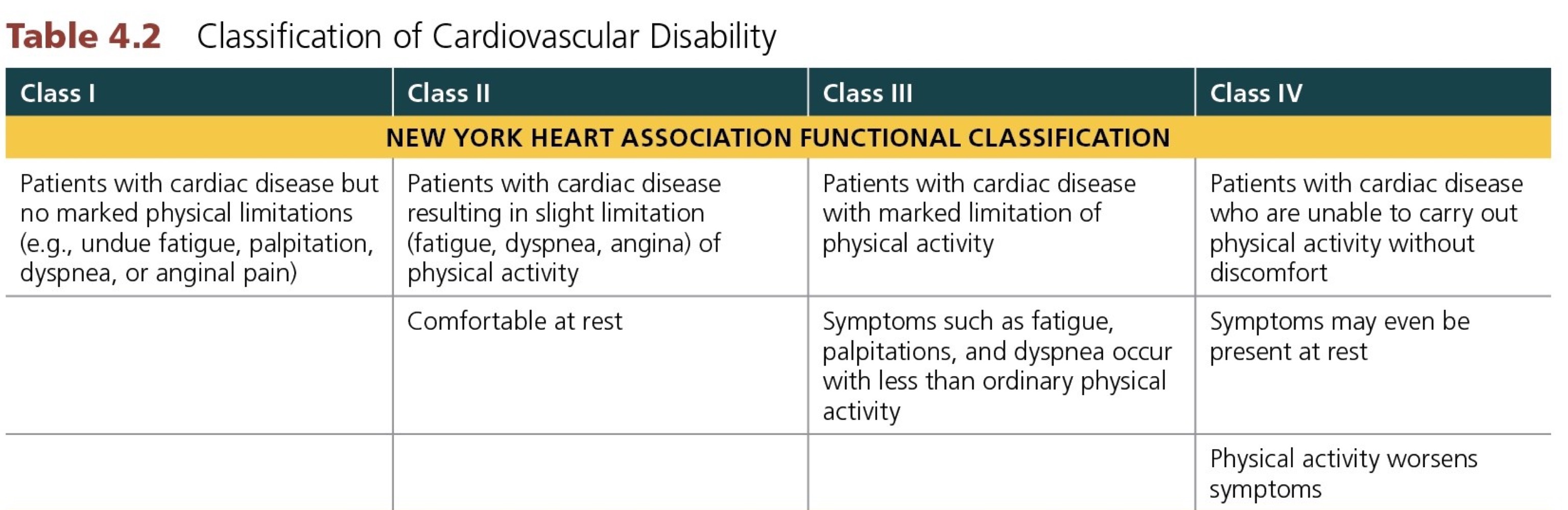
T/F: In regards to cardiovascular disability (NYHA), a patient who is slightly limited due to cardiac symptoms (fatigue, dyspnea, angina) with activity, but asymptomatic at rest is considered CLASS II.
True
T/F: Precordial limb lead V1 is placed on the 5th intercostal space on the right side of the sternum.
False; 4th intercostal space
T/F: Activities such as making the bed, washing the car, and hanging laundry are comparable to 5 METs.
False; 3 METs
T/F: Prognosis is an assessment of the probable future course and presence of cardiovascular disease symptoms.
False; an assessment of the probable future course and outcome of a disease
T/F: Predictable onset and relief of chest tightness, pressure, squeezing, and pain radiating down the left arm is characterized as unstable angina.
False; unstable angina is unpredictable
T/F: A patient that is prescribed Atenolol (Tenormin) will likely experience a lower Blood Pressure and heart Rate response with a decrease in exercise capacity due to the lower heart rate and blood pressure response.
False; will increase exercise capacity in patients with angina
T/F: During an initial assessment prior to beginning Cardiac Rehabilitation, a 55 year old male patient with a BMI of 31 kg/m2, indicates that they stopped smoking 5 months ago. Based only on the information provided here, the patient has 2 CVD Risk factors.
False; only has 1 CVD risk factor: Obesity (BMI >30). Smoking < 3 months is a risk factor.
T/F: Performing a GXT on an asymptomatic college age student who has a low pretest likelihood of CVD, is a clinically accepted reason for conducting a GXT.
False; GXT is not routinely performed on low-risk, asymptomatic individuals.
T/F: A patient who is reporting an acute episode of angina can take sublingual Isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil) to provide potential immediate relief of their anginal symptoms.
True
T/F: A patient taking Diltiazem (Cardizem) as prescribed will result in an increase in the resting HR and will result in no change in the blood pressure response.
False; is a calcium channel blocker (CCB) that primarily lowers heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) by reducing calcium influx into the heart and blood vessels.
T/F: Lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) results in vasoconstriction resulting in potential decrease in the blood pressure response.
False; causes vasodilation, not vasoconstriction
T/F: A patient taking Losartan (Cozaar) as prescribed, will have an increase in resting HR and SBP.
False; is an ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker), which lowers blood pressure (SBP) but does not increase resting HR.
T/F: The general interview is a static patient database established at the start of treatment.
False; is ongoing