(4)Osteology of Maxilla/Mandible Occlusion; Compensating Curves of Occlusion
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcard style
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
The maxilla is made up of what two bones?
Right maxilla and left maxilla
What is the plural of maxilla?
Maxillae
What is the function of the maxilla?
Gives contour to nose, cheeks, upper lip, and face
Located above teeth and below orbit (eye)
Body of Maxilla
How many processes project from the body?
4
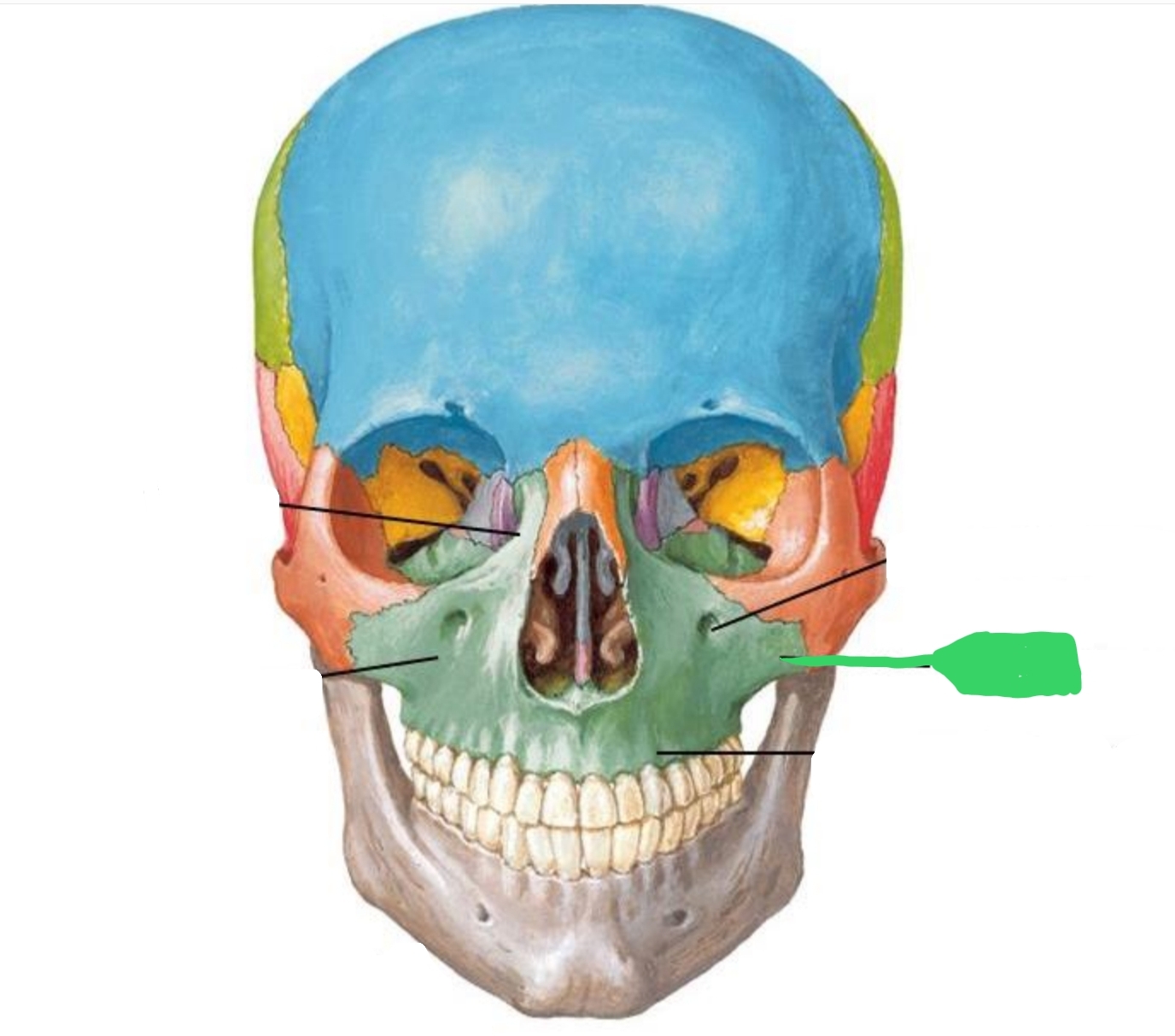
forms part of cheek bone
Can feel it under the eye
Gives shape to cheek
Look like a jug handle when viewed from occlusal
Zygomatic Process
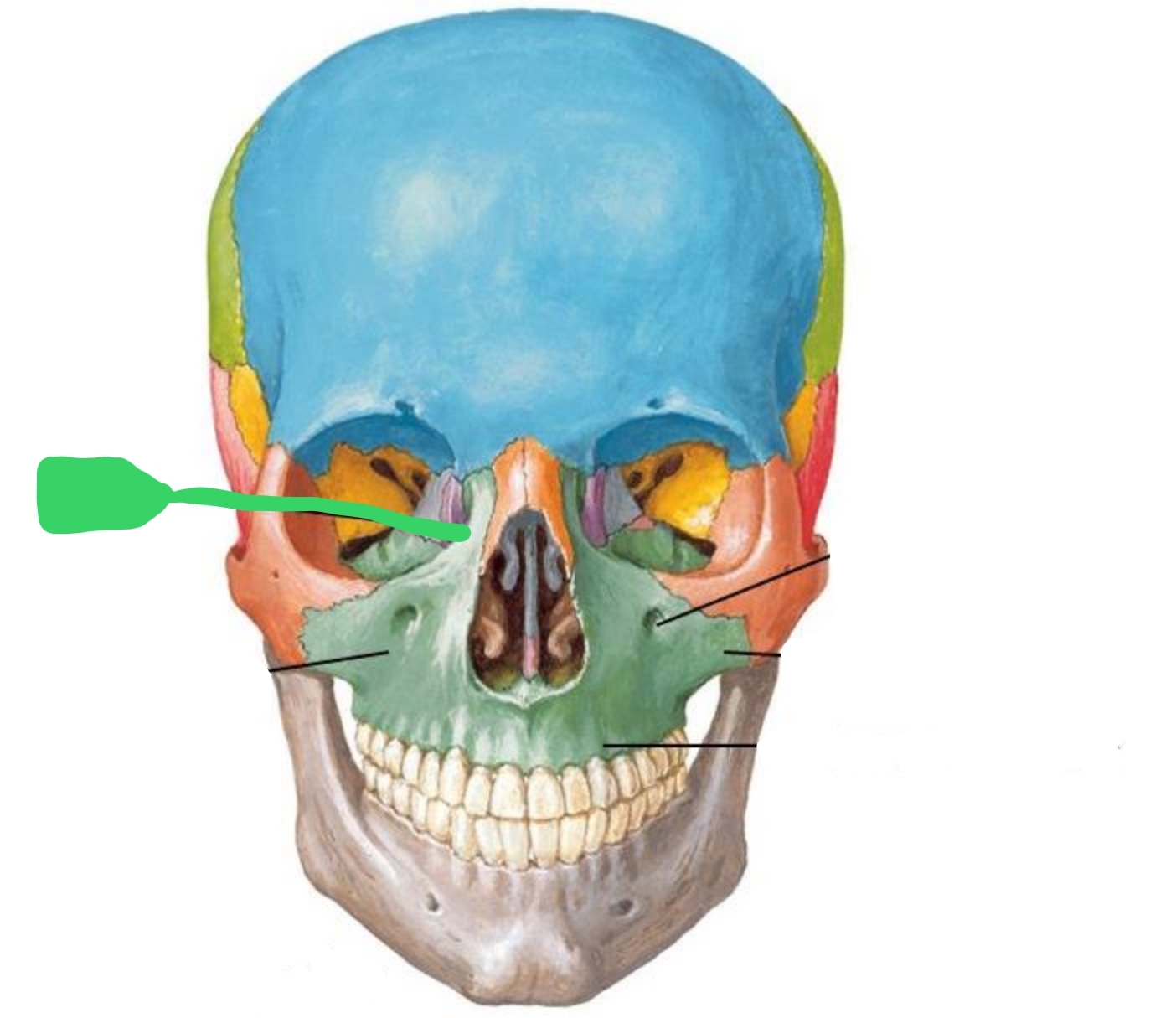
Extends from body toward nose
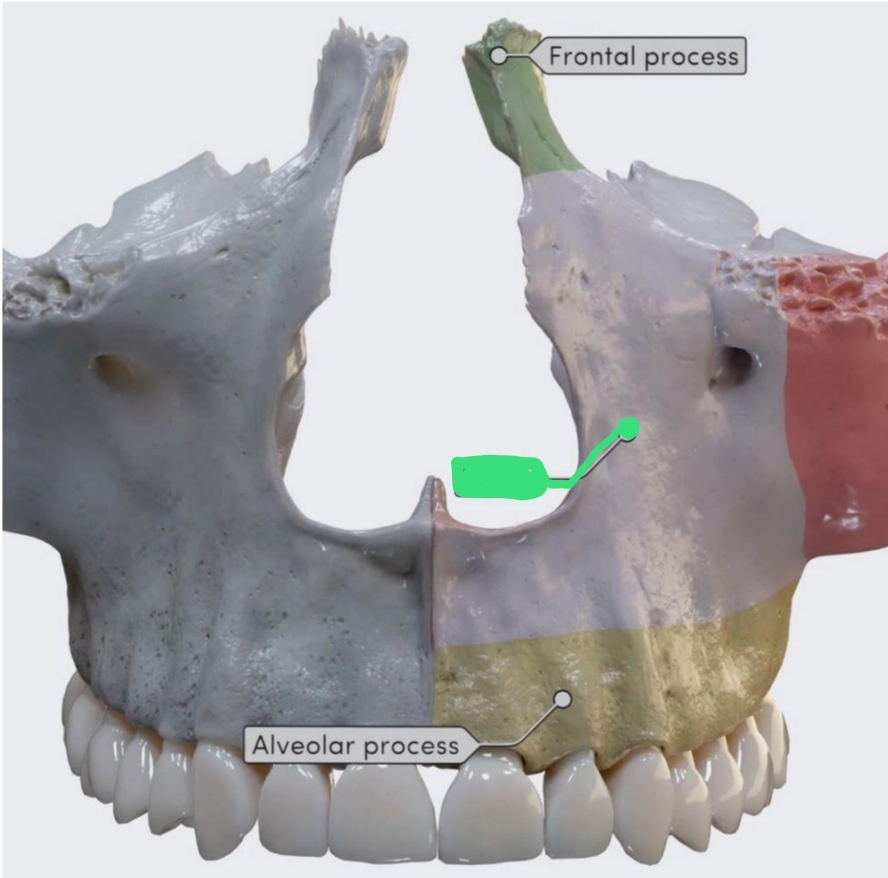
Frontal (nasal) Process
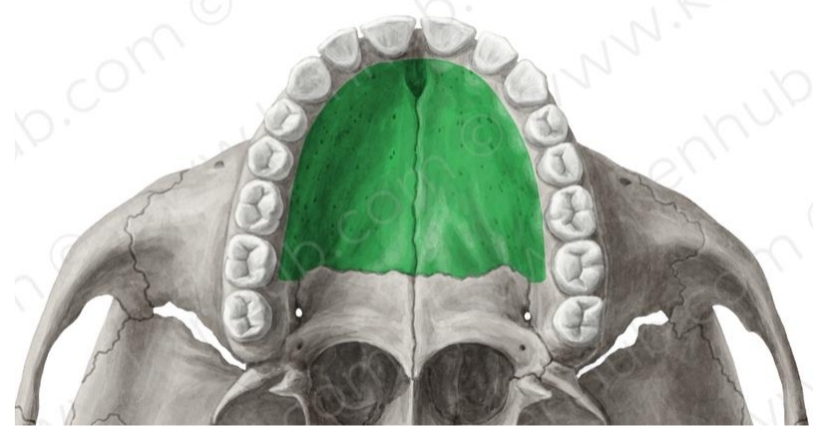
Hard palate
2 processes (R & L) that form roof of mouth or palate
Joints inner (lingual) portion of alveolar process
Palatine Process
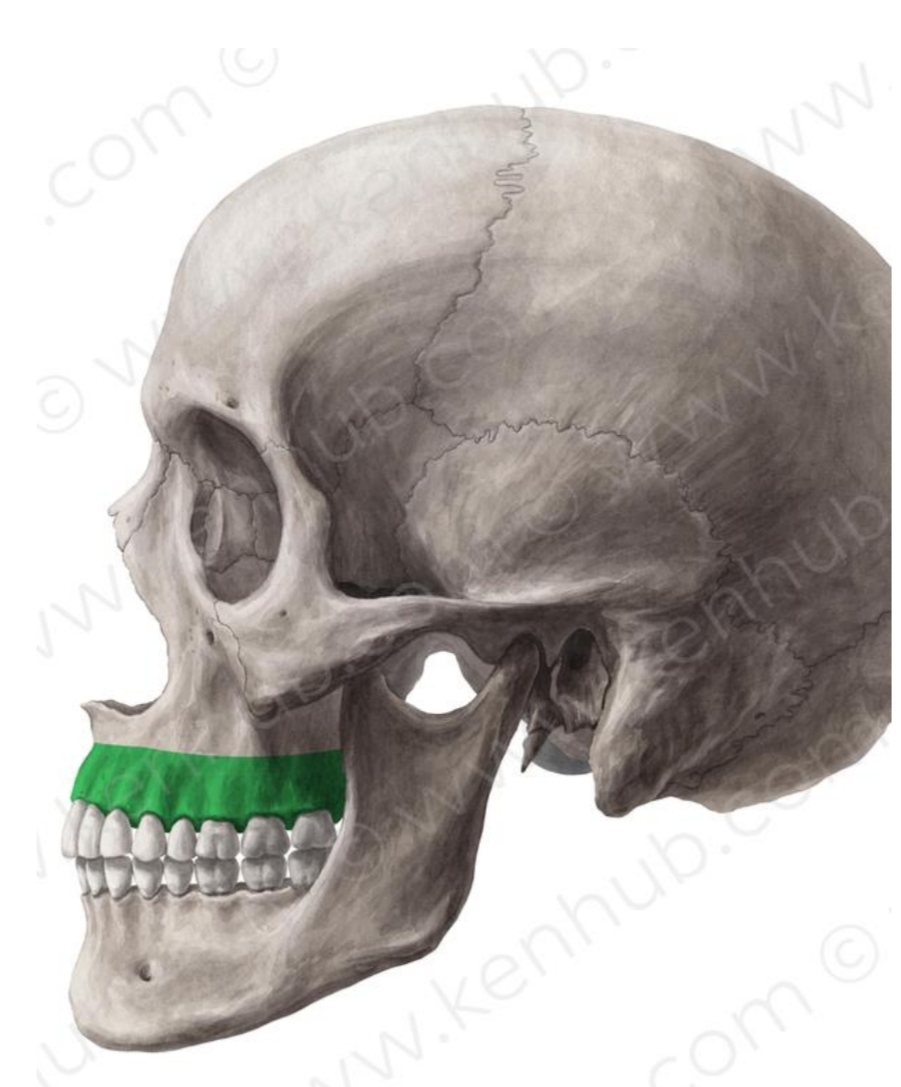
Most significant portion
Bone surrounding roots of teeth
Gives support to all maxillary teeth
Alveolar Process
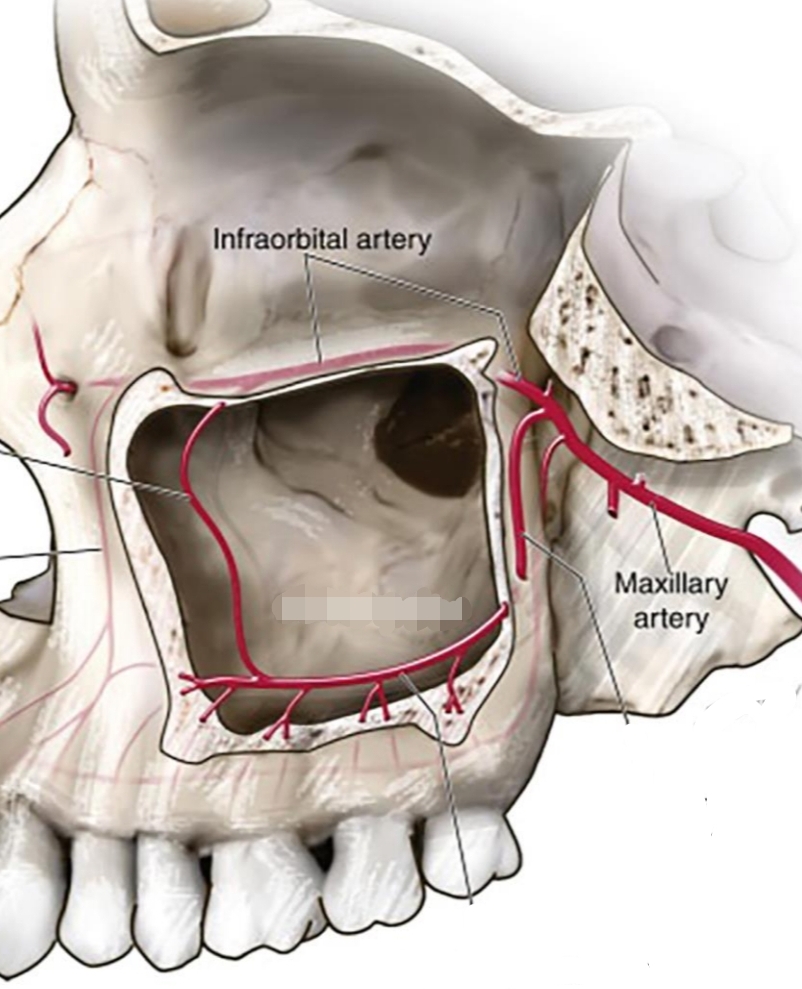
2 air-filled cavities located on lateral sides of nose, above maxillary premolars and molars
Maxillary Sinus
Depression or slight concavity, facially, above incisors where root tips are located
Incisive Fossa
Slight depression, facially, distal to canine
Canine Fossa
Heavy roll of bone over facial portion of root of canine
Canine Eminence
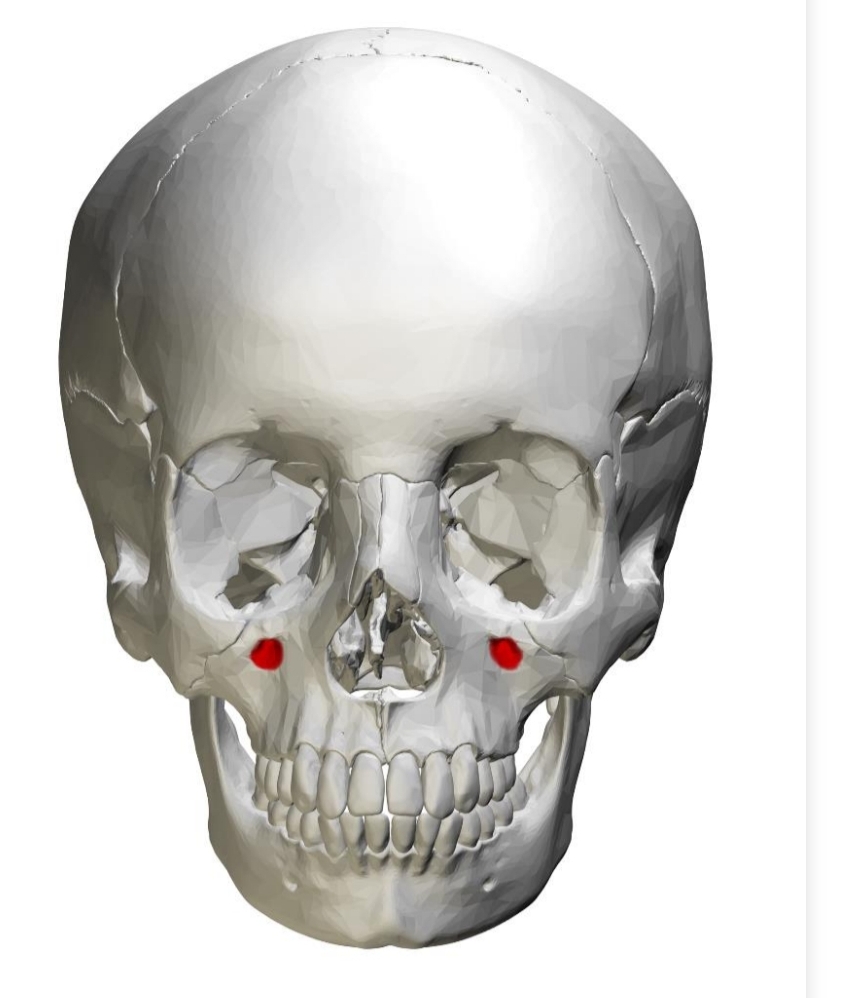
Opening in bone (slight depression)
Located bilaterally between eye (orbit) and canine/premolar root area
Infraorbital nerve infiltrates with anesthetic for maxillary anterior teeth
Infraorbital Foramen
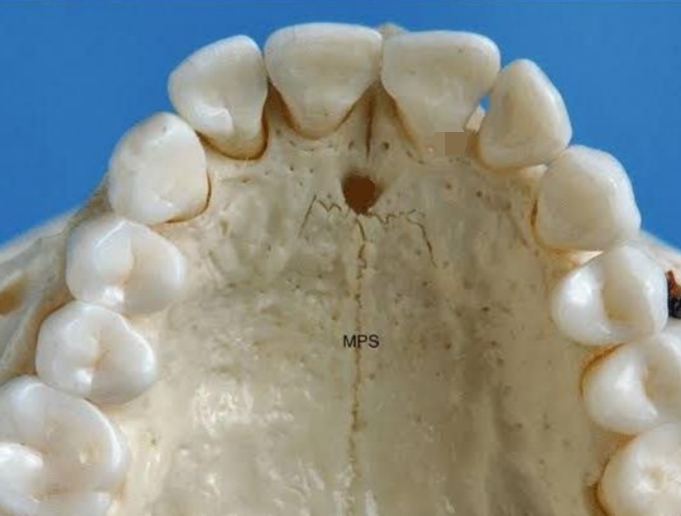
Located in anterior portion of hard palate
Location for anesthesia for anterior teeth
Incisive Canal and Foramen
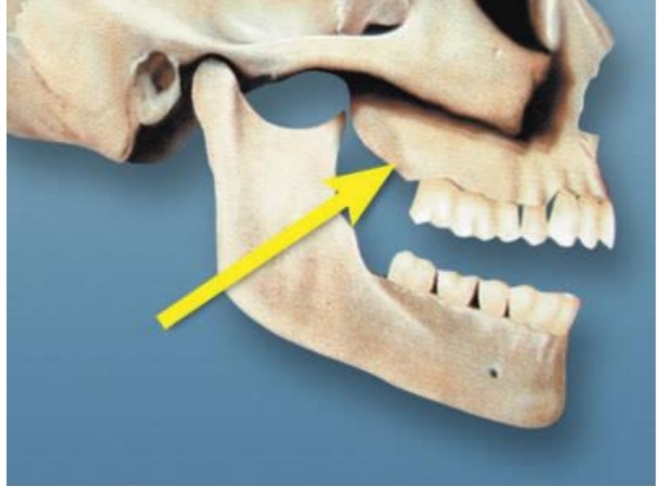
Heavy bone located distal to last posterior tooth
Very important when constructing a denture
Maxillary Tuberosity
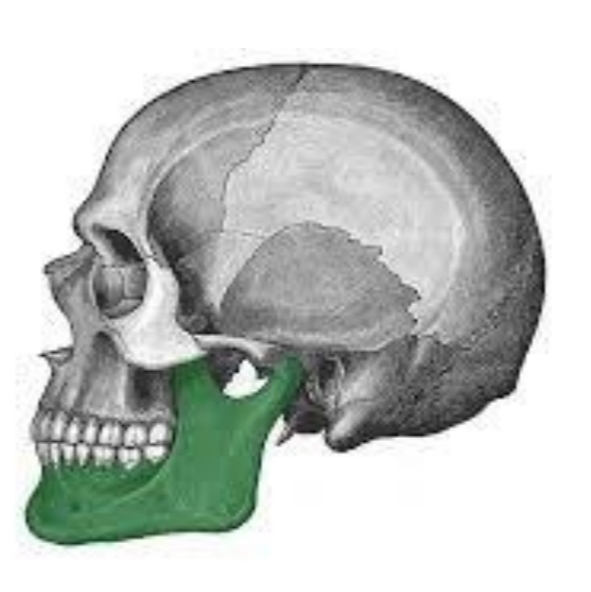
Gives shape to chin or jaw
Consists of one bone that is horseshoe shaped
Mandible
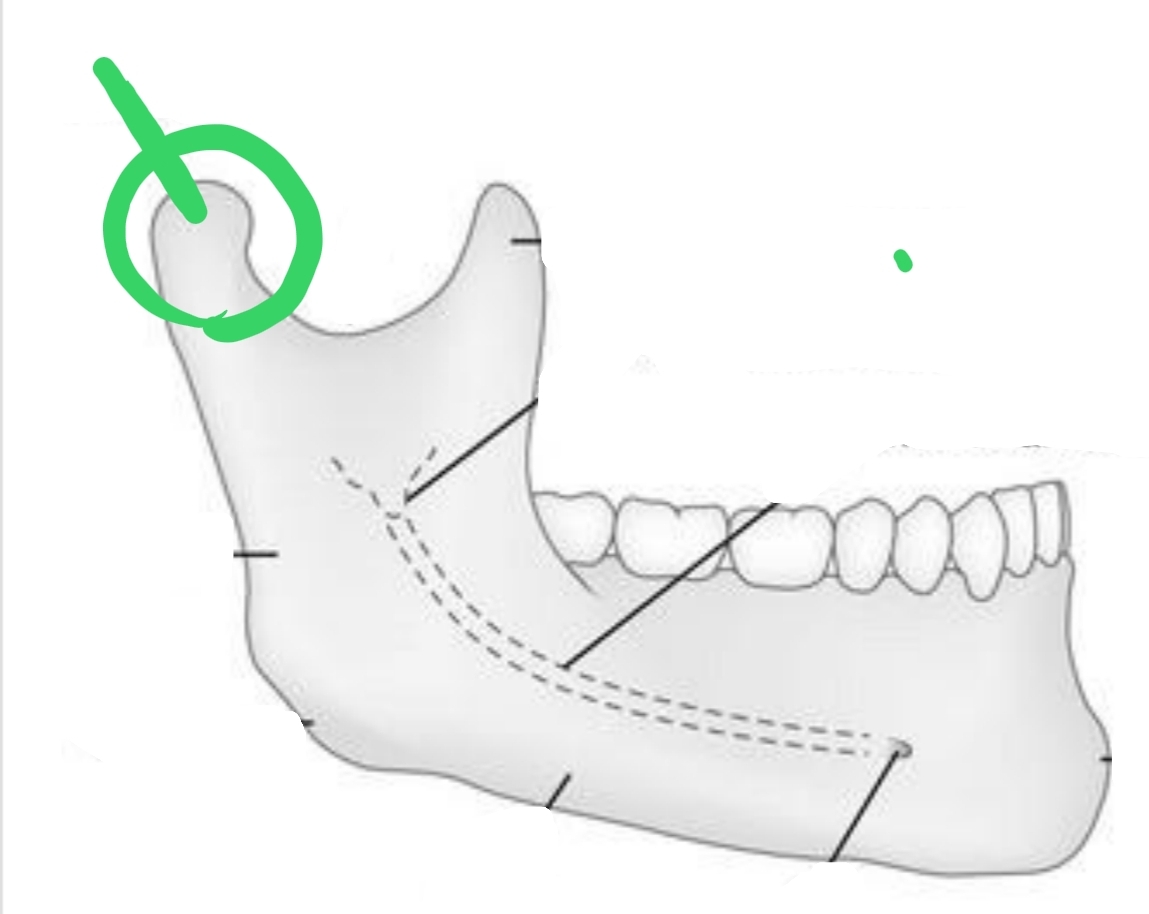
Ball-shaped portion distal to Sigmoid notch; contacts with temporal bone to form TMJ
Condyle (Condylar Process)
Bone that supports/surrounds roots of teeth
Alveolar Process
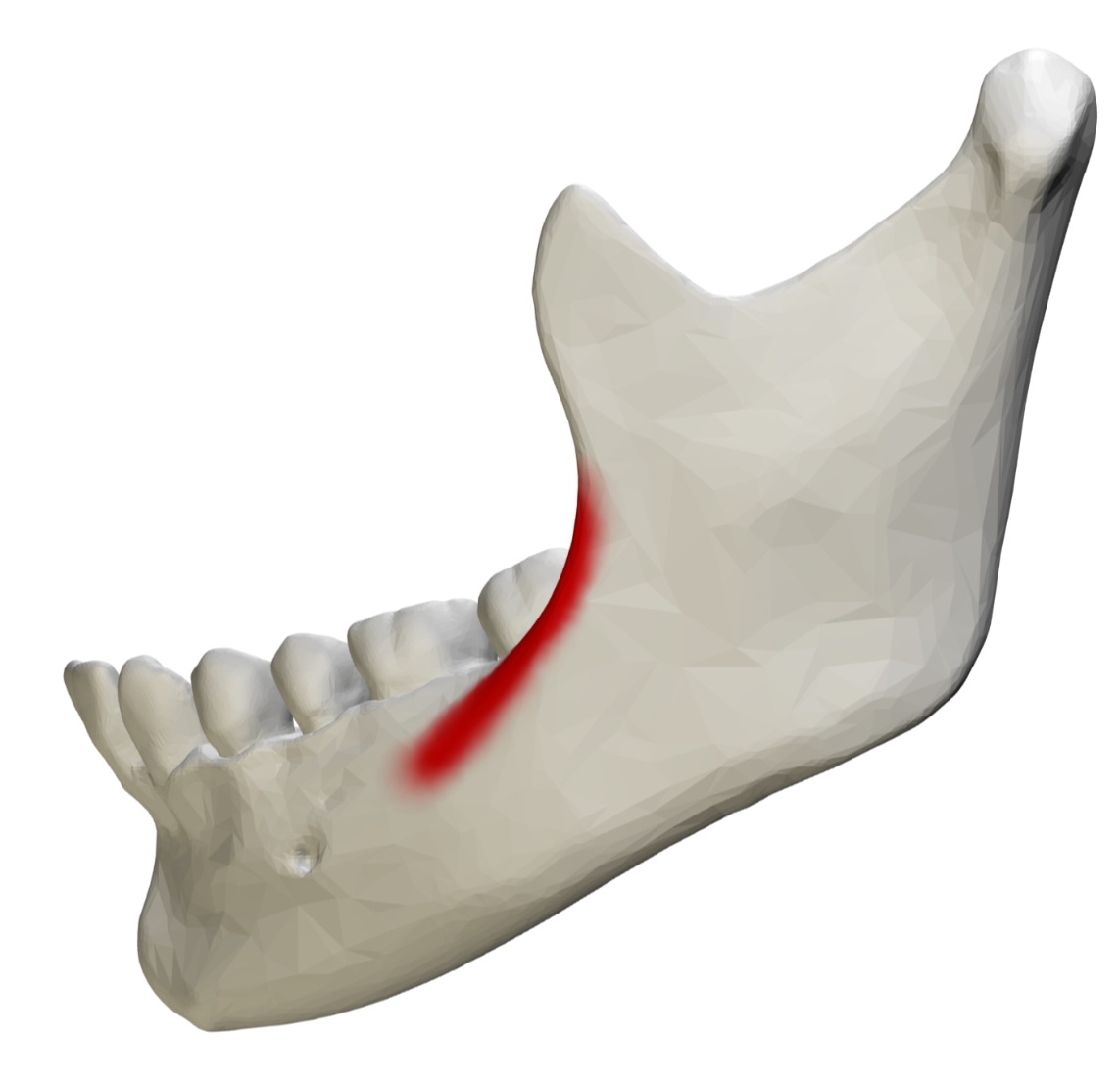
Large ridge of facial; located vertically on ramus
External Oblique Ridge
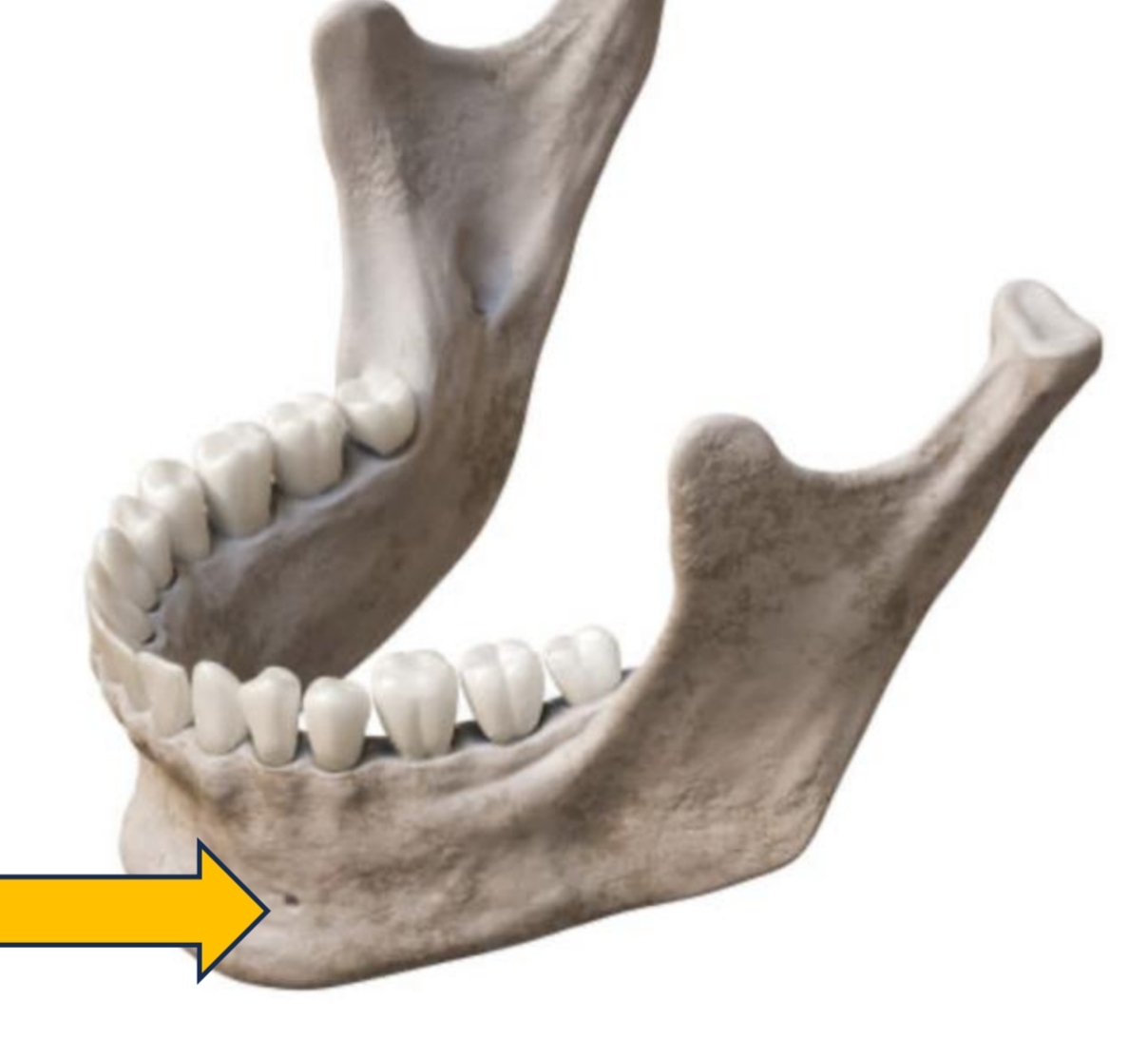
Opening between 1st and 2nd premolars (mental nerve)
Mental Foramen
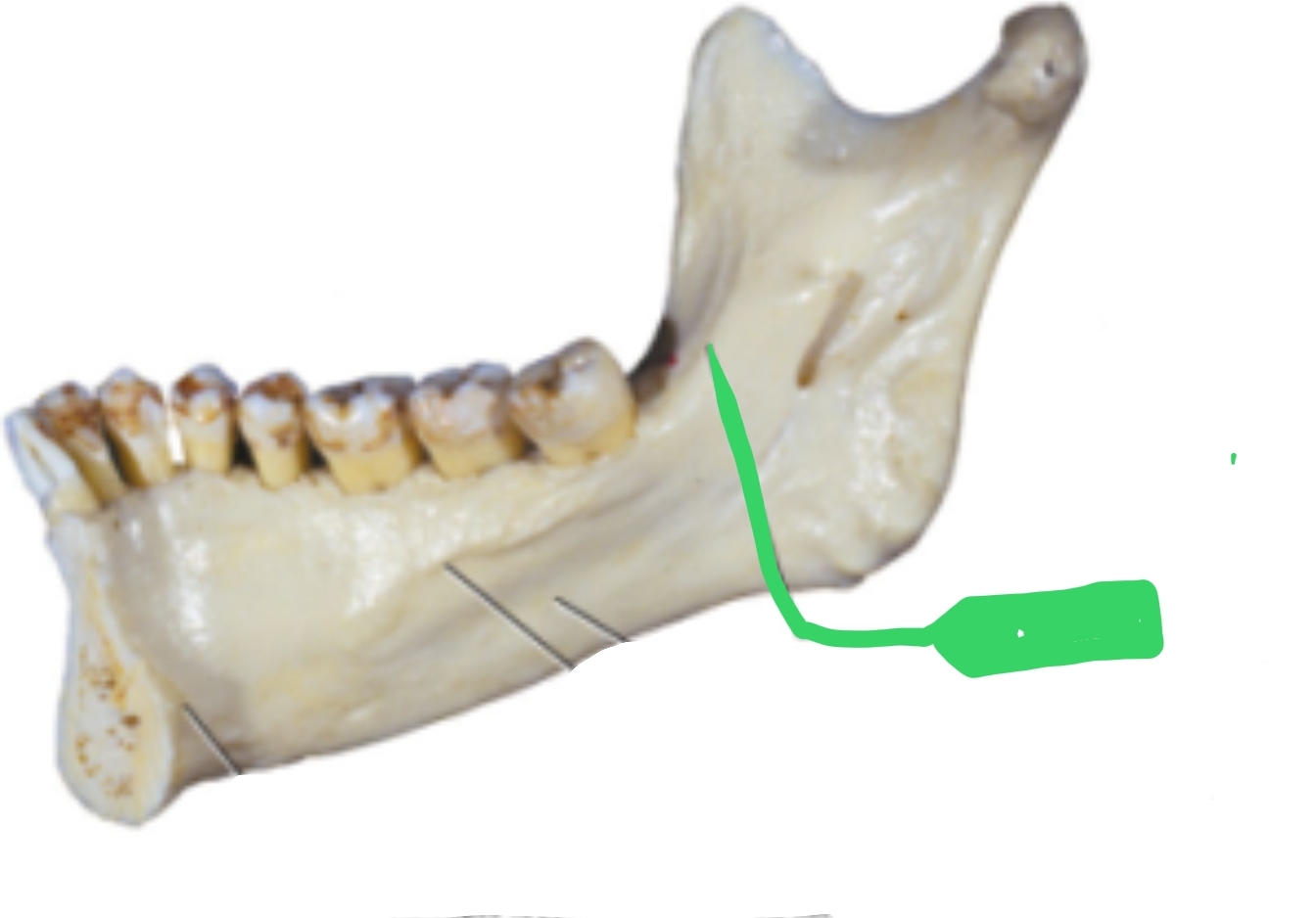
Also called Mylohyoid Ridge
Located on inside of mandible
Muscles attach here
Internal Oblique Ridge
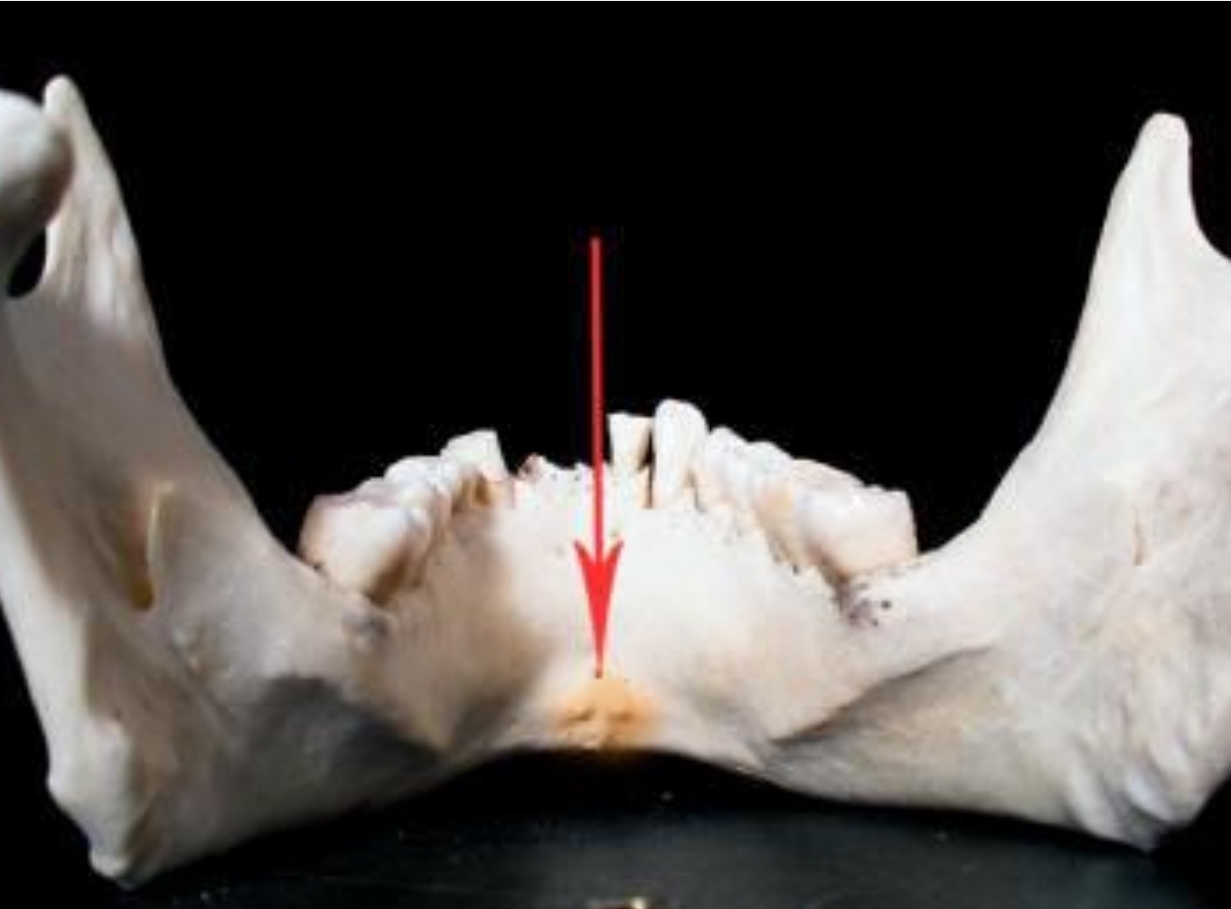
2 rolls of bone on lingual surface of anterior teeeth
Genial Tubercles
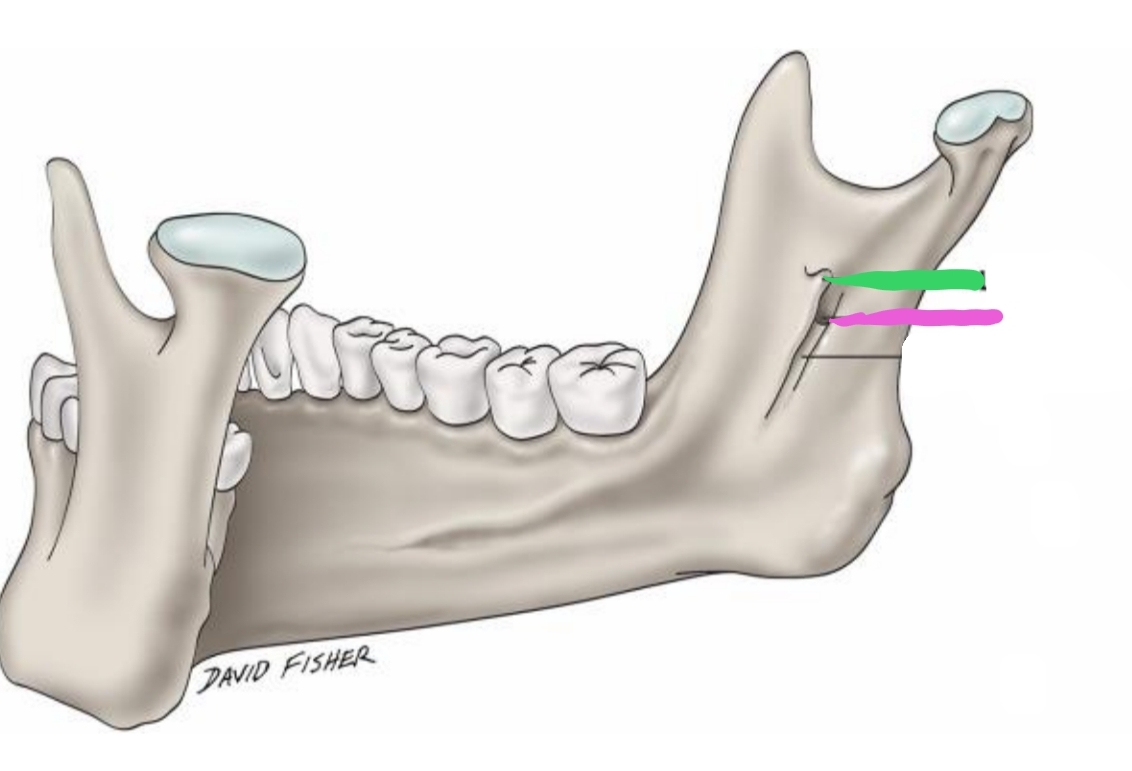
The _________(green) is located on inner surface of ramus; elevation of bone which protects entrance of _________(pink) (opening)
Lingula, mandibular foramen
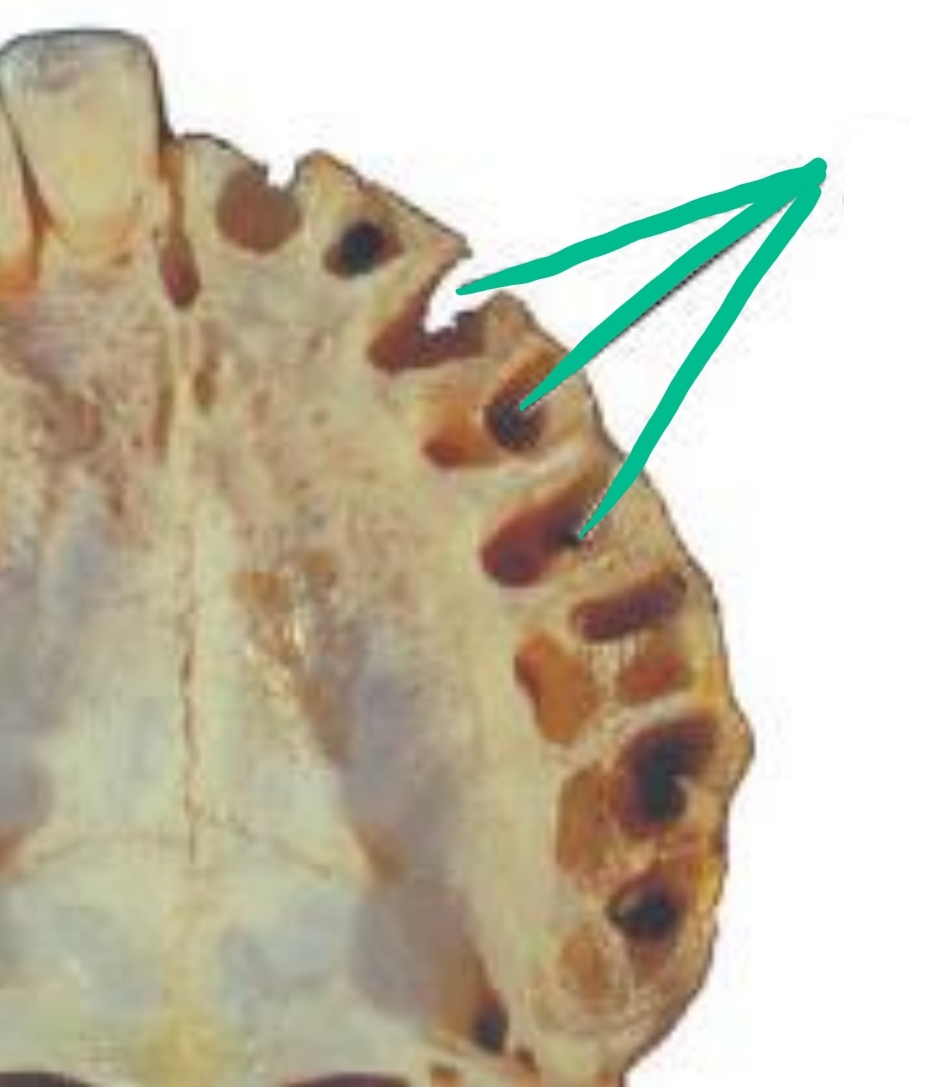
Socket (hole) where tooth is missing; where roots were
Alveolus
What two plates make up the Alveolus?
Buccal plate and Lingual plate
Outer surface of alveolus
Buccal plate
Lingual surface of alveolus
Lingual plate
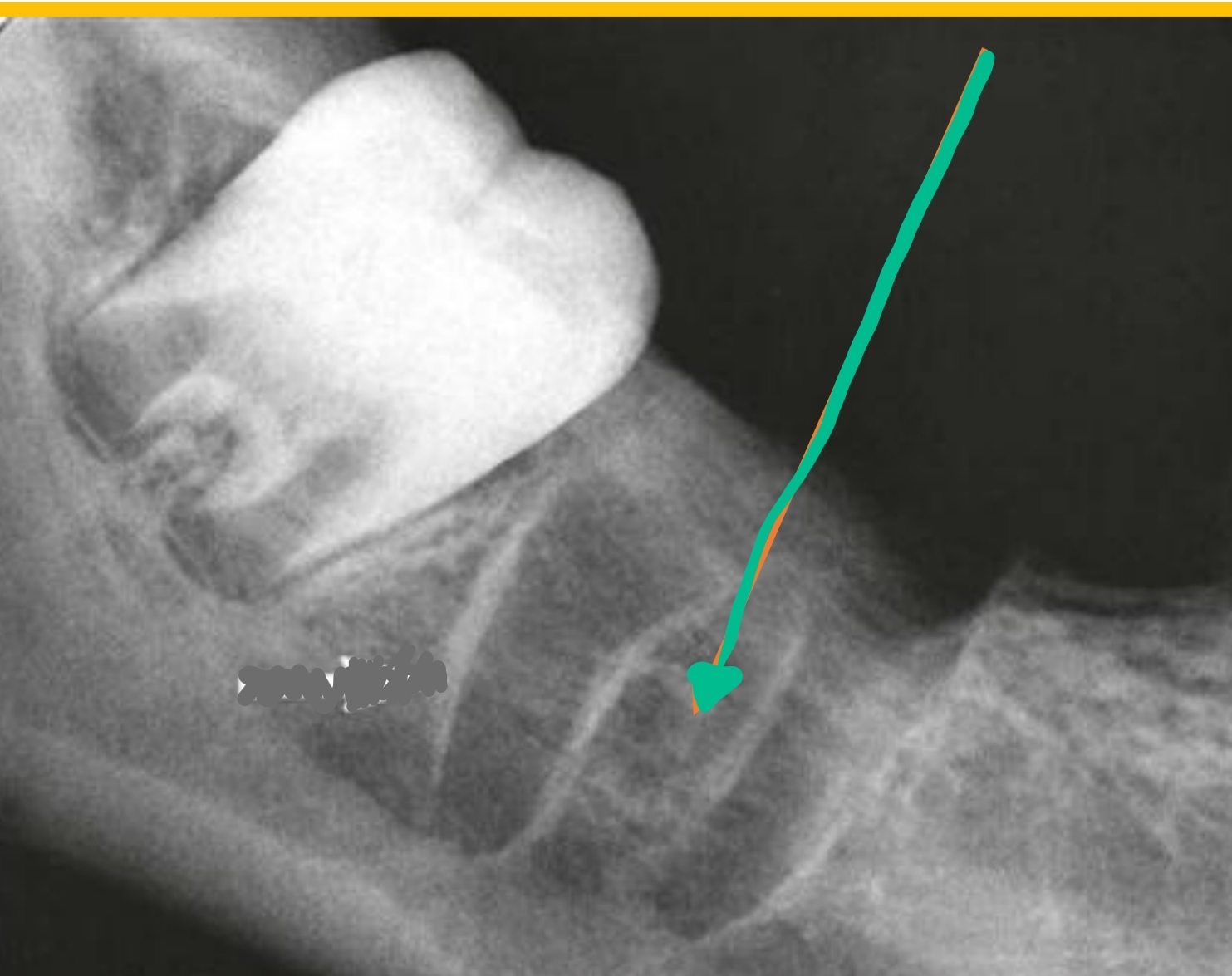
located between roots
Interradicular bone
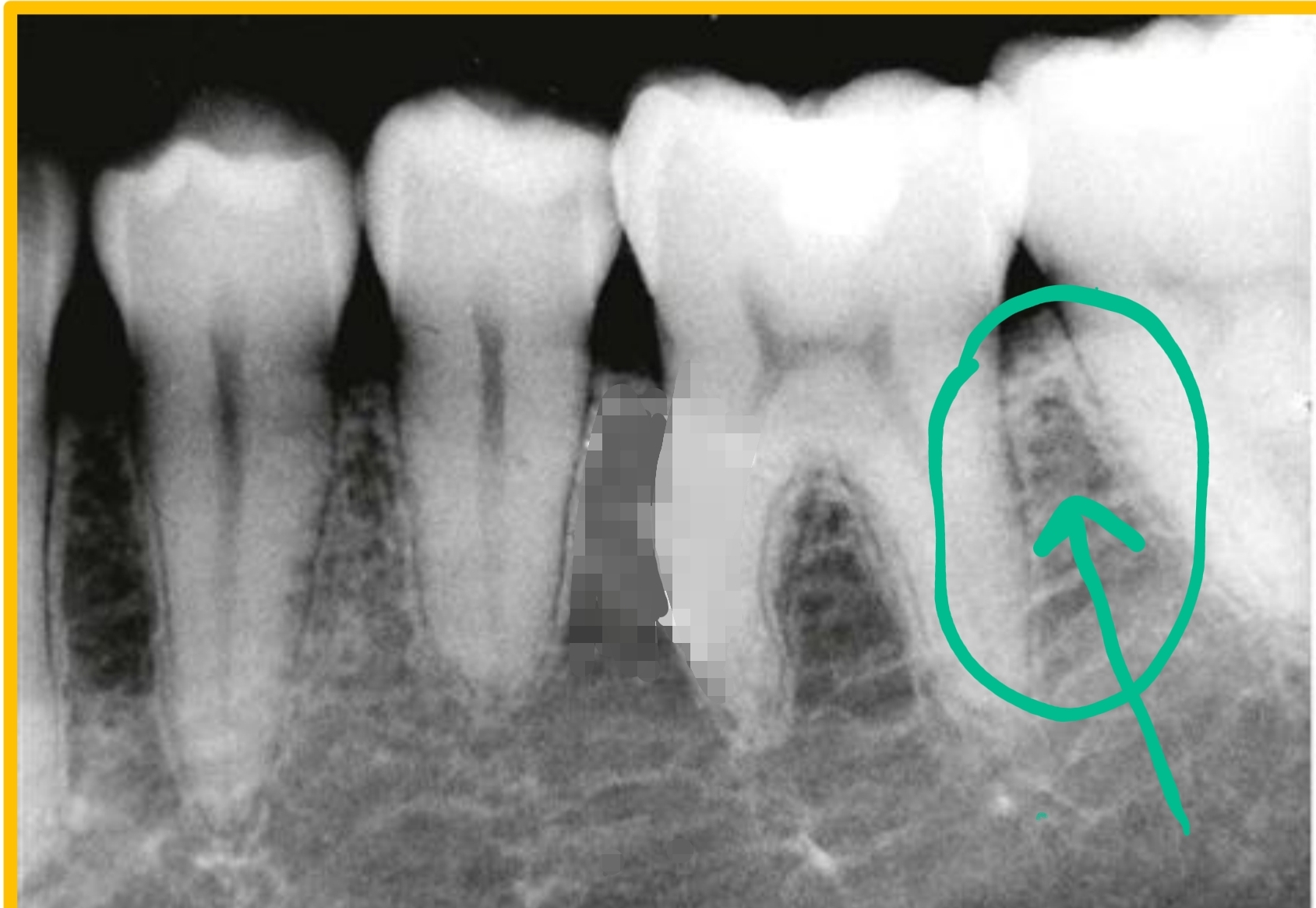
located between teeth
Interseptal bone
Coming together of teeth (contacting in function)
Occlusion
The way teeth come together that is most comfortable for patient; may not be ideal or typical
Habitual Occlusion (maximum interdigitation)
improper occlusion
Malocclusion
What are the reference points in occlusion?
Maxillary 1st molar to mandibular 1st molar
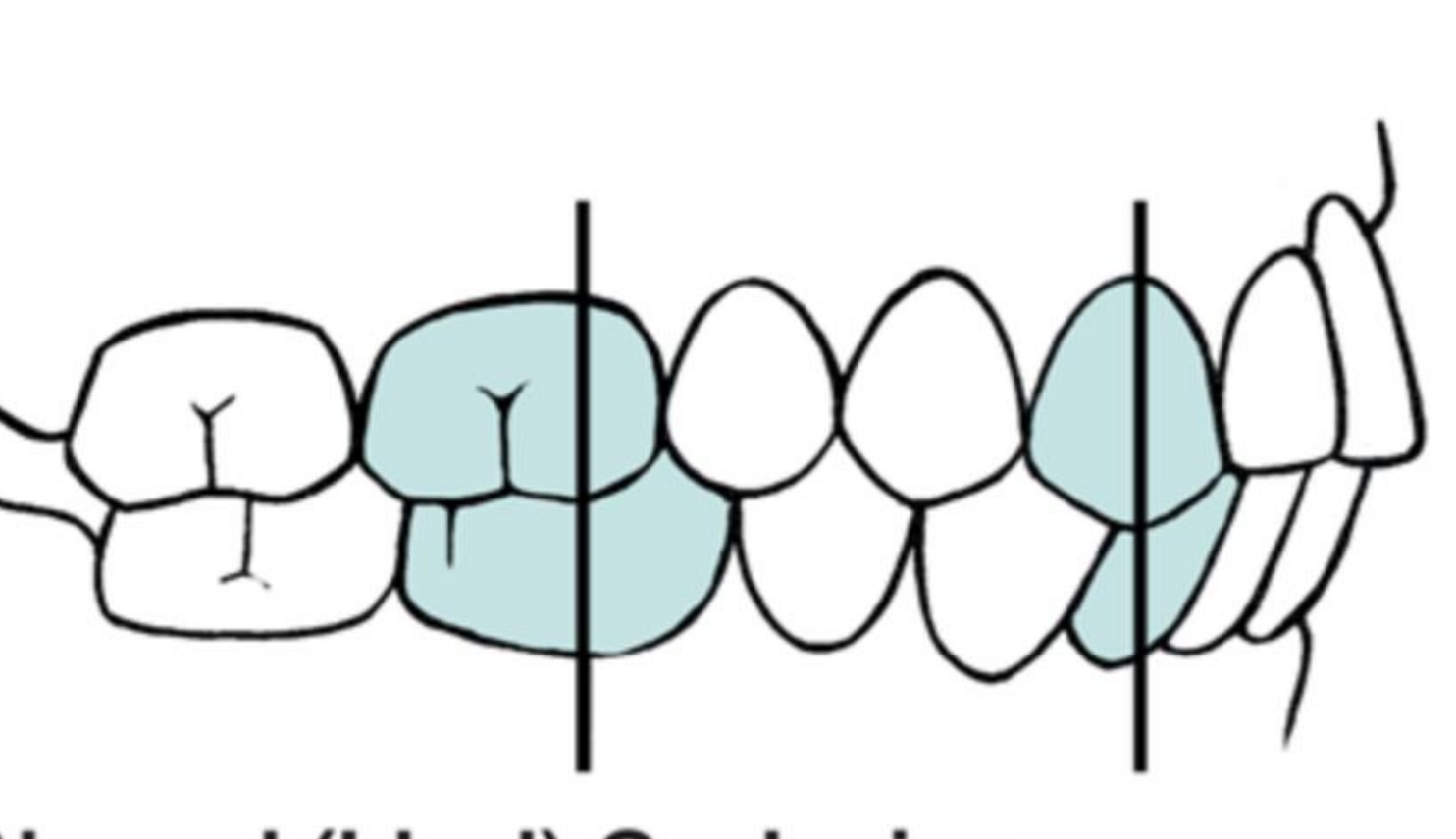
Anteriors - maxillary are to be labial to mandibular teeth, with contact
Maxillary 1st molar = ½ tooth distal to mandibular 1st molar
Maxillary teeth = facial or anterior to mandibular teeth
Maxillary canine is located distal to mandibular canine
Class I
Teeth are interrelated to allow for the most efficient use of forces for mastication, while protecting and stabilizing arches
Compensating Curves of Occlusion
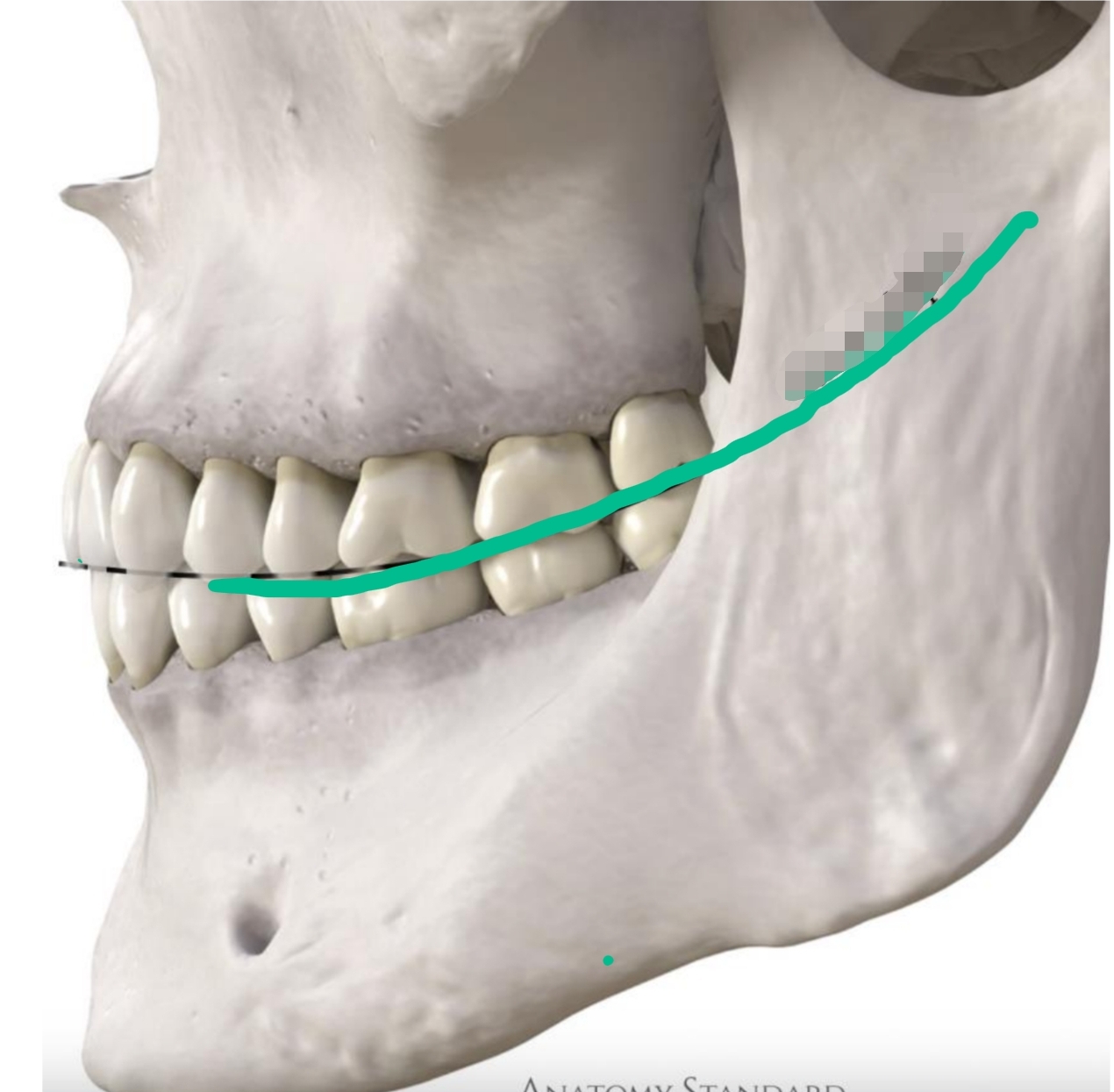
Anterior to posterior position (2 dimensional)
Begins at canines and follows posteriorly
Mandibular are concave
Maxillary are convex
Curve of Spee
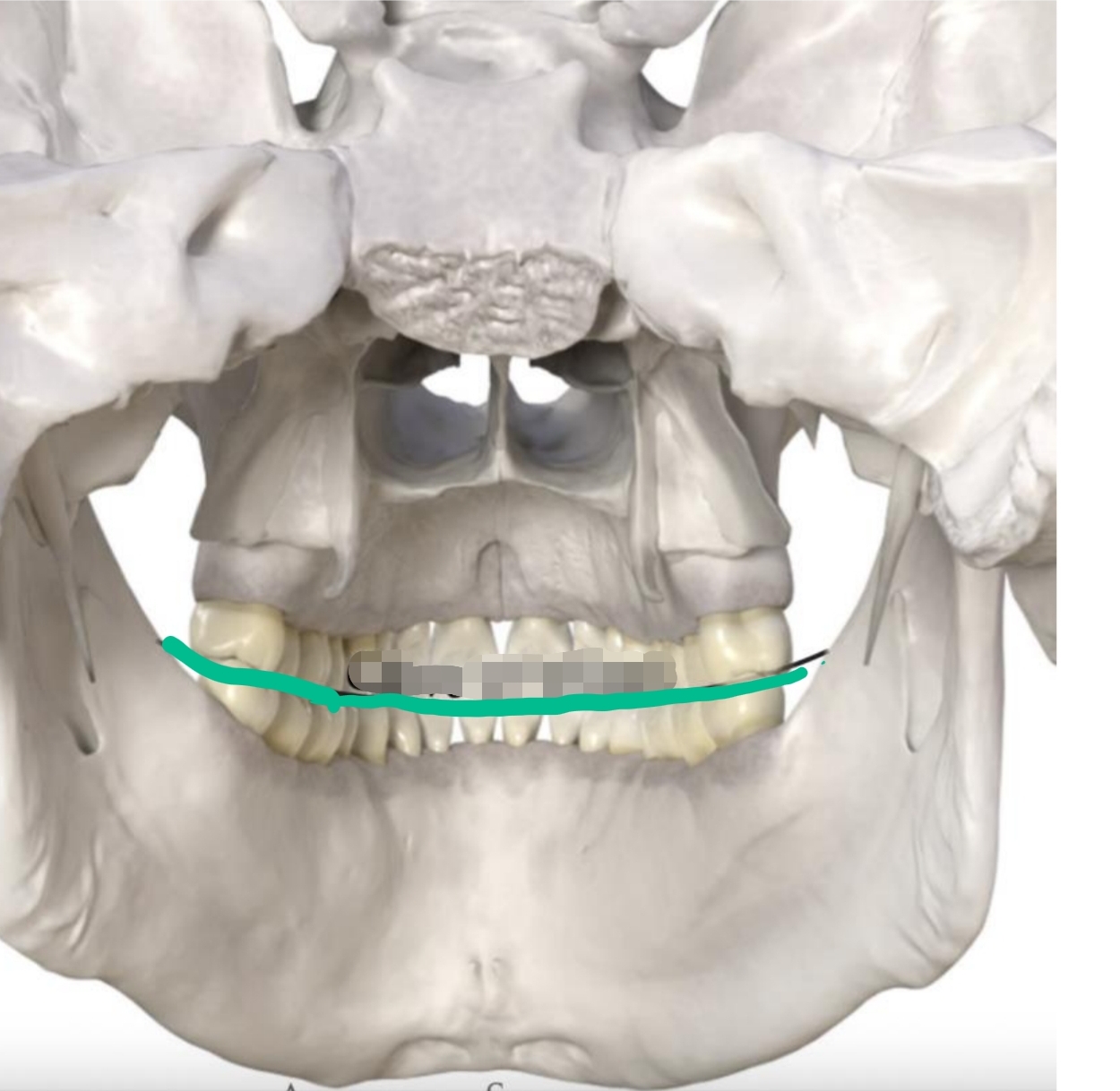
Medial/lateral curvature of occlusal plane of posterior teeth
2-dimensional
Opposite direction of Curve of Spee
Allows for sphere of motion in chewing
Curve of Wilson
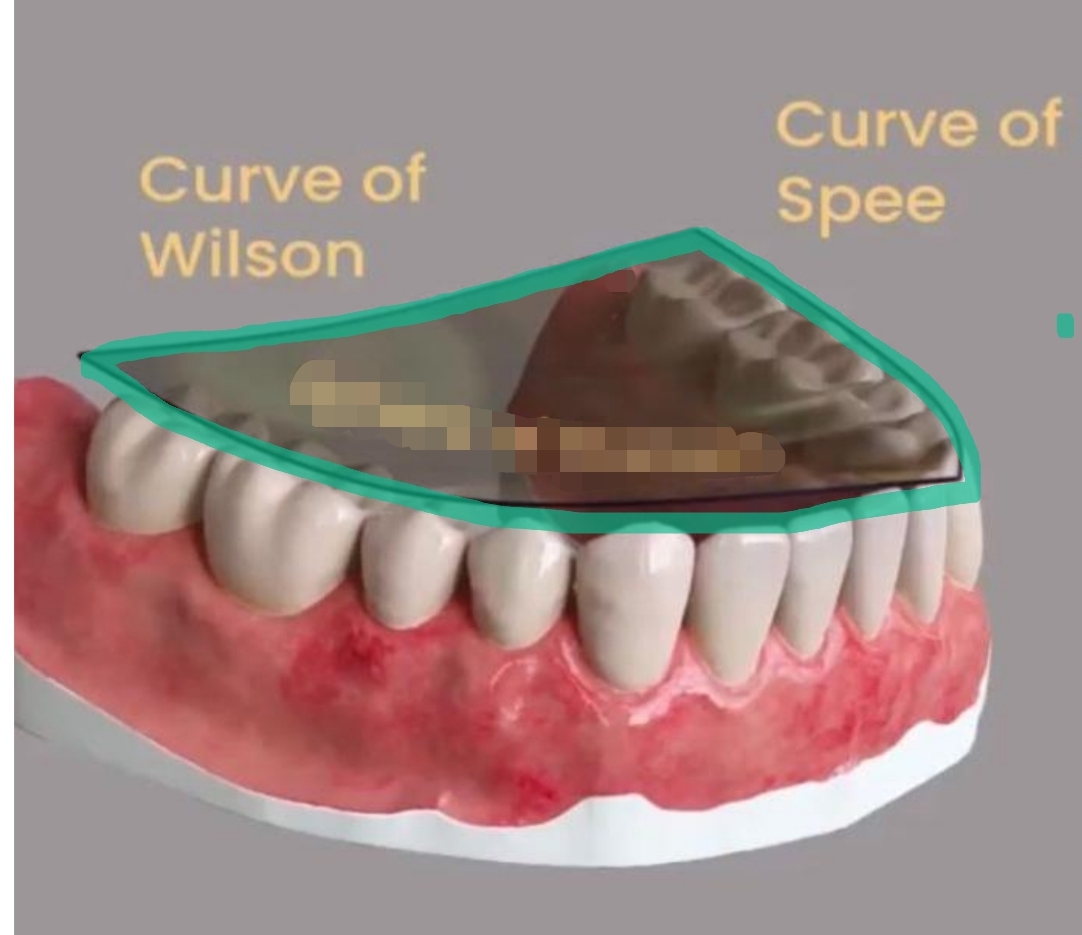
½ of a sphere
Combines Curve of Spee and Curve of Wilson
3-dimensional
Sphere of Monson