Second Law of thermodynamics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
how can something become more stable
lower energy/enthalpy
higher spreading energy/entropy
entropy
measures how energy spreads
related to various modes of motion in a molecule+randomness of a system
how does entropy relate to physical states
increased entropy increases w/ increasing freedom of motion of molecules
rules for determining entropy
phase - s<l«<g
amount of matter - more particles → more entropy
temperature - higher temp → higher entropy
volume of gasses only
structure of matter - as particle sizes increases, entropy increases
how does temp hellp determine entropy
particles can be arranged more diversely when temp is higher
how does structure of matter determine entropy
larger particles → more bonds → can store energy in more ways
entropy at 0K
0
molar entropy
entropy of one mol of something
units of molar entropy
J/K mol
standard entropy
S° measured under standard conditions
what type of rxn is entropy of a rxn
a state rxn
ΔS°
difference in randomness of reactions compraed to products
units of ΔS°
J/Kmolrxn
second law of thermodynamics
the total entropy (disorder) of an isolated system always increases over time
ΔSsystem+ΔSsurroundings>0
system+surroundings must go up
Changes in entropy of surroundings
When a process releases heat to the surroundings, the surroundings’ entropy increases (energy spreads out).
When a process absorbs heat from the surroundings, the surroundings’ entropy decreases (energy becomes less spread out).
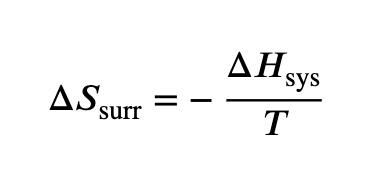
temp dependence of ΔSsurr
Higher temperature → smaller change in ∆Sₛᵤᵣᵣ
Lower temperature → bigger change in ∆Sₛᵤᵣᵣ
relative entropy by molar mass
relative entropy generally increases with molar mass