Bio 1105- test 2- Virginia Tech
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
thermodynamics
energy changes
Kinetic
energy of motion
potential
stored energy
Redox reactions
oxidation-atoms loses electrons
reduction-atoms gains electrons
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy
entropy- disorder
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Active site
pocket in an enzyme where substrates bind and a reaction occurs
factors that influence enzymes
temperature, pH, concentration
metabolism
the total of all chemical reactions in an organism, some of which are aerobic reactions that require oxygen.
feedback inhibition
the end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food ex-bacteria, algae, plants
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food. ex- humans
Respiration of glucose
glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain

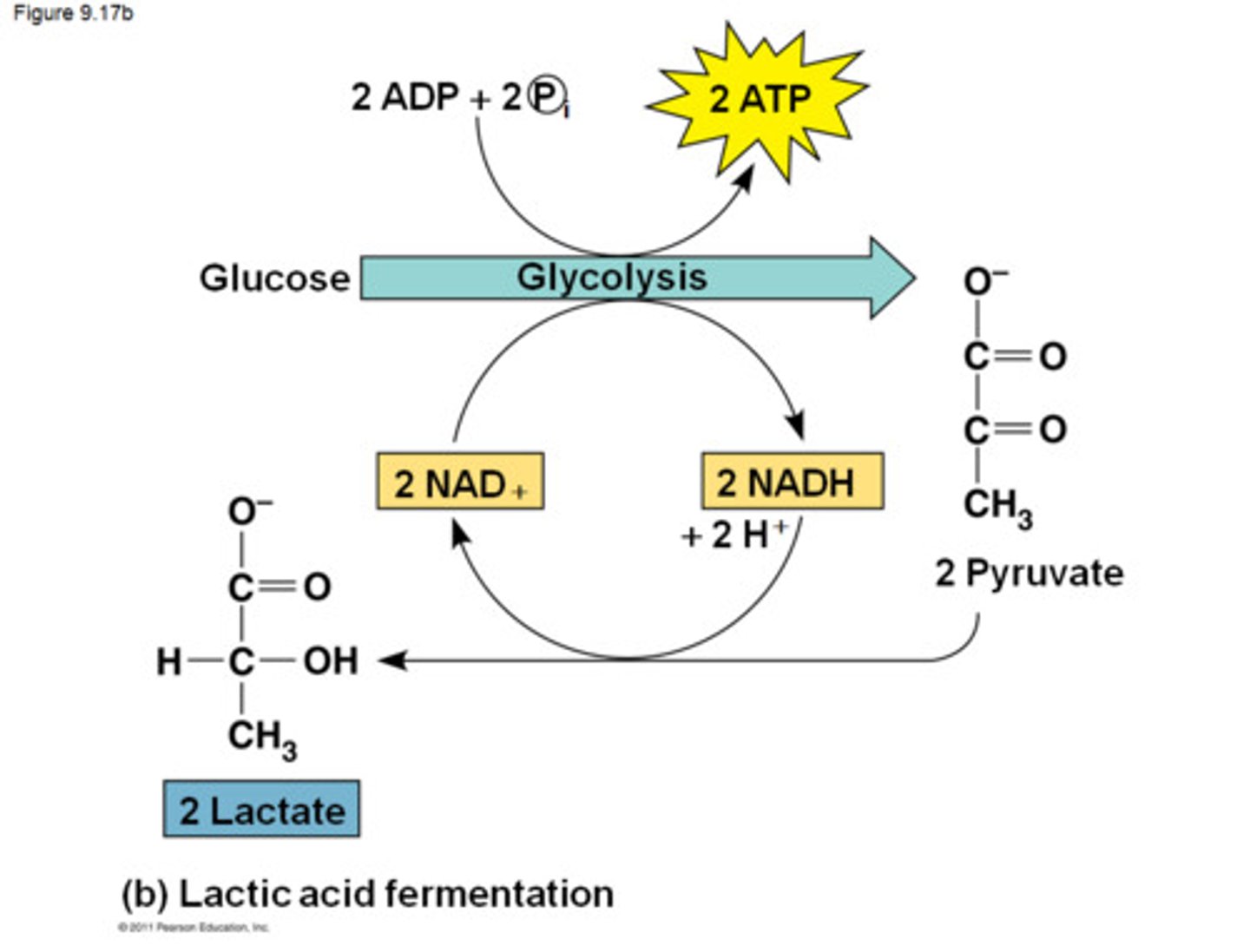
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
releases 4 ATP total
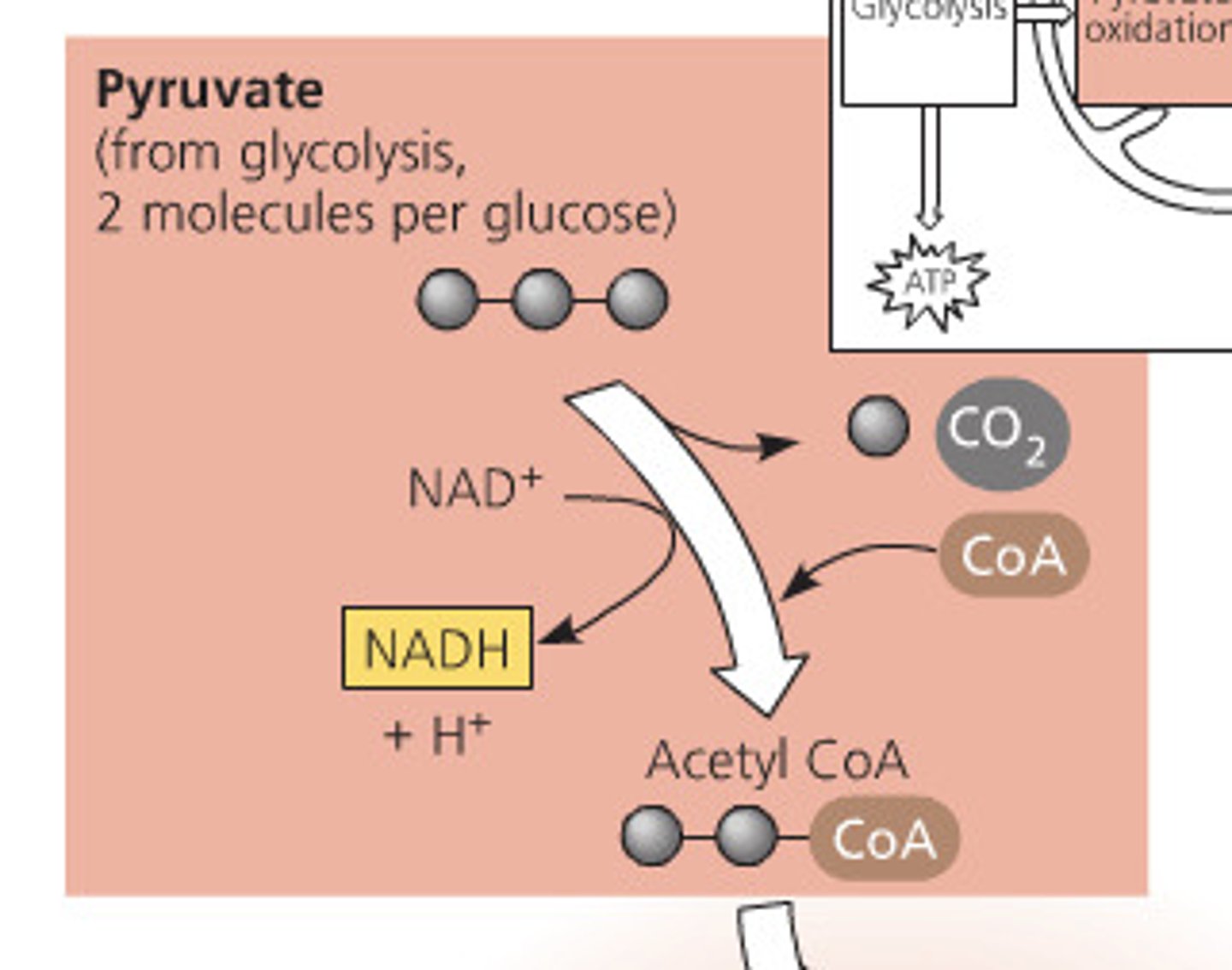
Pyruvate
Organic compound with a backbone of three carbon atoms. Two molecules form as end products of glycolysis
1 CO2, 1 NADH, 1 acetyle CoA, 1 ATP for each pyruvate2
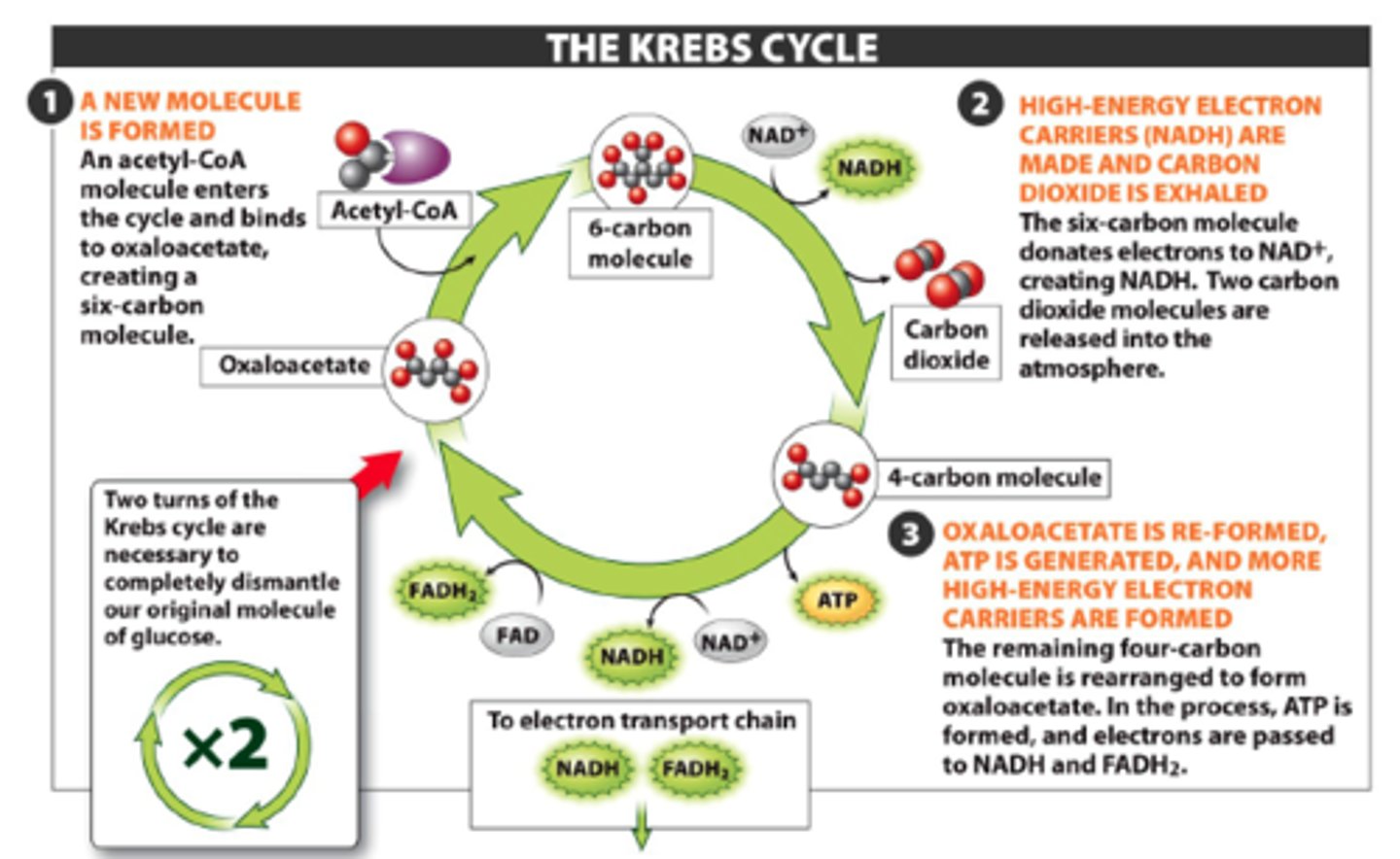
Krebs cycle
produces molecules that carry energy to the second part of cellular respiration for every Aceyle CoA entering(2) __releases-(2CO2, 3 NAD+ to 3 NADH, 1 FAD to FADH_2)
One Glucose molecule oxidizes to
6CO_2, 4ATP, 10 NADH, 2 FADH_2
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
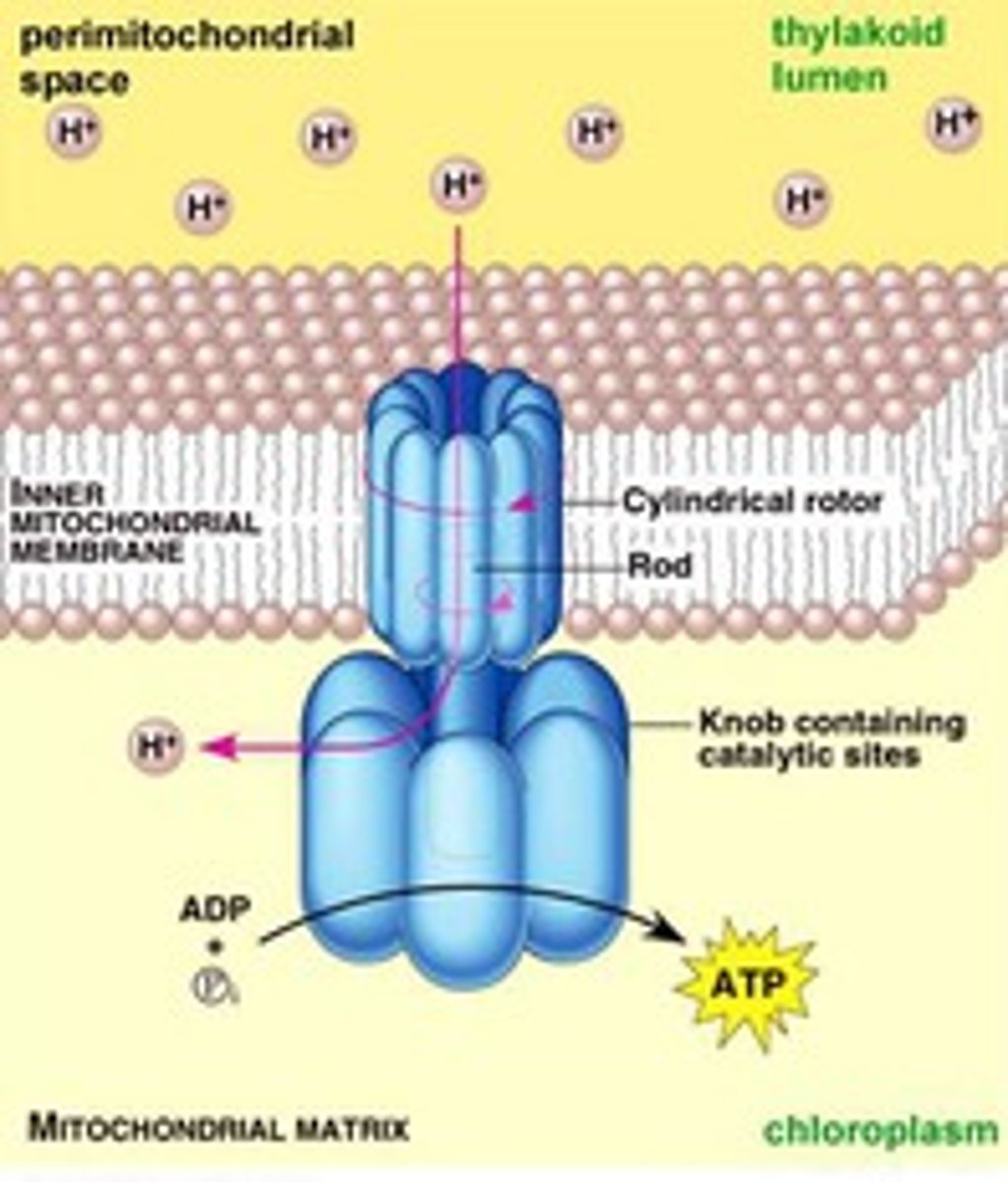
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
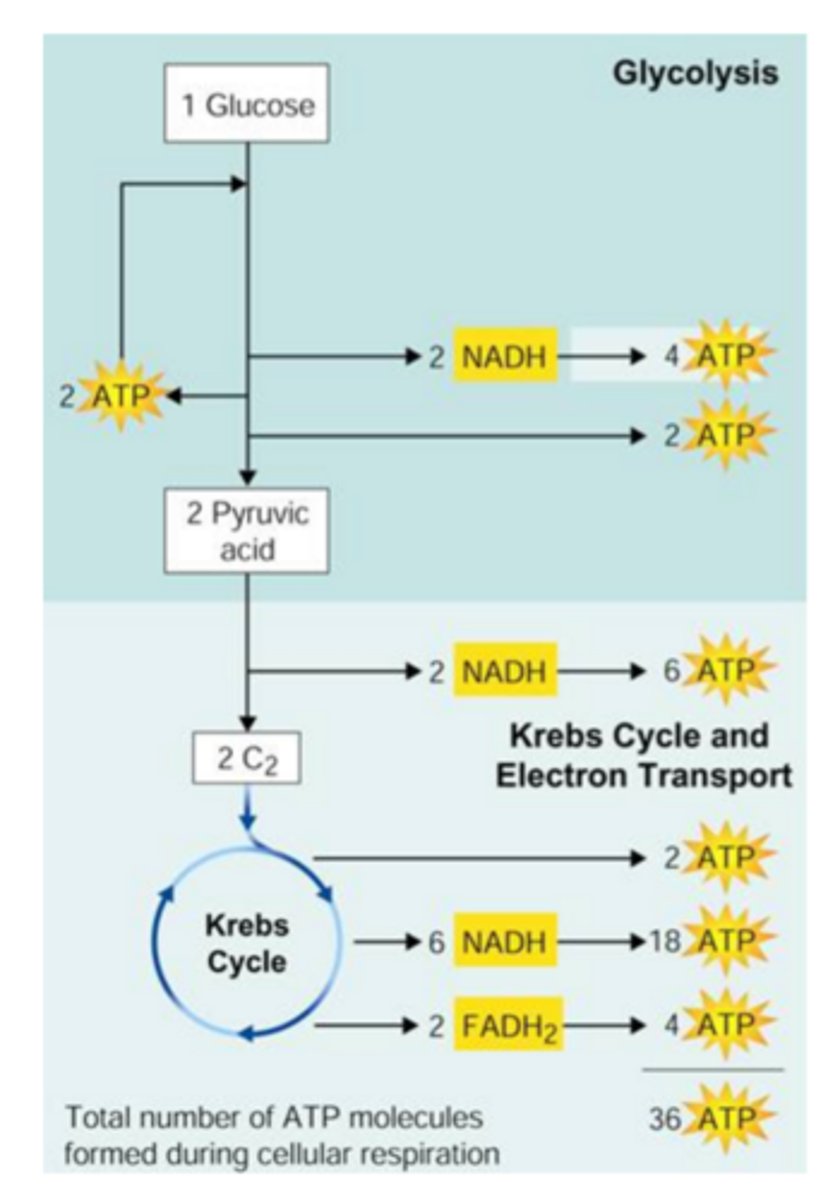
Energy yield of respiration
32 ATP per glucose for bacteria
30 ATP per glucose for eukaryotes
anerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
Fermentation
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
Catabolism of proteins
Amino acids undergo deamination to remove the amino group
Remainder of the amino acid is converted to a molecule that enters glycolysis or the Krebs cycle
Catabolism of fats
Fats are broken down to fatty acids and glycerol
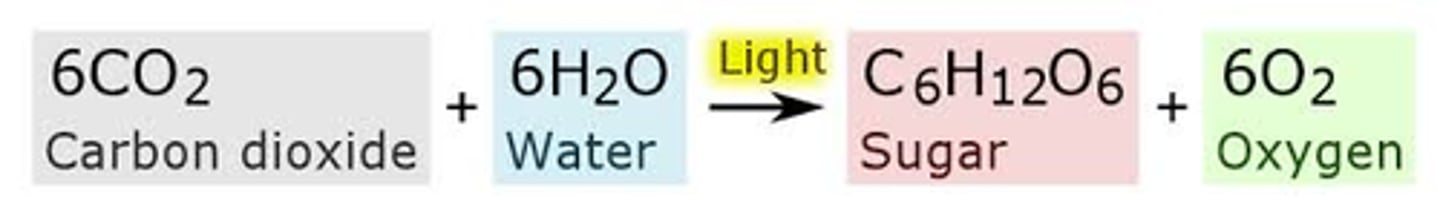
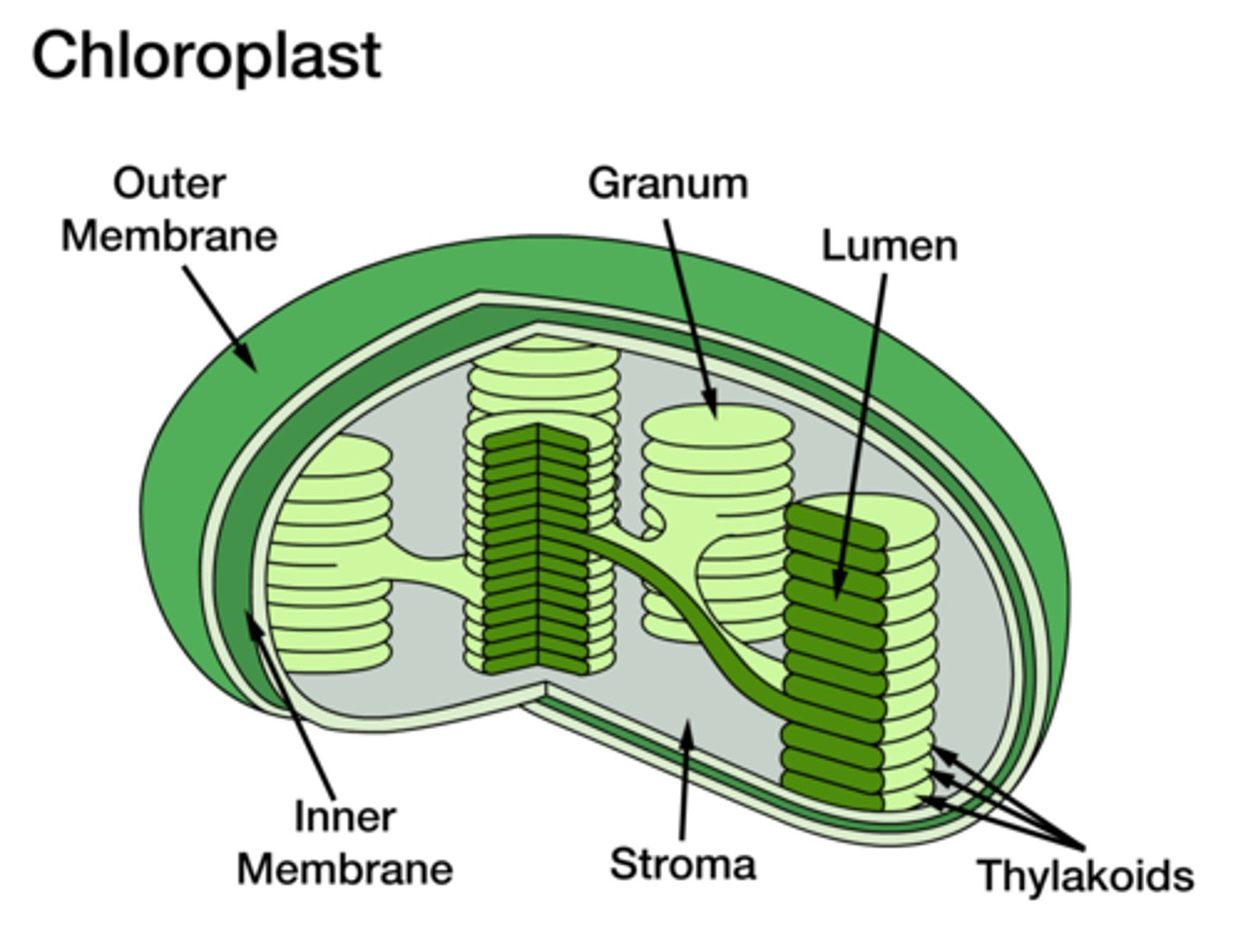
Photosynthesis
-Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
-opposite of respiration in terms of products and reactants
-occurs in chloroplast
light dependent
-requires light
-1/2 parts of photosynthesis
-makes ATP + NADP+ --> NADPH
-produces O_2
-in thylokoid membrane
light independent
-doesn't require light
-in stroma
-uses ATP+ NADPH to synthesis organic molecules from CO_2
The shorter the wavelength, the ________ the energy
higher
The longer the wavelength the _________ the energy.
lower
Photoelectric effect
light energy can remove electrons from some molecules
Chlorophylla
main photosynthetic pigment in plants, blue and red lights
-converts light energy to chemical energy
Photosystems
light-collecting units of the chloroplast
an antenna complex
gathers photons and feed the captured light and energy to the reaction center
Reaction center
The chlorophyll a molecule and the electron acceptor in a photosystem; they trigger the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll donates an electron, excited by light energy, to the primary electron acceptor, which passes an electron to an electron transport chain.
photosytems I and II
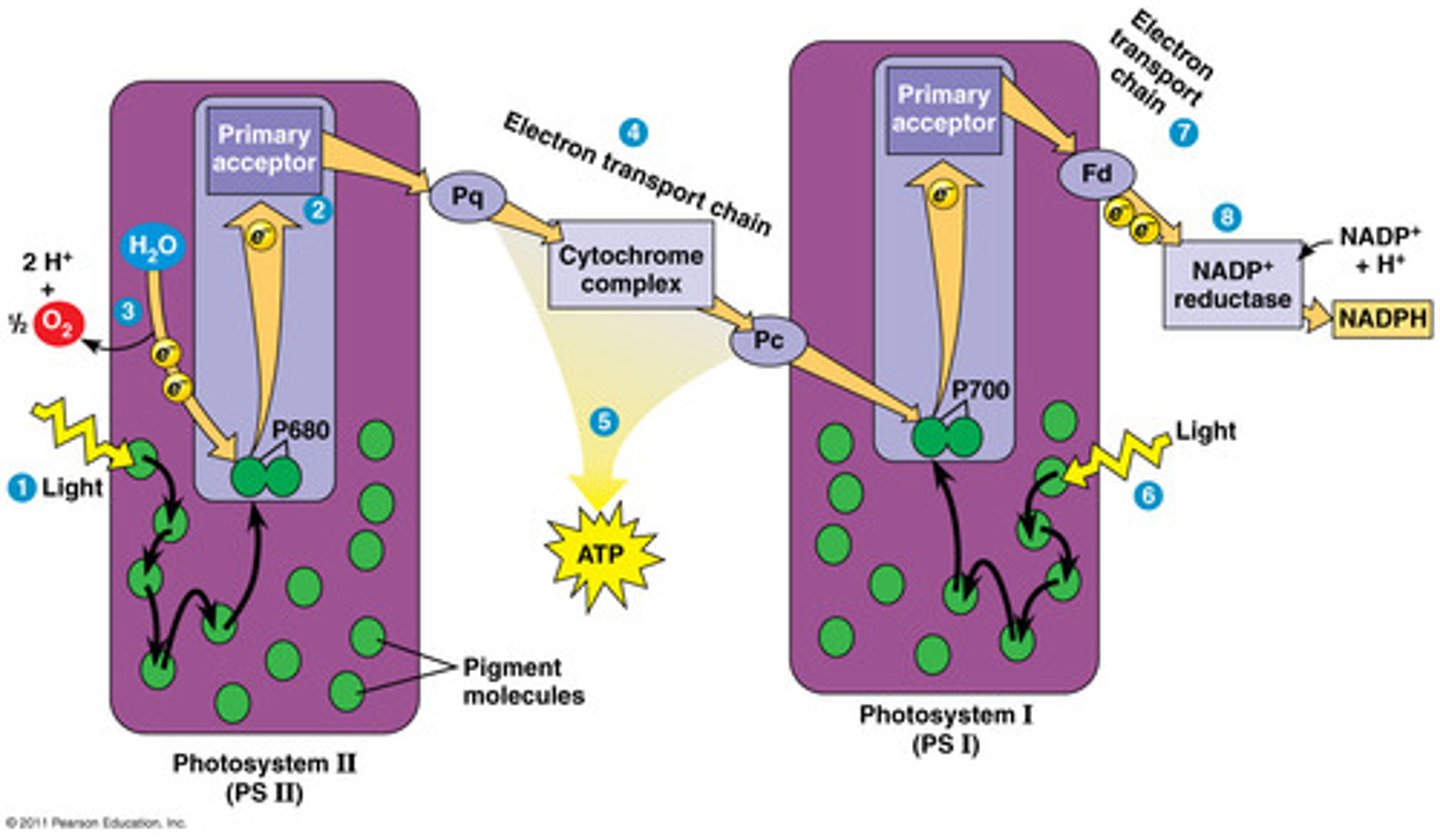
noncylic photophosphorylation
-generates NADPH + ATP
-building organic molecules requires more energy than that
cylic phosphorylation
-allows cells to produce additional ATP
Light Independent-The Calvin cycle
Stage of photosynthesis that forms glucose
Carbon Fixtation-Calvin Cycle
RuBP +CO_2 --> 2PGA
Reduction-Calvin Cycle
PGA is reduced to G3P
Regeneration
G3P regenerates to RuBP
- 3 turns have enough carbon to produce a new G3P
- 6 turns have enough carbon to have 1 glucose
Photorespiration
A metabolic pathway that consumes oxygen, releases carbon dioxide, generates no ATP, and decreases photosynthetic output; generally occurs on hot, dry, bright days, when stomata close and the oxygen concentration in the leaf exceeds that of carbon dioxide.
C4 pathway
a carbon-fixing process in which carbon dioxide is bound to a compound to form a four-carbon intermediate
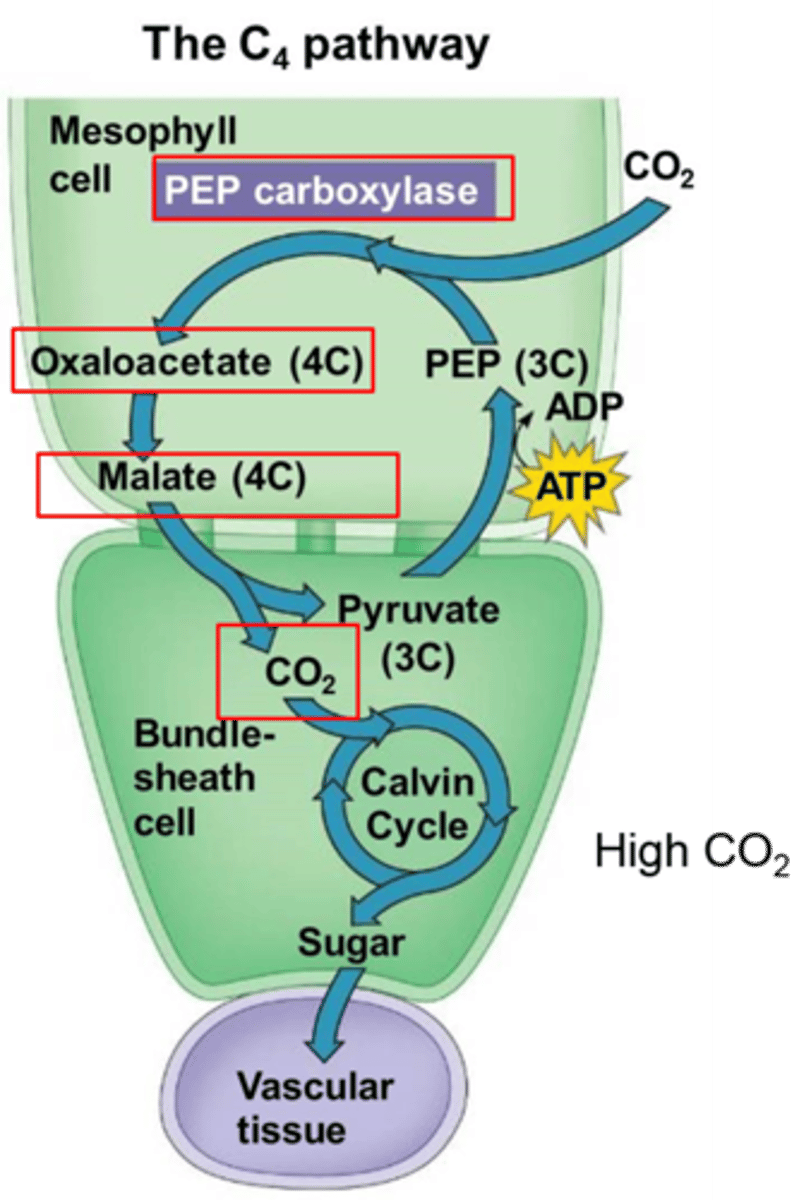
The CAM pathway
a water-conserving, carbon-fixing process; CAM plants take in carbon at night and fix it into various organic compounds and release it during the day
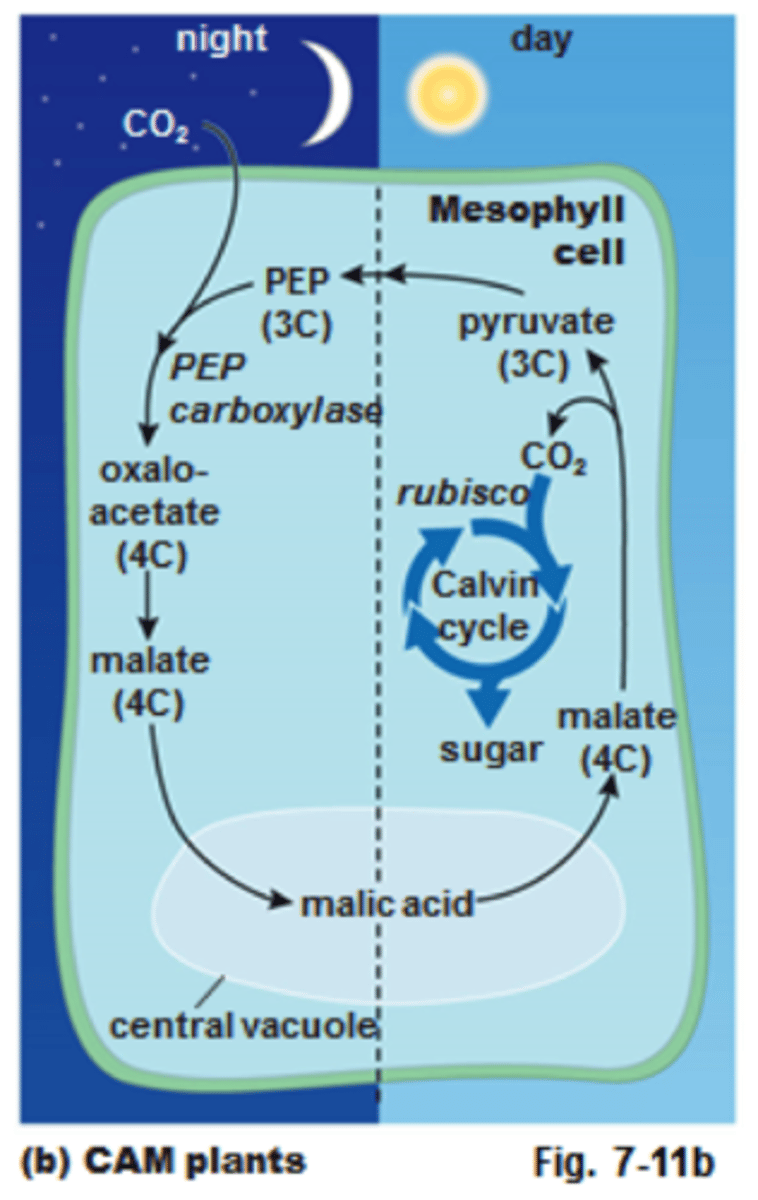
diagram of chloroplast
1st experiment for DNA question
1928
-Griffith
-discovered transformation(transfer of genetics between cells)
-he infected mice with diseases
2nd Expirement of DNA question
15 years later
- Avery, Maclead, McCarthy
-transofrmations includes DNA transfer between cells
3rd experiment of DNA
-The Hersey- Chase
- 8 years later
- DNA is the genetic makeup of a cell
- viruses that infected bacteria
Chargoff's Rule
-A=T
-G=C
- A+G=T+C
Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin
-X-ray diffraction studies to identify 3-D structures
-DNA is helical
-DNA diameter- 2nm, makes up every 3.4 n, turn
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.
G forms ___ hydrogen bonds with C
three
A forms __ hydrogen bonds with T
Two
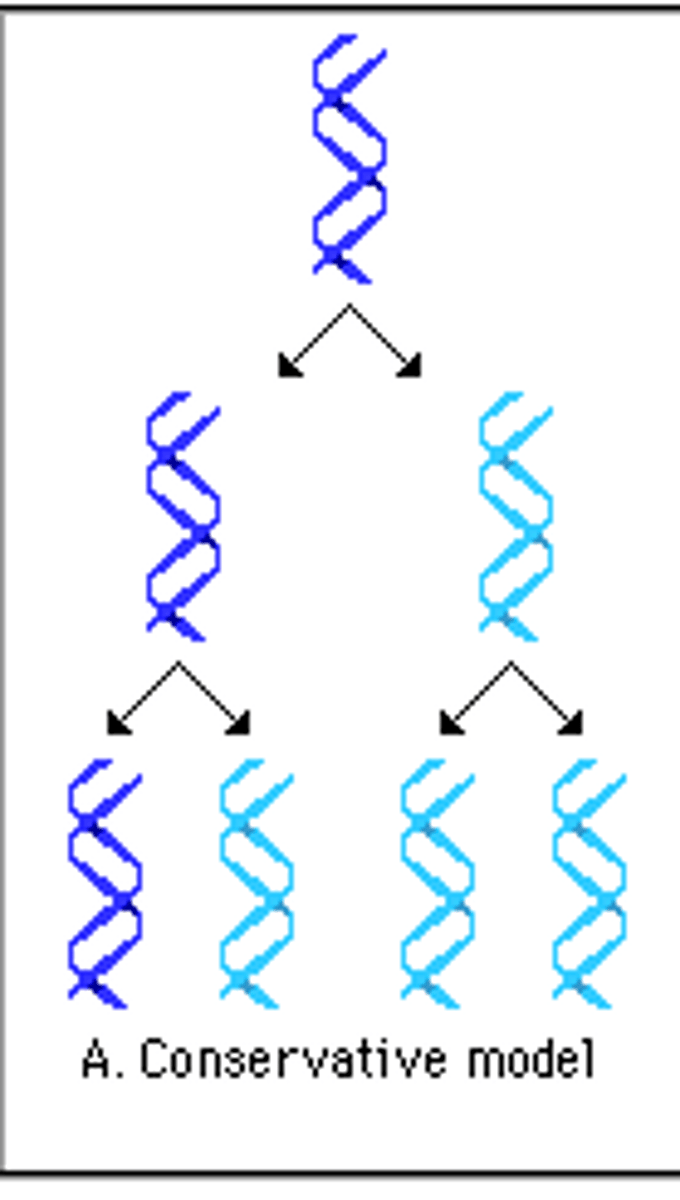
Conservative model
two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands thus restoring the parental double helix
semi-conservative replication
1 strand of parent molecules remains intact

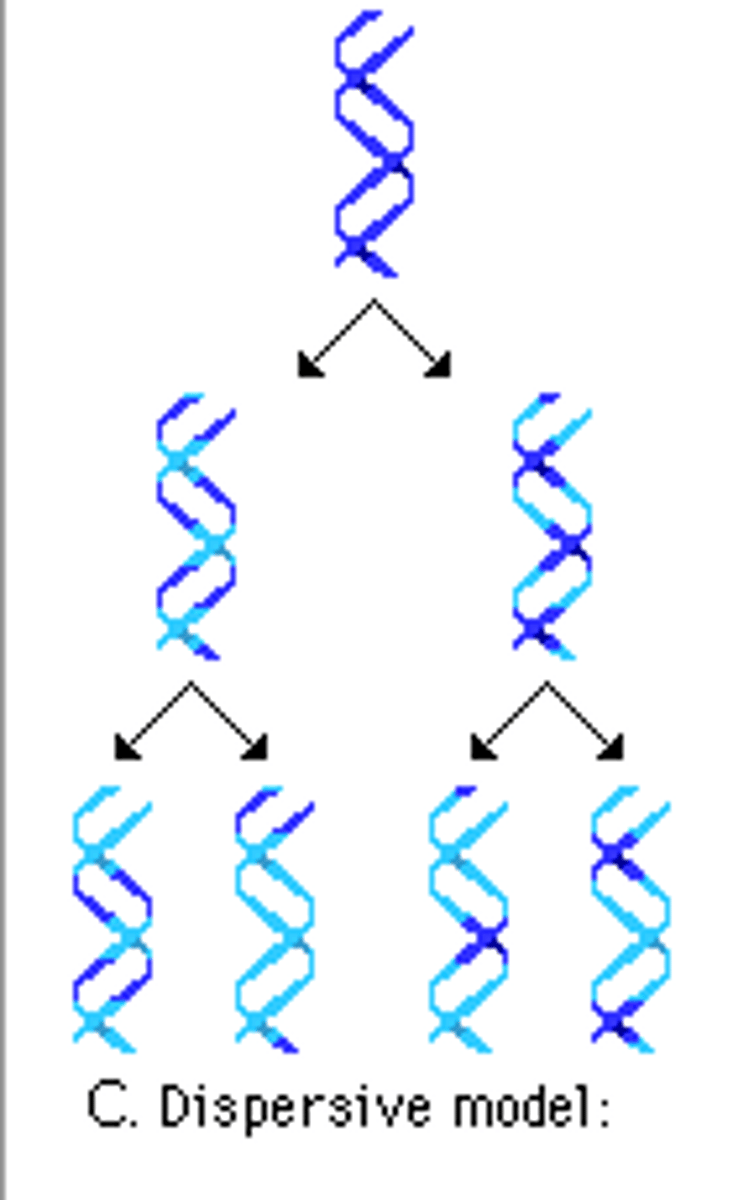
disperse- DNA
parts of parental molecules are dispersed throughout
The Meselson-Stahl experiment
Used isotope of nitrogen to change the weight of DNA N15 & N14, demonstrated that the semi-conservative model is the best description of replication.
Leading strand
DNA is synthesized continuously
lagging strand
DNA is synthesized discontinuously
ligase
seals the "nick" in DNA backbone
Okazaki fragments
Short fragments of DNA that are a result of the synthesis of the lagging strand during DNA replication.
sliding B clamp
holds DNA pol (I) to the DNA as it moves along the strand
clamp loader
loads B clamp onto SNA template strand
DNA gyrase
relieves torsional strain
DNA pol (I)
replaces RNA primer with DNA nucleotides
RNA primer
short RNA segment needed to start DNA replication
single stranded DNA binding proteins
coats strands to keep them apart
DNA pol (II)
synthesizes fragments of DNA
Primase
unwinds and synthesizes primer
Helicase
uses ATP to unwind DNA