QUIZ 3 1031
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
what type of bone is Phalanges
Long Bones
what type of bone is Metacarpals
Long Bones
what type of bone is Carpal Bones
Short Bones
what type of bone is Radius / Ulna
Long Bones
what are the centers of ossification? (2)
primary
secondary
Primary Ossification Center
location?
when does it occur?
Forms the shaft (Diaphysis) of long bones
Occurs before birth
Secondary Ossification Center
location?
when does it occur?
Found in the epiphyses (ends) of long bones
Occurs after birth
what are the layers of a bone? (5)
Compact / Cortical Bone
Periosteum
Cancellous Bone
Medullary Cavity
Endosteum
Periosteum
what is it?
what is it used for?
Tough fibrous connective tissue covering bone
bone growth, repair, & nutrition.
Compact / Cortical Bone
what is it?
what is it used for?
Dense outer layer of bone
provides strength.
Cancellous Bone
what is it?
what is it used for?
Spongy inner bone
contains trabeculae and red marrow.
Medullary Cavity
what is it?
what is it used for?
Hollow shaft of long bones
contains red marrow (children) or yellow marrow (adults).
Endosteum
what is it?
Membrane lining the medullary cavity.
what joint is Intercarpal Joints
Gliding
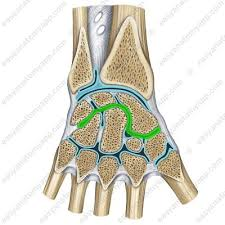
what joint is Interphalangeal Joints
Hinge
what joint is Metacarpophalangeal Joints (2–5)
Condyloid
what joint is Carpometacarpal Joints (2–5)
Gliding
what joint is 1st Carpometacarpal (Thumb)
Saddle
what joint is Distal Radioulnar Joint
pivot
what joint is Wrist Joint Proper (Radiocarpal)
condyloid
what does a gliding joint do?
Sliding / gliding movement.
what does a Hinge joint do?
Flexion & Extension only.
what does a Condyloid joint do?
Flexion/extension + abduction/adduction.
what does a Saddle joint do?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction.
what does a Pivot joint do?
one bone rotates around another
Avulsion Fracture
Fragment pulled away by tendon/ligament force.
Colles Fracture
Distal radius fracture with fragment displaced posteriorly; often from fall on outstretched hand.
Boxer’s Fracture
Transverse fracture of neck of 5th metacarpal (from punching).
Bennett Fracture
fracture at base of 1st metacarpal bone
Monteggia Fracture
Fracture of the proximal ulna with dislocation of the radial head.
Subluxation
Partial loss of continuity between joint surfaces (not a full dislocation).
Callus Bone
New bone that forms around fracture during healing.
Reduction
Restoring fragments to normal alignment (closed = manual; open = surgical).
Fixation
Holding fragments in place after reduction (internal, external, or intramedullary devices).
LECTURE 7
how many bones are in the hand?
27
in regards to the 2nd-5th digits, what are the 3 Phalanges (3)? (name them and picture where they go)
Distal, Middle, Proximal
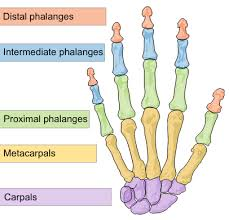
in regards to the 2nd-5th digits, what are their Joints(2)? (name them and picture where they go)
Distal Interphalangeal Joint, Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
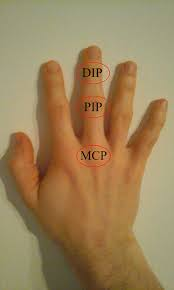
in regards to the 1st digits, what are their Phalanges (2)? (name them and picture where they go)
Distal, Proximal
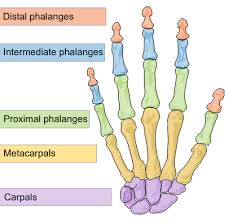
Largest Carpal Bone is what bone?
Capitate
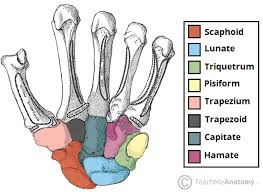
Smallest Carpal Bone is what bone?
Pisiform
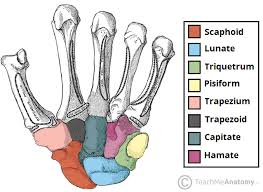
“Helps form the Saddle Joint” refers to what bone?
Trapezium
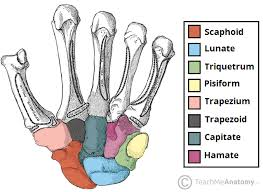
“Largest bone in Proximal Row” refers to what bone?
Scaphoid
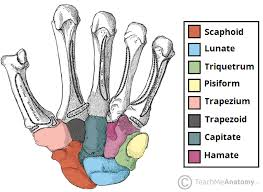
“Has hook-like process” refers to what bone?
Hamate
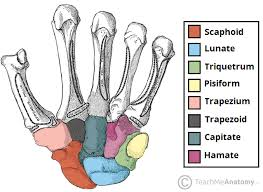
“Half-moon shaped” refers to what bone?
Lunate
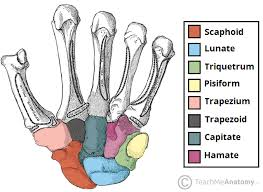
“Superimposed on Triquetrum” refers to what bone?
pisiform rests on top of it
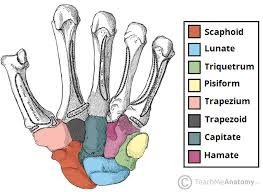
“Most commonly fractured” refers to what bone?
Scaphoid
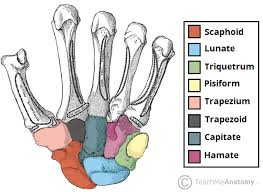
what is the proximal row?
what carpal bones are in the proximal row(4)?
hand bones closets to the forearm
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform
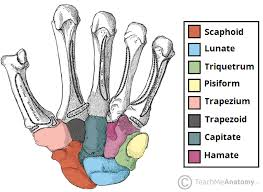
what is the distal row?
what carpal bones are in the distal row(4)?
closest to the metacarpals / palm
Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
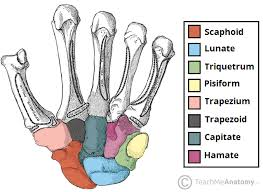
posterior surfaces of the carpal bones:
Carpal Bridge
Anterior surface (palmar) of carpal bones (3 names)
Carpal Tunnel, Carpal Sulcus, Carpal Canal
Nerve that passes through the anterior Carpal Region
Median Nerve
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
what is it?
what are the symptoms?
Compression of the Median Nerve
Causing pain/tingling from repetitive use.
1st Carpometacarpal joints: bones that form it (2), type of joint, movements allowed:
1st Metacarpal + Trapezium
saddle
Flex, Extend, Abd, Add, Circumduction
Interphalangeal Joint of 1st Digit: bones that form it (2), type of joint, movements allowed:
Prox + Distal phalanx (Thumb)
Hinge
flex/extend
Distal Interphalangeal Joints of 2-5 Digits: bones that form this joint(2), type of joint, movements allowed:
Between middle phalanx and distal phalanx
hinge
flex/extend
Proximal Interphalangeal Joints of 2-5 Digits: bones that form this joint(2), type of joint, movements allowed:
Between proximal phalanx and middle phalanx
Hinge
flex/extend
routine projections for the fingers 2-5
PA, 45° Oblique, Lateral
routine projections for the thumb
AP (preferred) or PA, 45° Oblique, Lateral
routine projections for the hand
PA, 45° Semi-Pronated Oblique, Lateral (Fingers Fanned)
Central Ray location for PA Finger
Metacarpophalangeal (MP) Joint of affected digit
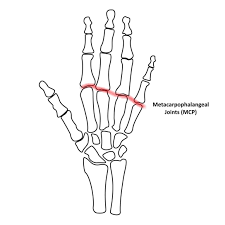
Central Ray location for Lateral Finger
Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) Joint
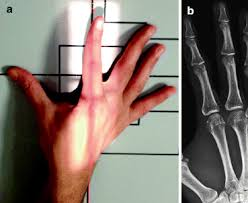
Central Ray location for AP Thumb
1st metacarpophalangeal (MP) Joint

Central Ray location for PA Hand
3rd metacarpophalangeal (MP) Joint
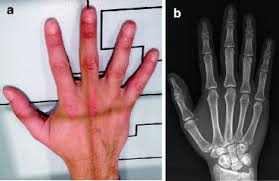
Position that best demonstrates an avulsion fracture of the finger
45° Oblique Finger
what bone of the finger is an avulsion fracture most common?
Distal Phalanx
Disadvantage of performing a PA projection of the Thumb instead of the AP
Increased OID = reduced detail.
What structures must be included on all thumb projections?
say the distance it needs to include from top bone to bottom
then if you want list all the bones from distal to proximal
nail to the wrist thus including
Distal phalanx, Interphalangeal (IP) joint, Proximal phalanx, First metacarpophalangeal (MP) joint, First metacarpal, First carpometacarpal joint, Trapezium
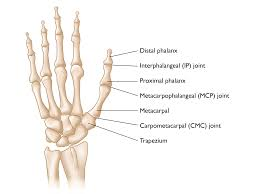
Describe the positioning for a Modified Robert’s Method of the Thumb to include:
o Type of Fracture best demonstrated
o Patient position
o CR angle, centered where, and in what direction
Bennett’s fracture
Arm internally rotated, thumb flat on IR
15° proximal (toward wrist) to 1st CMC joint

specifically regarding the oblique that is performed of the Hand / degree of obliquity / Purpose of using the step wedge sponge
Semi-Pronated
45°
keeps fingers parallel to IR + keeps joint spaces open.
Purpose of the Lateral Hand positioning (2)
Evaluate foreign bodies & metacarpal fracture displacement.
in regards to Bone Age Hand for Pediatric Patients:
what image image to take?
what is the image supposed to show?
PA Left Hand
lets you compare ossification centers to growth charts in pediatrics
LECTURE 8
Routine Projections of the Wrist (4)
Lateral
Posteroanterior (PA)
45° Semi-pronated Oblique
45° Semi-supinated Oblique
Why are the fingers flexed when performing the PA projection of the Wrist?
brings carpal bones closer to the image receptor =reduces OID = improves detail.
Alternative AP Wrist:
what structures will be best demonstrated?
why?
carpal interspaces
bc in the AP position they align more closely with the divergent x-ray beam, making the joint spaces more open.
Carpal best demonstrated on a 45 Semi-pronated Oblique
Trapezium
Structure best demonstrated on a 45 Semi-supinated Oblique
Pisiform
Structure best demonstrated on a Lateral
Lunate
positioning for “Stetcher Method”s for Scaphoid aka Navicular (say 2 different IR positioning and 1 hand positioning)
Place the image receptor on a 20° angle sponge, wrist in PA with ulnar deviation.
Wrist flat on IR in PA with ulnar deviation.
(notice only the IR positioning changes)
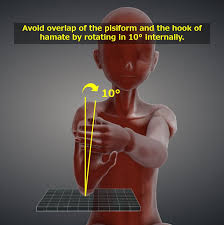
Gaynor Hart position of the Carpal Tunnel
positioning?
CR ? degree and where is it centered?
Forearm resting on table, Wrist hyperextended (fingers pulled back), Hand slightly rotated toward the radius to avoid superimposition
25–30° toward the palm (toward the elbow).
CR enters 1 inch distal to the base of the 3rd metacarpal.
What projection was performed to produce this image? What is the structure best demonstrated?
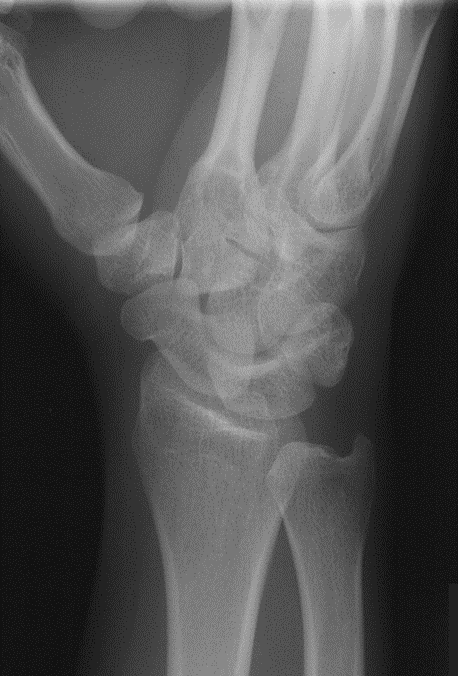
45° Semi-pronated Oblique
Radial side of carpal bones aka trapezium, scaphoid, lunar NOTCH
What projection was performed to produce this image? What is the structure best demonstrated?
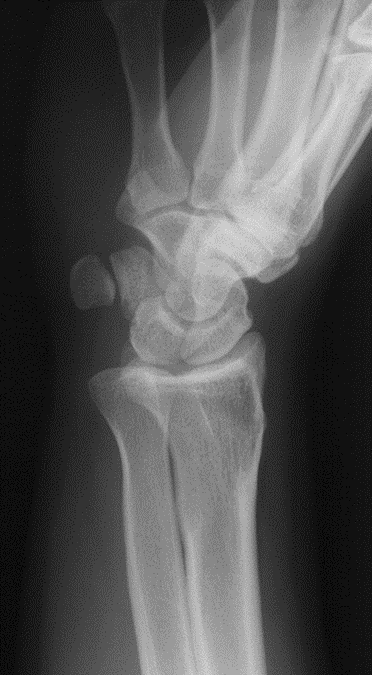
Lateral Wrist
Lunate
What projection was performed to produce this image? What is the structure best demonstrated?
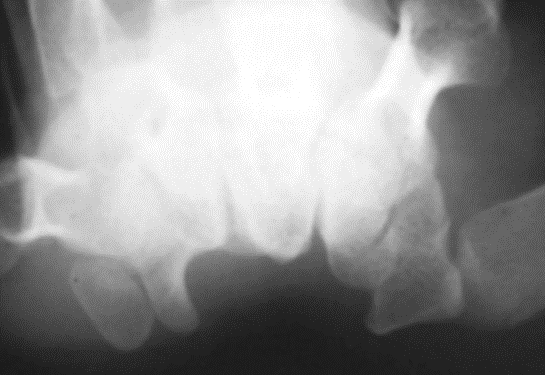
Gaynor-Hart (Tangential Carpal Tunnel)
carpal bridge
LECTURE 9
ulna is located in what part of the body and where?
forearm
medially
radius is located in what part of the body and where?
forearm
laterally
What are the pointed processes on the distal radius and ulna called?
styloid process
Distal Radioulnar Joint:
what bones form it?
what type of joint is it?
what movements r allowed?
Ulnar Head + Ulnar Notch of Radius
Pivot
Supination / Pronation
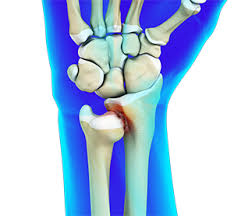
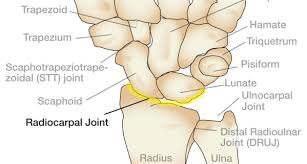
Wrist Joint Proper
what bones form it?
what type of joint is it?
what movements r allowed?
Distal Radius + Scaphoid + Lunate
Condyloid
Flex, Extend, Abduct, Adduct
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
what bones form it?
what type of joint is it?
what movements r allowed?
Radial Head + Radial Notch of Ulna
Pivot
Supination / Pronation
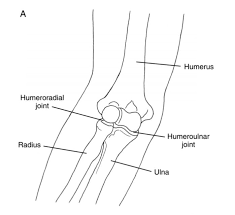
Humeroulnar Joint
what bones form it?
what type of joint is it?
what movements r allowed?
Trochlea of the humerus+ Semilunar (Trochlear) Notch of Ulna
Hinge
Flex / Extend
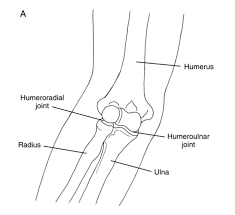
Humeroradial Joint
what bones form it?
what type of joint is it?
what movements r allowed?
Capitellum + Radial Head
Hinge
Flex / Extend
Where are the heads of the bones of the forearm located? (2)
radius is proximal (like elbow)
ulna is distal (like wrist)
When the hand is pronated, which bone of the forearm crosses over medially?
radius crosses over the ulna
What structure on the Radius is the attachment site for the Biceps Tendon?
Radial Tuberosity
The Head of the Radius articulates with what structure in:
o Extension
o Flexion
Capitellum
Radial Fossa
What structures form the Semilunar Notch of the Proximal Ulna? (2)
Olecranon Process
Coronoid Process
The Coronoid Process of the Ulna articulates with what structure in:
o Extension
o Flexion
Trochlea of Humerus
Coronoid Fossa of Humerus