EXAM 4 COMBINED- KHAN
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What are the names of the natural androgens?
testosterone
DHT
DHEA
Androstenedione
Which anatomical structures are responsible for androgen secretions in MEN?
testis, adrenal cortex
Which anatomical structures are responsible for androgen secretions in WOMEN?
corpus luteum, adrenal cortex
Why is DHT more potent than testosterone?
DHT has a -H group AT POSITION 5
How is testosterone secretion regulated?
LH is the main stimulus for T secretion
What are the androgenic properties of testosterone?
growth- penis, scrotum, prostate, seminal vesicles, larynx, vocal cord
increase body hair, sebum secretion
lean body mass alterations
What are the receptor properties of androgen receptors?
nuclear receptors
ligand+ receptor act as transcription factor and modulate gene expression
What are the 2 subtypes of 5-alpha reductase? What tissues are each subtype expressed in?
Type 1- non-genital skin, bone liver
Type 2- urogenital tissues/skin
How is testosterone converted into estradiol?
using aromatase enzyme
What anabolic property in men is mediated partly by estradiol?
skeletal growth
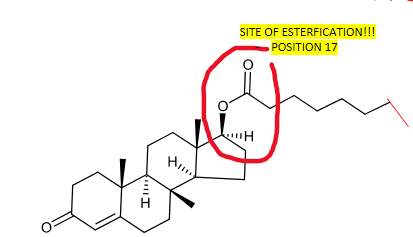
How is testosterone ester produced? What is the site of esterfication?
How it is produced? Esterifying a fatty acid to make it 17b-hydroxyl group of testosterone
SITE OF ESTERFICATION—> POSITION 17
How is testosterone released from its esters?
hydrolysis of the ester in vivo
Why are testosterone esters not used as much as other formulations?
painful
variable conc
What is a problem with testosterone patches?
skin reactions
What is the main problem with testosterone gels and topical solutions (1%)?
transfer to children through contact
Where is testosterone gel and topical solution (1%) applied
gel- upper arms, shoulder
topical- armpits
What are two formulations of testosterone made to reduce accidental contact of testosterone to normal individuals?
nasal gel
topical gel for front/inner thigh
What is the BBW for testosterone undecanoate?
POME (pulmonary oil microembolism)
What are the ADRs of androgens (testosterone)?
decreased T and sperm production
bc of negative feedback inhibition
increased appetite
gynecomastia
prostate growth, increase PSA
acne
edema
hepatotoxicity
What is BPH?
noncancerous enlargement of the prostate
What is the selectivity of each 5a- reductase inhibitor?
Finasteride - selective
Dutasteride- nonselective
Names of 5a-reductase inhibitors:
Finasteride (Proscar)
Dutasteride (Avodart)
What is the MOA and the effect on prostate gland of 5a- reductase inhibitors?
MOA: inhibit 5a-reductase (conversion of Testosterone to DHT)
Effect: decrease prostatic volume, increase urine flow
What is an ADR of 5a-reductase inhibitors?
low libido
What are the names (brand/generic) of the selective and non-selective a1-antagonists?
Selective- Tamsulosin (Flomax)
Nonselective- Terazosin (Hytrin), Doxazosin (Cardura)
Which alpha 1 receptor is located in the prostate?
alpha 1a receptor
What are ADRs of non-specific a1-antagonists?
dizzy, hypotension, fatigue
What are the names, MOA, and ADRs of PDE-5 Inhibitors?
Names: Sildenafil(Viagra), Tadalafil(Cialis), Vardenafil(Levitra)
MOA: inhibit PDE-5, increase cGMP, relaxation in penis
ADRs: HA, flushing, blurred vision
Why do PDE-5 Inhibitors interact with nitrates?
PDE-5’s: Inhibit breakdown of cGMP, increase cGMP
Nitrates: Increase GC, which increases conversion to cGMP
Both: increase cGMP= severe vasodilation
What are some major concerns with PDE-5 Inhibitor use?
vision loss
hearing loss
hypotension
priapism
Which PDE-5 Inhibitor can also be used for BPH?
Tadalafil (Cialis)
What are the effects when GnRH agonists are administered in pulsatile/intermittent fashion?
proper release of gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
What are the names of the GnRH agonists?
Nafarelin
Leuprolide
Goserelin
What is the cellular signaling of GnRH?
GnRH receptors are GCPRs
Gq—> PLC—> IP3—> DAG and Ca++
What are the effects when GnRH agonists are administered continuously? What initial effect do you expect in sex hormones levels?
Effect: inhibit the release of gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
Initial effect: increase in sex hormones
Do you see an increase in sex hormone levels with GnRH antagonists?
no! only in GnRH agonists
What are the MOA and effect of GnRH antagonists?
MOA: GnRH receptor antagonists
Effect: inhibit LH surge
What are the names of the GnRH antagonists?
Cetrorelix
Ganirelix
Elagolix
ALL END IN -LIX
What are the composition of gonadotropin preparations? (aka the names of each and whether they have LH, FSH, or both)
human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG)- FSH+ LH
Urofollitropin (uFSH)- FSH
Recombinant follitropin alpha - FSH
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)- LH
tip: the ones with “follitropin” only have FSH
What are the LH and FSH functions in male and females?
Male
LH- acts on leydig cells to stimulate testosterone production
FSH- stimulate spermatogenesis
Female
LH- follicular growth, induce ovulation, stimulate corpus luteum
FSH- follicular development
What are the ADRs of hCG and FSH?
hCG
injection site rxns, HA, depression, edema, gynecomastia
FSH
injection site rxns, multiple births, HA, pain
OVARIAN ENLARGEMENT
HYPERSTIMULATION syndrome
Why are dopamine agonists used in infertility tx?
basically if you have hyperprolactinemia that can cause infertility, so were treating the underlying condition in this case (high levels of prolactin decreases GnRH pulses, LH, and FSH)
What are the MOA, names, and ADRs comparison of dopamine agonists?
names: bromocriptine, cabergoline
MOA: D2 receptor agonist
ADRs: n/v, HA, postural hypotension
REMEBER CAB> BRO because greater efficacy, less ADRs
Why is metformin used to treat infertility?
increases insulin sensitivity by increasing AMPK
in PCOS there is insulin resistance, by treating that, we increase fertility
What is the MOA of danazol?
suppress pituitary-ovarian axis
What is the MOA of tranexamic acid?
inhibits fibrinolysis (binds to plasminogen and plasmin= can’t form fibrin)
What are some other agents used in infertility, menstral-related disorders, and endometriosis?
clomiphene- estrogen antagonist
aromatase inhibitors (Anastrozole, Letrozole)- induce ovulation
What are the effects of estrogen in COC?
LH, FSH suppressed (E+P)
impair transit or sperm, egg, and fertilized ovum (E+P)
suppress FSH, decrease follicular development
What are the effects of progesterone in COC?
LH, FSH suppressed (E+P)
impair transit or sperm, egg, and fertilized ovum (E+P)
inhibit LH surge
decrease frequency of GnRH pulses
What are the effects of progestin in progestin-only contraceptives?
same effects as in progesterone in COC +
increase cervical mucus
endometrial alterations—> impair implantation
What are the advantages of progestin-only contraceptives?
no clotting risk
no period/menstruation
can use when estrogen is CONTRAINDICATED
like in migraine with aura, breast feeding, HTN
What are the advantages and disadvantages of COC?
advantages
decrease endometrial and ovarian cancer risk
minimal breast cancer risk
disadvantages
DVT (estrogen)
What agents increase the metabolism of OC?
antiepileptics (seizure medications)
carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
What is the problem with antibiotics and OC?
antibiotics inhibit enterohepatic recycling of OC’s
What are the 2 classes of progesterone?
17a-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives
19-norandrostane derivatives
What are the androgenic side effects of norethindrone and norgestrel?
hirsutism
acne
oily skin
What are the advantages of using norgestimate?
less androgenic properties
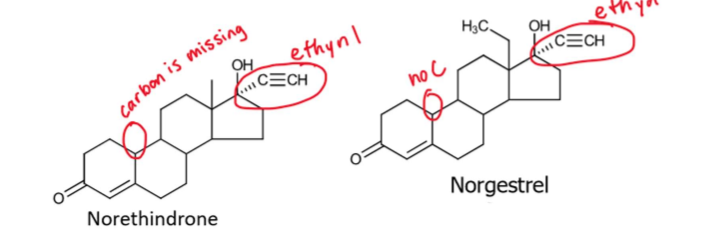
How do you identify whether a compound is a 19-norandrostane derivative?
will not have -CH3 at position 19
will have ethynyl group
What are the advantages of drosperinone?
no androgenic effects
What are the side effects of drospirinone?
hyperkalemia
higher risk of blood clot
What is the adverse effect of MPA?
DECREASE BONE DENSITY
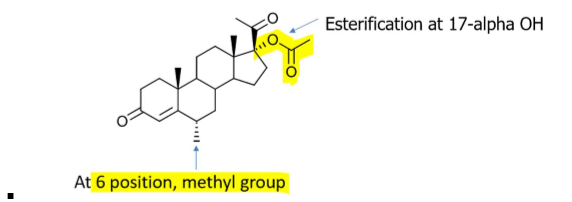
How do you identify the functional group and site of esterification in MPA?
has methyl (CH3) group on POSITION 6
ESTERFICATION IS AT 17a-hydroxy position
Answer the following about extended cycle formulations:
how often do you have a period?
______ days of E+P, then ____ days of placebo/low EE pills
Brand name example
period every 3 months
84 days of E+P, then 7 days of placebo/low EE pills
Brand name: Seasonique
Answer the following about the transdermal patch (Xulane):
contains what 2 hormones?
higher what than pills?
C/I?
Duration/ how often it is applied?
contains norlgestromin and EE
higher AUC than pills
C/I:
women >35 years old who smoke
women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m²
apply once weekly for 3 weeks, 1 week off
Answer the following about long-acting reversible contraceptives:
Name the 3 long-acting reversible contraceptives (brand/generic)
Name what type of implant/device it is
Which is non-hormonal?
WHAT IS THE DURATION?
3 devices- IUD (Mirena), Copper IUD (Paraguard), Subdermal Implant (Nexplanon)
Copper is NON-HORMONAL
Duration:
IUD- 5 or 8 years
Copper- 10
Subdermal implant- 3 years
What are the effects of emergency contraceptive Plan B? When does Plan B need to be taken to provide protection from pregnancy?
Plan B is just levonorgestrel so it…
blocks LH surge, prevents ovulation, thickens cervical mucus
taken within 72 hours (3 days)
What are the effects of emergency contraceptive ELLA? When does ELLA need to be taken to provide protection from pregnancy?
aka Ulipristal acetate
effect: selective progesterone receptor modulator (NOT ANTAGONIST)
inhibits ovulation
MUST BE TAKEN WITHIN 5 DAYS (of unprotected sex)
What is Mifepristone’s MOA?
progesterone receptor antagonist
induces abortion
What is Misoprostol’s MOA?
causes uterine contractions/ potent oxytoxic
“prostaglandin analog”