Serology Methods
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
prozone vs postzone
xs antibody // xs antigen
agglutination principle
lattice formation = Ag binds w Fab sites of 2 Ab forming bridges
agglutination direct vs passive
direct ie blood bank, Ag is naturally there
passive = treating cells or latex agglutination (unnatural)
if competitive assay, what makes a pos?
pos if result is less than the cutoff
if non-competitive assay, what makes a pos?
pos if result is more than cutoff value
agglutination inhibition
indicator = latex bead w target Ag
pos: no agglutination
neg: agglutination
complement fixation (CF)
indicator = srbc coated w hemolysin
pos: no hemolysis
neg: hemolysis
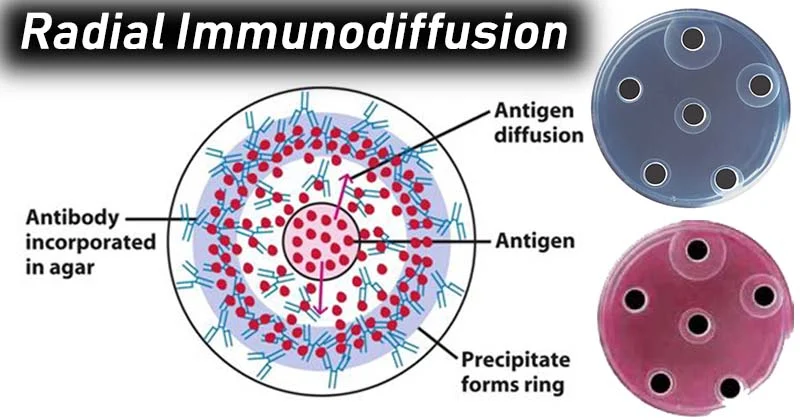
radial immunodiffusion (aka single immunodiffusion) (RID) steps
a. unlimited Ab incorporated into agar
b. serum + standards are in circular wells precut in agar
c. incubate
d. diffusion occurs & rings of ppt forms
e. meas diameter of ring
RID methods
Fahey (kinetic)
read before ring reaches max size (6-12 hr)
logarithmic relationship b/t d of ppt ring & Ag conc → read from plotted stnd curve
Mancini (end-point)
read at max size 24-48h
linear relationship b/t area of ppt ring (d²) and Ag conc→ ““
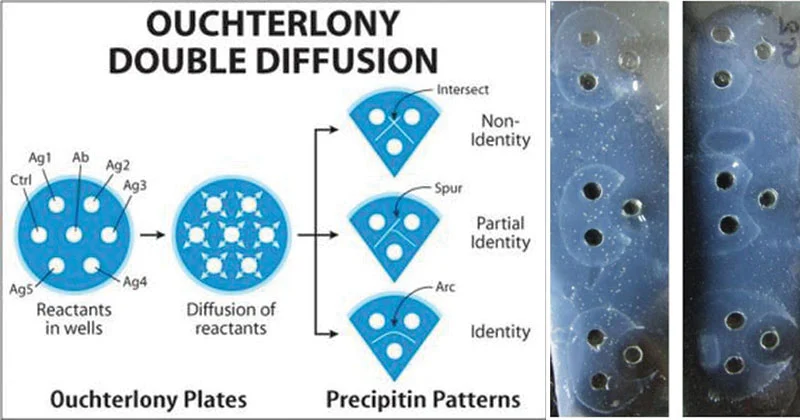
double diffusion (aka Ouchterlony)
used to determine relationship b/t Ag & Ab
AB added to wells in center of agar
pt sera & stnds are alternated in wells around center
incubate
diffusion → band of ppt
pt wells are read in relation to stnd in adjacent wells
location of bands dep on conc & rate of diffusion
immunoelectrophoresis
m/c used to determine heavy & light chains involved
serum IEP: monoclonal (sharp peak) gammopathies or polyclonal (inc but wider peak)
urine IEP: Bence Jones protein
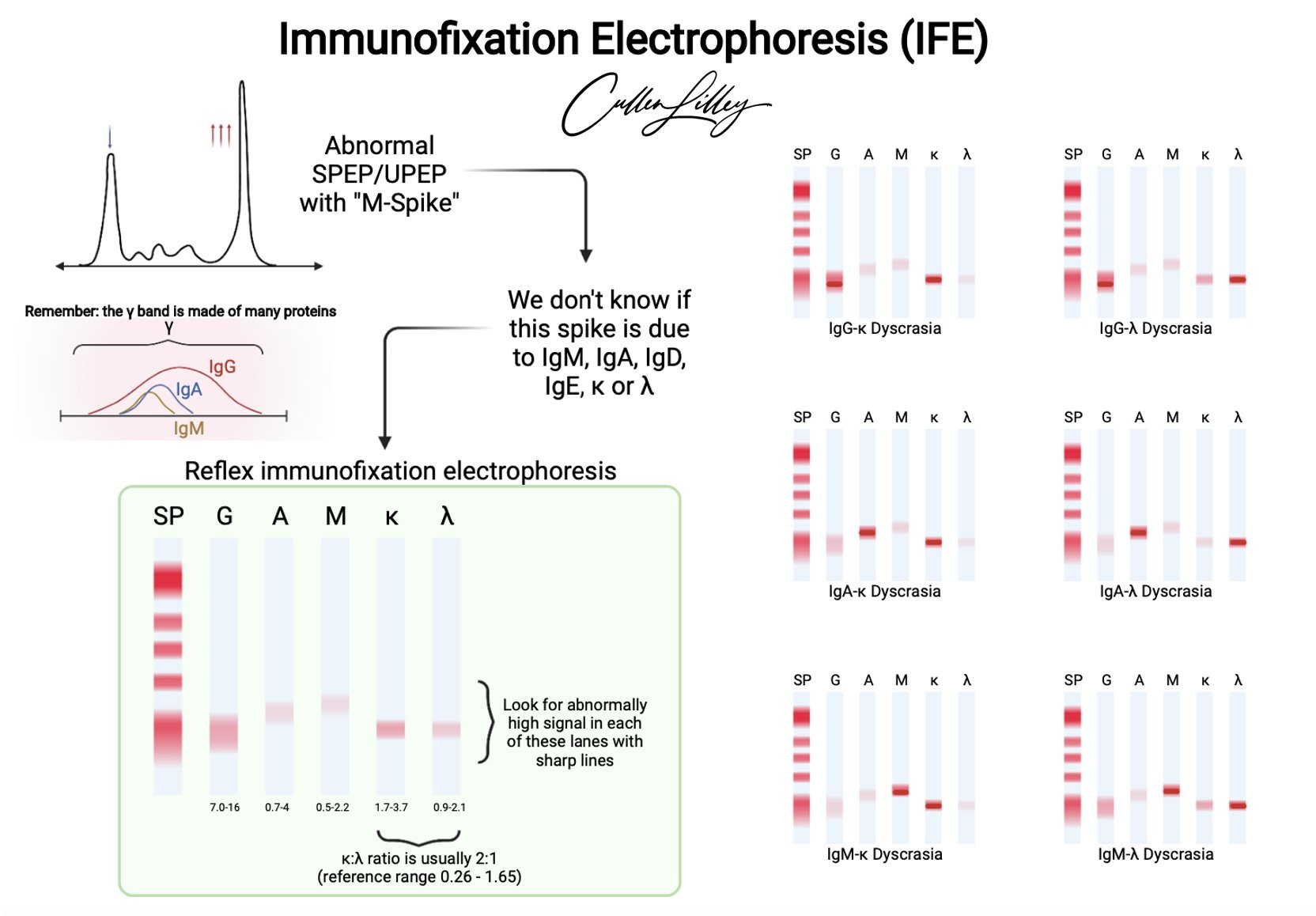
immunofixation
PEL + immunoppt
a. apply spcm to 6 positions on agar
b. electrophorese to sep proteins
c. apply monospecific antisera to 5 lanes
d. if Ag present, Ag-Ab complexes form & ppt; wash, stain
v sensitive, used to classify monoclonal gammopathies
rocket IEL (Laurel)
similar to RID but EL is used to speed formation of ppt
cone-shaped area of ppt forms, meas height & compare to stnd curve
countercurrent IEL
a. 2 rows of wells in gel
b. add Ag in one row & Ab in other
c. elec current
d. migrate towards each other
e. ppt forms if specific
radioimmunoassay (RIA)
detects Ag or Ab
ie RIST (total IgE) or RAST (IgE to specific allergens)
EIA/ELISA
sandwich technique
a. mono or polyclonal Ab adsorbed on solid surface (bead or well)
b. add pt serum; if Ag is present, binds to Ab-bead
c. add xs enzyme-labeled Ab (Ab conjugate) > forms Ag-Ab-label Ab sandwich
d. add enzyme substrate, incubated & read absorbance
e. **wash req b/t each step
f. absorbance = direct proportional to Ag conc
enzyme multiplied immunoassay (EMIT)
used to measure conc of small molecules ie drugs & hormones
add pt serum to enzyme-drug conjugate; also add anti-drug Ab
add enzyme substrate & incubate
pos: color produced
neg: no color
nephelometry
a. serum substance reacts w specific antisera & forms insoluble complexes
b. light is passed through suspension
c. scattered (reflected) light is proportional to number of insoluble complexes; comp to stnd
immunofluorescence
direct: add fluorescein-labeled Ab to pt tissue, wash & examine under fluor microscope
indirect (IIF) - add pt serum to tissue w known Ag, wash, add fluorescein label antiglobulin, wash, examine under fluor microscope
ie testing for antinuclear Ab (ANA) or fluorescent treponemal Ab test (FTA-Abs)
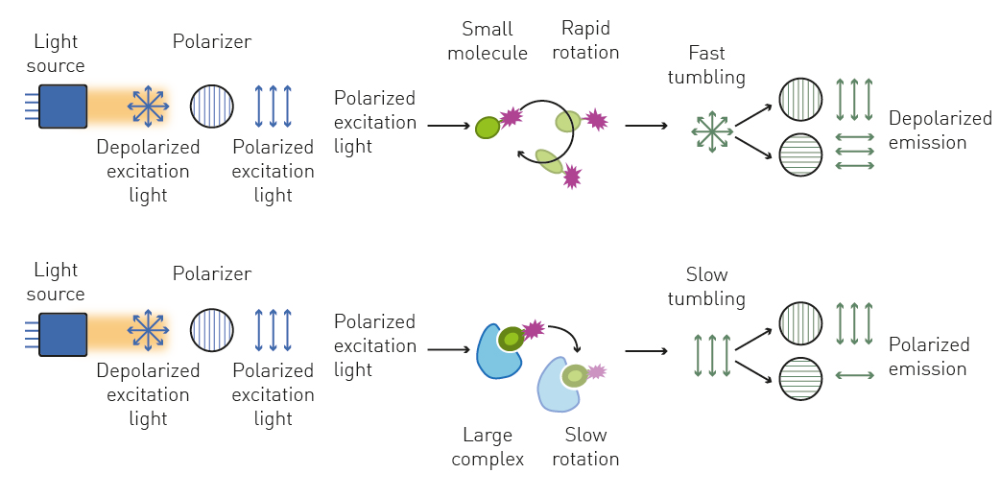
fluoresence polarization immunoassay (FPIA)
add rgt Ab & fluor-tagged Ag to pt serum
pos: unbound tagged Ag rotate quickly → reduce amount of polarized light
neg: tagged Ag bind to rgt Ab → tagged Ag rotates slowly → inc polarized light
serial dilutions
testing for inf dz on acute & convalescent (recovering) spcms coll abt 2 weeks apart
must see 4-fold or 2 tube rise in titer to be clin sig
sensitivity vs specificity
detect v small amounts, gives pos result if pt has dz (no false neg)
detect substance w/o x-reacting; gives neg result if pt doesn’t have dz (no false pos)
test sensitivites
most sensi = immunoassays
RIA, EIA, FIA, nephelometry
less sensi = lattice
CIE, CF, agglutination, flocculation (pptn), rocket elp, RID, ouchterlony, IFE< IEP
titers for current infn
2 weeks apart titers, need at least 4 fold inc (or 2 tubes)
ie 320 → 1280
if not may be past infn
if given 1:20 titer, what should you do next
rpt titer in 10 days - 2 weeks
1:10 neg (why neg?)
1:20 +
1:40 +
1:80 +
1:160 +
1:320 neg
what is the titer to report?
160 bc last tube w agglutination
1:10 is showing prozone (xs ab)