AP Human Geo Unit 6 Vocab
1/89
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
City
a relatively large, densely populated settlement w/a much larger population than rural towns & villages; cities serve as important commercial, governmental & cultural hubs for their surrounding regions
Urban
relating to a city
Agricultural surplus
crop yields that are sufficient to feed more ppl than the farmer & their family
Socioeconomic stratification
the structuring of society into socioeconomic classes including leadership (gov’t/ruling class) that exercise control over goods & ppl
1st urban revolution
the agriculture & socioeconomic innovations that led to the rise of the earliest cities
Urban hearth areas
regions in which the world’s 1st cities evolved
Site
an absolute location on Earth
Situation
the relative location of a place in reference to it’s surrounding features/its regional position w/reference to other places
Capitalism
an economic & political system in which a country’s trade & industry are controlled by private owners for profit rather than owned & run by the state
Communism
an economic & political system in which all property is publicly owned & managed
Streetcar suburb
a settlement outside of a city w/ streetcar lines; the streetcars take residents into & out of the city easily
Second urban revolution
the industrial innovations in mining & manufacturing that led to increased urban growth
Redevelopment
a set of activities intended to revitalize an area that has fallen on hard times
Metropolis
a very large and densely populated city, particularly the capital or major city of a country or region
Urban area
any self-governing place in the US that contains at least 2500 people
Urbanized area
in the US, an urban area w/ 50,000 ppl or more
Urban cluster
in the US, an urban area w/ fewer than 50,000 inhabitants
Metropolitan statistical area
in the US, a region w/ at least one urbanized area as its core
Micropolitan statistical area
in the US, a region w/ one or more urban clusters of at least 10,000 ppl as its cores
Suburb
a populated area on the outskirts of a city
Urbanization rate
the percentage of a nation’s population living in towns and cities
Suburbanization
the movement of people from urban core areas to the surrounding outskirts of a city
Sprawl
the tendency of cities to grow outward in an unchecked manner
Automobile cities
cities whose size and shape are dictated by and almost require individual automobile ownership
Decentralize
in an urban context, to move business operations from core city areas into outlying areas such as suburbs
Edge city
a concentration of business, shopping, and entertainment that developed in the suburbs, outside of a city’s traditional downtown or central business district
Boomburb/boomburg
a place w/ more than 100,000 residents that is not a core city in a metropolitan area, a large suburb w/ its own government
Infill development
the building of new retail, business, or residential spaces on vacant or underused parcels in already-developed areas
Exurb
a semirural district located beyond the suburbs that is often inhabited by well-to-do families
World city
a city that is a control center for the global economy, in which major decisions are made about the world’s commercial networks & financial markets (also called a global city)
Gated community
privately governed & highly secured residential area w/in the bounds of a city; often has a fence/gate surrounding it
Urban system
a set of interdependent cities/ urban places connected by networks
Urban hierarchy
a ranking of cities w/ the largest & most powerful at the top of that hierarchy
Rank-size rule
the population of a settlement is inversely proportional to its rank in the urban hierarchy
Primate city
a city that is much larger than any other city in the country & that dominates the country's economic, political & cultural life
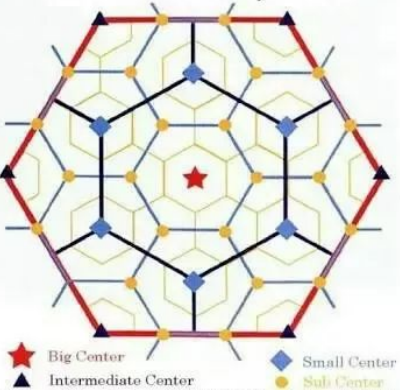
Central place theory
a model developed by Walter Christaller, that attempts to understand why cities are located where they are
Central place
a settlement that makes certain types of products & services available to consumers
Threshold
in central place theory, the number of ppl required to support businesses
Range
in central place theory, the distance people will travel to acquire a good
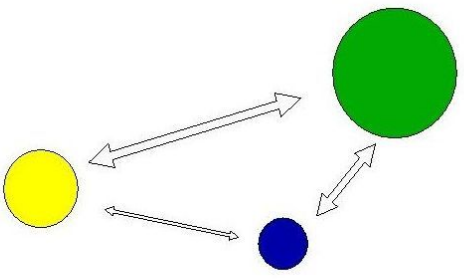
Gravity model
the idea that the closer two places are, the more they will influence each other (influenced by size & distance)
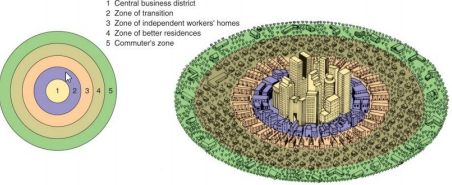
Concentric zone model
a model of a city’s internal organization developed by E.W. Burgess organized in five concentric rings that model the arrangement of different residential zones radiating outward from a central business district
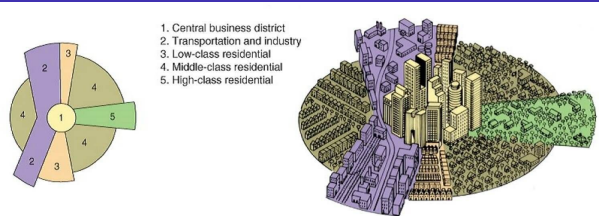
Hoyt model / sector model
a model of a city’s internal organization, developed by Homer Hoyt, that focuses on transportation and communication as the drivers of the city’s layout
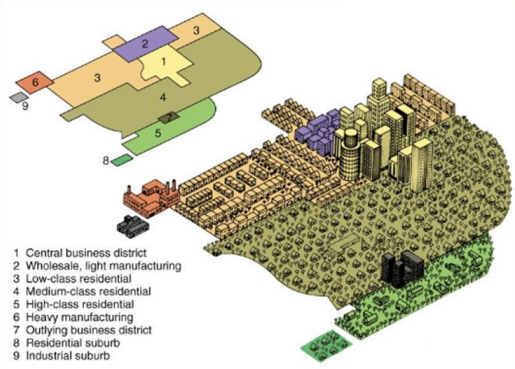
Multiple nuclei model
a model of a city’s internal organization, developed by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, showing residential districts organized around several nodes (nuclei) rather than one central business district
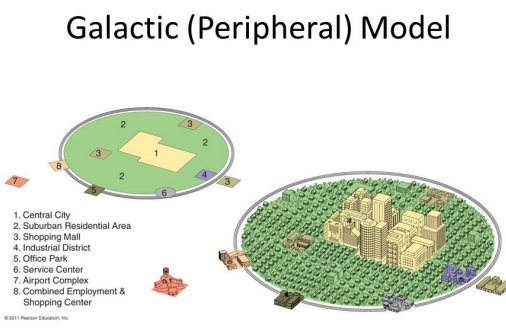
Galactic city model/ peripheral model
a model of a city’s internal organization in which the central business district remains central, but multiple shopping areas, office parks, and industrial districts are scattered throughout the surrounding suburbs and linked by metropolitan expressway systems
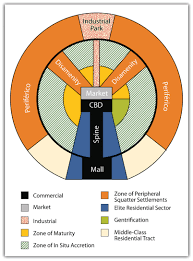
Griffin-Ford model
a model of the internal structure of the Latin American city developed by Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford
Gentrification
the displacement of lower-income residents by higher-income residents as an area or neighborhood improves
Perceived density
the general impression of the estimated number of people present in a given area
Zoning regulations
laws that dictate how land can be used
Fiscal squeeze
occurs when city revenues cannot keep up w/ increasing demands for city services and expenditures on decaying urban infrastructure
Built environment
the human-made space in which people live, work and engage in leisure activities on a daily basis
Smart growth
policies that combat regional sprawl by addressing issues of population density and transportation
Compact design
development that grows up (in the form of taller buildings) rather than out (in the form of urban sprawl)
Diverse housing options
policy that encourages building quality housing for people and families of all life stages and income levels in a range of prices within a neighborhood
New urbanism
an approach to city planning that focuses on fostering European-style cities of dense settlements, attractive architecture, and housing of different types and prices within walking distance to shopping, restaurants, jobs, and public transportation
Greenbelt
a zone of grassy, forested, or agricultural land separating urban areas
Zoning
the classification of land according to restrictions on its use and development
Slow-growth city
a city that changes its zoning laws to decrease the rate at which the city spreads horizontally, with the goal of avoiding the negative effects of sprawl
Anti-displacement tenant activists
advocates for poor and working-class residents who are at risk of losing their affordable housing to new development
De facto segregation
racial segregation that is not supported by law but is still apparent
Mortgage
a loan that is taken out to purchase a home
Redlining
the practice of identifying high-risk neighborhoods on a city map and refusing to lend money to people who want to buy property in those neighborhoods
Blockbusting
a practice in which realtors persuade white homeowners in a neighborhood to sell their homes by convincing them that the neighborhood is declining due to black families moving in
White flight
the mass movement of white people form the city to the suburbs
Affordability
the maximum price that a buyer can afford to pay for a house or apartment
Housing choice voucher program
a federal government program to assist very low income families, the elderly, and the disabled with affordable, decent, safe, and sanitary housing
Violent crime
a catgory of crime that includes murder, rape, robbery, and aggravated assault
Social controls
formal or informal institutions that help to maintain law and order in a place
Environmental injustice
occurs when certain groups carry a larger share of environmental risks and hazards than groups who have the power to influence decisions about the environment
Environmental racism
occurs when areas inhabited by low-income people of color are targeted for environmental contamination
Environmental justice
the movement to fix environmental discrimination
Squatter settlement
an area of degraded, seemingly temporary, inadequate, and often illegal housing
Land tenure
the right to own or hold property; it defines the ways in which rights to that property are managed
Inclusionary zoning (IZ)
municipal and county planning ordinances that require a given share of new construction to be affordable for people with low to moderate incomes
Exclusionary zoning
zoning that attempts to keep low-to-moderate-income people out of a neighborhood
NIMBYs
Abbreviation for “not in my backyard”; term for people who try to prevent the construction of affordable housing and other types of development in their neighborhood
Below market rate housing
housing that costs much less than the going rate
Urban renewal
large-scale redevelopment of the built environment in downtown and older inner-city neighborhoods
Fiscal imbalance
occurs when a government must spend more than it receives in taxes
Fiscal zoning
the practice of using local land-use regulation to preserve and possibly enhance the local property tax base
Ecological footprint
the total amount of natural resources used and their impact on the natural environment
Urban heat island
a mass of warm air in cities, generated by urban building materials and human activities, that sites over a city
Urban footprint
the spatial extent of an urban area’s impacts on the natural environment
Urban risk divide
the idea that disasters and disaster risk become urban phenomena as the world’s population becomes increasingly concentrated in large cities
Brownfields
properties whose use or development may be complicated by the potential presence of hazardous substances or pollutants
Brownfield remediation
the process of removing or sealing off contaminants so that a site may be used again without any health concerns
Phytoremediation
the removal of contaminants with plant species that react with or degrade contaminants or draw up contaminants from the soil into shoots and leaves
Farmland Protection Policy Act (FPPA)
US law that grants municipalities oversight over federally funded development projects on farmland
Scattered developments
subdivisions or developments that do not border on existing settlements and that remove agricultural land from production
Southeast Asia Model/McGee Model
an urban land use model describing the layout of cities in Southeast Asia, highlighting the lack of a traditional CBD and the presence of various zones catering to different functions, often influenced by colonial history.
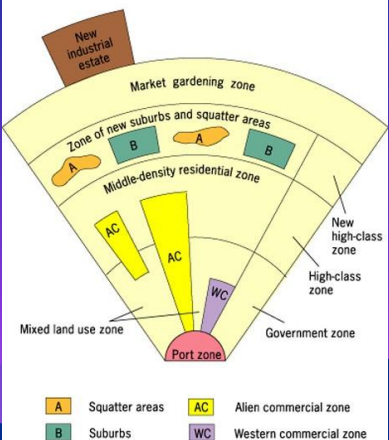
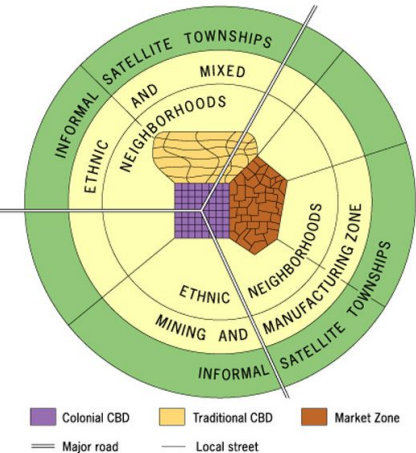
Sub Saharan African Model
an urban land use model that illustrates the structure of cities in Sub-Saharan Africa, characterized by a central city with various areas of development influenced by traditional, colonial, and post-colonial patterns.