3. Capillaries
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
capillaries
Main function: allow transport/exchange of materials with blood
Microscopic blood vessels that connect arterioles to venules
have the greatest surface area of any vessel type
approximately 2 acres of surface area within the body and about 1 RBC in diameter
facilitates efficient functions
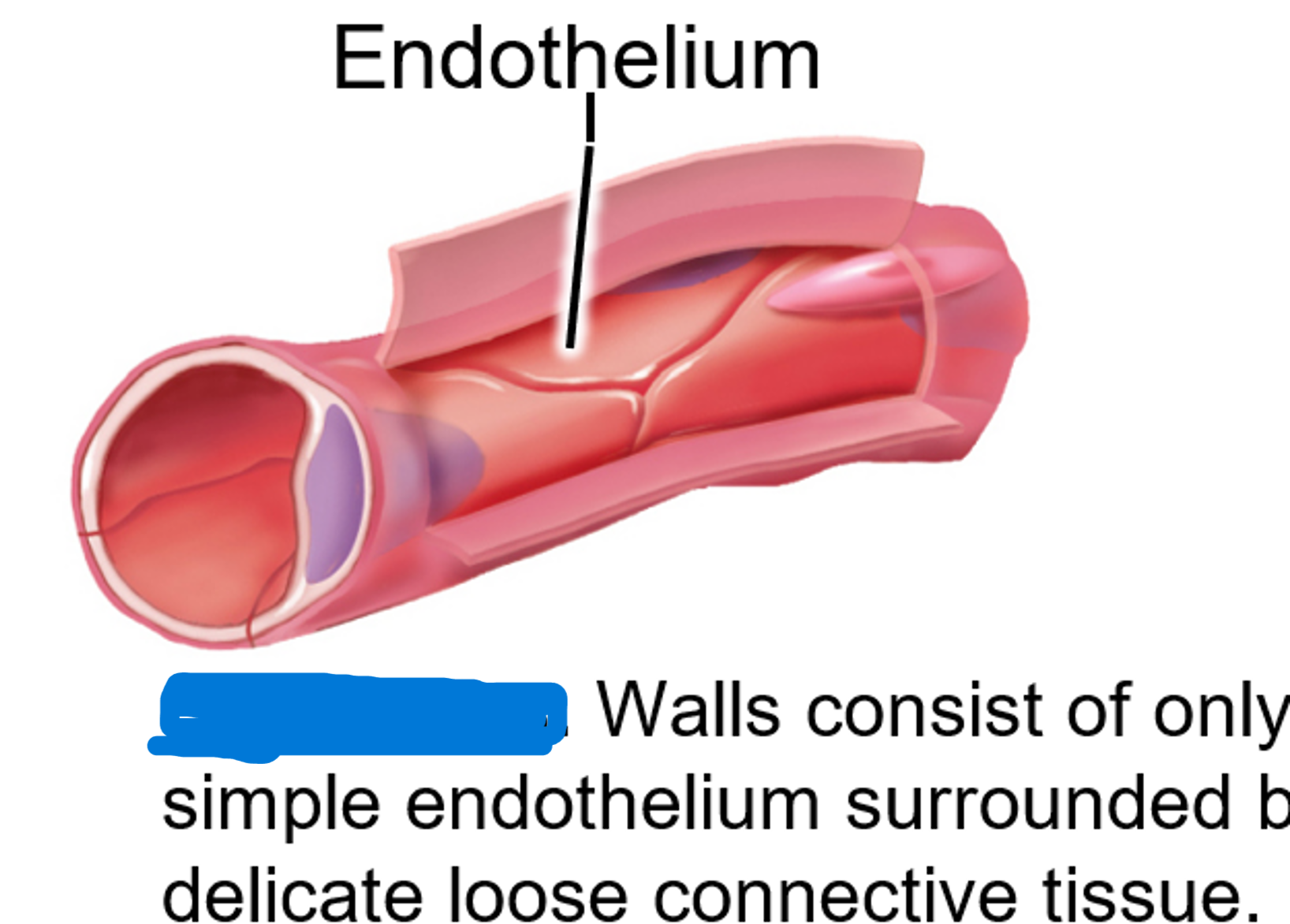
thin walls consist of endothelium (tunica intima) only
have very low blood pressure
continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoids
what are the three types of capillaries?
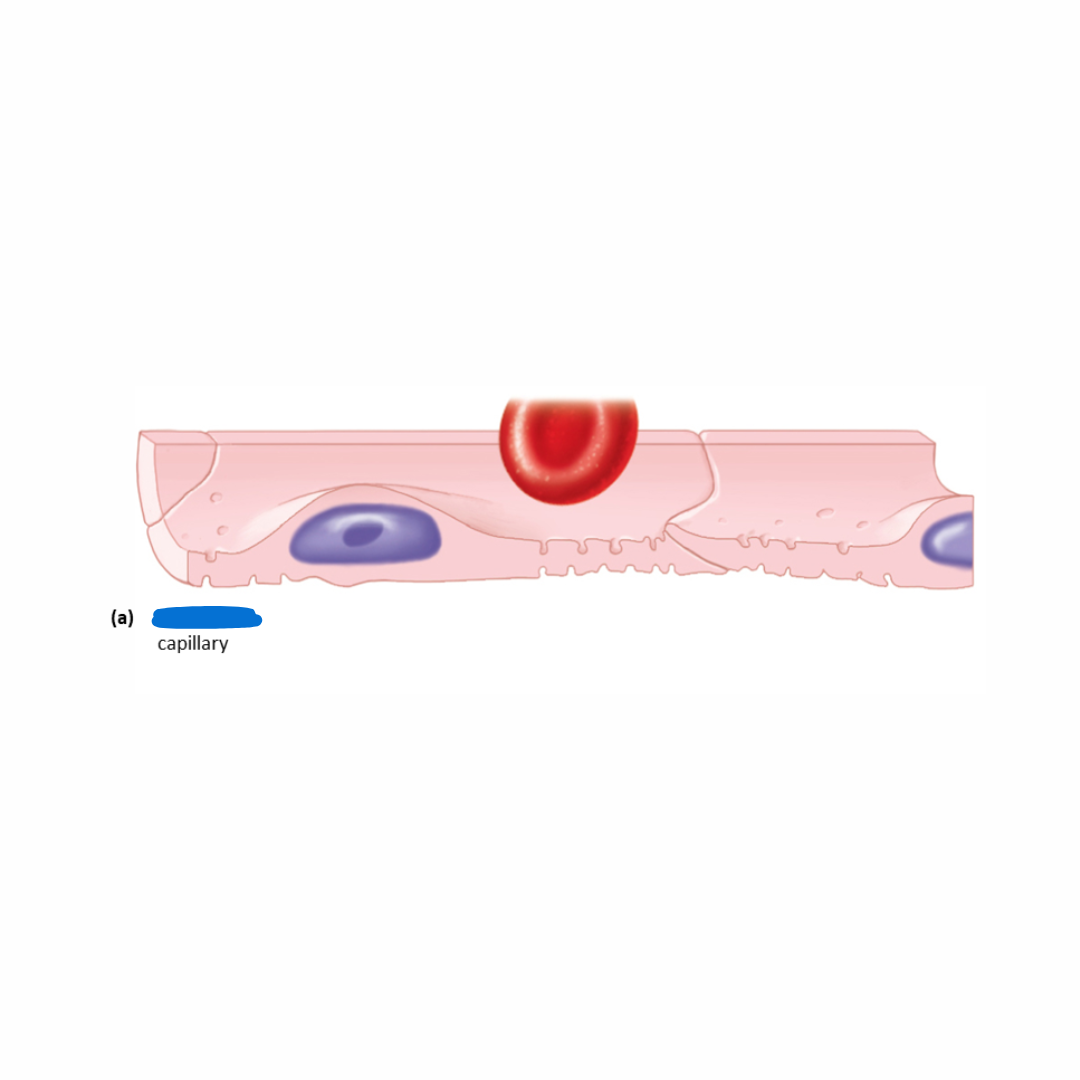
Continuous capillaries
most common type of capillary
endothelial cells form the unbroken lining
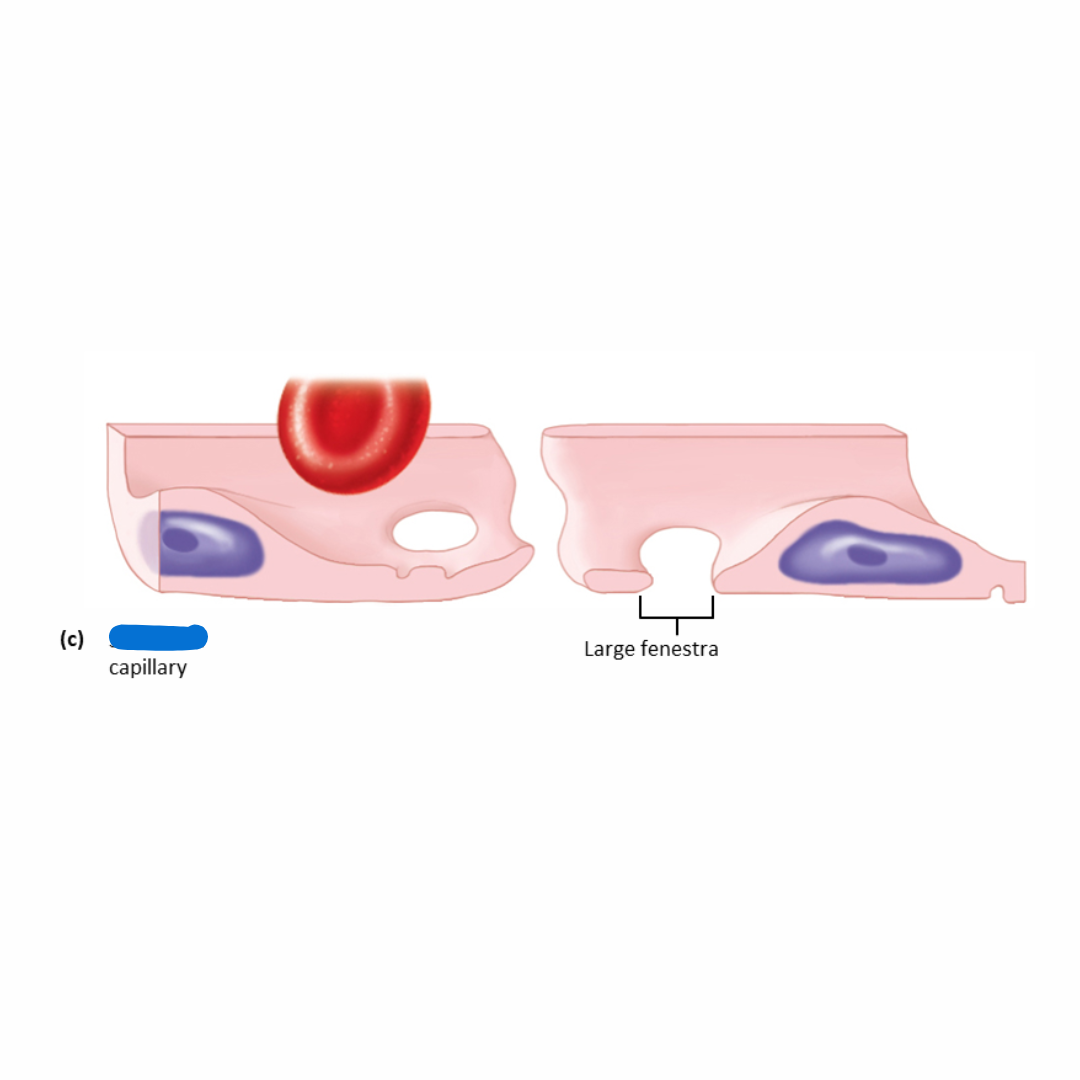
fenestrated capillaries
similar to continuous capillaries except some of the endothelial cells contain small pores or windows, which make it more permeable
(pores/windows are in the name)
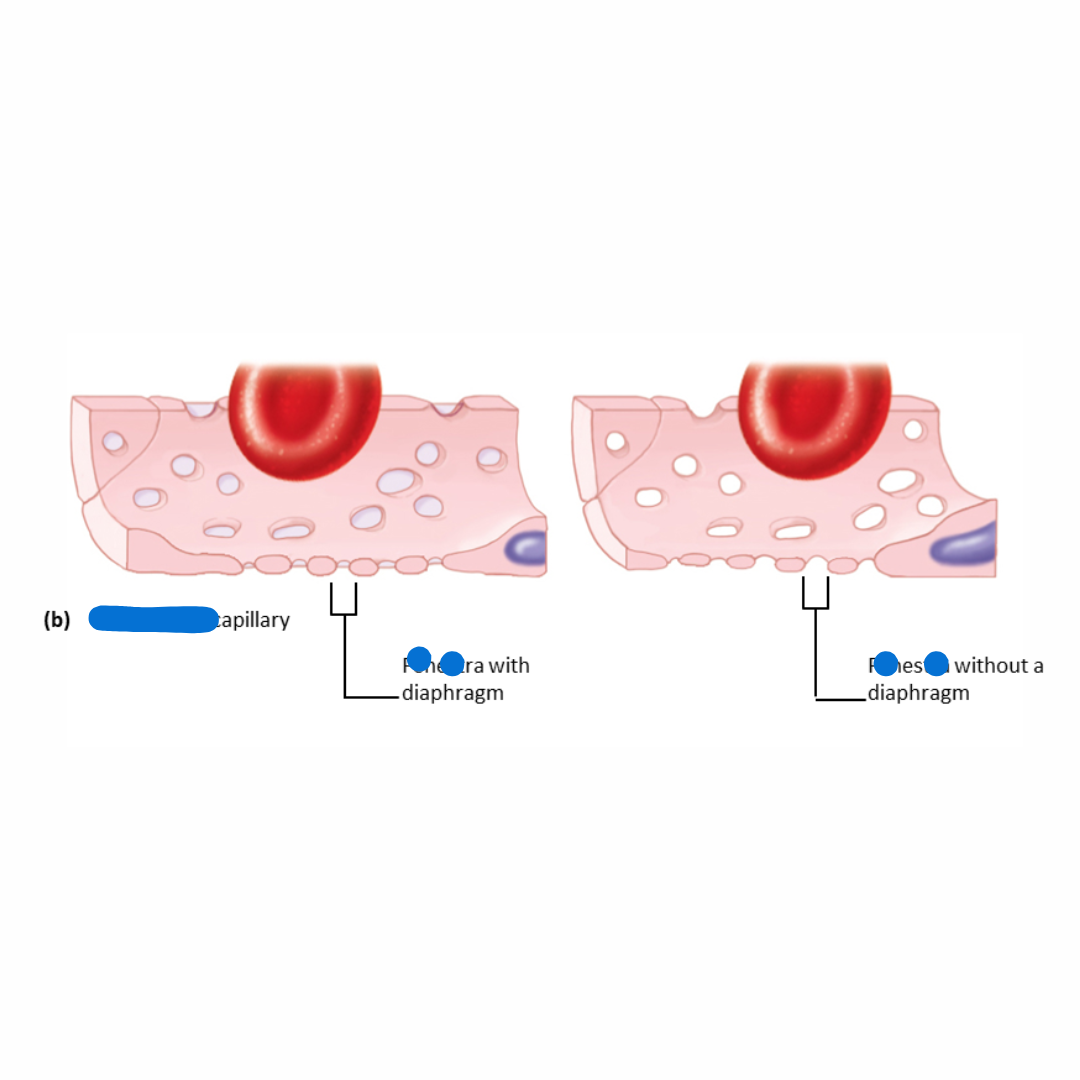
sinusoids/sinusoidal capillaries
larger capillaries with large fenestrations that allow molecules or whole cells to move their walls
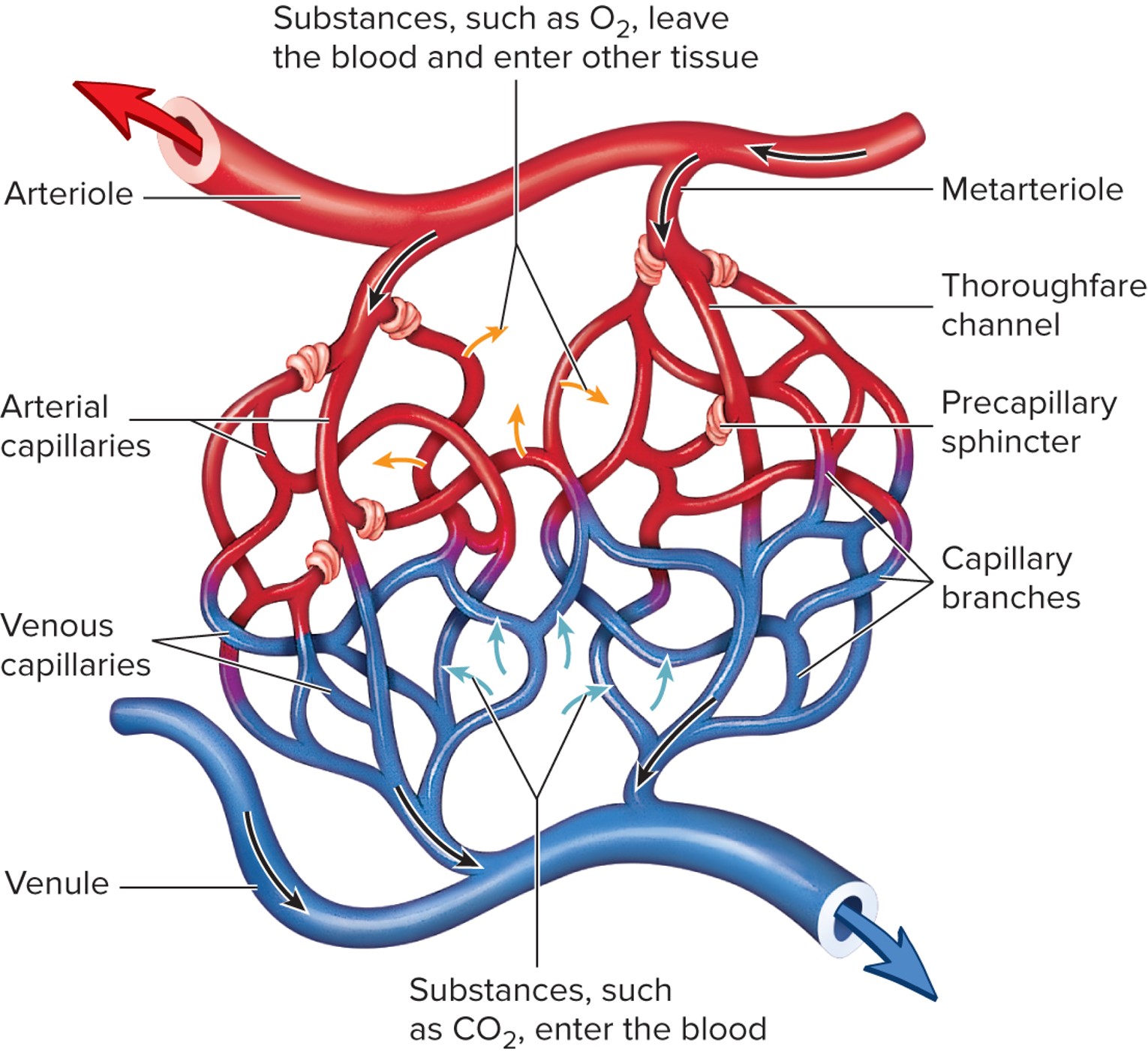
capillary networks
blood enters the [blank] from an arteriole
![<p>blood enters the [blank] from an arteriole</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/659233c6-cb15-4f50-95f5-6ec7093e541c.jpg)
precapillary sphincters
Blood flow into and through the capillary beds is regulated by [blank]
![<p>Blood flow into and through the capillary beds is regulated by [blank]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ba9264ef-486c-415a-86dd-d7b853e099cf.jpg)
diffusion
While blood is in the capillary beds, [blank] of materials into/out of the interstitial spaces can occur
![<p>While blood is in the capillary beds, [blank] of materials into/out of the interstitial spaces can occur</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f4a3f89-9b13-4449-8b7a-be9ab4cca61c.jpg)
venule
Blood exits the capillary bed via a [blank]
![<p>Blood exits the capillary bed via a [blank]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac834652-3a3c-4424-ac05-d0d1acd4d30b.jpg)
high metabolism
Tissues with [blank] have more capillary networks – lungs, liver, kidneys skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle
![<p>Tissues with [blank] have more capillary networks – lungs, liver, kidneys skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8c0abf2d-da24-4a6f-a381-a57901e03790.jpg)
thermoregulation
Capillary networks in the skin aid in [blank]
![<p>Capillary networks in the skin aid in [blank]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e6075f7b-44a0-49d1-8e44-62fc8f0fc30b.jpg)
nutrient and waste product exchange
Major function of capillaries is…