Childbirth Process and Newborn Assessment
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Stages of Labor
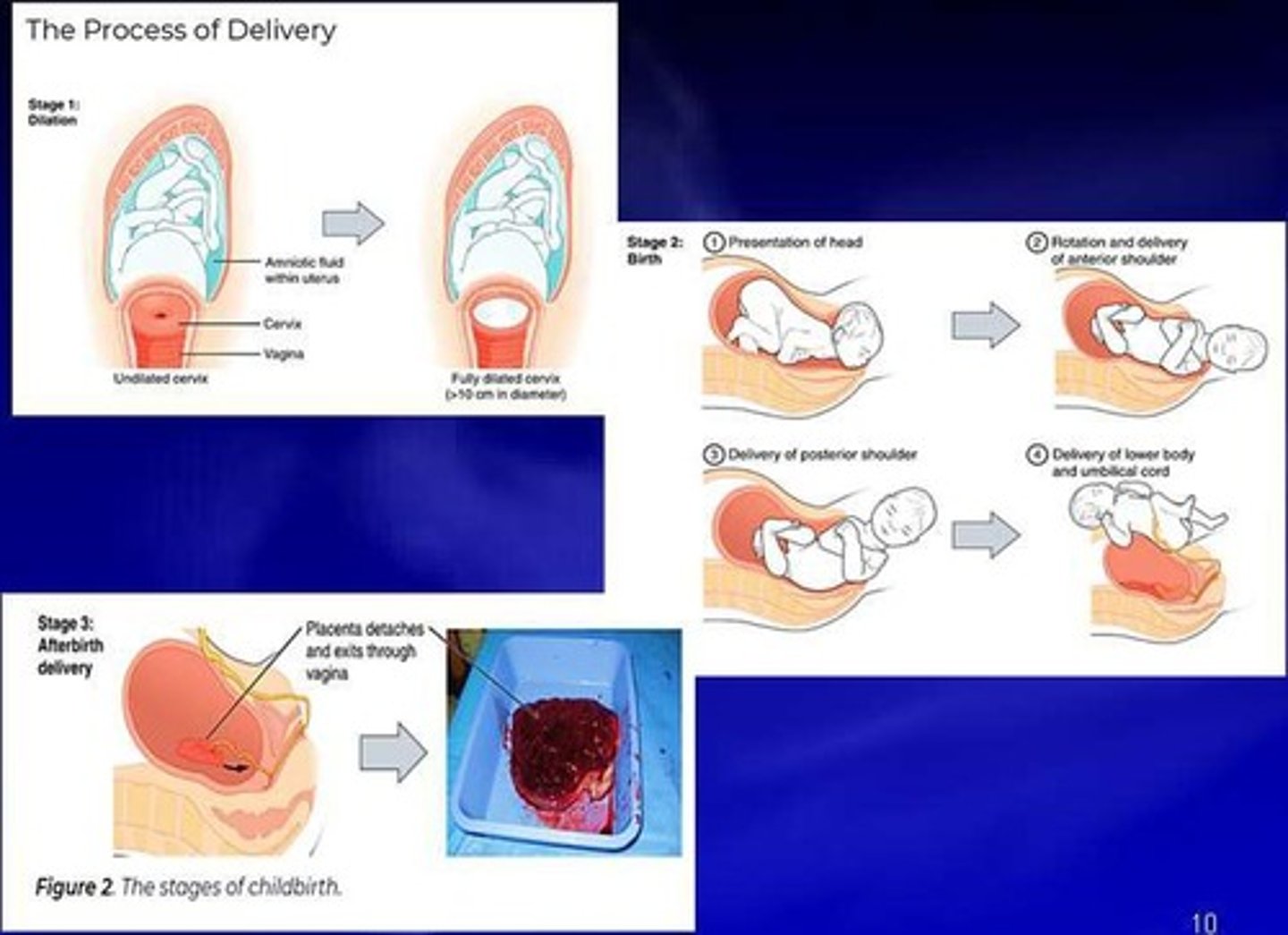
Four phases of childbirth: dilation, expulsion, placenta delivery, recovery.
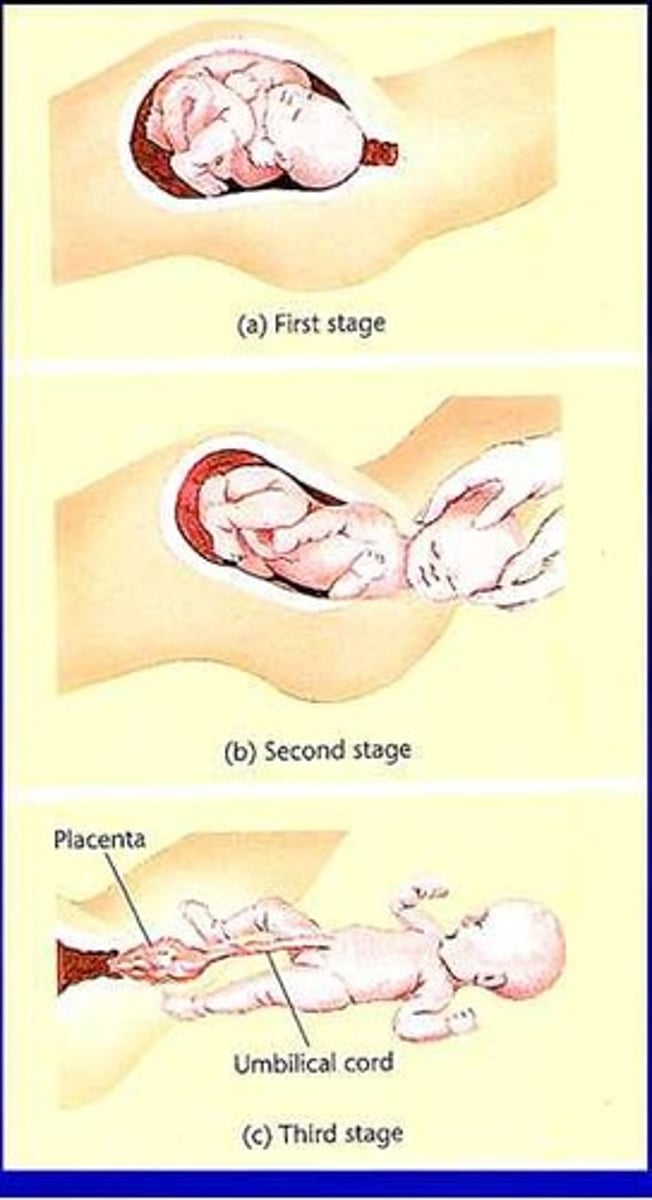
1st Stage of Labor
Longest stage; cervical dilation to 10 cm.
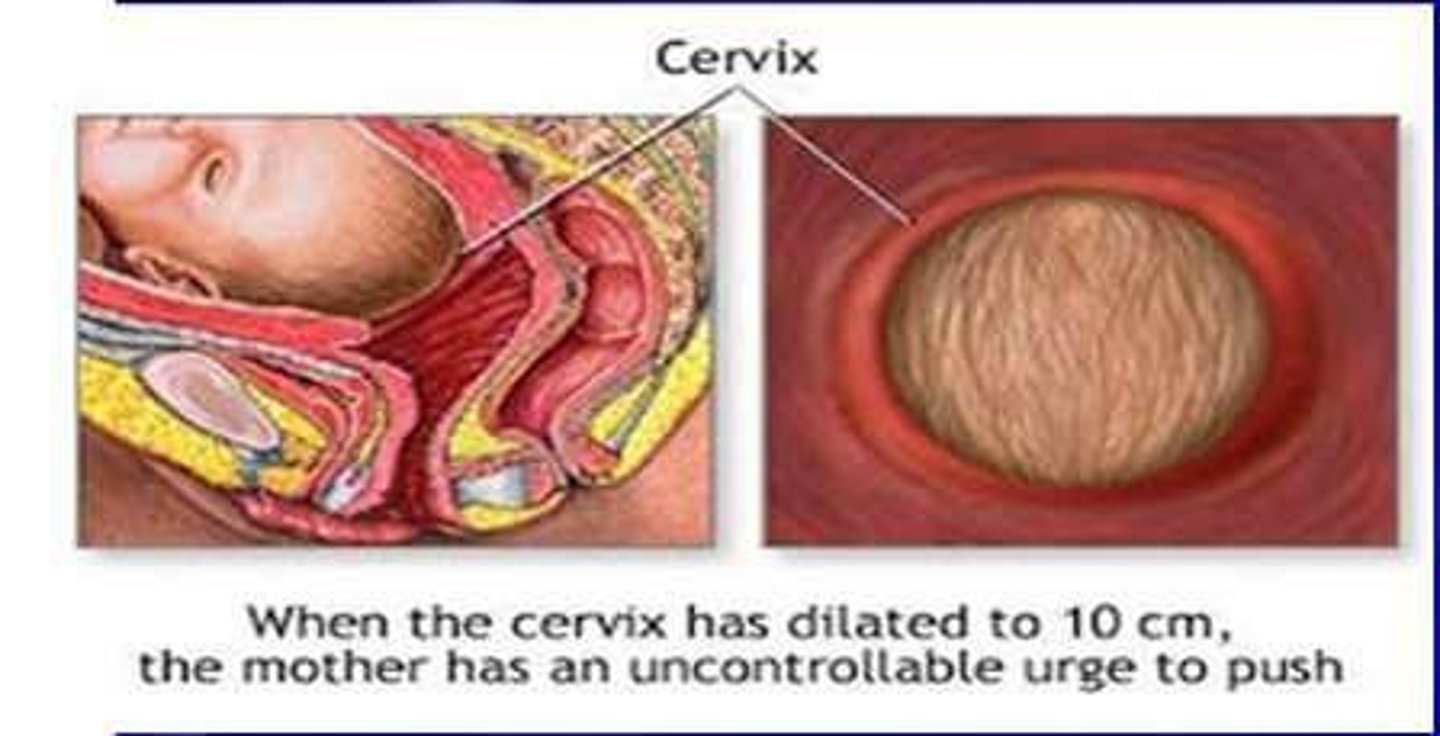
Cervical Effacement
Thinning and shortening of the cervix.
2nd Stage of Labor
Delivery of the fetus; lasts 10-40 minutes.
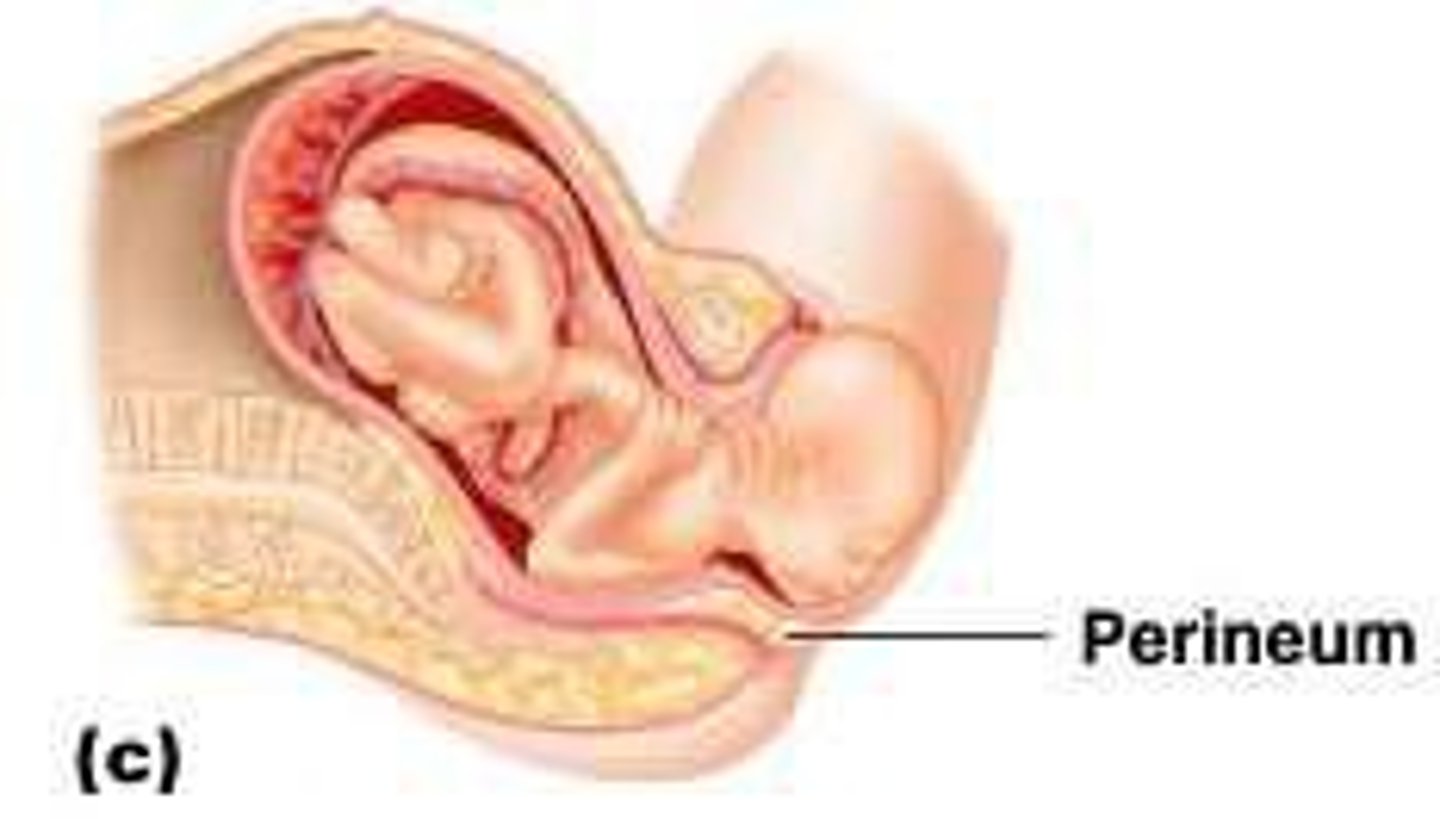
Crowning
Fetal head visible at vaginal opening.
3rd Stage of Labor
Delivery of placenta and fetal membranes.
4th Stage of Labor
Recovery phase; monitoring mother's health.
Natural Birth
Fetus emerges head-first without intervention.
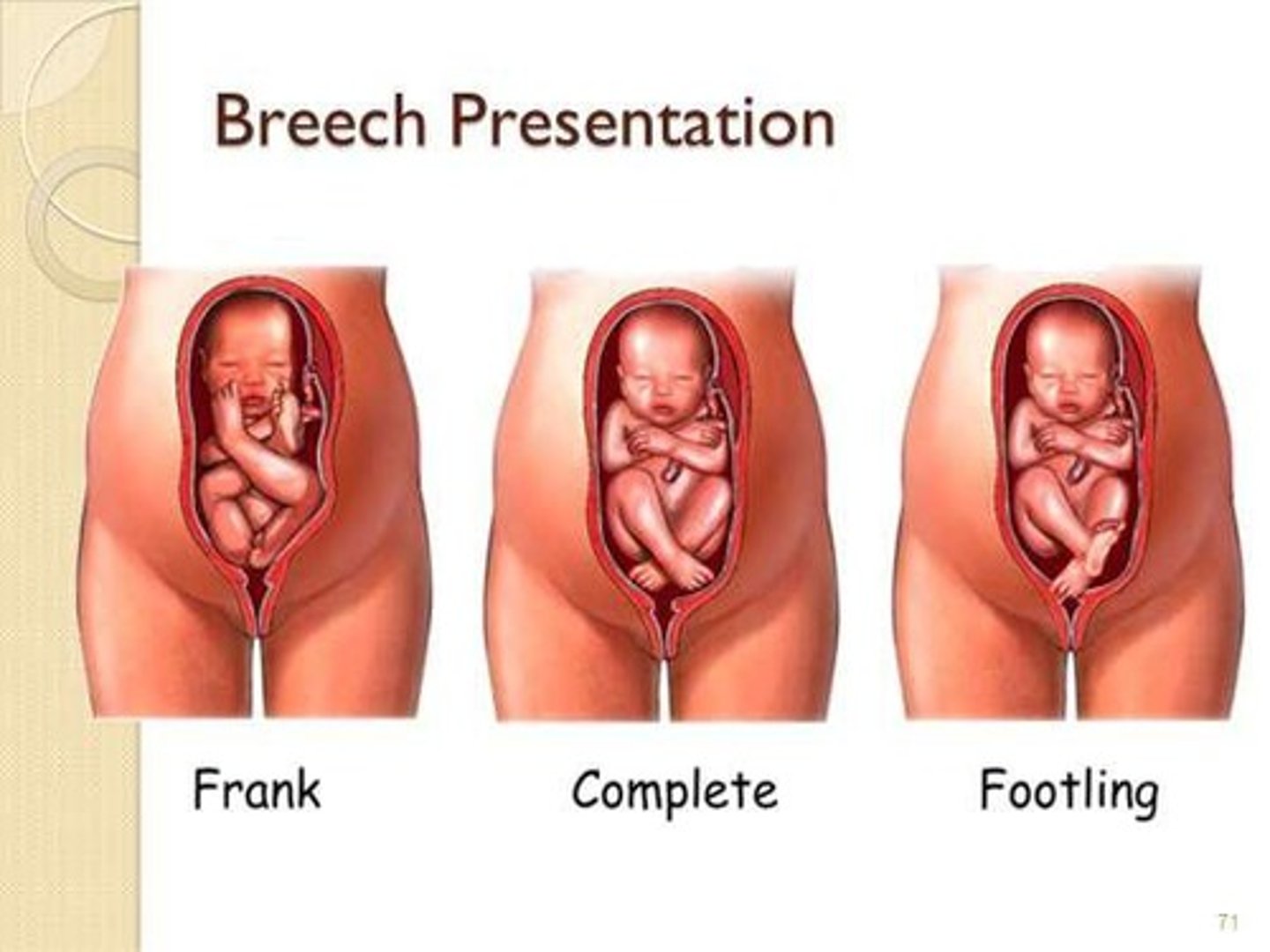
Breech Birth
Buttocks appear first during delivery.
Transverse Birth
Fetus positioned crosswise in uterus.
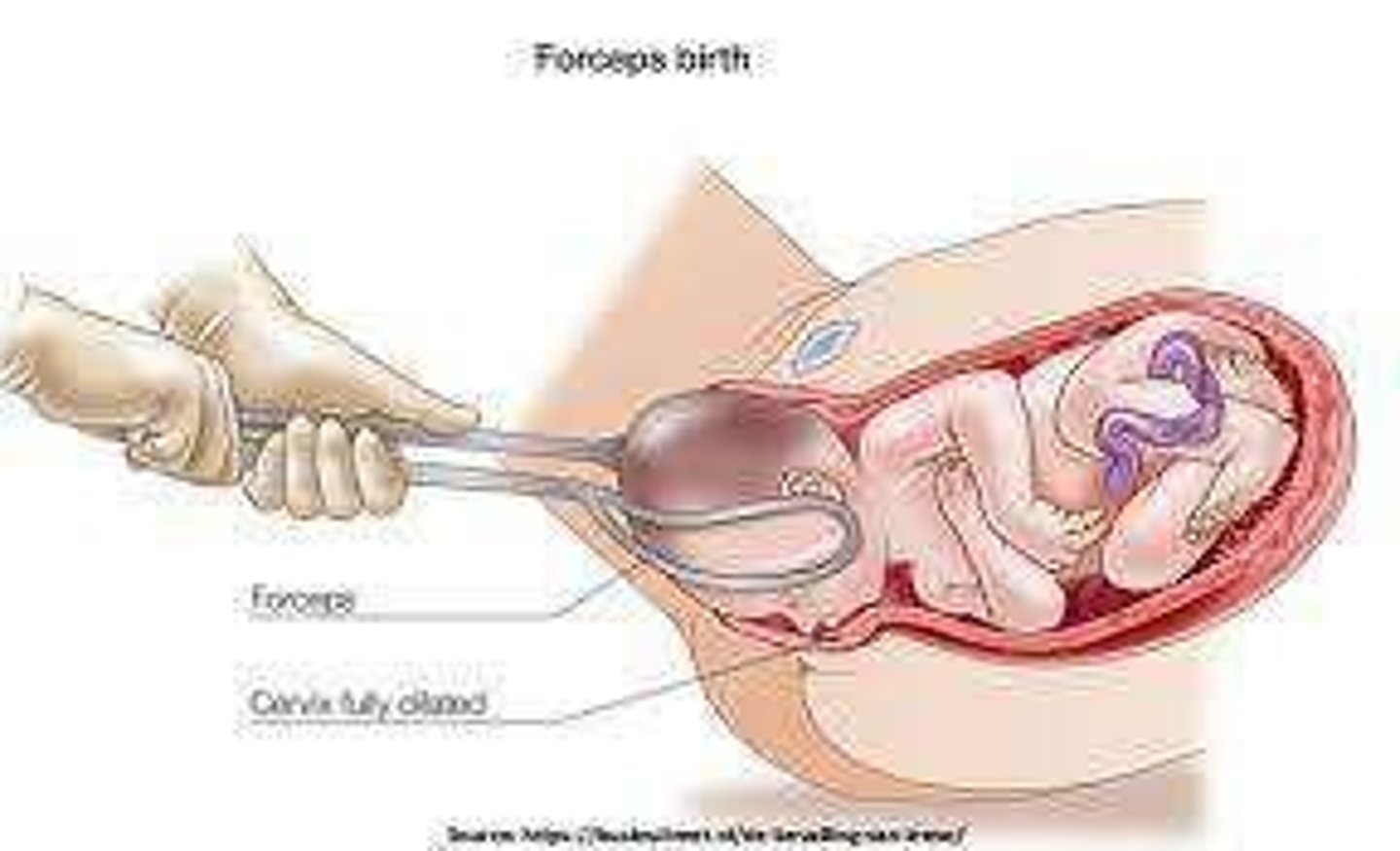
Instrument Birth
Use of tools for difficult deliveries.
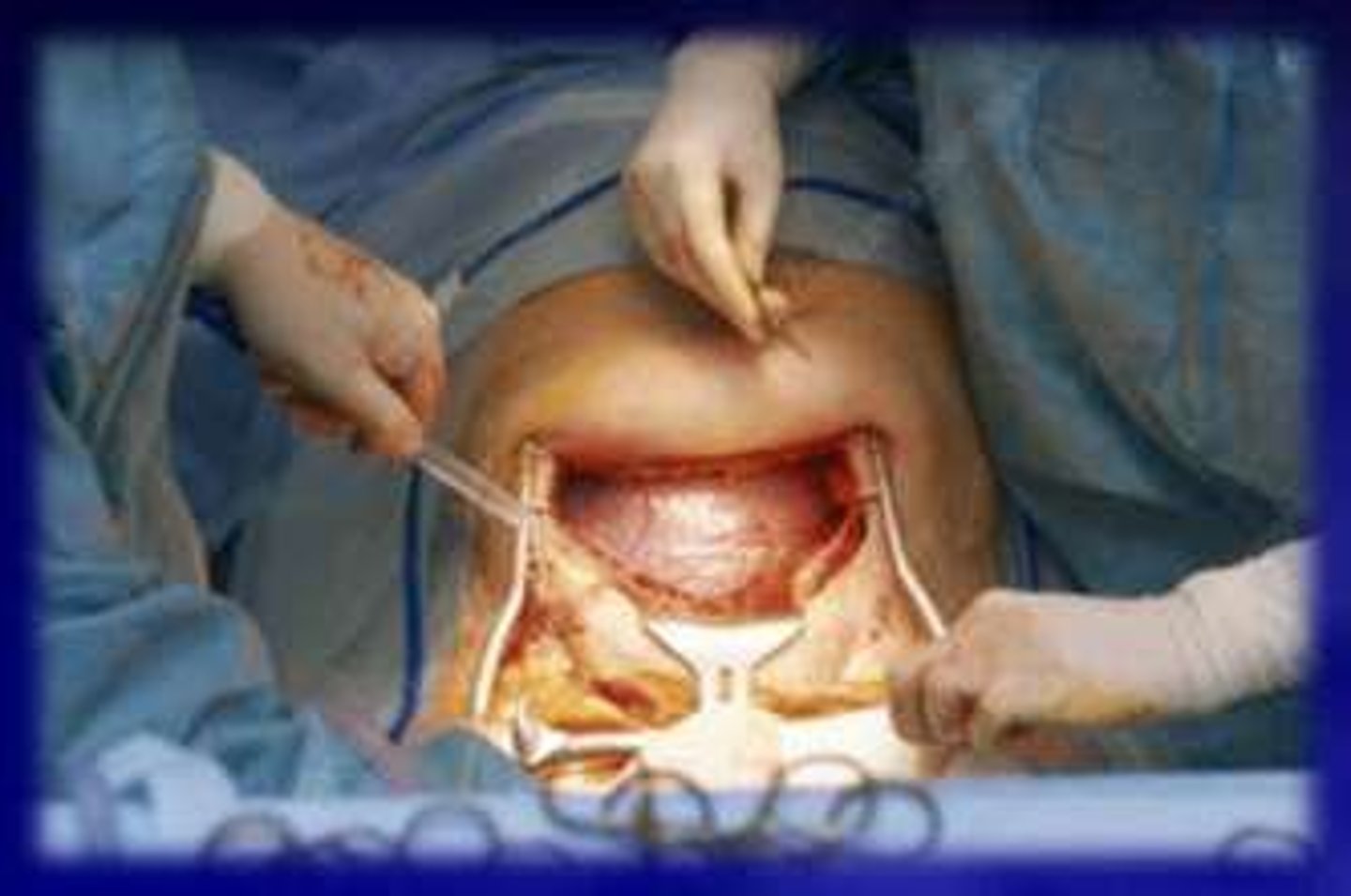
Caesarian Section
Surgical removal of fetus through abdomen.
Low Birthweight
Weight < 2,500 grams (5.5 pounds).
Very Low Birthweight
Weight < 1,500 grams (3 pounds, 5 ounces).
Hypoxia
Insufficient oxygen leading to brain damage.
Anoxia
Total lack of oxygen causing severe damage.
Cerebral Palsy
Disorder caused by brain injury, affecting movement.
Prematurity
Birth before 37 weeks of gestation.
Postmaturity
Birth after 42 weeks of gestation.
APGAR Score
Assessment tool for newborn's health at birth.
Brazelton Scale
Neonatal behavioral assessment scale for newborns.
Developmental Lag
Delayed physical and cognitive milestones.
Birth Trauma
Injury sustained during childbirth.
Facial Paralysis
Nerve damage causing loss of facial movement.
Brachial Plexus Palsy
Nerve injury affecting arm movement.
Key Assumptions
Infants are capable and communicate purposefully.
Behavioral Items
28 behavioral and 18 reflex items assessed.
Development Tasks
Four vital tasks for newborn growth.
Autonomic System Function
Includes respiration and temperature regulation.
State Organization
Levels from quiet sleep to full cry.
Social Interaction
Newborns are social beings ready to communicate.
APGAR
Assessment tool for newborn health at birth.
Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale
Evaluates newborn's behavioral responses.
Pull-to-Sit
Test for head control in infants.
Cuddliness
Infant's response to being held.
Self-Quieting Activity
Infants soothe themselves, e.g., thumb sucking.
Vital Signs
Normal ranges: Temp 36.5-37.5°C, Pulse 120-160 bpm.
Neonatal Period
First 4 weeks of life.
Mongolian Spot
Bruise-like marks, common in Black and Asian infants.
Erythema Toxicum
Red skin areas with yellow-white papules.
Caput Succedaneum
Swelling of scalp tissue from delivery.
Cephalhematoma
Hemorrhage under the skull, does not cross sutures.
Neural Tube Defects
Congenital defects from improper neural tube closure.
Anencephaly
Failure of cranial folds to close, severe brain damage.
Craniosynostosis
Premature skull suture closure, causes skull deformity.
Down's Syndrome
Trisomy 21, characterized by distinct physical traits.
Epstein Pearls
Gingival cysts found in newborns' mouths.
Breath Sounds
Assessment of lung function and respiratory patterns.
Surfactant
Substance preventing alveolar collapse in lungs.
Fluid Shifts
Changes in body fluids reduce pulmonary resistance.
Initiation of Respiration
Triggered by chemical, mechanical, thermal, and sensory factors.
Heart Rate
Normal range is 30-80 beats per minute.
Murmurs
Abnormal heart sounds indicating potential issues.
Dextrocardia
Heart positioned on the right side of the chest.
Abdominal Masses
Presence of abnormal growths in the abdomen.
Organomegaly
Enlargement of organs, often detectable on examination.
Omphalocele
Congenital defect with abdominal contents outside body.
Gastroschisis
Evisceration of abdominal contents through wall defect.
Prune Belly Syndrome
Characterized by absent abdominal muscles and cryptorchidism.
Cryptorchidism
Undescended testicles, common in males.
Hypospadias
Abnormal positioning of the urinary meatus.
Syndactyly
Abnormal fusion of fingers or toes.
Polydactyly
Presence of extra fingers or toes.
Talipes Equinovarus
Commonly known as clubfoot, a congenital deformity.
Spina Bifida
Congenital defect involving incomplete closure of the spine.
Hypertrichosis
Excessive hair growth associated with spina bifida.
Average Neonate Weight
Typically ranges from 2,500 to 3,000 grams.
Neonatal Respiration Rate
Normal range is 40-50 breaths per minute.
Neonatal Heartbeat
Faster than adults, indicating higher metabolic rate.
Cranial Proportions
Head is ¼ of total body length at birth.
Visual Capacity
Fixed focal length of 8-12 inches.
Optic Nystagmus
Ability to follow moving objects with eyes.
Tactile Sensitivity
Well-developed, especially on skin surface.
Neonatal Sleep Patterns
Newborns sleep 14-17 hours daily, mostly REM.
Behavioral States
Includes quiet sleep, active sleep, and alert states.
Vocalization
Crying is primary form of communication.
Organic Sensitivity
Physiological responses fully developed at birth.
Reflexes
Involuntary responses crucial for survival.
Emotional Development
Beginnings of individuality and temperament observed.