Materials - Stress, strain and Young’s modulus, Graphs, Ductile, Brittle and Polymeric
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
tensile stress
the force per unit cross-section area, measured in Pa (Nm⁻²)
stress equation
σ = F/A
tensile strain
the extension per unit length, a dimensionless quantity
strain equation
ε = x/L
Young’s Modulus Equation(s)
E - σ/ε
E= FL/Ax
What does a large Young’s Modulus/steep gradient on a σ-ε graph represent?
a stiff material
yield point
a point on a stress-strain graph beyond which the deformation is no longer entirely elastic (between two yield points strain increases largely with a small applied stress)
UTS (Ultimate tensile strength)
the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it breaks
beyond the UTS, material becomes thinner+longer (necking)
Breaking strength
the stress value at the point of snapping (value of stress)
σ-ε graph for a ductile material (and labels)
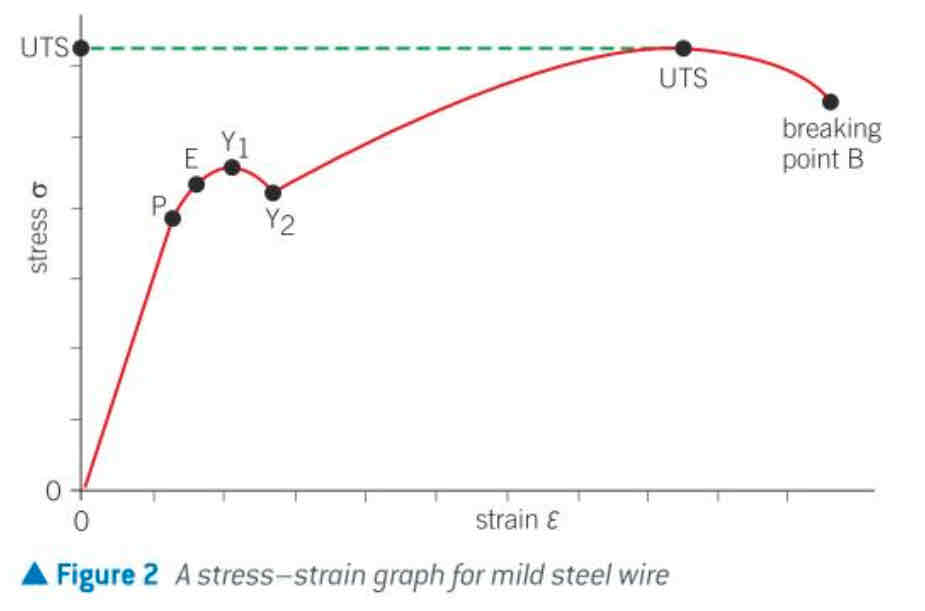
ductile
property of a material that has a large plastic region in a σ-ε graph, so can be drawn into wires
σ-ε graph for brittle materials (and properties)
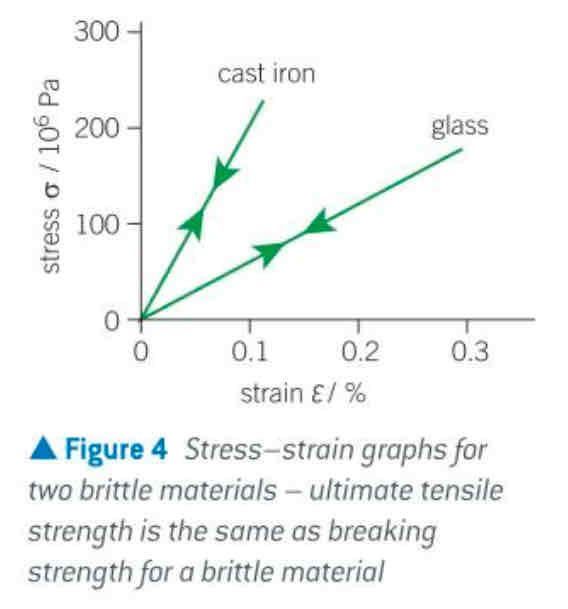
brittle
property of a material that does not show plastic deformation and deforms very little (if at all) under high stress
σ-ε graph for polymeric materials (and properties)
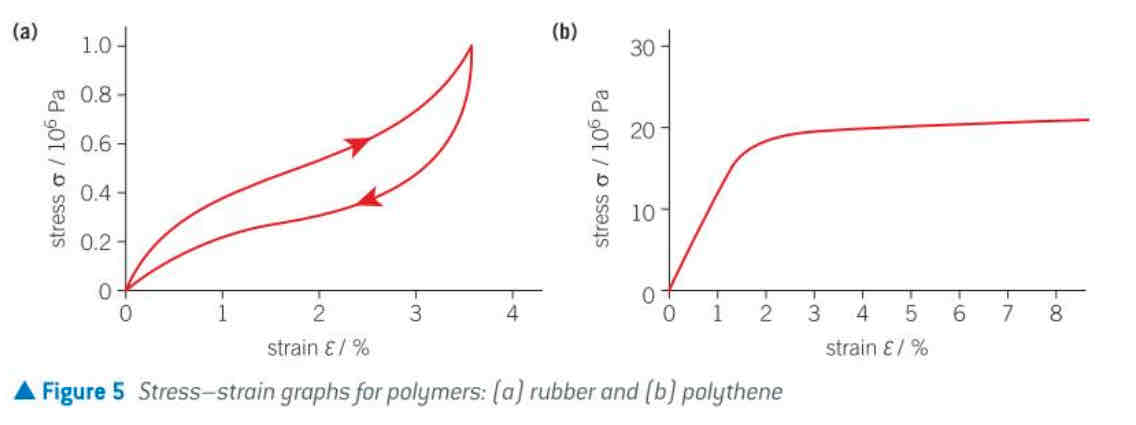
polymeric
description of a material comprising of long-chain molecules, such as rubber, which may show large strains