C1: Biological Molecules
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Name the four key inorganic ions in living organisms
Magnesium (Mg2+) Iron (Fe2+) Calcium (Ca2+) Phosphate (PO43-)
What is the role of Mg2+ in plants?
Mg2+ is used to produce chlorophyll.
What is the role of Fe2+ in animals?
Fe2+ is found in haemoglobin and is involved in oxygen transport.
What is the role of PO43- in living organisms?
PO43- is used to produce ADP and ATP.
What is the role of Ca2+ in living organisms?
Ca2+ strengthens tissues such as bones and teeth in animals and cell walls in plants.
Why is water a polar molecule?
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. Oxygen attracts the electron density in the covalent bond more strongly forming δ- O and δ+ H.
Describe hydrogen bonding between water molecules.
Weak intermolecular forces of attraction between a lone pair on a δ- oxygen and δ+ H on an adjacent molecules.
What is a metabolite?
A molecule formed or used in metabolic reactions.
Describe the role of water as a metabolite.
A reactant in photosynthesis and hydrolysis reactions, is also a product in respiration and condensation reactions.
Why is water’s high specific heat capacity important for organisms and plants?
Water acts as a temperature buffer, enabling endotherms to resist fluctuations in core temperature and to maintain optimum enzyme activity. Ensures stability in environmental temperatures for aquatic organisms.
Why is water’s high latent heat of vaporisation important for organisms and plants?
Large amounts of heat energy needed for water to evaporate, so when water evaporates it has a cooling effect. Important in homeostasis as organisms lose heat through sweating and panting.
Why is water an important solvent for organisms?
Water is a polar solvent enabling chemical reactions to take place within cells, the transport of materials in the plasma and the removal of metabolic waste.
Why does water have a high surface tension?
Due to cohesion and ordered arrangement of molecules at the surface of the water.
Why is water’s high surface tension important?
Enables the transport of water and nutrients through plant stems and small blood vessels in the body
Allows small insects to walk on water- pondskater
What is a monosaccharide?
Simple sugar with formula Cn(H2O)n.
Give some examples of monosaccharides.
ribose
deoxyribose
α-glucose
β-glucose
fructose
galactose
Draw α-glucose.
A monosaccharide where the OH on carbon-1 is below the C1 atom.
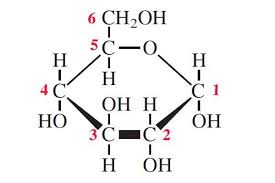
Draw β-glucose.
A monosaccharide where the OH on carbon-1 is above the C1 atom.
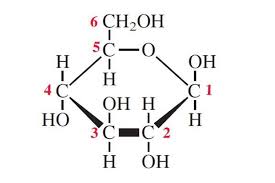
What is the difference between deoxyribose and ribose sugars?
Deoxyribose lacks one oxygen atom compared to ribose.
What bond is formed when two monosaccharides react?
Glycosidic bond.
What is a disaccharide?
Two monosaccharides joined by condensation reaction forming a glycosidic bond
Formula - (C12H22O11)
Give examples of disaccharides and their constituents.
sucrose glucose-fructose
maltose α-glucose–α-glucose
lactose glucose–galactose.
What is a polysaccharide?
A polymer of monosaccharides formed by many condensation reactions.
Give examples of polysaccharides.
starch
glycogen
cellulose
chitin
What are characteristics of polysaccharides?
Unable to diffuse out of the cell
Compact in shape so glucose can be stored in a cell
Insoluble in water so they do not alter the water potential, no osmotic effect
easily hydrolysed into constituent monosaccharides
What is the function of starch?
Energy storage in plants.
Describe the structure of starch- amylose and amylopectin
Polymer of alpha glucose monomers
Amylose: alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds unbranched
Amylopectin: alpha 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds branched
Amylopectin more branched means there are more exposed ends that can be hydrolysed resulting in a rapid release of glucose
What is the function of glycogen?
Energy storage in animals.
How does glycogen’s structure relate to its function?
Highly branched for rapid hydrolysis of glucose, more branched than amylopectin.
Describe the structure and function of cellulose.
Linear polysaccharide that is the main component of the cell wall in plants
β-glucose molecules joined by β-1 4 glycosidic bonds
alternate glucose molecules rotated 180^ allowing hydrogen bonds between parallel chains forming myofibrils
Describe the structure and function of chitin.
Linear polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of insects and fungal cell walls
Consists of many β-glucose molecules with acetyl amine side group joined by 1-4 β-glycosidic bonds
Alternate glucose molecules rotated 180^ allowing h bonds between parallel chains, forming myofibrils
Explain how a triglyceride is formed.
One molecule of glycerol joins three fatty acids via condensation forming ester bonds.
Relate triglyceride structure to function.
Energy storage, high calorific value from oxidation
Insoluble hydrocarbon chain- no effect on water potential of cells, used for waterproofing
Thermal insulation- slow conductor of heat
Buoyancy of aquatic animals- less dense than water
What is a phospholipid?
Lipid formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acid and a phosphate group.
Relate phospholipid structure to function.
Glycerol backbone attached to two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and one hydrophilic polar phosphate head
forming phospholipid bilayer in water- component of cell membrane
waterproofing, tail splays outwards
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fats.
Saturated no C=C bonds and are solid at room temperature due to strong intermolecular forces
Unsaturated one or more C=C liquid at room temperature due to weak intermolecular forces
Difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Monounsaturated- one C=C bond Polyunsaturated- more than one C=C bond.
What is a low density lipoprotein (LDL)?
Combination of triglycerides from saturated fats and protein
blocks receptor sites reducing cholesterol absorption
‘bad’ lipoprotein
How do LDLs contribute to cardiovascular disease?
Cause high blood cholesterol leading to atherosclerosis plaque formation.
Describe the general structure of an amino acid and draw it.
Amine group carboxyl group hydrogen variable R group.
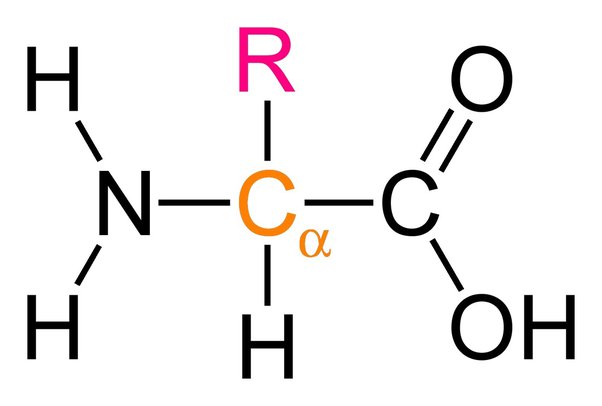
How are polypeptides formed?
Many amino acids join via condensation forming peptide bonds and water.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
Individual sequence of amino acids in a chain.
Describe the secondary structure of a protein.
Folding of primary structure into a 3D shape held together by hydrogen bonds creating alpha helices and beta pleated sheets.
Describe the tertiary structure of a protein.
Folding of alpha helices into a compact shape maintained by disulphide, ionic, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Gives globular proteinstheir functional 3D shape.
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein.
Combination of two or more polypeptide chains in tertiary from combined. May involve prosthetic groups- haem group in haemoglobin.
How does fibrous protein structure relate to function?
Long polypeptide chains folded in parallel. Cross-links for strength making them insoluble, good for structural roles.
How does globular protein structure relate to function?
Compact spherical highly folded with tertiary/quaternary structures
Hydrophilic R groups face outwards and hydrophobic R groups face inwards making it water-soluble
Example is haemoglobin- 4 polypeptide chains haem group containing iron in the middle
Difference between reducing and non-reducing sugars.
Reducing sugars have free aldehyde or ketone group non-reducing do not.
Describe the Benedict’s test for reducing sugars.
Add and equal volume of sample being tested and Benedict’s reagent
Heat the mixture in an electric water bath at 100^ for 5 minutes
Observe the colour of the precipitate formed
Positive result for reducing sugars.
Colour changes from green to yellow to orange to brown to brick red depending on quantity of sugar.
Describe Benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars.
Negative test for reducing sugar
Hydrolyse non-reducing sugars with an equal volume of dilute HCL
Heat in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes
Add sodium hydrogen carbonate to neutralise the acid
Re-test resulting solution with Benedict’s reagent
Observe colour of precipitate formed
Positive result for non-reducing sugars.
Colour change from green to yellow to orange to brown to brick red depending on quanitity of sugar.
Food test for proteins
Biuret test.
Describe the Biuret test
Add a few drops of biuret reagent to sample.
Positive result of Biuret test.
Colour change from pale blue to purple.
Describe iodine-potassium iodide test for starch.
Add iodine-KI solution, orange to blue-black if starch present.
Describe the emulsion test for fats and oils.
Add ethanol and shake allowing mixture to settle, add equal volume of water and observe mixture.
Positive result of emulsion test.
White cloudy emulsion forms.