Chapter 16 Urinary System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Urinary System Anatomy
two kidneys
two ureters
one urinary bladder
one urethra
Main function Urinary System
production of urine and its elimination
how much do kidneys normally excrete a day?
1 - 2 liters of urine per day
suprarenal glands
aka Adrenal glands - are NOT part of the urinary system
what do the adrenal glands do?
secrete epinephrin and cortical hormones
Which kidney is larger and higher?
Left kidney slightly longer and narrower, lower than right
Where is the retroperitoneal located?
in contact with posterior abdominal wall
Where do the kidneys lie?
lie in oblique plane approx. 30 degree anterior toward the aorta
Kidney Anatomy: outer covering
Renal Capsule
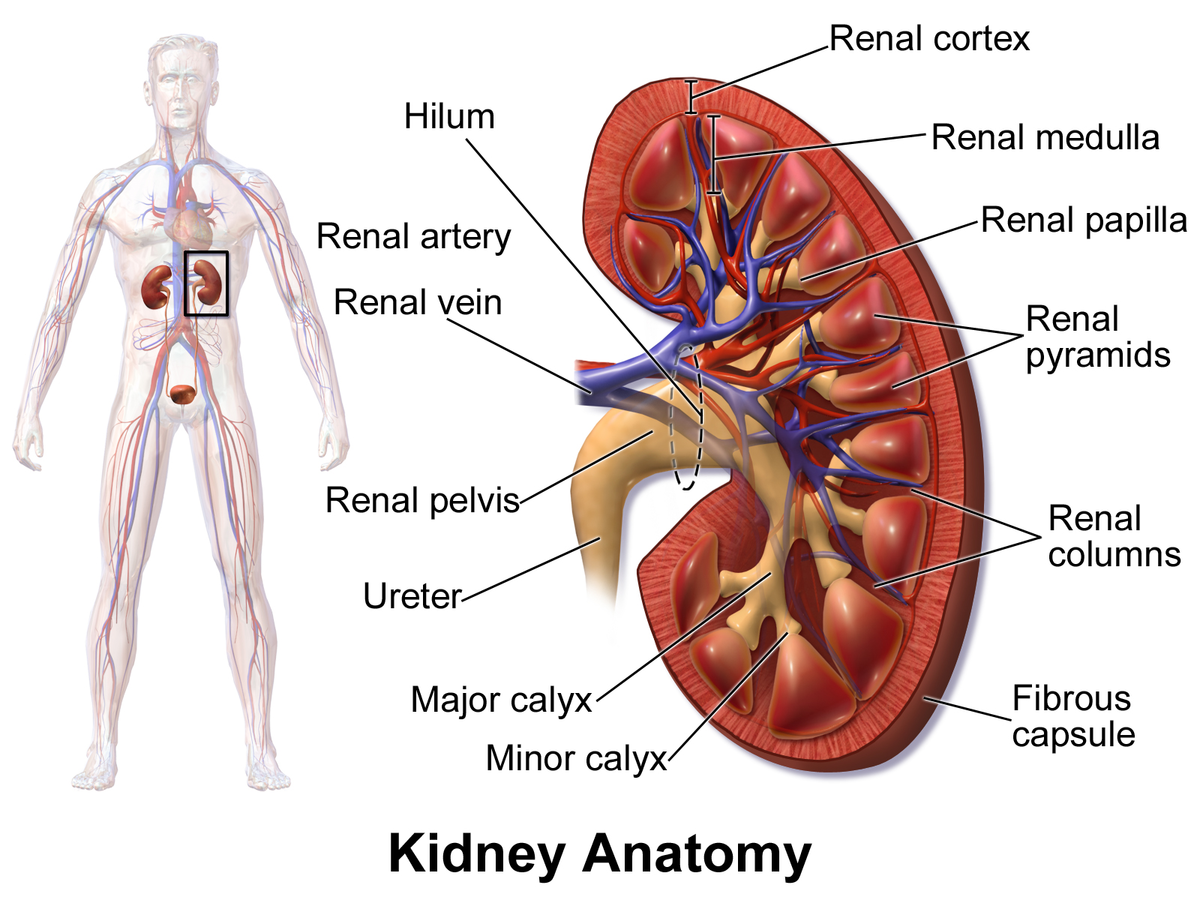
Kidney Anatomy: outer layer of rental tissue
Renal Cortex
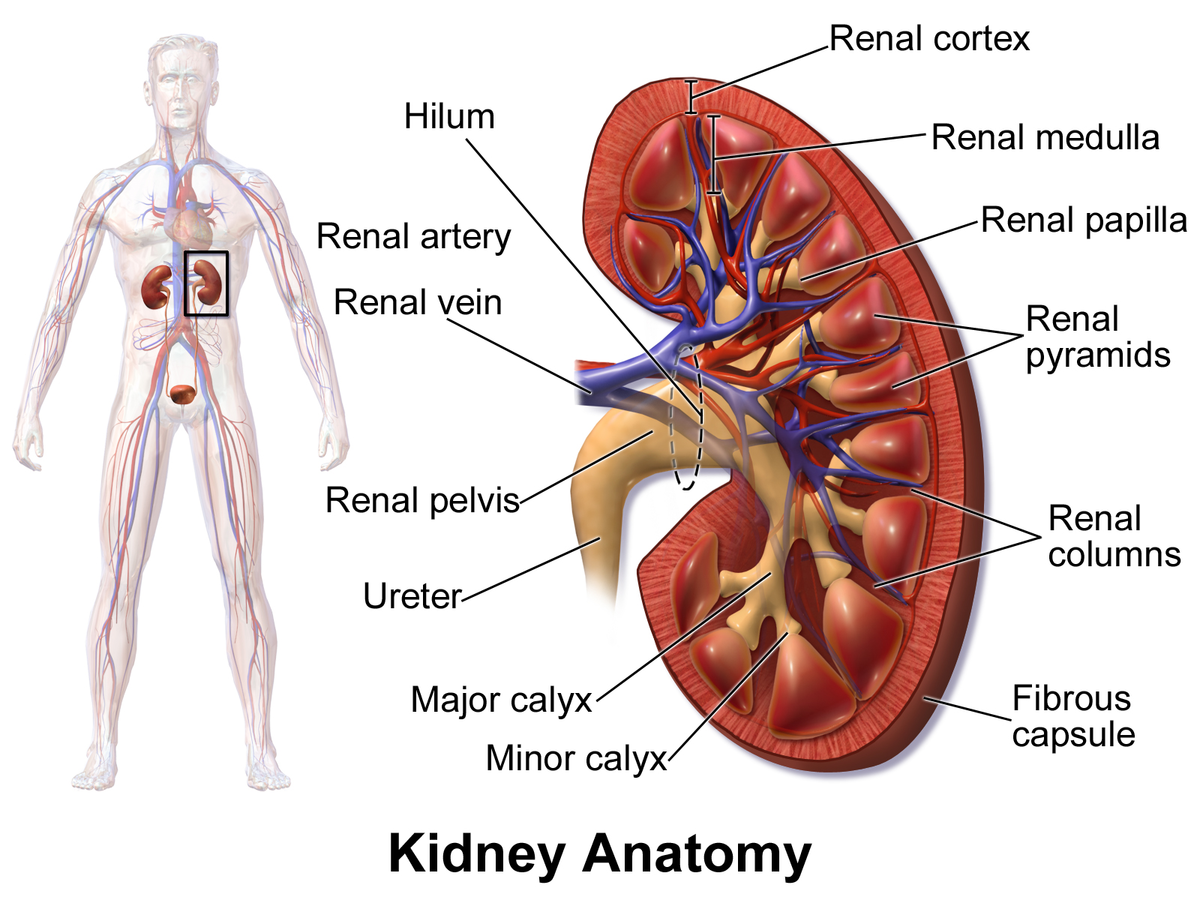
Kidney Anatomy = inner layer of renal tissue
Renal Medulla
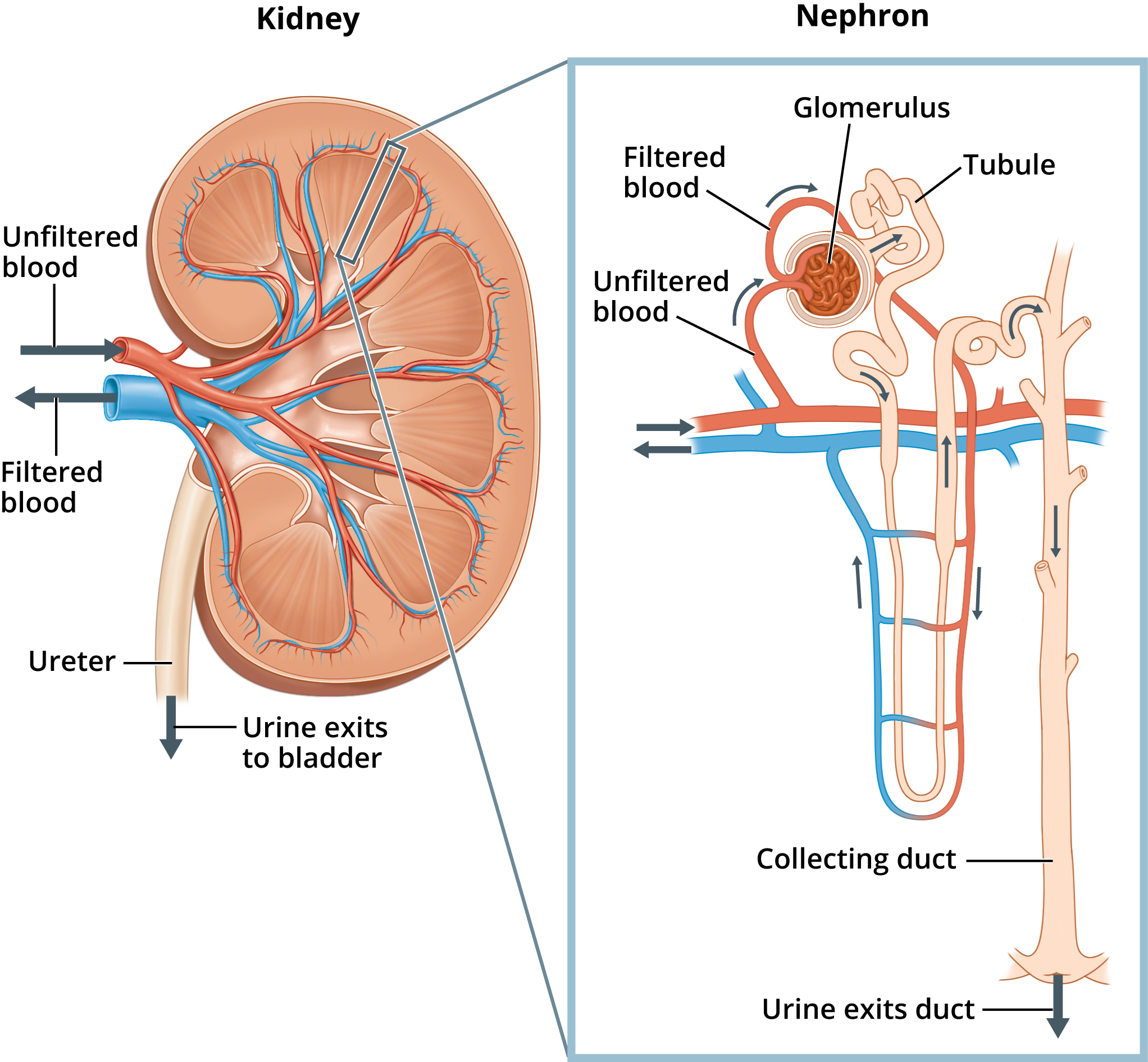
Nehron
Essential microscopic component of kidney
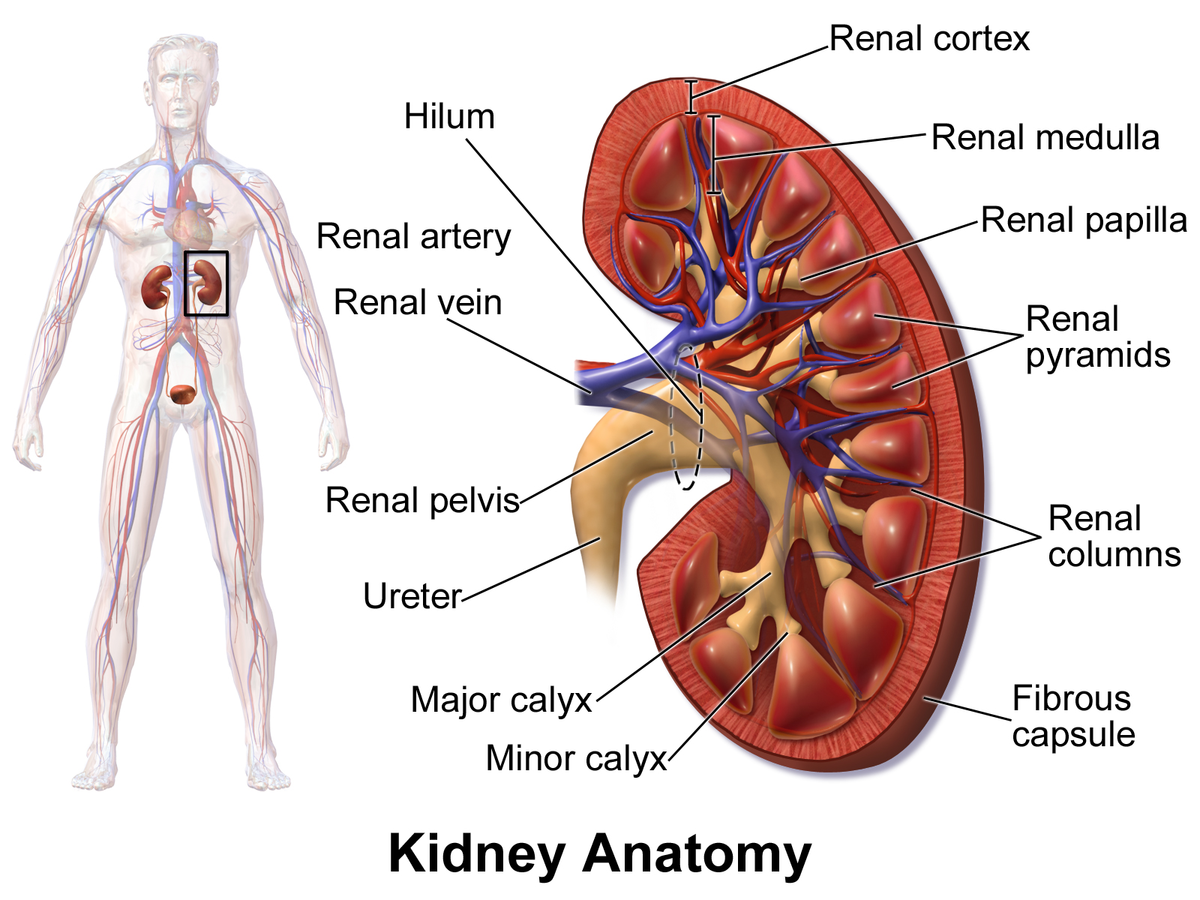
how many cone shaped segments are the kidneys composed of?
8 to 15
how long are the ureters?
10 - 12 inches
What is the bladder
musculomembranous sac
Trigone
Triangular area of bladder base between three openings (bladder anatomy)
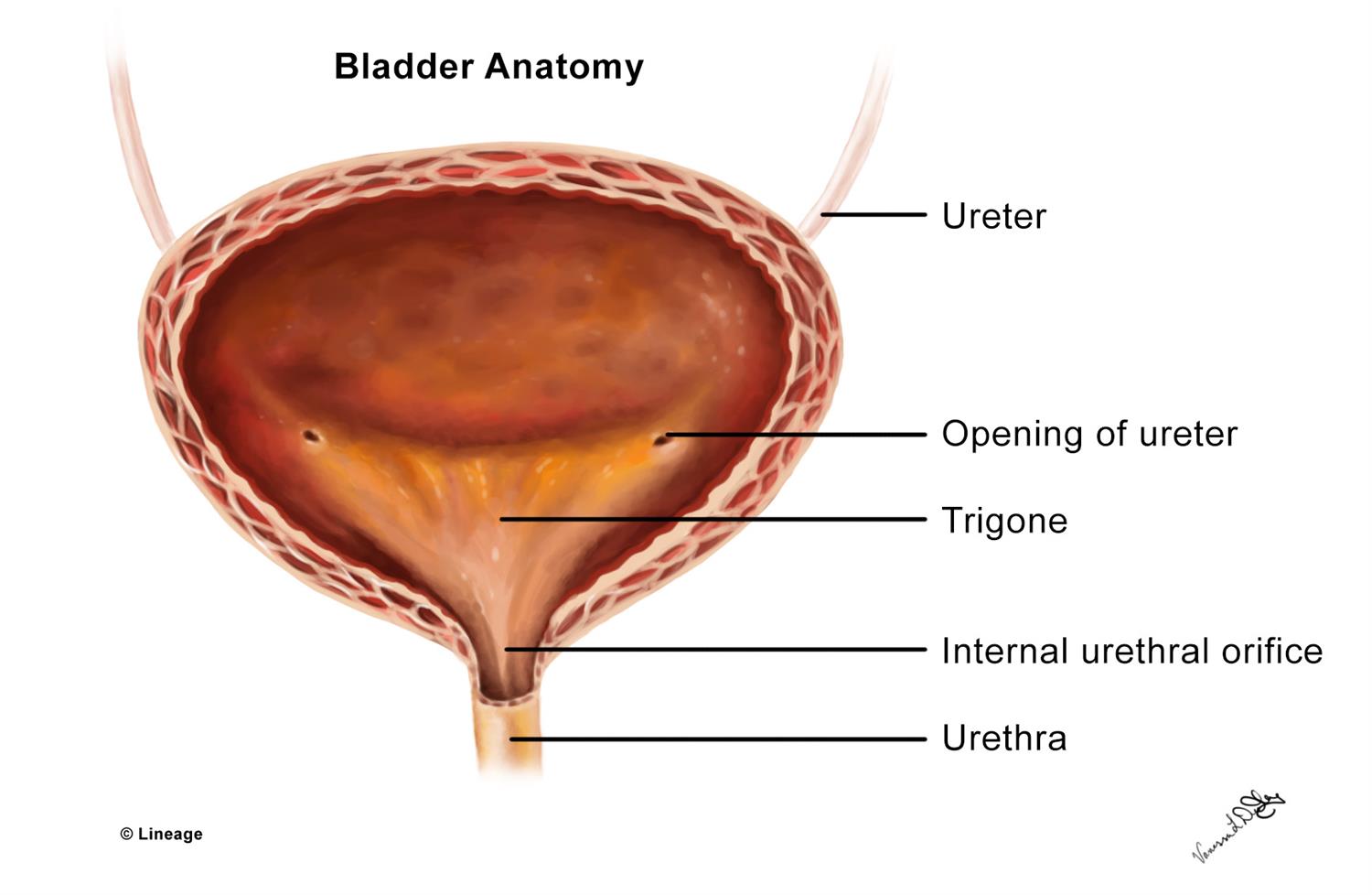
Urethra Size Females / Males
Females 1 ½ “ long
Males 7 to 8 “ long
what is a Scout Image
Demonstrated position and mobility of kidneys
Urography
general term used for radiographic procedure used to investigate the renal drainage system
What is always needed for Renal Parenchyma?
Contrast medium is needed, done in Antegrade
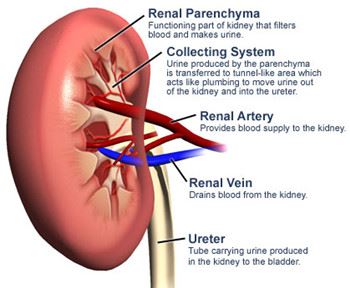
Antegrade
with the flow of bodily fluids
How is Antegrade administered
Percutaneous or IV
How is Antegrade work
Contrast enters kidneys in normal direction of blood flow, usually intravenously
Intravenous Urography
IVU - Includes all parts of Urinary System
Percutaneous Urography
involves direct injection into renal pelvis through percutaneous access of the kidney, NOT IV
Pyelography
means demonstration of renal pelvis and calyces only
Retrograde
against the flow; contrast is introduced against normal flow into ureters or bladder via catheter
When is Retrogade used?
bladder, lower ureters, urethra
What type of concentration is required for bladder studies and why?
Lower concentration; because a large amount required to fill bladder
What type of concentration is used for excretory urography?
Higher
Which contrast medias is less likely to cause an adverse reaction?
Nonionic
Patient Prep
low residue diet for 1-2 days
non-gas laxative when indicated the day before the exam
NPO after midnight the day of exam
pt should be well hydrated
Retrograde Urography hydration prep
should drink 4 - 5 cups of water several hours before exam
oscopy
through a scope
gram/graphy
x-ray pictures
Why is ureteral compression applied?
in excretory urography, compression is sometimes applied over the distal ends of the ureters
centered over the ASIS
When do you NOT use Compression?
if patient has:
Urinary Stones
Abd mass
Aortic Aneurysm
Colostomy
Suprapubic cath
Trauma inury
Respiration
made at end of expiration
Intravenous Urography demonstrates
structures and function of kidneys
Recurrent Urolithiasis
Stones cogenital abdnomalities
GFR
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Normal GFR
90 to 120 mL/min
Normal Creatinine
0.5 to 1.2mg/100mL
GFR With Renal Dysfunction
<90 mL/min
Time needed for Nephogram, Renal Pelvis, Kidneys
30 seconds - best demonstrates a nephrogram
2 - 8 min contrast begins to appear in the renal pelvis
15 - 20 min greatest concentration of contrast within kidneys
Most common IVU projections
AP with 3- 20min intervals
how often are obliques taken for IVU
30* posterior oblique taken 5 - 10 min intervals
AP Urinary Sytem PT Position
upright to demonstrate kidney mobility
kidneys drop 2” from supine to upright
to best demonstrate distal ureters
transdelenburg position, head lowered 15 - 20 *
Urinary System C/R
Perp to center of IR at level of iliac crest
Urinary System AP Demonstrates
kidney, ureters and bladder
pubic symphysis
prostate region for males
Can be done PA to demonstrate ureteropelvic region and for filling the obstructed ureter in presence of hydronephrosis
AP Oblique Part Position
30*
Kidney farthest away will appear parallel with IR
Kidney closest will appear perpendicular
AP Oblqiue C/R
Enters approx 2 inches lateral to midline on elevated side at the iliac crest
Lateral Urinary Sytem CR
Perp to IR at iliac crest
Dorsal Decubitus Urinary System CR
Horizontal and perp to center of IR
enters patient at MCP at level of iliac crest
Doral Decubitus Urinary Sytem demonstrates
UPJ in the presence of hydronephrosis
can demonstrate extrarenal mass in intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal
Hydronephrosis
Stones, kidney or bladder
Retrograde Urography
Done to examine pelcialyseal system and ureters by using catheters to administer contrast directly into the area against normal flow
Retrograde Cystography
Exams of urinary bladder after introducing contrast into bladder with a cath passing through urethra
Projections Retrograde Cystogram
AP/PA Axial, Lateral, AP Oblique, Post Voide
AP Axial urinary Bladder CR
Angled 10 to 15 * caudad to center of IR
enters 2 inches above upper pubic symphysis
CR depends on lumbar lordosis
PA Axial Bladder
angled 10 - 15* cephlada
enters 1 in distal to coccyx
exits above superior boarder of pubic symphysis
AP Oblqiue pt Position
40 - 60 * posterior oblique position
AP Oblique Bladder CR
Perp to IR
CR will fall 2 in above the upper boarder of pubis symphysis and 2 in medial to upper ASIS
IF bladder neck is of interest AP OBLIQUE
10 * CAUDAL of CR will project pubic bones below them
Lateral Bladder CR
perp to IR
enters patient level 2 in above upper boarder of pubic symphysis
Male CYSTOURETHROGRAPHY (on test) pt position
Recumbent 35 - 40 * posterior oblique