Paper 1: Theme 3 - Business behaviour and the labour market
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
A firm
A firm is a production unit that transforms resources into goods and services
Reasons why some firms tend to grow:
Increase market share
Benefit from greater profits
Increase economies of scale
Gain power to prevent potential takedowns by larger businesses
What is the principal-agent problem
The principal is the shareholder/owner of the business, while the person in charge of the day-to-day runnings is the agent.
A private-sector firm
Those that are not owned by the government
A public sector firm
A firm that is owned by the government, either because they could not survive without significant state funding or the government wishes to determine the direction the business takes.
Organic/internal growth
Achieved by investment within the firm by the firm, expanding the scale of operations and gaining market share
Advantages/Disadvantages of organic growth
Lowest-risk form of growth
Control of the firm remains unchanged
Good for worker’s morale as there will be more job opportunities within the firm
Tends to be slow
Building on the existing knowledge of current employees = people might be unaware of or unwilling to take on new innovations
Inorganic growth
Through the horizontal/vertical integration of firms
Horizontal integration
Merger of two firms at the same stage of production
Advantages/Disadvantages of horizontal integration:
Increased market share
Reduced competition
Economies of scale
Risks - too many eggs in one basket
Weakening/ ‘dilution’ of brand name
unknown costs
Diseconomies of scale
Conglomerate integration
Merger between firms in unrelated industries
Constraints on business growth
Regulation: licenses and patents
Marketing barriers: imposed by businesses currently operating in the market. failed marketing investment is sunk costs
Pricing barriers: limit and predatory pricing
Technical barriers: some firms have such large economies of scale that no small firm can have a competitive price. to compete, the new firm would have to operate on the same scale - but then there’d be so much supply that profit would be eroded
Size of the market: niche market won’t support expansion
Lack of resources: growth may be beyond the owner’s knowledge, expertise or funds
Already operating at Minimum Efficient Scale
Owner objectives: not worth the lost leisure time or risk of investing money
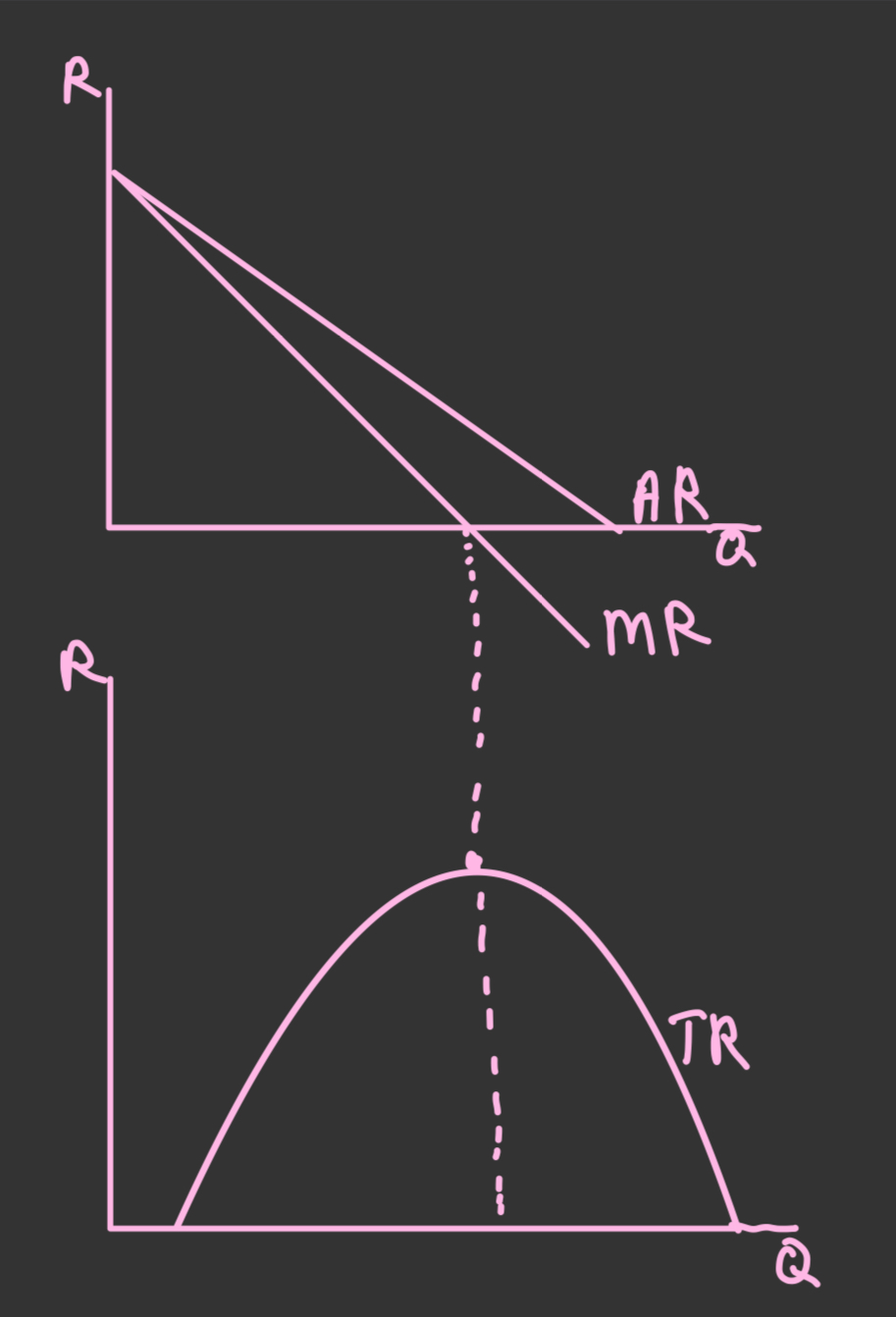
Total revenue
The amount the firm recieves from all its sales over a certain period
TR = price x quantity
Average revenue
How much people pay per unit (price) and also the demand curve
Total revenue
——————- = AR
Quantity
Marginal revenue
The revenue associated with each additional unit sold, i.e. the change in total revenue from selling one more unit/
Is the gradient of the total revenue curve
PED
% change in QD
———————- = PED
% change in P
Calculate percentage change
New value - Old value
—————————— = % change
Old value
Short run
The time period in which at least one factor of production is fixed
Fixed costs
Costs that do not vary with output
These can occur in the short run only
Total cost
All the rewards to the factors of production: wages, rent, interest, normal profit
Average cost
Average cost per unit of output
Marginal cost
The change in total cost when one additional unit of output is produced.
change in total cost / change in quantity
Economies of scale
A fall in long-run average costs as output increases
Internal v.s. External economies of scale
Internal: Occur when an individual firm expands
External: Have an impact on the entire industry, lowering the Long Run Average Cost curve
Types of internal economies of scale:
Financial economies: as a firm grows, it’s more able to access loans at a low cost
Risk-bearing economies: wider customer base and range of products minimise risk
Marketing economies: as a firm expands its product range, it is able to use any central brand marketing to advertise the range
Relationship between short-run and long-run average cost curves
The LRAC is made up of many SRACs joined together at their lowest points
Profit maximisation
Occurs where MC = MR, and MC is rising
It is where the firm maximises profits or minimises losses
Revenue maximisation
When MR = 0
Occurs when a firm seeks to make as much revenue as possible
Sales maximisation
AR = AC
When a firm maximises sales of its output while still achieving normal profit
Allocative efficiency / welfare maximisation
Producing where P = MC, maximising producer and consumer surplus
When goods are produced in a way that maximises overall societal welfare and utility
Productive efficiency
Occurs at the lowest point on the AC curve
Producing goods and services at the lowest possible cost
Dynamic efficiency
The ability of a firm to innovate and adapt to new technologies and techniques over time
X-inefficiency
Occurs when the average cost is higher than the lowest possible average cost - the firm is operating above the AC curve
Satisficing
When a firm aims to make a minimum accepted level of profit and then pursues other aims
Predatory pricing
Pricing below costs to drive out other firms.
Firm makes a loss in the short run, but as the other firms leave the prices are raised higher as theres less competition.
This is an anti-competitive practice and can lead to fines by competition authorities
Limit pricing
Pricing at a level low enough to discourage entry of new firms
Exploits economies of scale that an incumbent firm has, and is not necessarily illegal in the UK
Cost-plus pricing
Making a fixed percentage mark-up on average costs
Methods of non-price competition:
Advertising
Branding - loyalty cards
Customer service
Packaging - free gifts
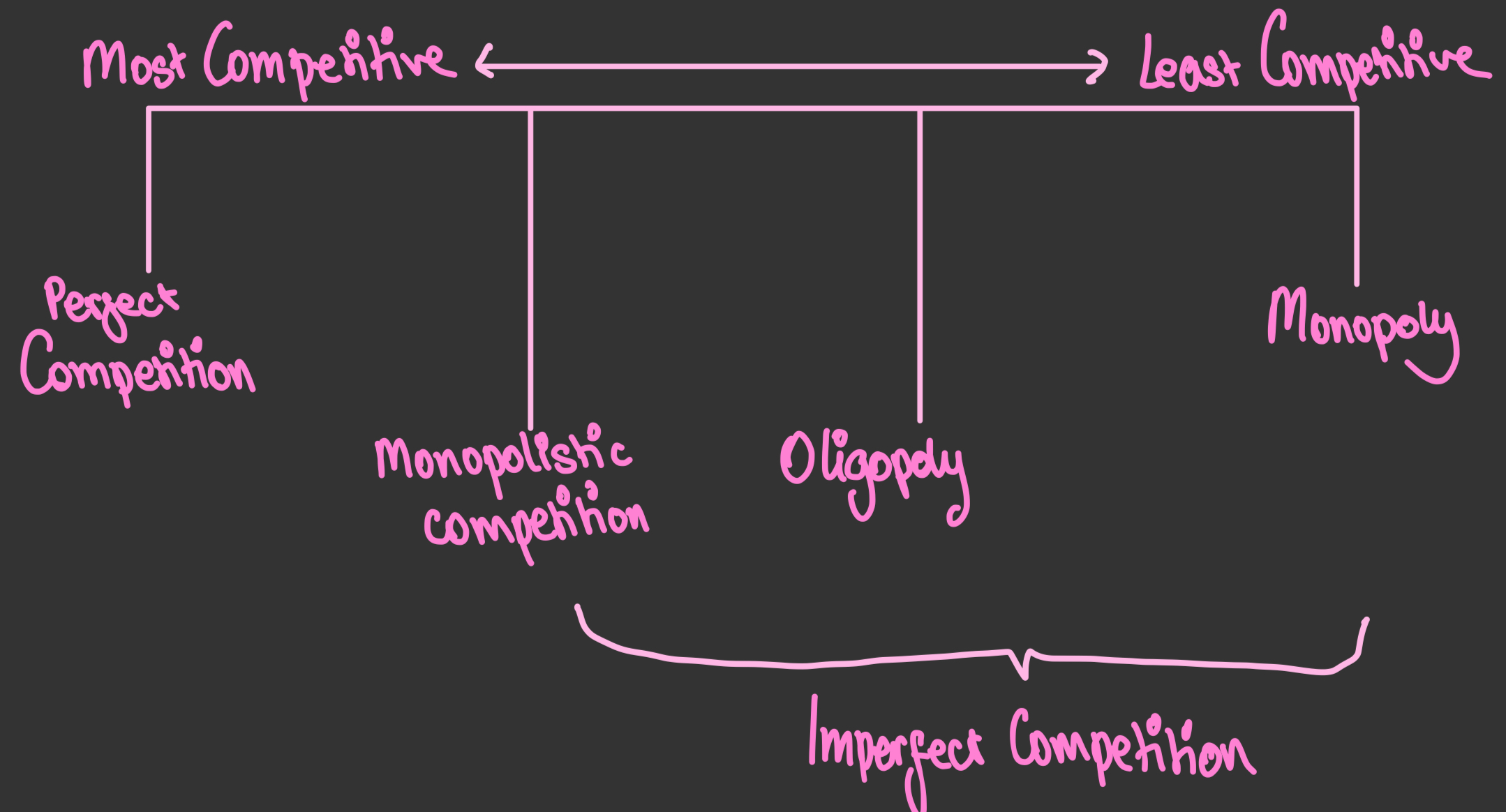
What are the four models of market sellers?
Concentration ratio
The market share controlled by the ‘n’ largest firms - e.g. four firm concentration ratio
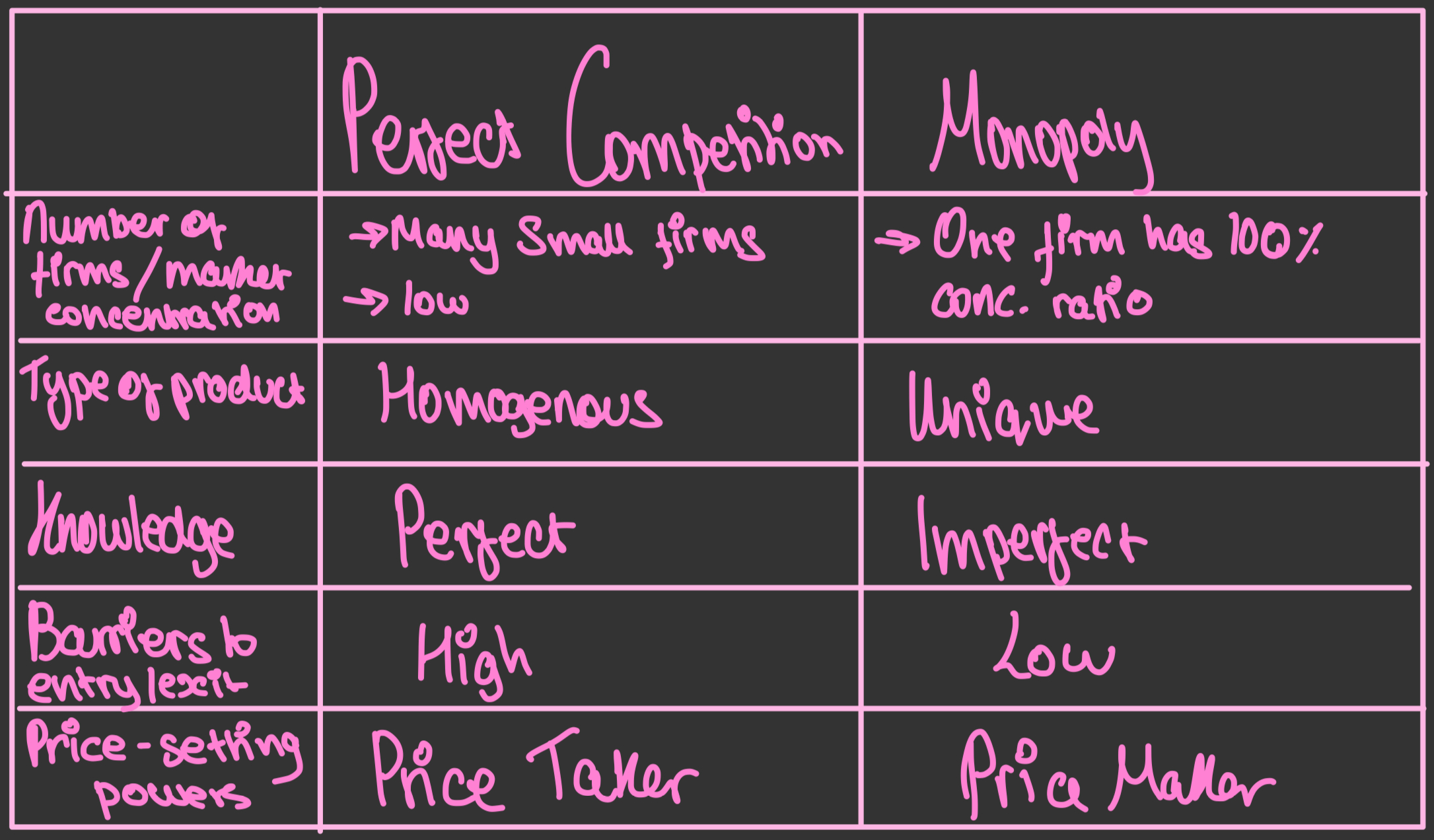
Perfect competition VS Monopoly
When does the shutdown point of a firm occur
When the firm is no longer covering Average Variable Costs
Monopolistic Competition
A market with many small firms that supply goods that are slightly differentiated, allowing them some price-setting powers
Oligopoly
A market dominated by a few large firms - often associated with interdependence and collusion
Interdependence
The actions of one firm in an industry will impact on the other firms in the industry
Why is there low price competition in oligopolies?
If one firm were to lower prices, the others would follow, and they would lose revenue from the price war that would ensue
Collusion
An agreement between two or more firms to limit competition and work together to fix prices and avoid price wars
Overt collusion VS tacit collusion
Overt collusion: when firms openly fix prices, output, marketing, or the sharing of customers
Tacit collusion: implicit collusion with maybe no spoken agreement
Price fixing
Firms coming together to ensure that prices remain stable, thus avoiding price competition
Advantages of monopoly power:
Supernormal profit means:
finance for investment and Research and Development
Firms can create savings to overcome difficulties = job stability for employees
Monopoly power means firms will have the financial power to match large overseas competitiors
May be able to take the best advantage of economies of scale
Disadvantages of monopoly power:
Supernormal profit means less incentive to be efficient and innovative
More ability to raise barriers to entry, e.g. exerting pressure on suppliers that rely on the monopoly
Higher prices and lower output
May waste resources by undertaking cross-subsidisation, using profits from one sector to finance losses in another
Price discrimination
The sale of the same good to two different markets at different prices
Under what conditions will price discrimination be successful?
There are high barriers to entry and a degree of monopoly power
There are at least two seperate markets with differing price elasticities of demand
The markets can be kept separate at a cost that is lower than the gain in profits.
This is to prevent resale between the markets
Natural monopoly
One that exists when an industry can only support one firm
When an industry has high sunk costs and requires very large levels of output to exploit economies of scale
Sunk costs
Costs that a firm cannot recover, e.g. advertising
Monopsony
Where there is a sole buyer of a good. Firms can use these powers to exploit their suppliers and drive down prices
Advantages and disadvantages of monopsony
Lower prices are passed on to consumers
Quality may be better than perfect competition - buyers can be extremely picky
Monopsony power may balance out monopoly power - monopoly charges a high price, monopsony forces them to drive the price back down
Contestable market
A market with low sunk costs and therefore low barriers to entry and exit.
Nationalisation
Refers to the process by which the government takes ownership of a private company or industry
Advantages of nationalisation:
Public interest: essential services such as healthcare and education operated for public interest instead of private profit
Social equality: when certain industries owned and operated by the state, the benefits generated can be more evenly distributed among the population
Service quality: less focus on profits = more focus on quality
Job security: people argue that private companies prioritise profits over job security
Disadvantages of nationalisation:
Inefficiency and bureaucracy: State-owned enterprises lack the incentives for innovation and cost-effectiveness
Risk aversion: due to the lack of direct compeitition and guarantee of government support. This can hinder entreprenaurial spirit and potential rewards
Misallocation of resources: without the price mechanism
Competitive tendering
The process by which a number of private sector firms compete to win the right to perform a task on behalf of the government. They will charge the government for the particular task and seek to make a profit.
What are two types of market failure from labour:
Geographical immobility: Occurs when people cannot relocate to another part of the country to take up job opportunities
Occupational immobility: When workers are unable to change jobs due to a lack of skills or training