Glucocorticoids
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
3 layers of adrenal cortex
zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis
Glucocorticoid Effects
Promote normal intermediary metabolism (Hepatic glucose production, lipolysis)
Increase resistance to stress
Alter blood cell levels in plasma (decrease eiosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes - increase RBCs and PLTs
Anti-inflammatory action
name the short acting glucocorticoids
Hydrocortisone
Cortisone
name the intermediate acting glucocorticoids
prednisone
prednisolone
methylprednisolone
triamcinolone
name the long acting glucocorticoids
Betamethasone
Dexamethasone
corticosteroids includes
glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
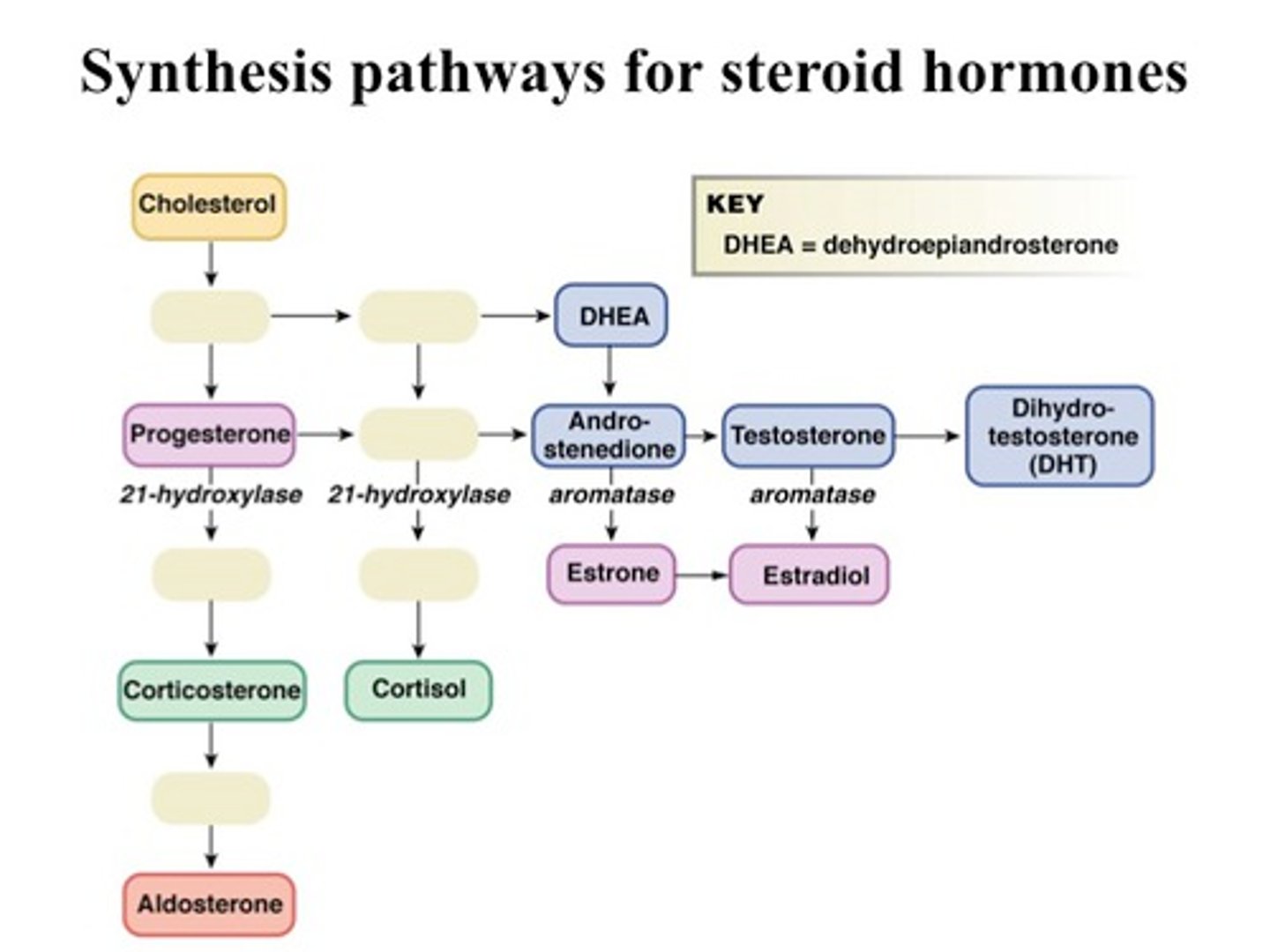
Name the mineralocorticoids
Fludrocortisone
Name the mineralocorticoid antagonists
Spironolactone, Eplerenone
MOA hydrocortisone
Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
Therapeutic use hydrocortisone
Addison disease replacement therapy
ADE hydrocortisone
HPA suppression; Cushingoid effects; hyperglycemia; infection risk; osteoporosis
Pearls hydrocortisone
2/3 AM + 1/3 PM dosing; may need fludrocortisone
MOA betamethasone
Glucocorticoid receptor activation
Therapeutic use betamethasone
Promote fetal lung maturation
ADE betamethasone
Hyperglycemia; infection risk
Pearls betamethasone
Crosses placenta; given IM 48 hours before delivery
MOA dexamethasone
Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
Therapeutic use dexamethasone
Dexamethasone suppression test (Used to diagnose Cushing syndrome); fetal lung maturation; inflammation
ADE dexamethasone
Typical glucocorticoid ADEs
Name the 3 layers of the adrenal glands and what they secrete
zona glomerulosa -> aldosterone
zona fasiculata -> cortisol and androgens
zona reticularis -> NE and Epi
MOA prednisolone
Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
Therapeutic use prednisolone
Inflammatory conditions
ADE prednisolone
Systemic steroid ADEs
what do corticosteroids regulate?
carbohydrate metabolism
MOA fludrocortisone
Mineralocorticoid agonist
Therapeutic use fludrocortisone
Adrenal insufficiency
ADE fludrocortisone
Hypertension; fluid retention; hypokalemia
Pearls fludrocortisone
Titrate based on BP and upright posture; half-life >24 hrs
MOA spironolactone
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; androgen blocker
Therapeutic use spironolactone
CHF; hyperaldosteronism; hirsutism in women
ADE spironolactone
Hyperkalemia; gynecomastia; menstrual irregularities
MOA eplerenone
Selective aldosterone receptor antagonist
Therapeutic use eplerenone
CHF; hyperaldosteronism
ADE eplerenone
Hyperkalemia
Pearls eplerenone
Lower endocrine side effects than spironolactone
ADE of long-term glucocorticoids
HPA suppression; drug-induced Cushing syndrome; osteoporosis; hyperglycemia; infections; mood changes; hypertension; GI ulcers
what do mineralcorticoids regulate?
electrolytes
Signs of Cushingoid appearance
Buffalo hump; moon face; hirsutism; central fat redistribution
which glucocorticoid have mineralocorticoid activity
Fludocortisone
effect of sudden discontinuation of steroids
exogenous steroids suppress the HPA axis, leaving the patient unable to produce endogenous cortisol, which can lead to adrenal crisis and death when supplemental steroids are discontinued
someone taking >20 mg prednisone for more than 3 weeks and/or has a cushingoid appearance likely has:
HPA suppression
how do glucocorticoids promote normal intermediary metabolism?
increase hepatic glucose production
stimulate lipolysis
how do glucocorticoids increase resistance to stress?
improve energy availability (mobilize fuel)
how do glucocorticoids alter blood cells in plasma?
decrease eisinophils, basophils, lymphocytes
increase RBCs and platelets
How do glucocorticoids produce anti-inflammatory actions?
decrease inflammatory cytokines
stablize mast cells
block arachidonic acid
inhibit immune cells
Do glucorticoids improve immunity?
NO. They improve survival during infection by preventing the host from being killed by its own inflammatory response.