Unit 3 Aleks Homeworks
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
232 Terms
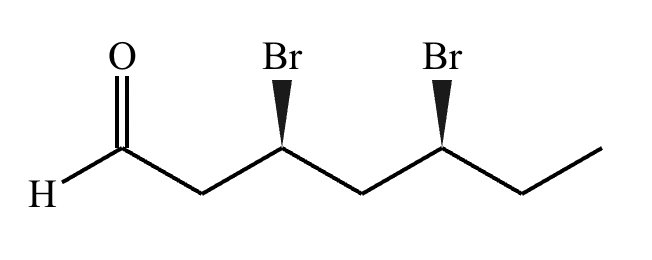
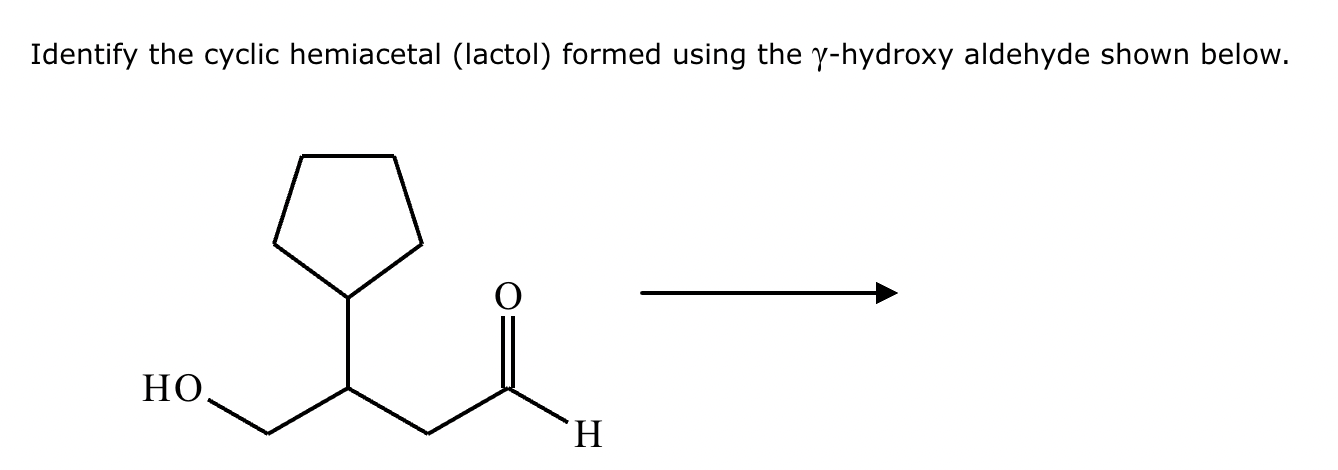
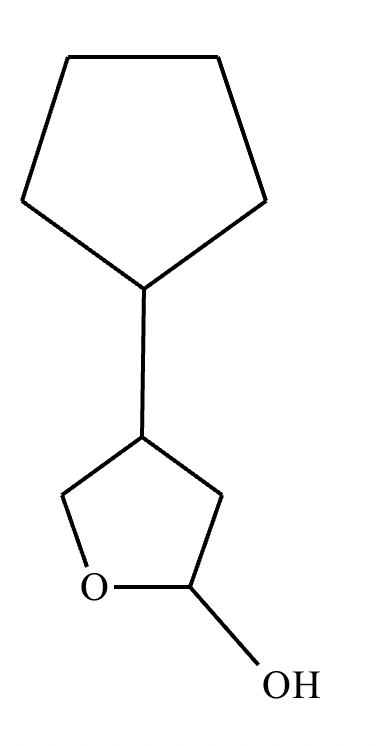
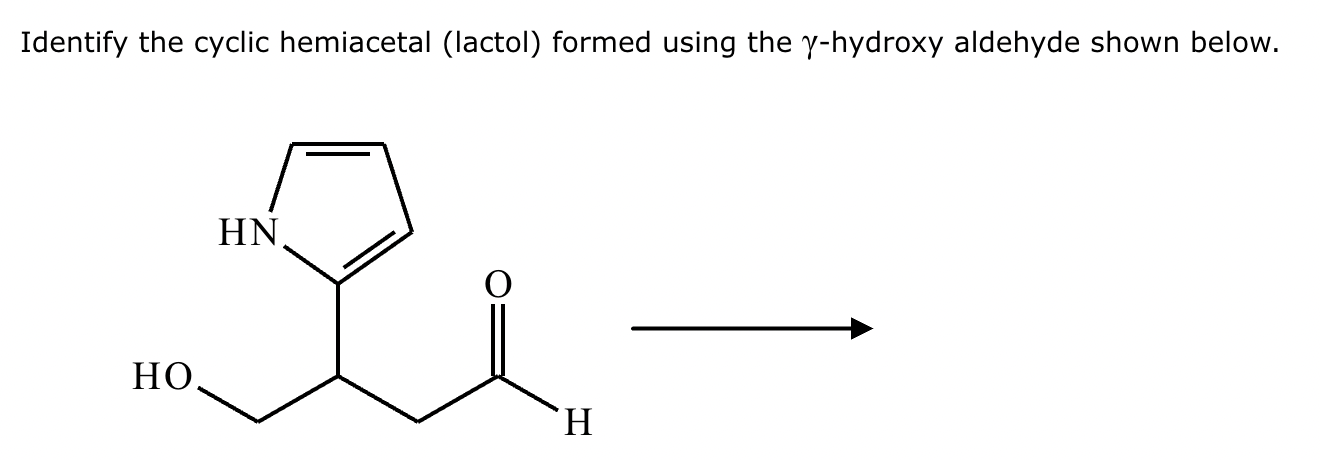
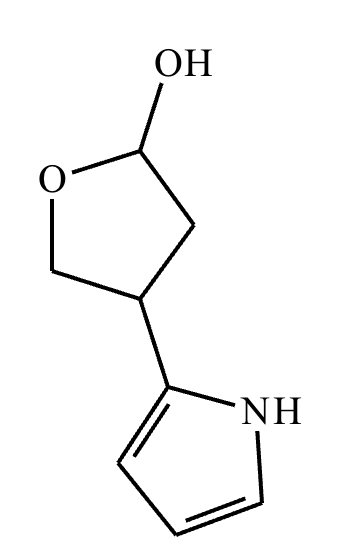
Draw the structure of (3R, 5S)-3,5-dibromoheptanal.
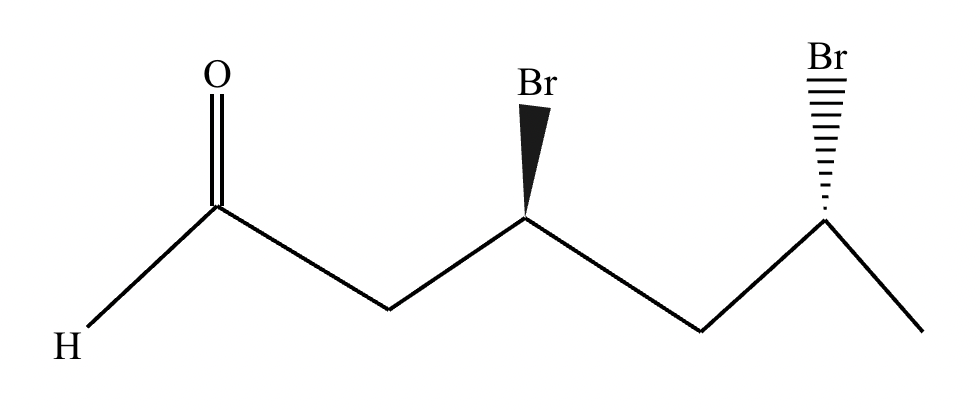
Draw the structure of (3R, 5R)-3,5-dibromohexanal.
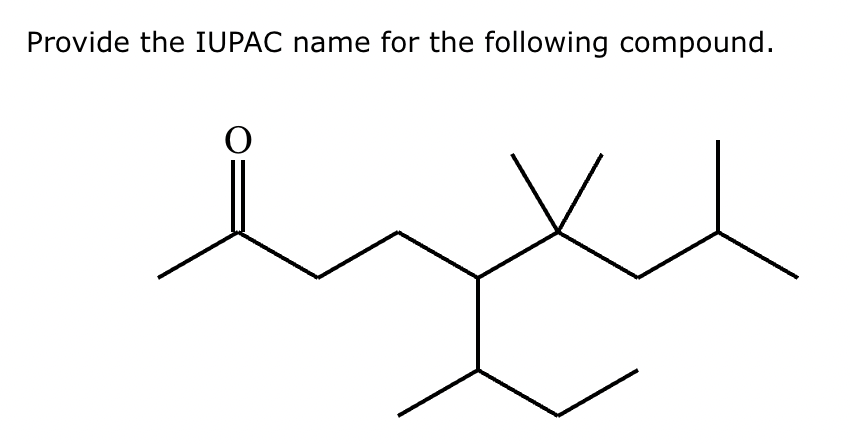
5-sec-butyl-6,6,8-trimethylnonan-2-one.
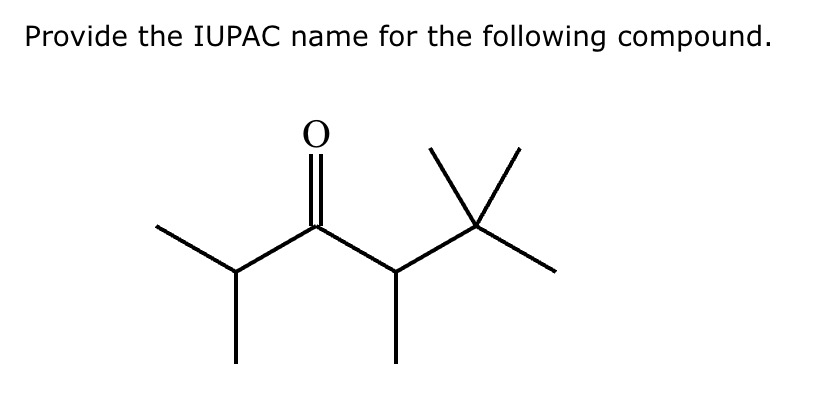
2,4,5,5-tetramethylhexan-3-one.

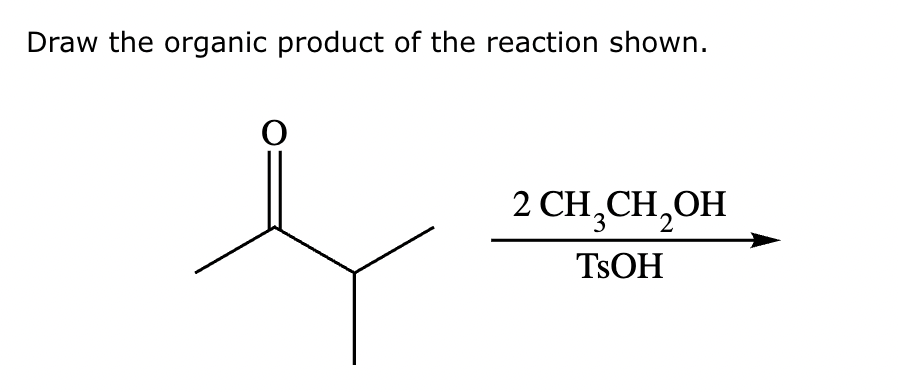
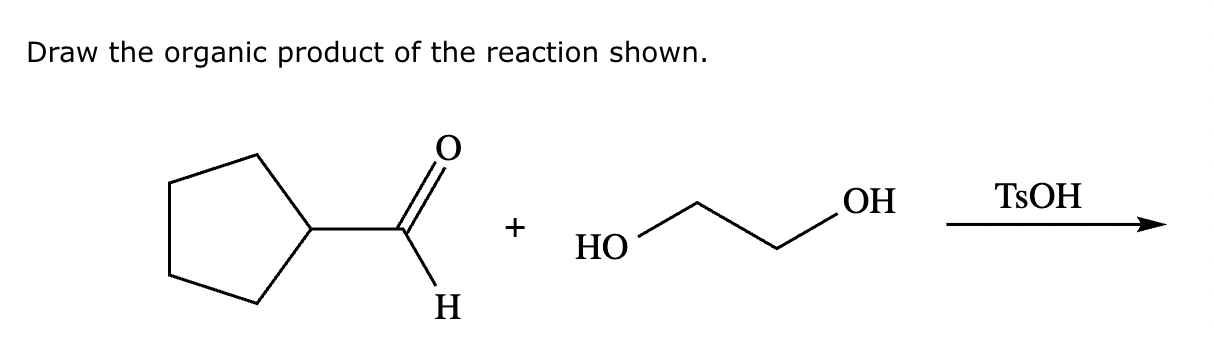
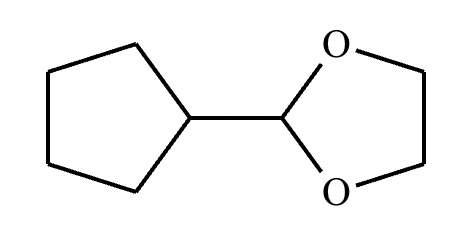
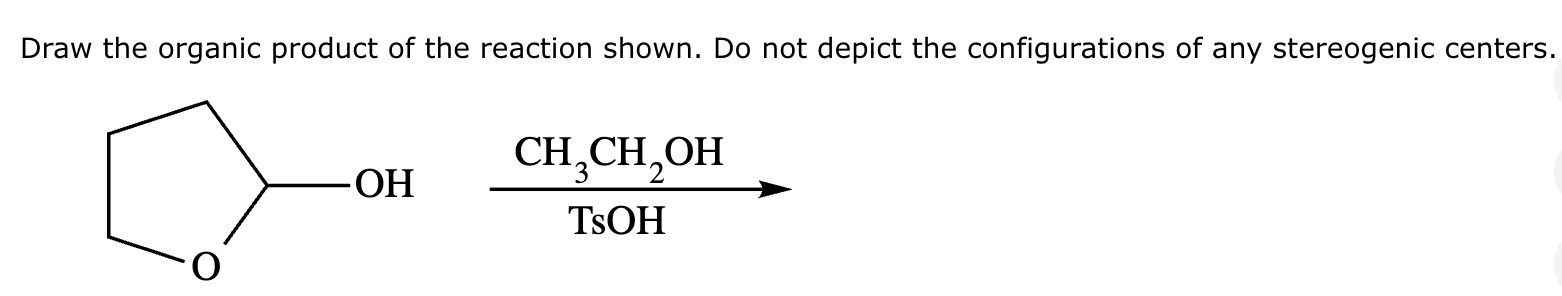
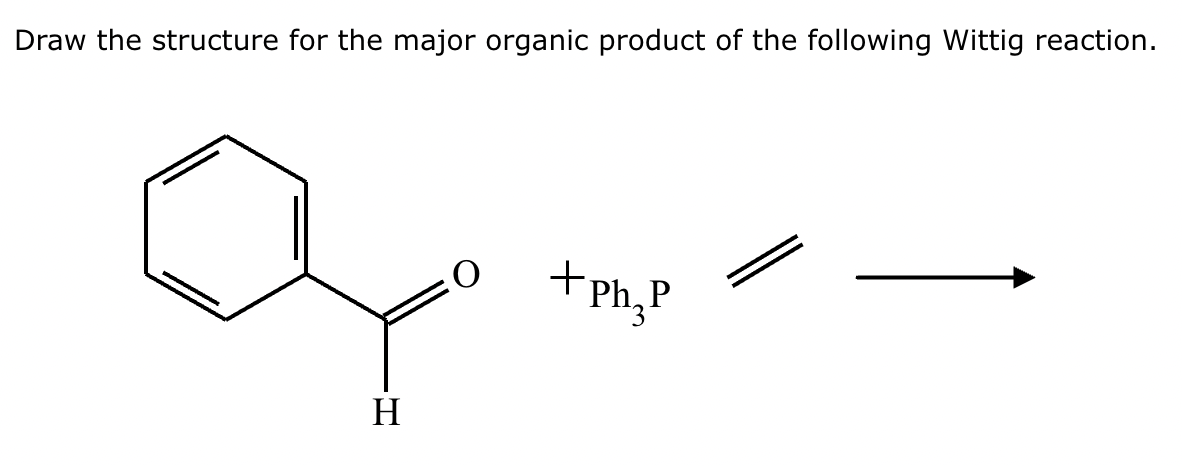
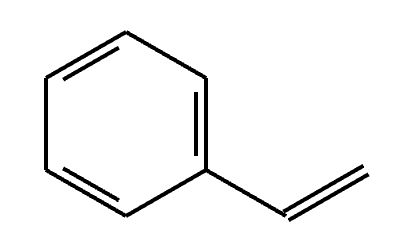
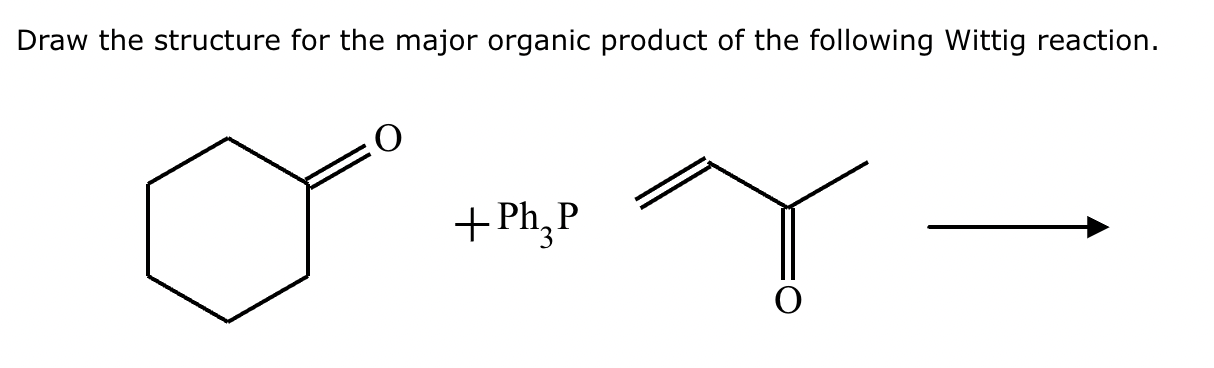
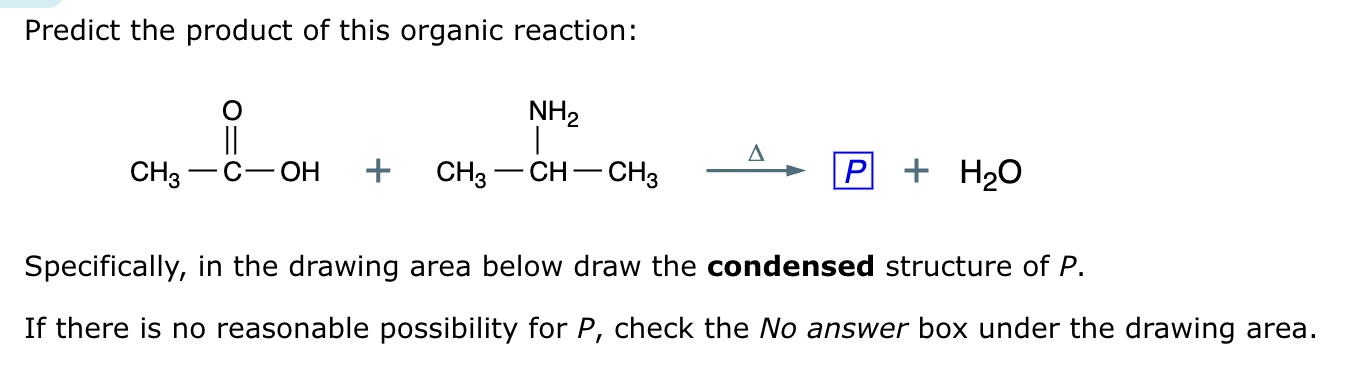
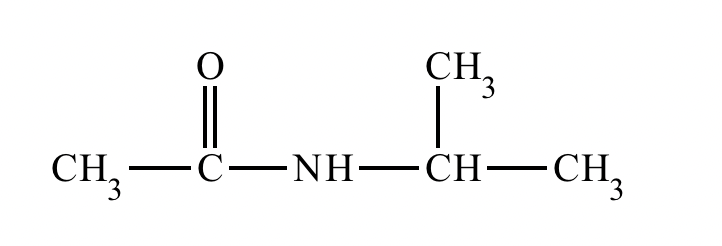
Draw the product of the following reaction. Omit stereochemistry from the product structure.
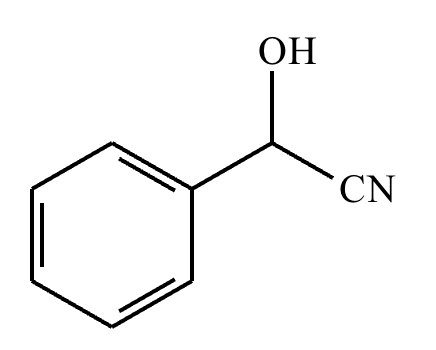
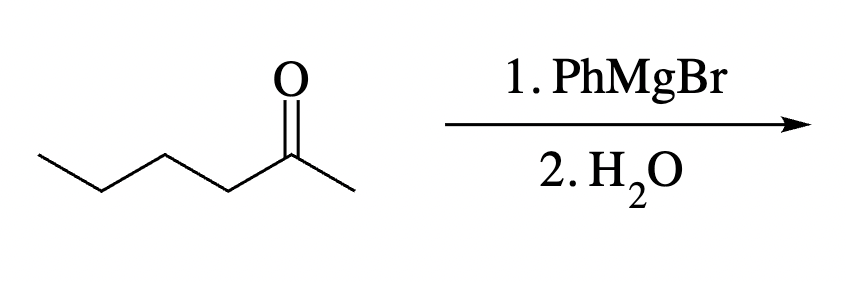
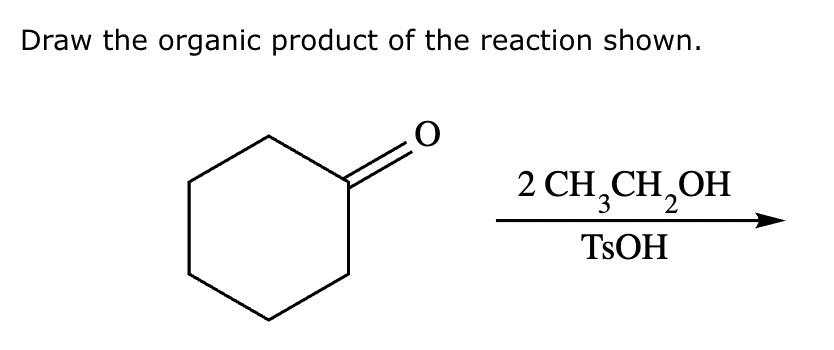
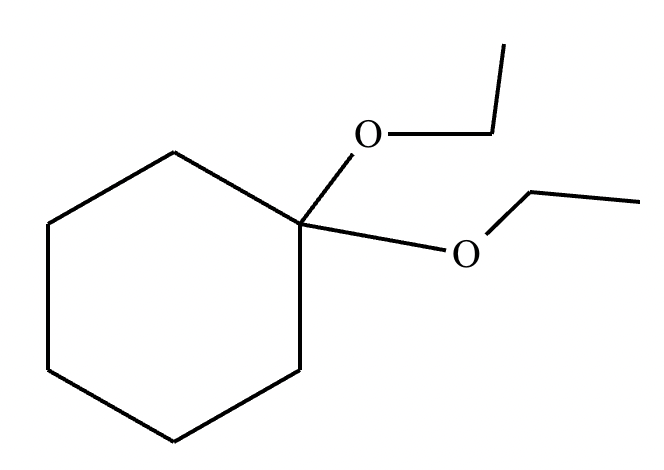
Draw the product of the following reaction. Omit stereochemistry from the product structure.
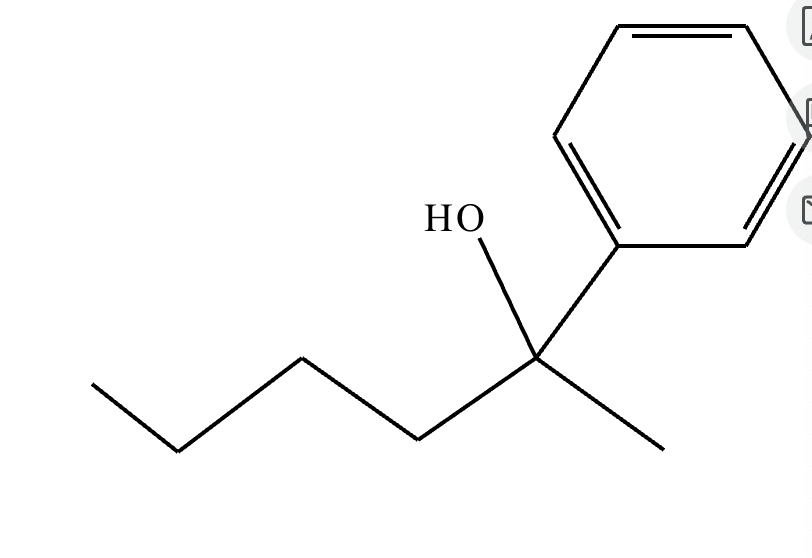
Ph means a phenol group.
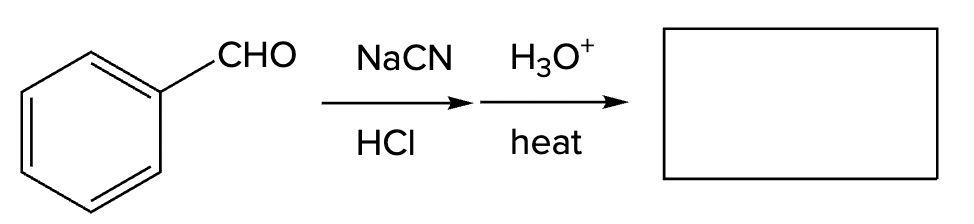
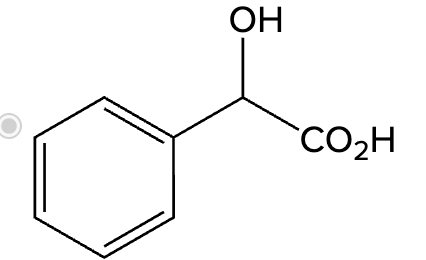
What is the product of this reaction sequence?
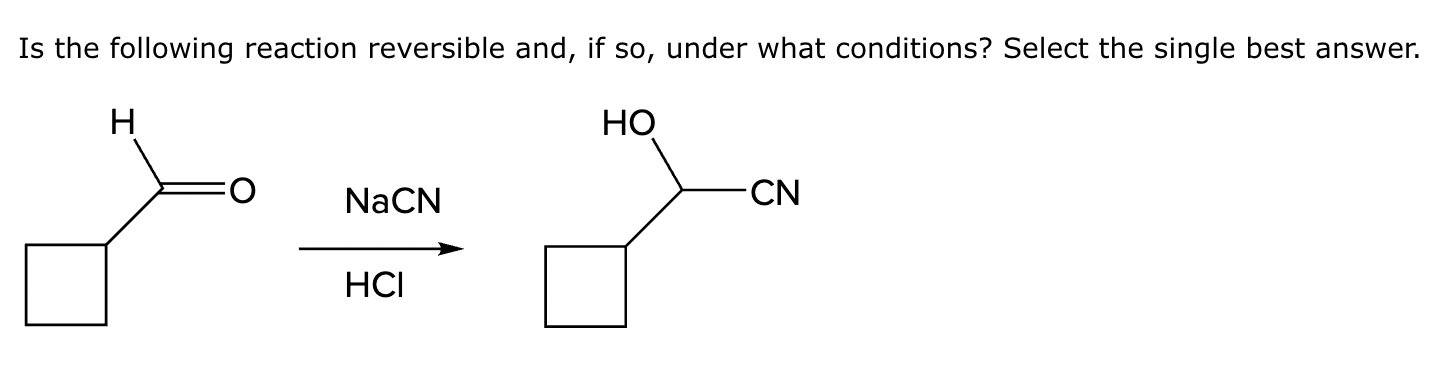
Yes, under basic conditions.
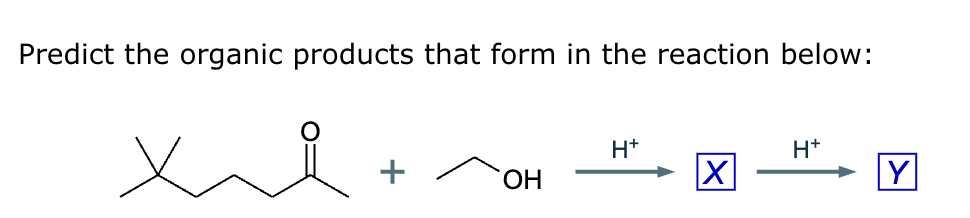
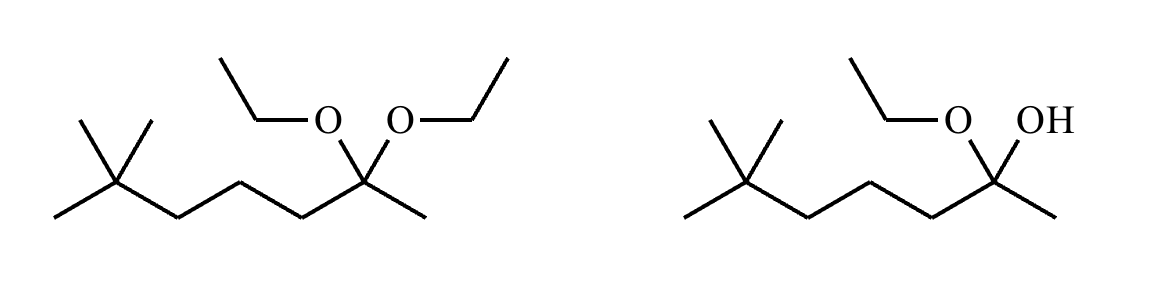
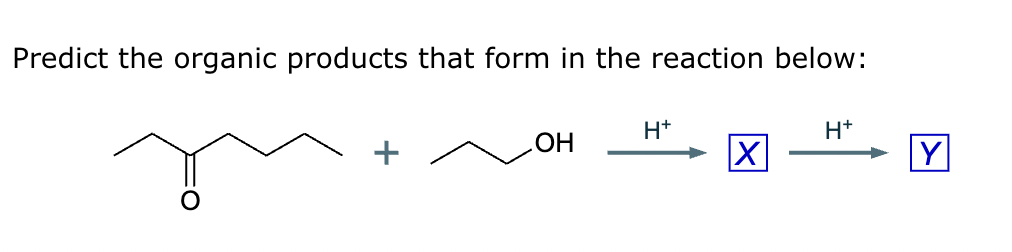
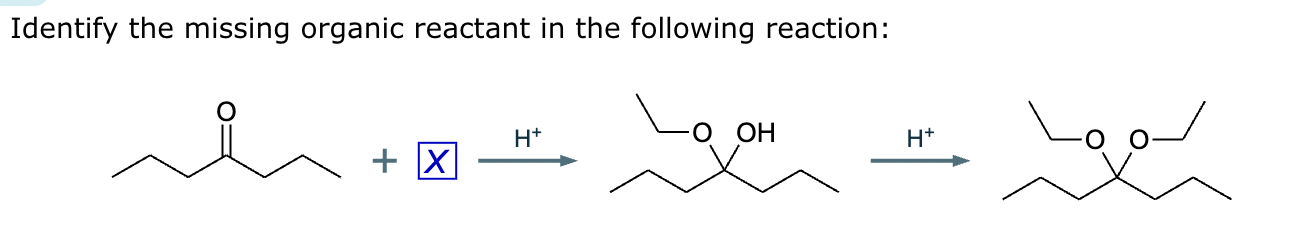
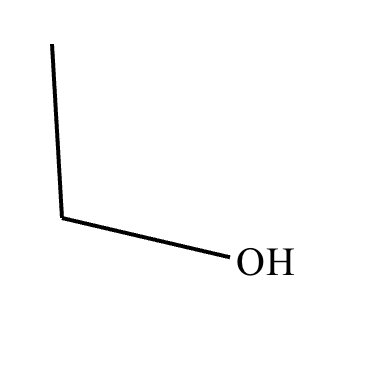




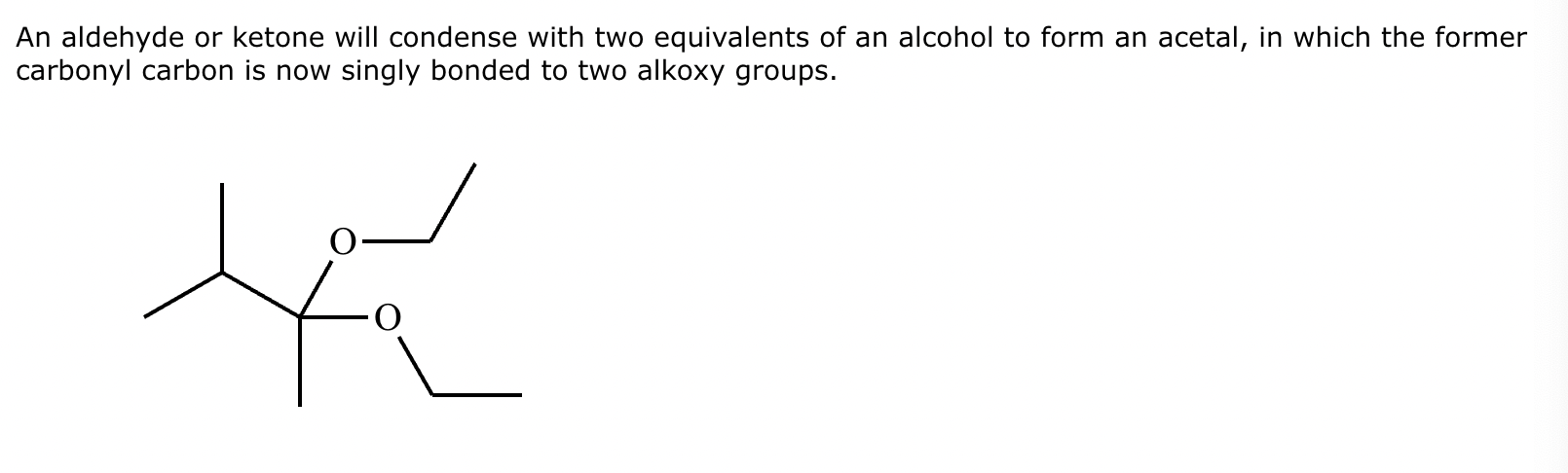
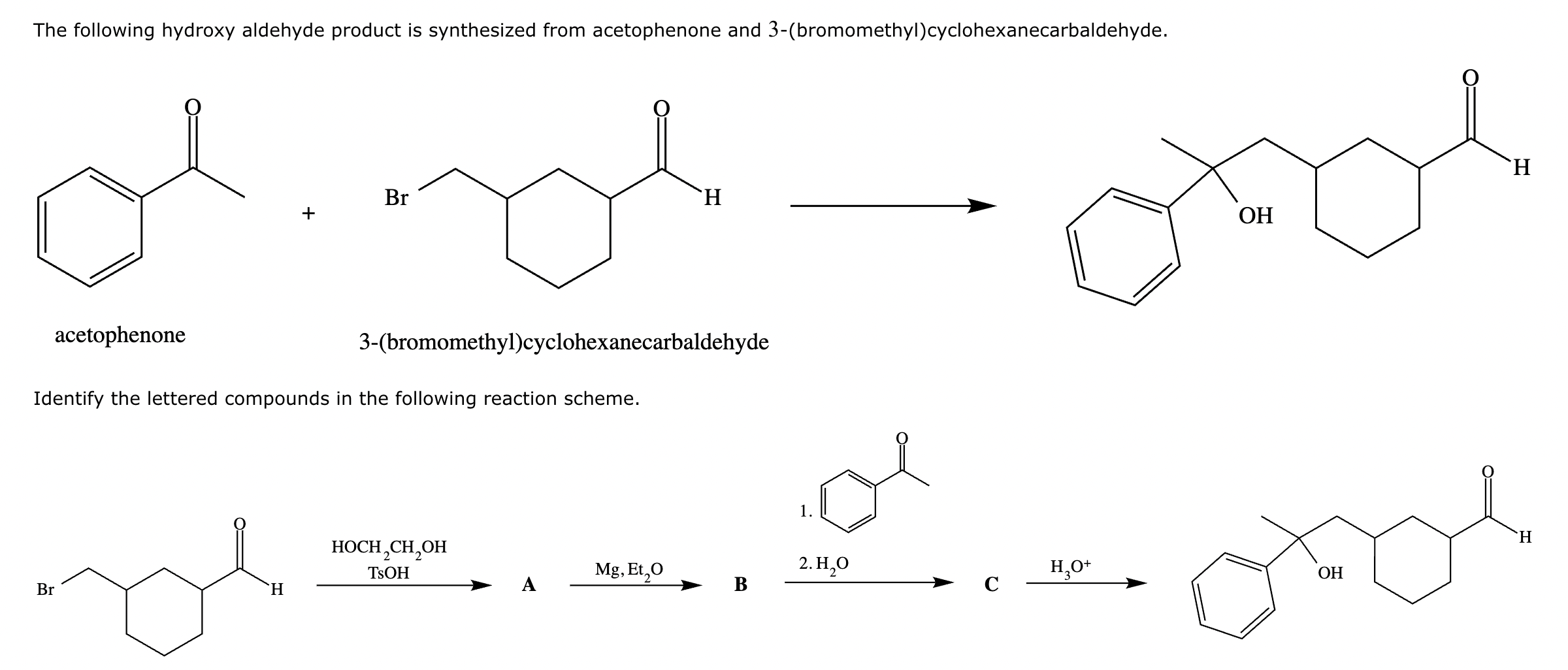
Compound A:
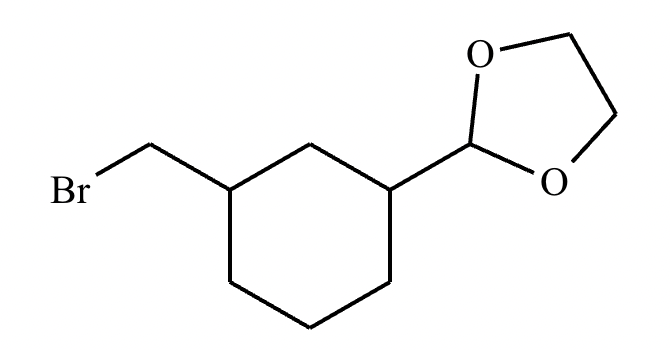
Compound B:
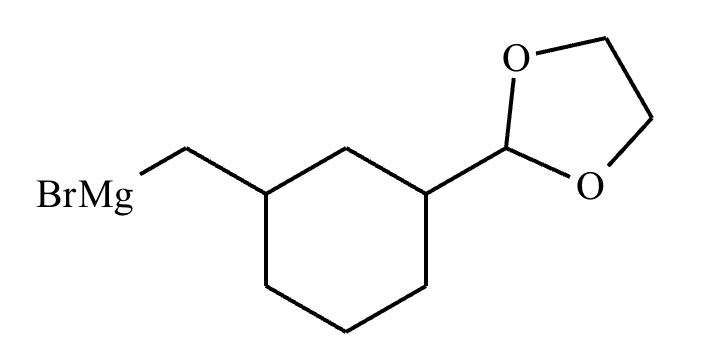
Compound C:
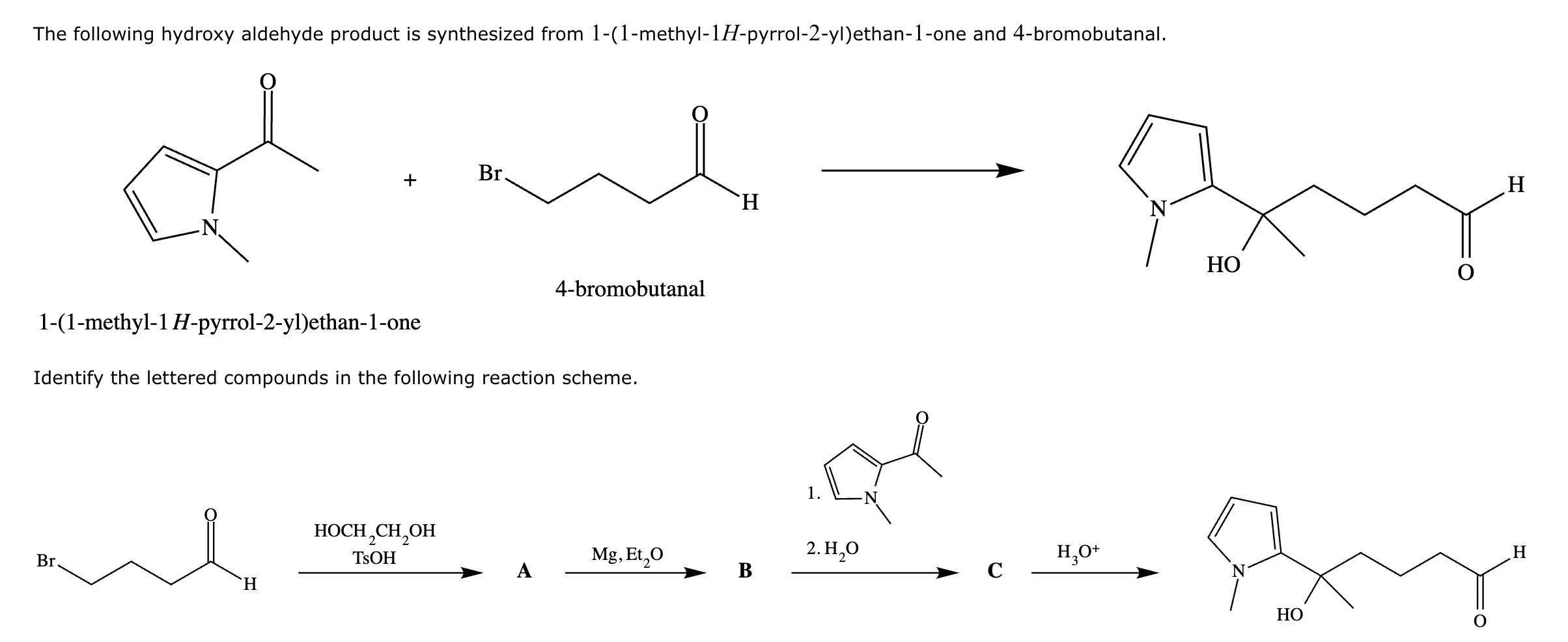
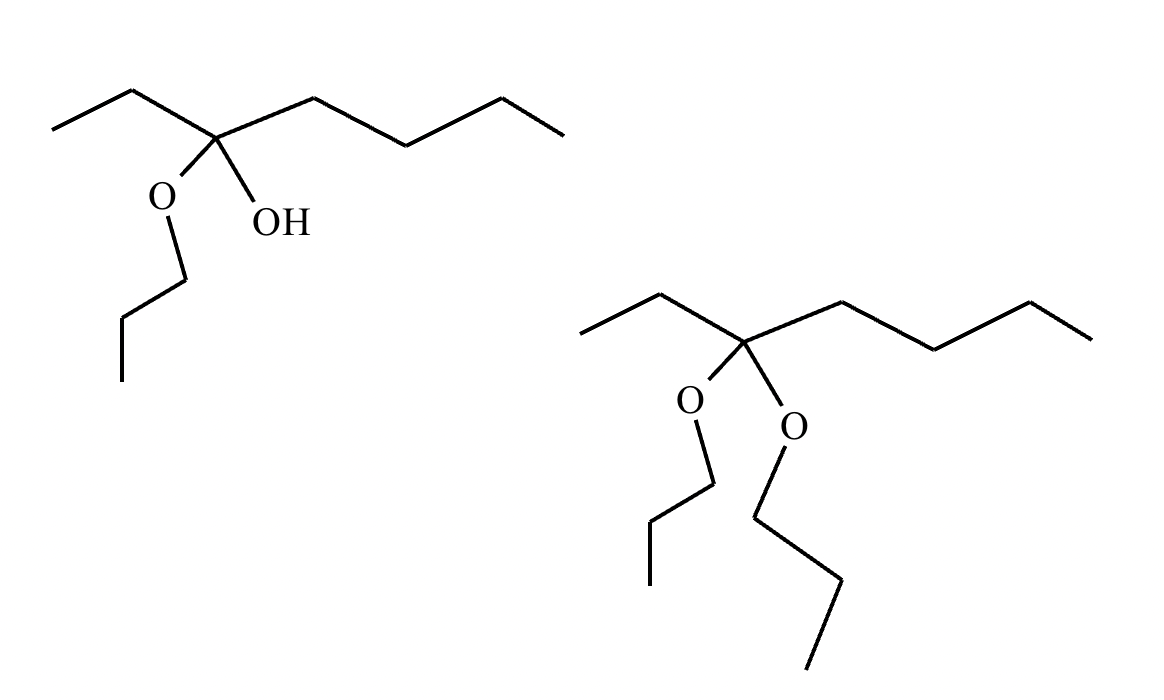
Compound A:
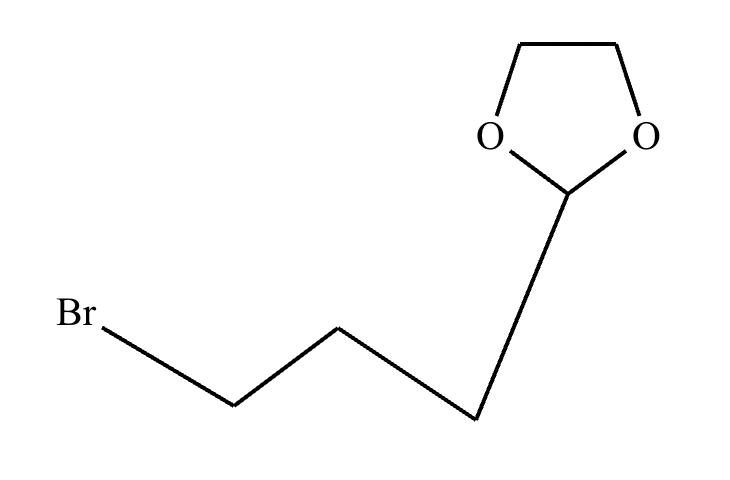
Compound B:
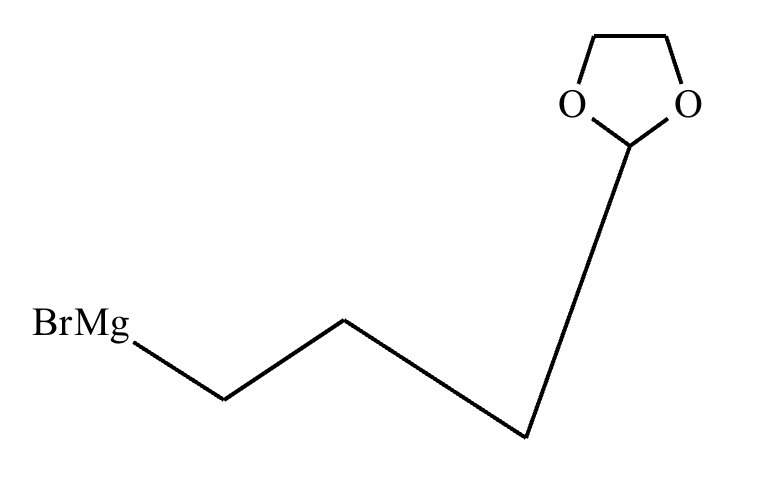
Compound C:
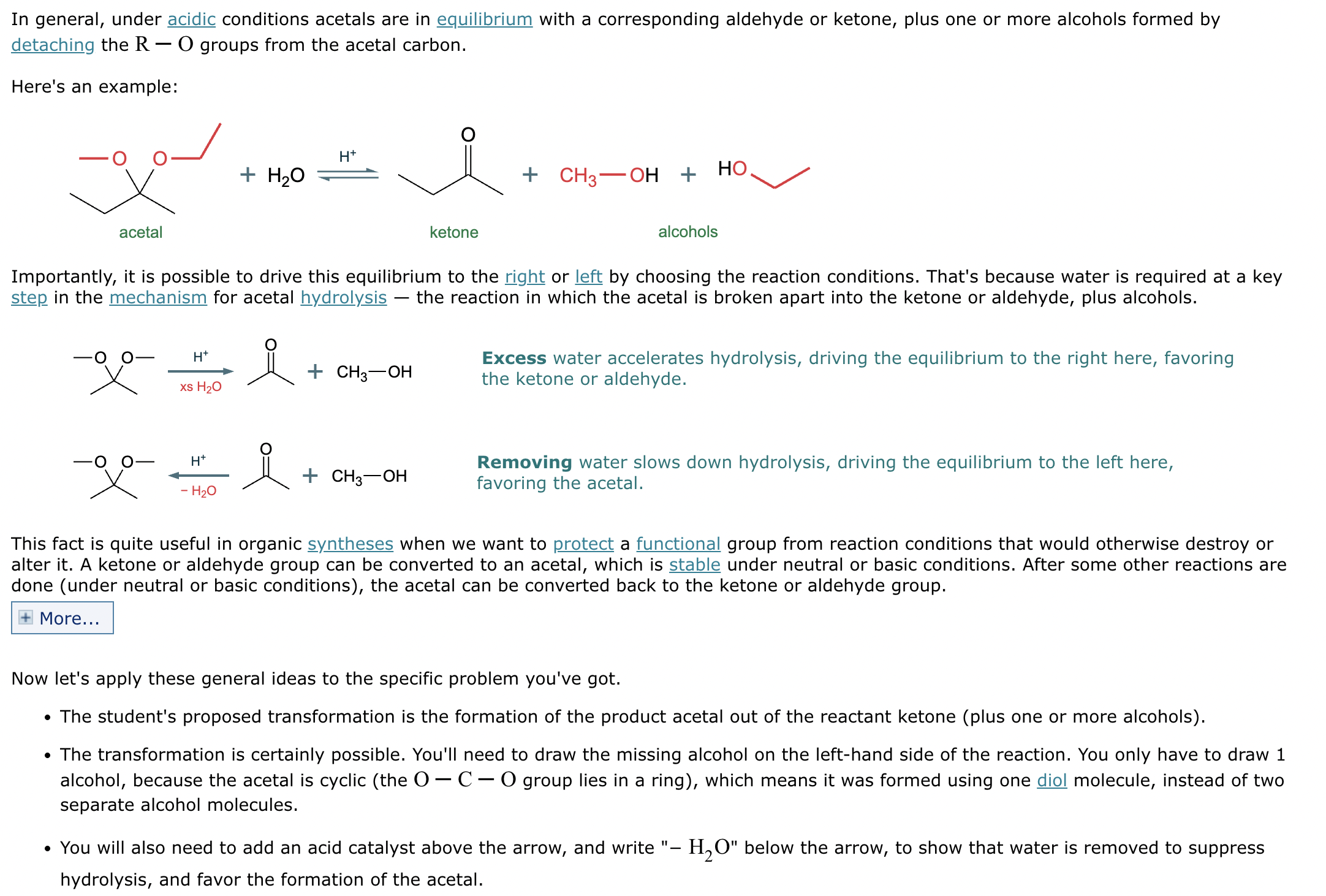
Cyclic acetals are used as protecting groups for ketones or aldehydes because they are inert to many common reagents. Which of the following reagents is an exception, meaning that they will react with cyclic acetals? Select the single best answer.
(a) Reducing reagents
(b) Aqueous base
(c) Aqueous acid
(d) Oxidizing reagents
(c) Aqueous acid
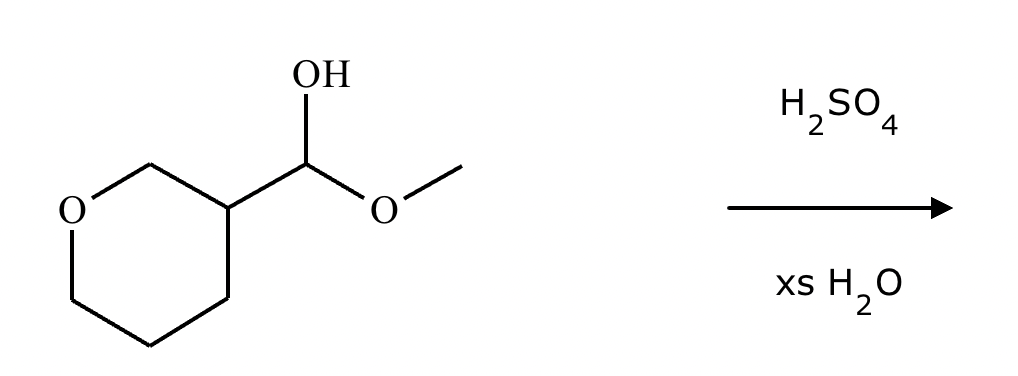
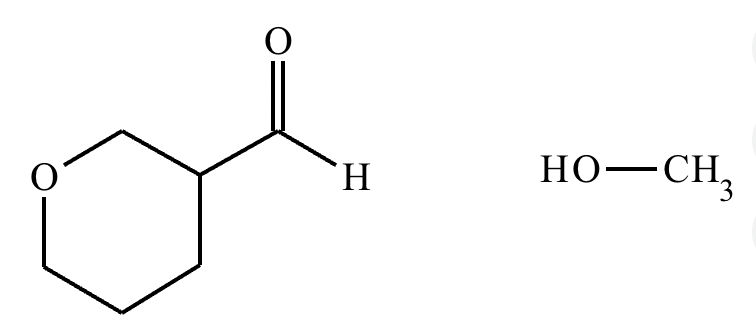
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren’t any products, mark “No reaction.””
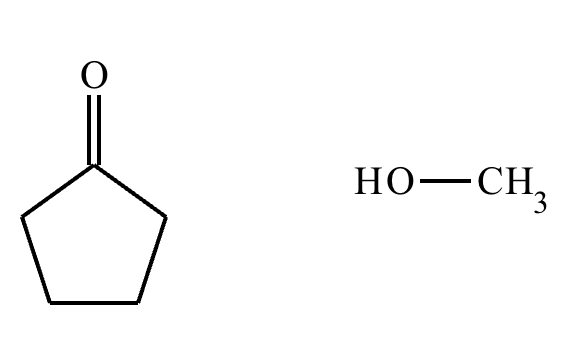
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren’t any products, mark “No reaction.””
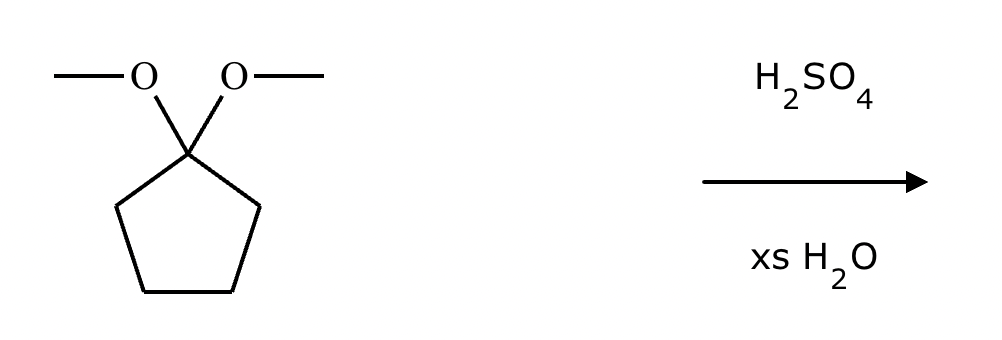
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren’t any products, mark “No reaction.””
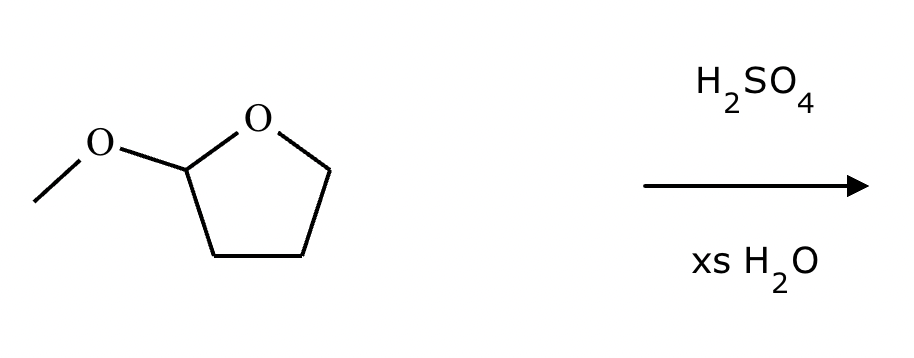
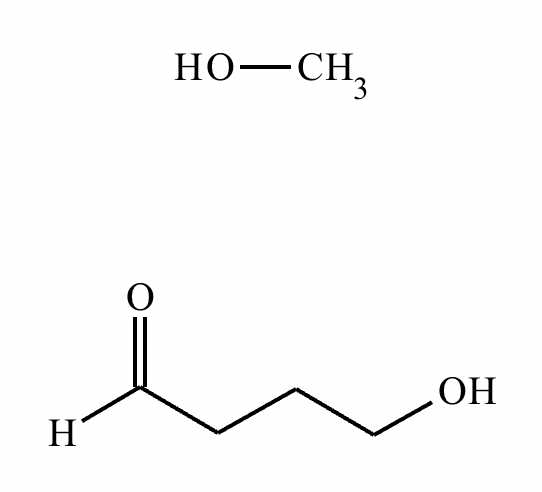
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren’t any products, mark “No reaction.””
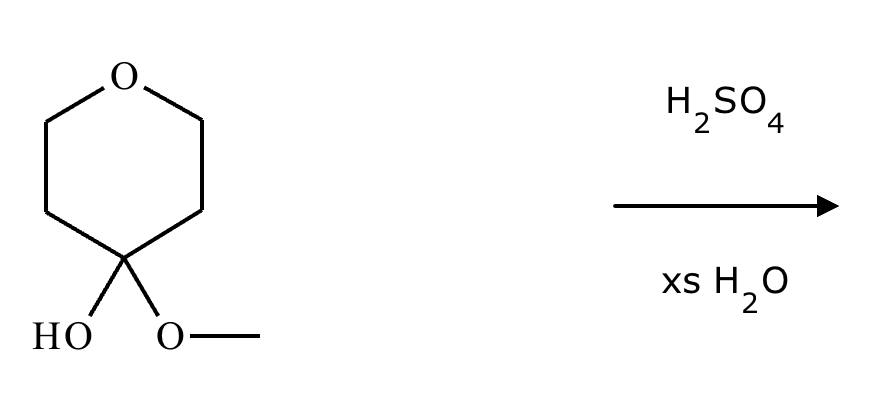
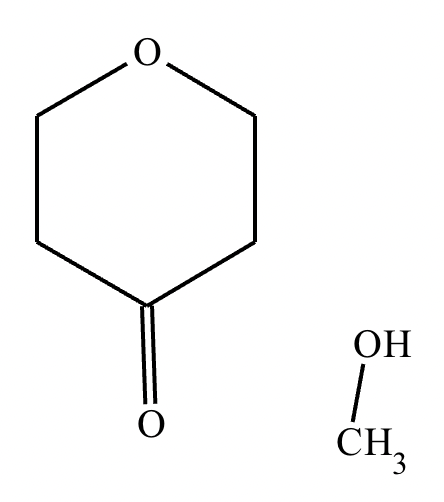
Determine whether the following molecule is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither, and select the appropriate box below. Also, highlight the hemiacetal or acetal carbon if there is one.
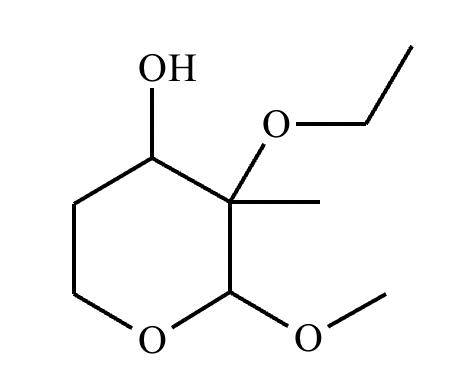
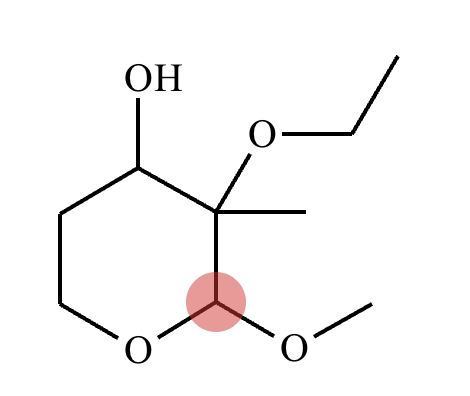
Acetal.

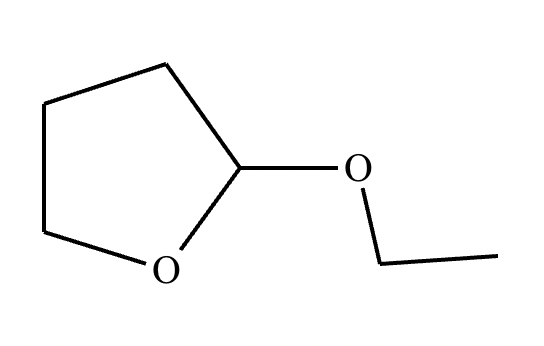
Forms an acetal.
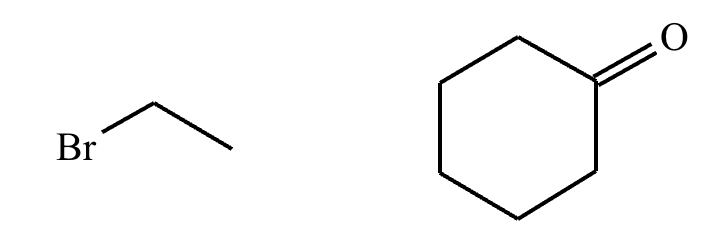
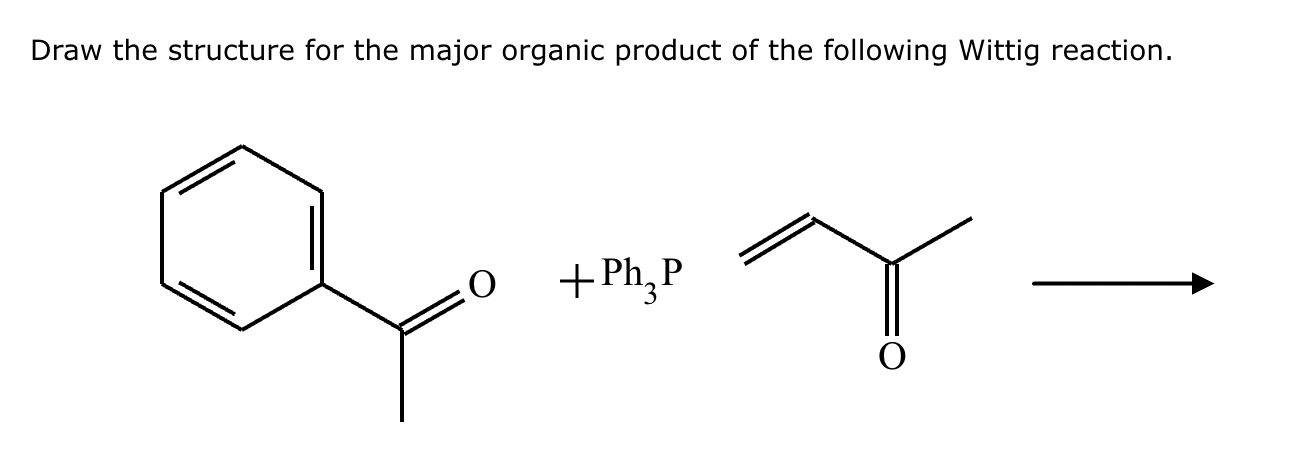
Two different methods can be used to carry out the following transformation: a one-step reaction using a Wittig reagent and a two-step method using a Grignard sequence.
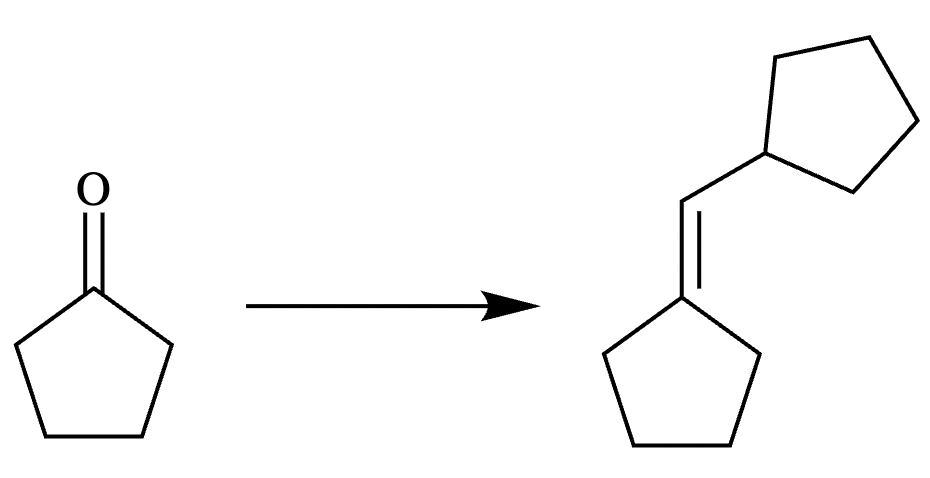
(a) Draw the structure of the required Wittig reagent used for the transformation.
(b) Draw the structure of the required Bromo-Grignard reagent used for the transformation shown below.
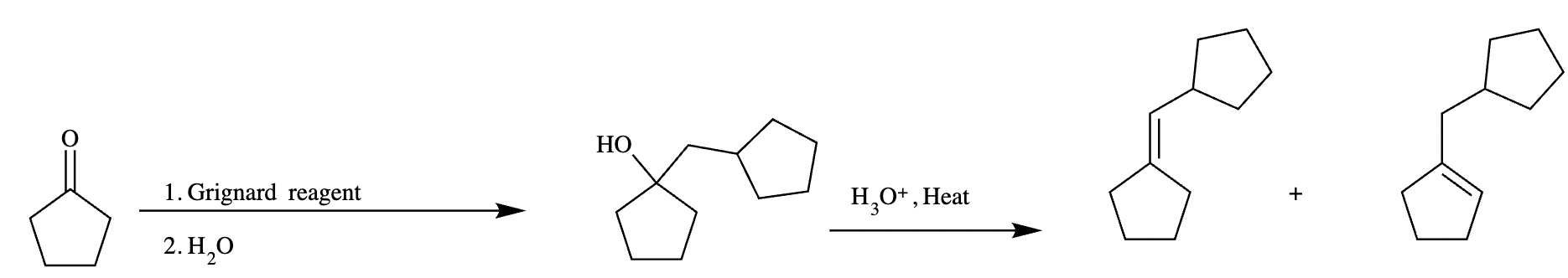
(c) Which route is preferred? The Wittig reaction or the Grignard reaction?
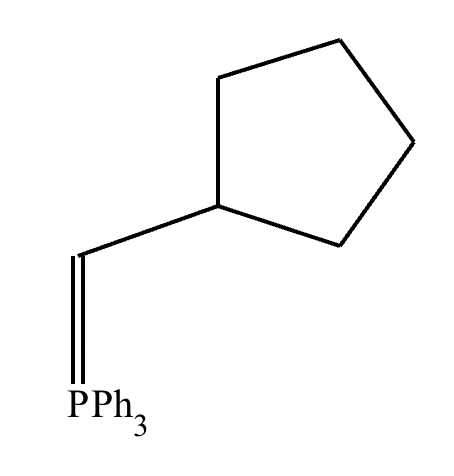
(a)
(b)
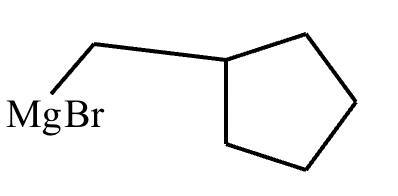
(c) Wittig reaction.
Explanation: The Wittig reaction is often preferred over the Grignard reaction for alkene synthesis because it's a one-step process, yields higher alkene purity, and allows better control over stereochemistry, whereas Grignard reactions are typically used for forming alcohols and are a two-step process.
Wittig reaction produces alkene in a single step and produces a specific product. Mixture of products is not possible in this method. Whereas in the Grignard reagent method mixture of products is obtained. Therefore, the Wittig method is preferred over the Grignard method.
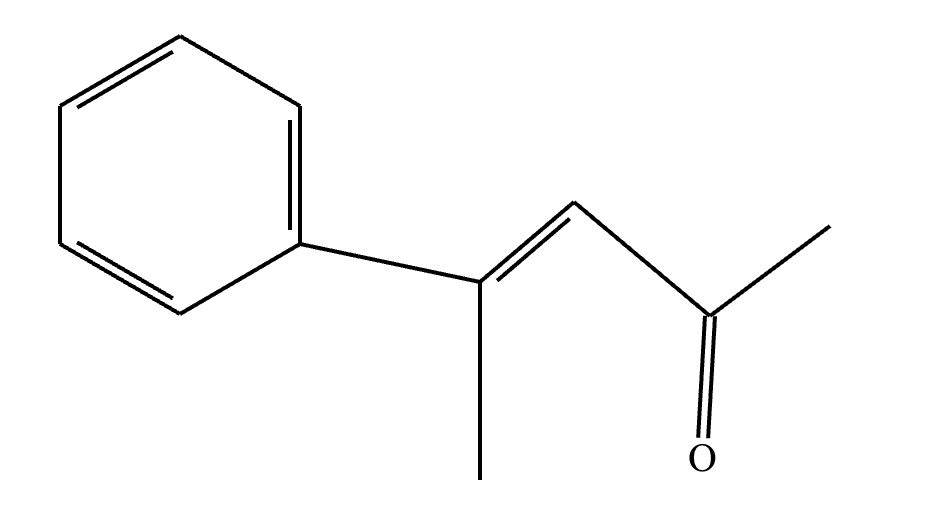
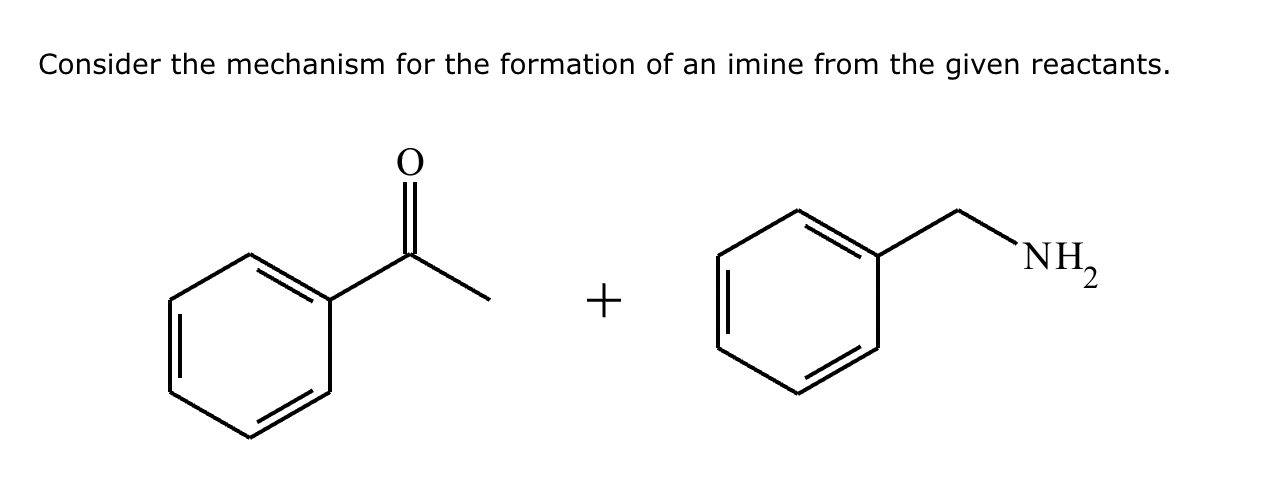
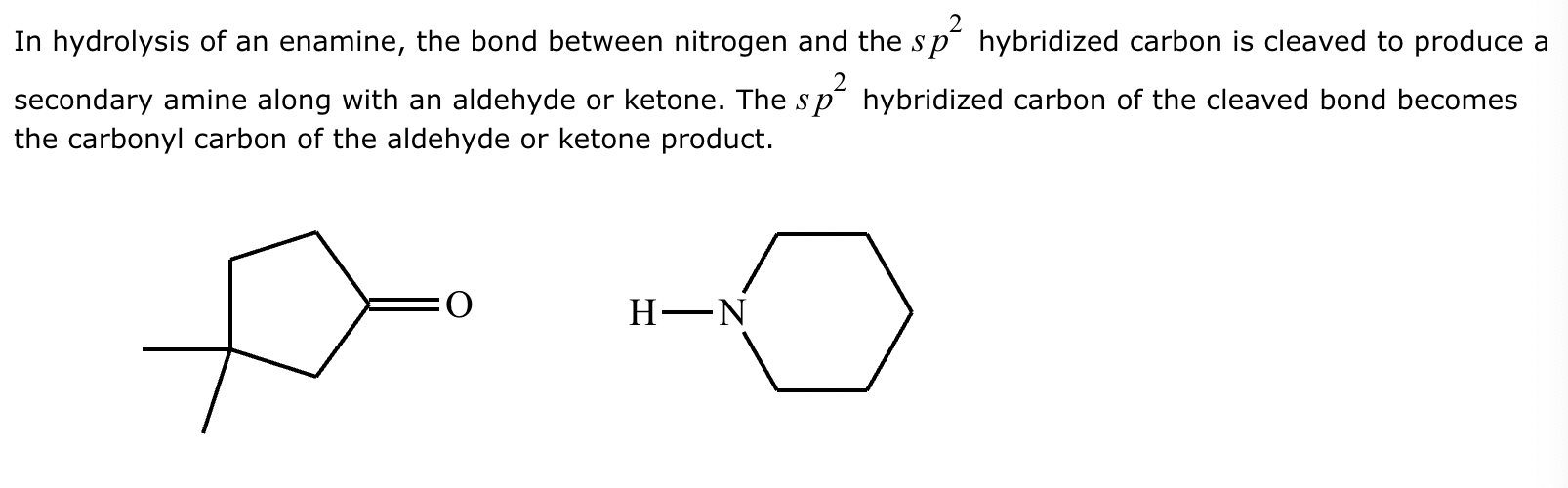
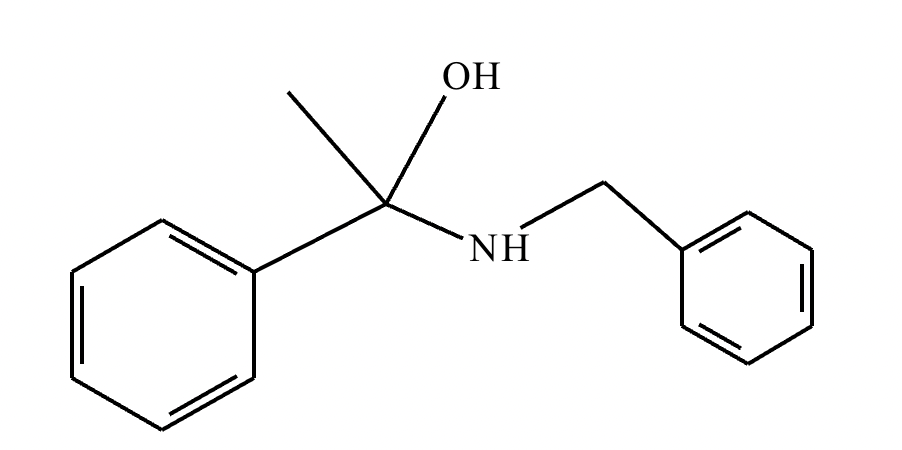
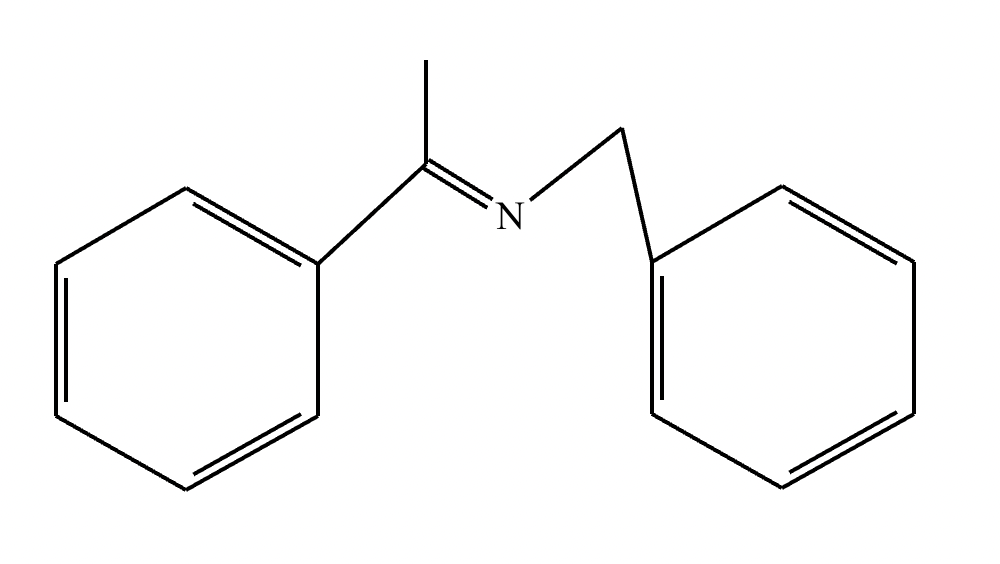
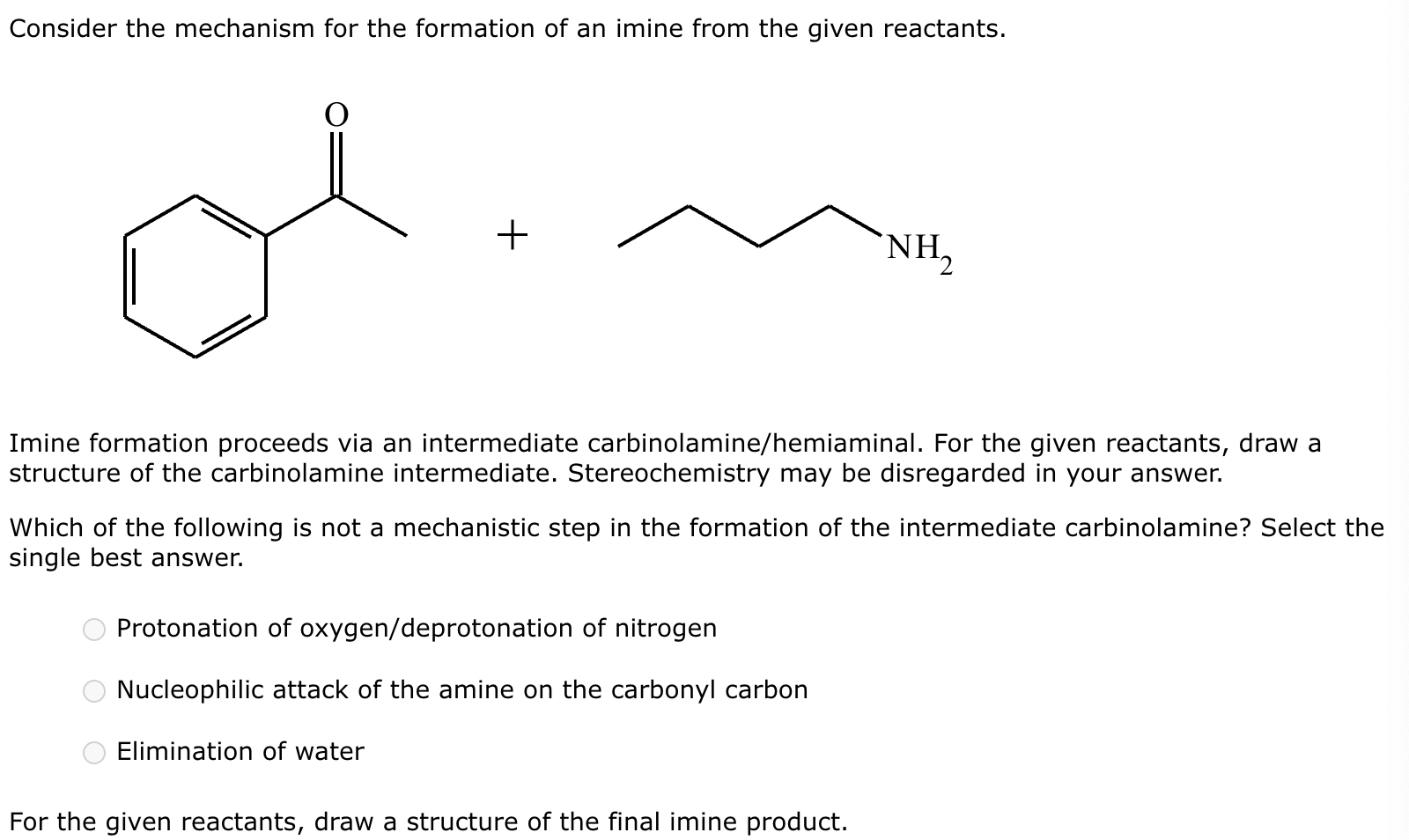
(1) Imine formation proceeds via an intermediate carbinolamine/hemiaminal. For the given reactants, draw a structure of the carbinolamine intermediate. Stereochemistry may be disregarded in your answer.
(2)

(3) For the given reactants, draw a structure of the final imine product.
(4)
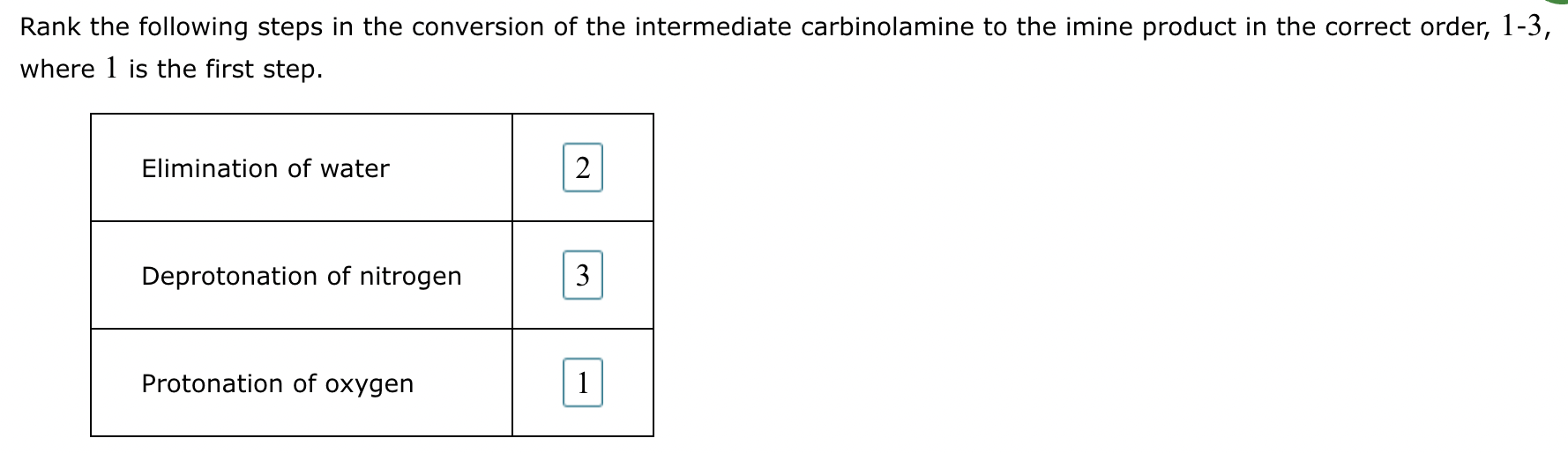
(5) Determine the pH range at which the overall process of imine formation occurs most rapidly: Strongly acidic, 4-5, 7, 9-10, or strongly basic.
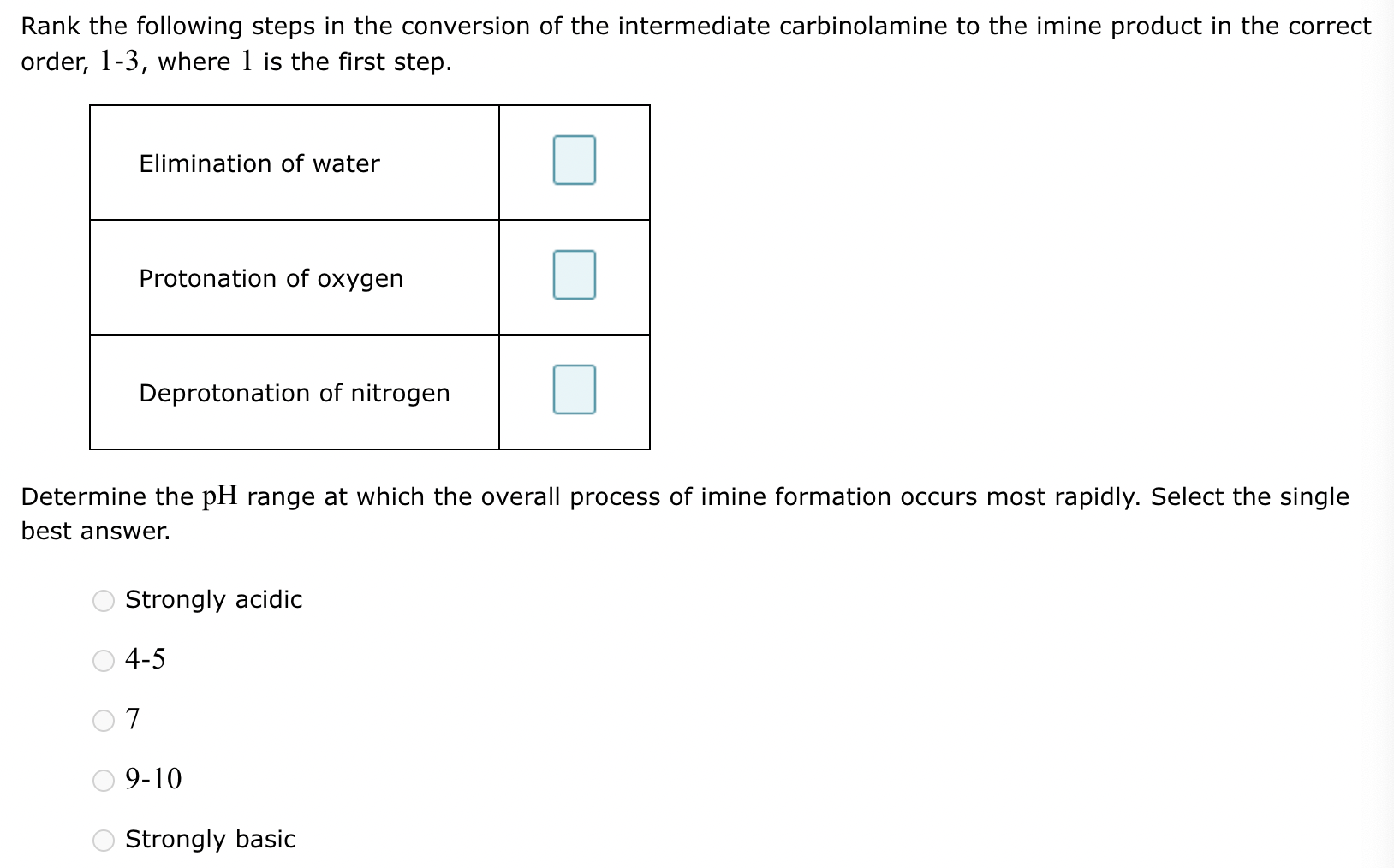
(1)
(2) Elimination of water
(3)
(4) Elimination of water: 2
Protonation of oxygen: 3
Deprotonation of nitrogen: 1
(5) 4-5
(1)
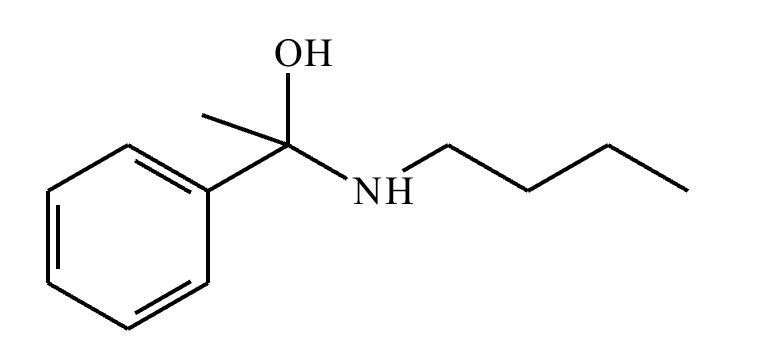
(2) Elimination of water
(3)
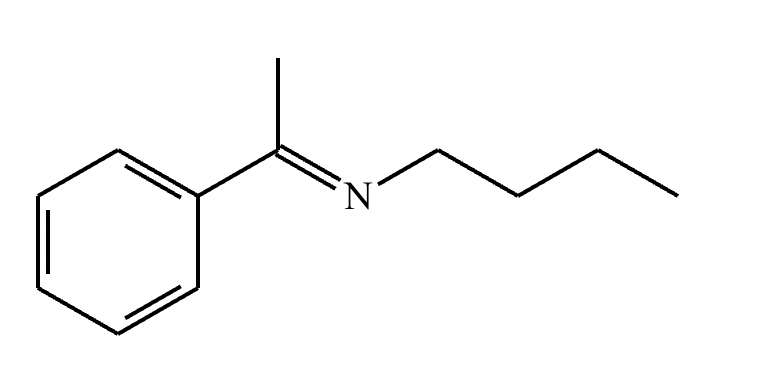
(4) Elimination of water: 2
Protonation of oxygen: 1
Deprotonation of nitrogen: 3
(5) 4-5
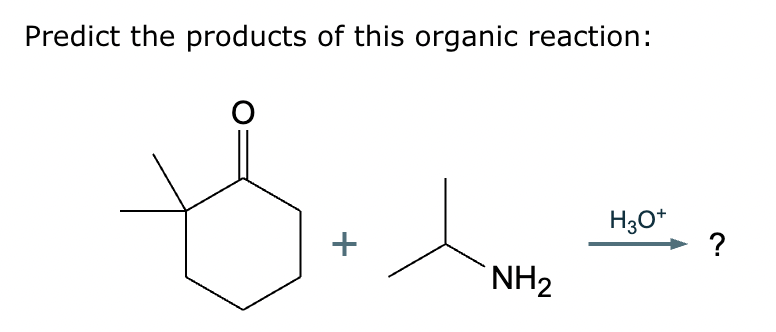
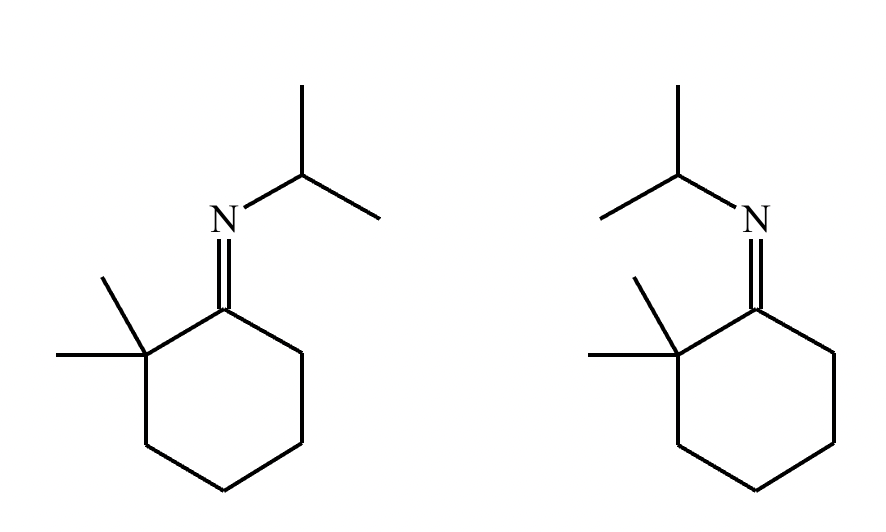
Draw the structure of the major organic product for the reaction of the carbonyl and amine under mildly acidic conditions.
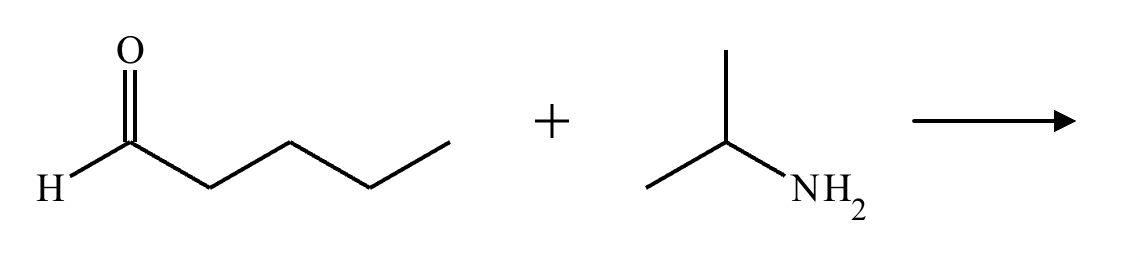
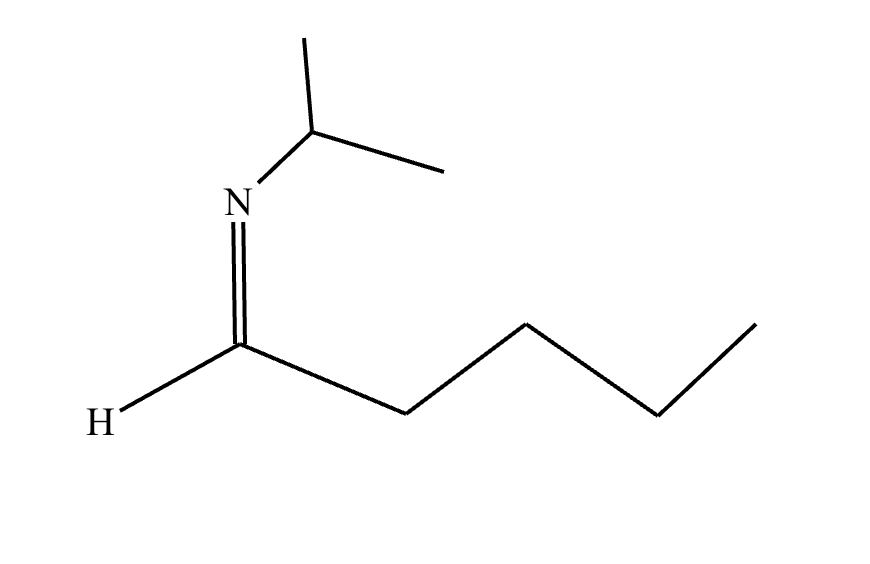
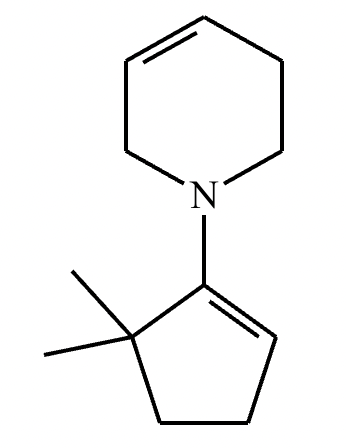
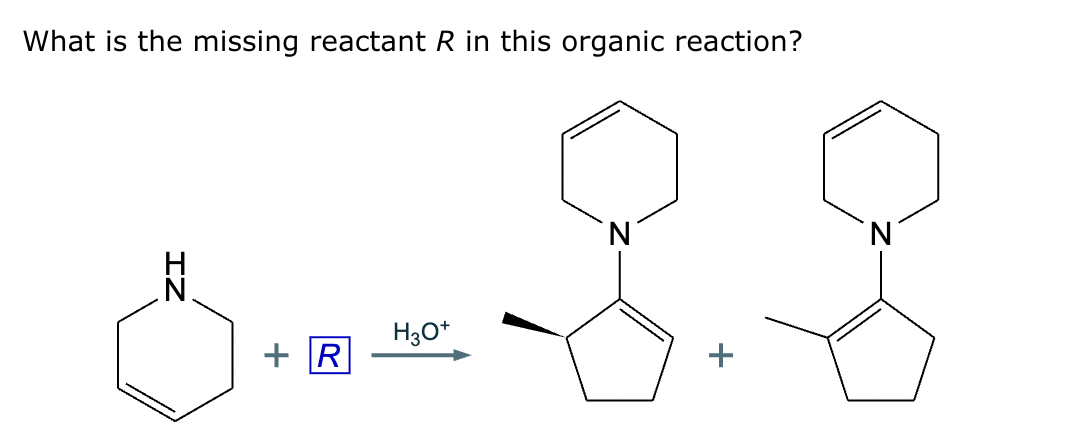
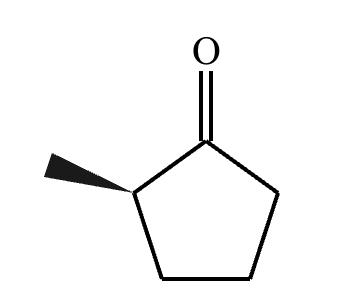
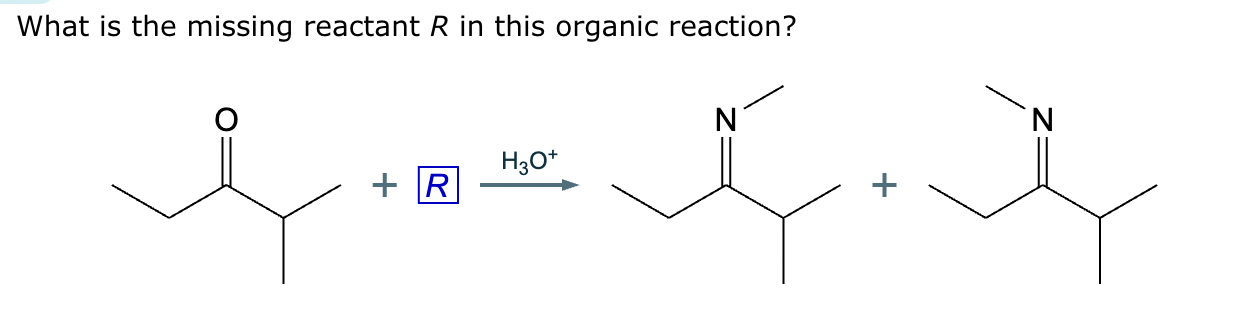
CH3—NH2
Explanation:
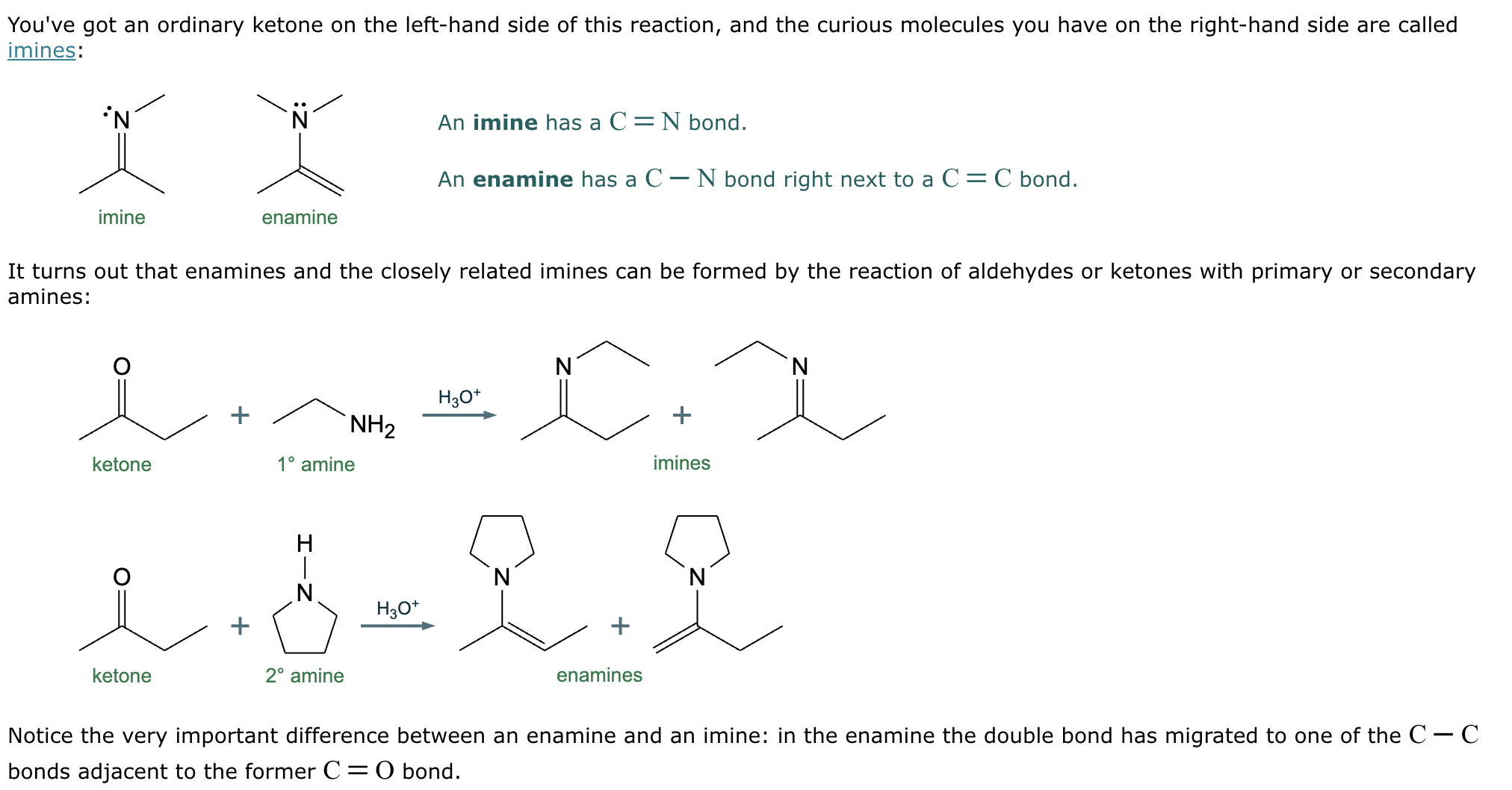
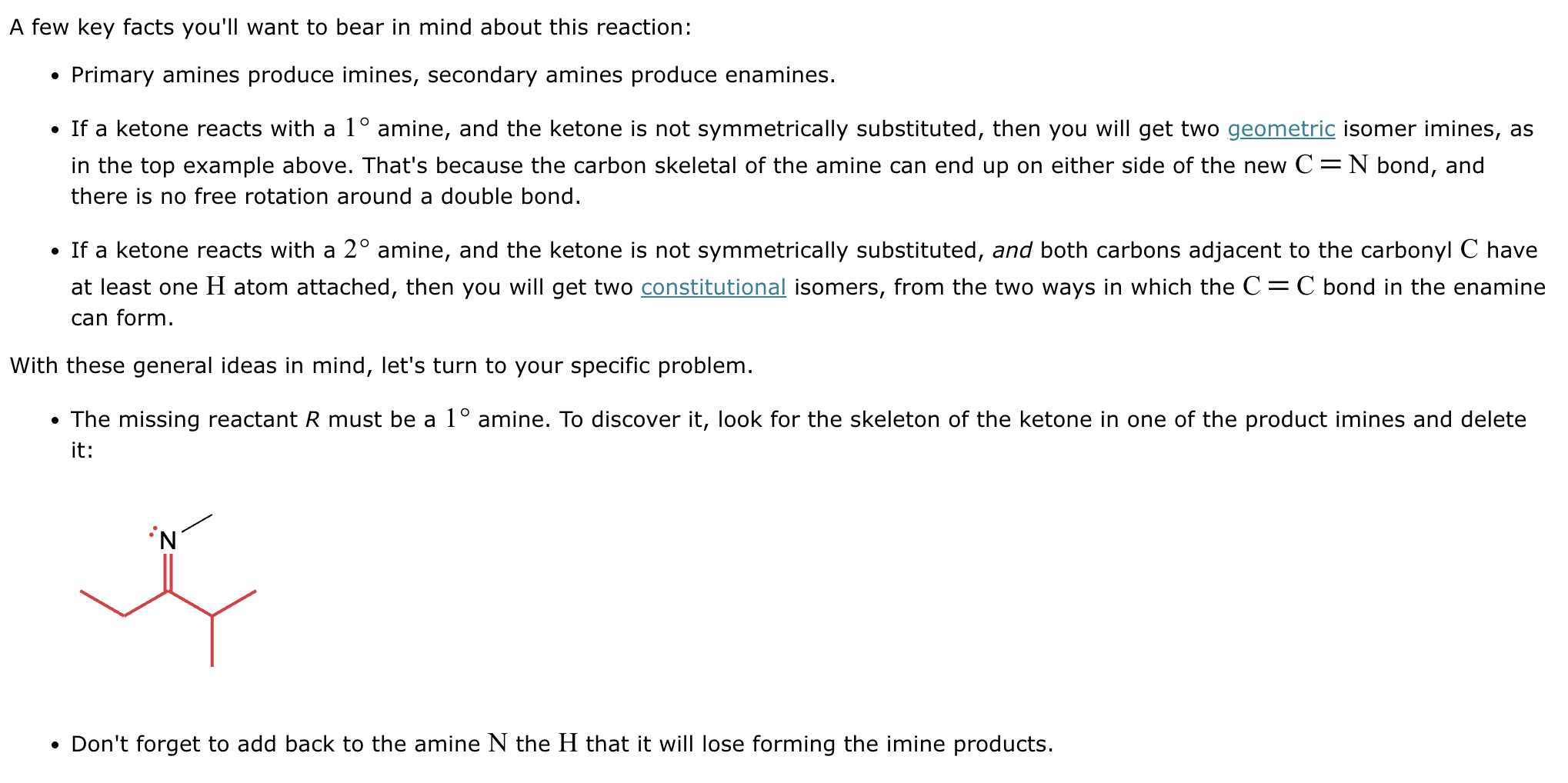
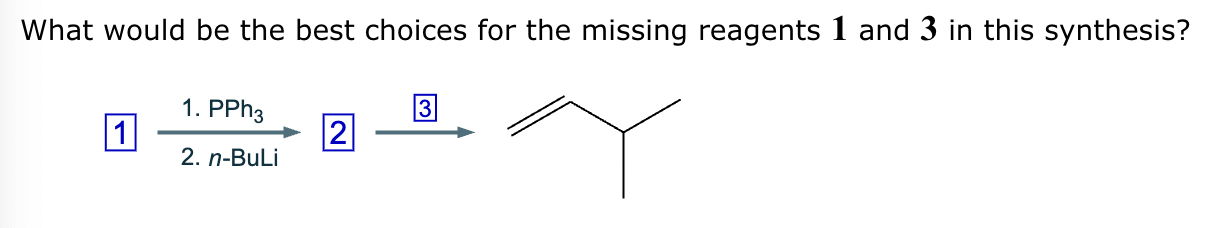
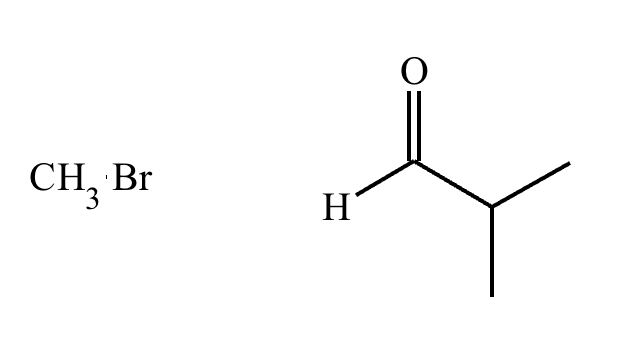
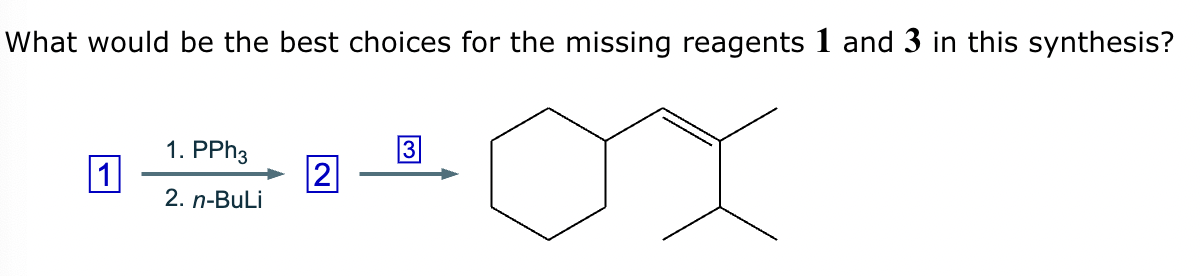
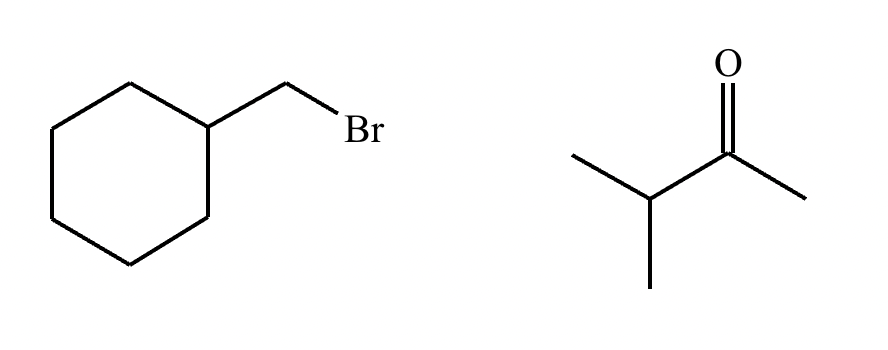
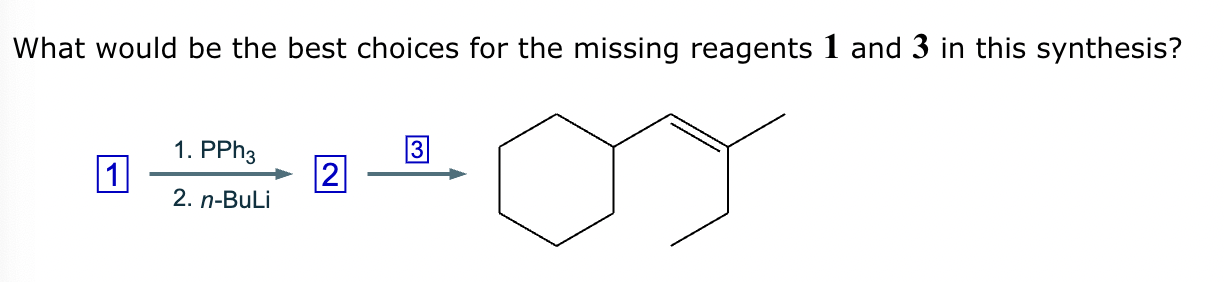
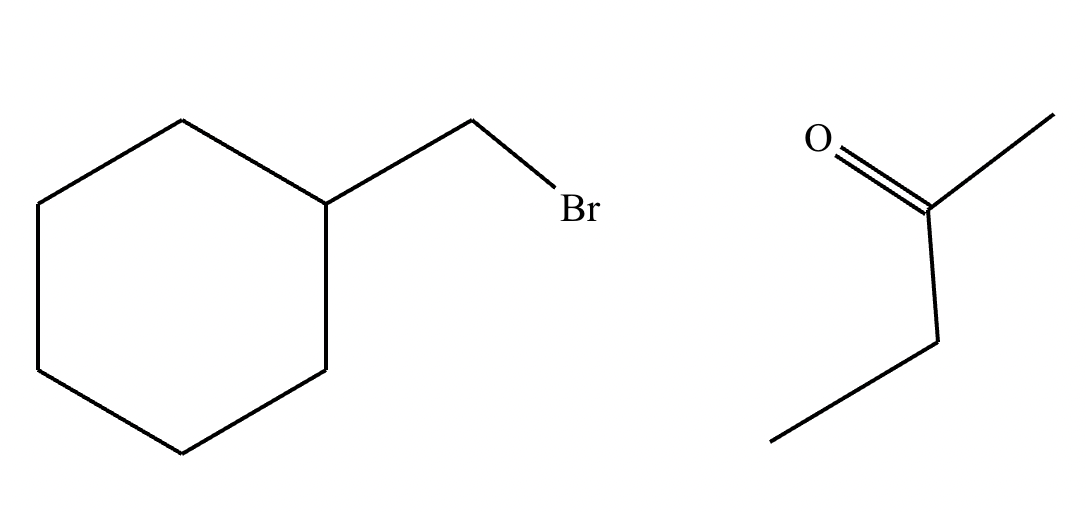
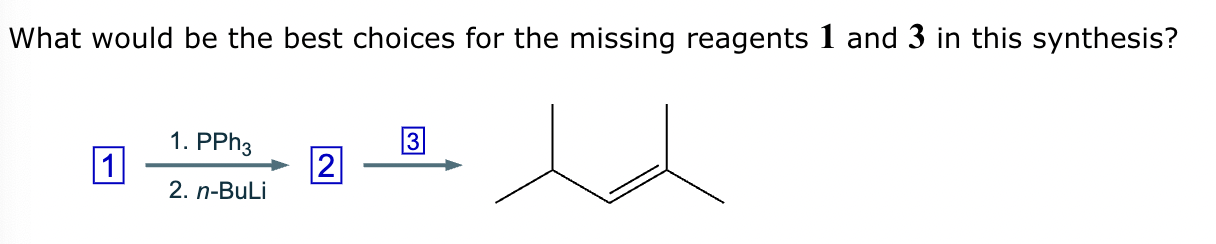
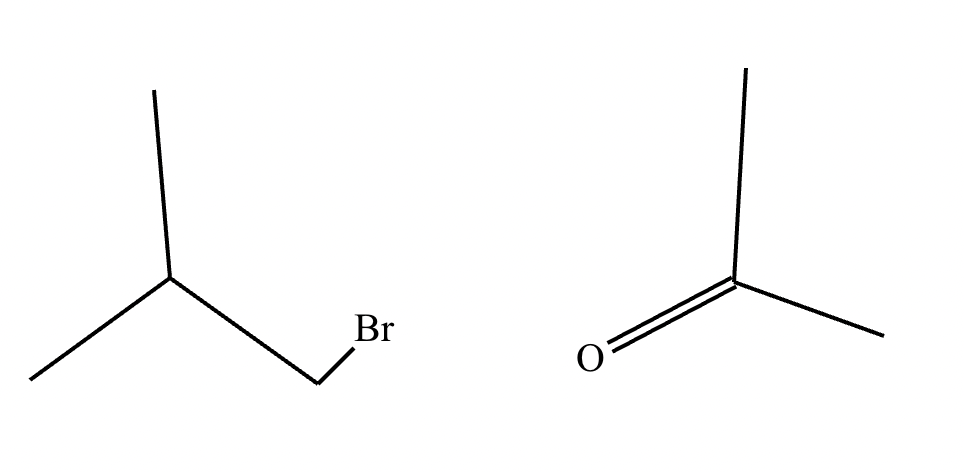
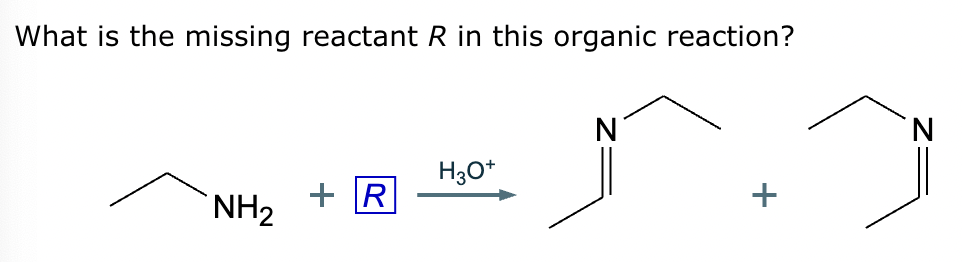
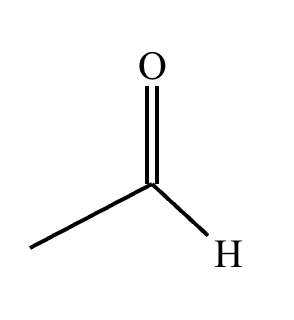
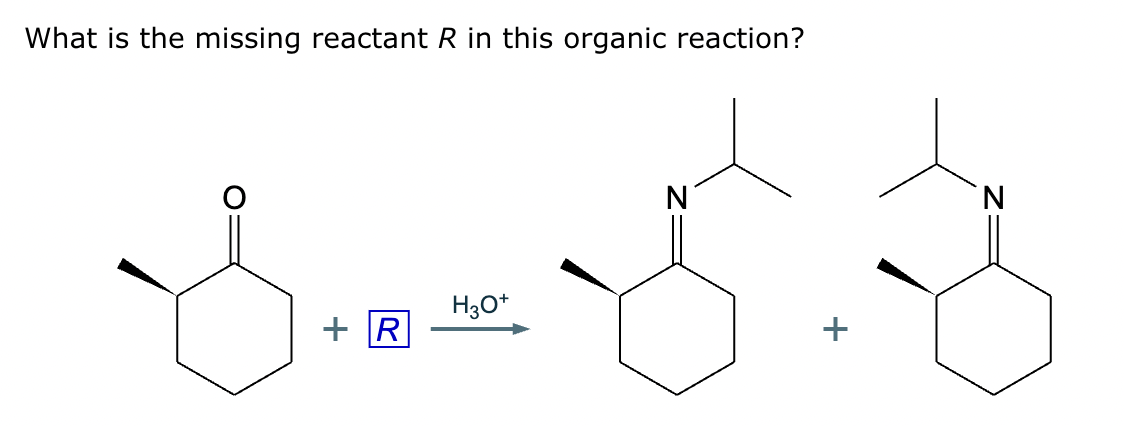
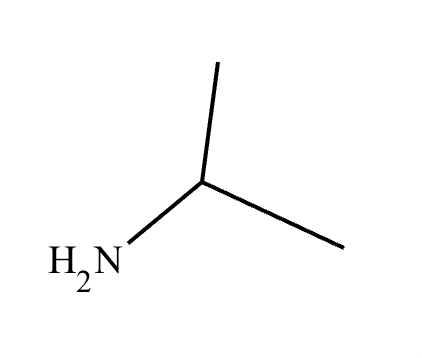
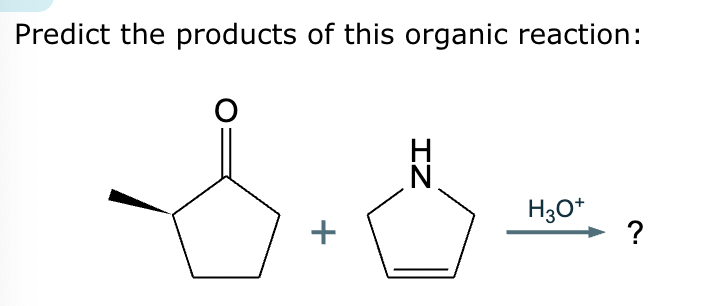
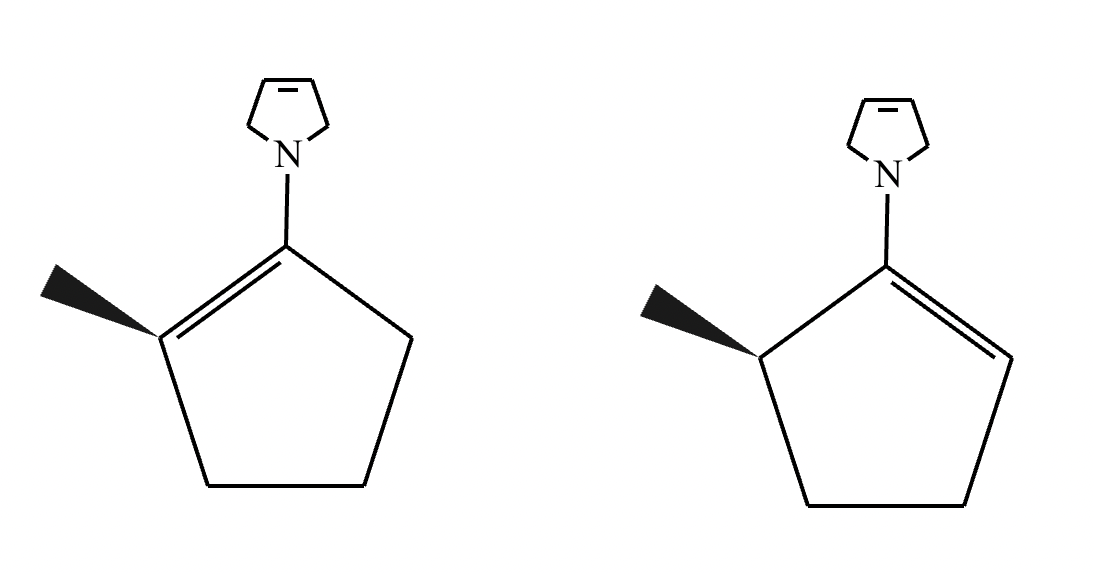
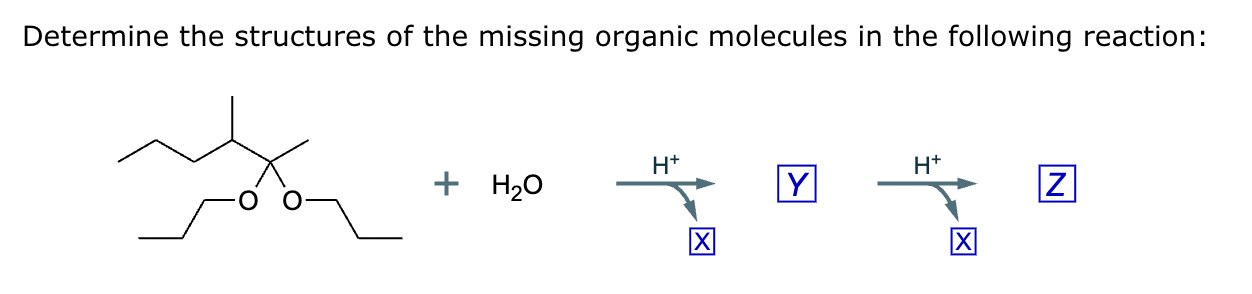
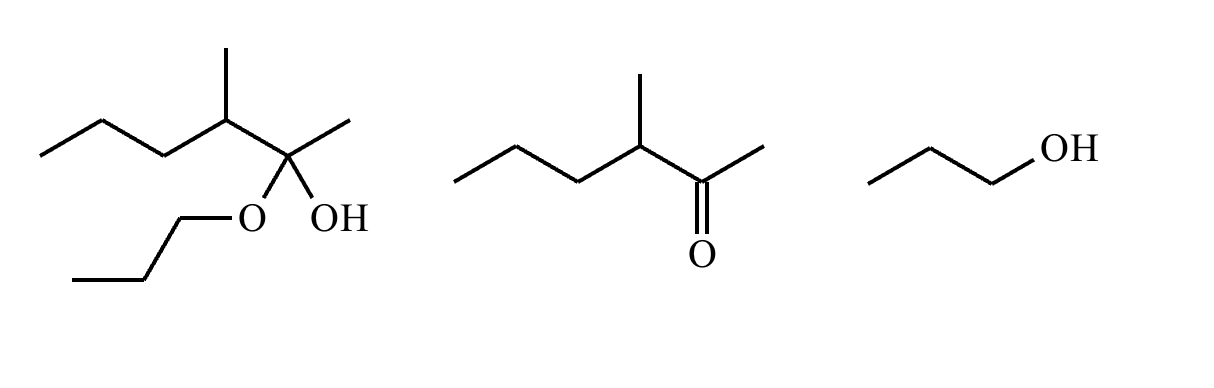
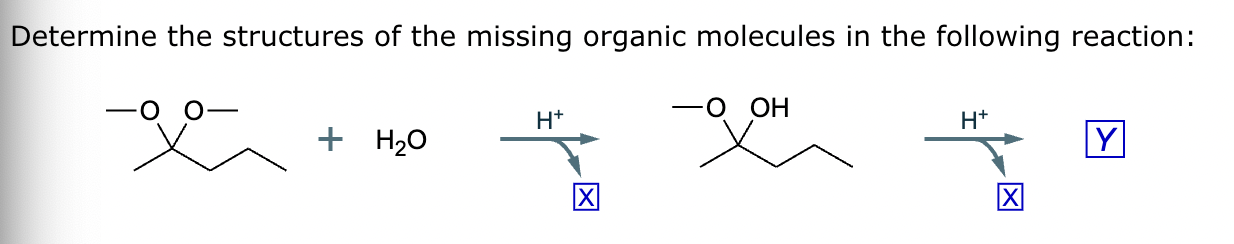
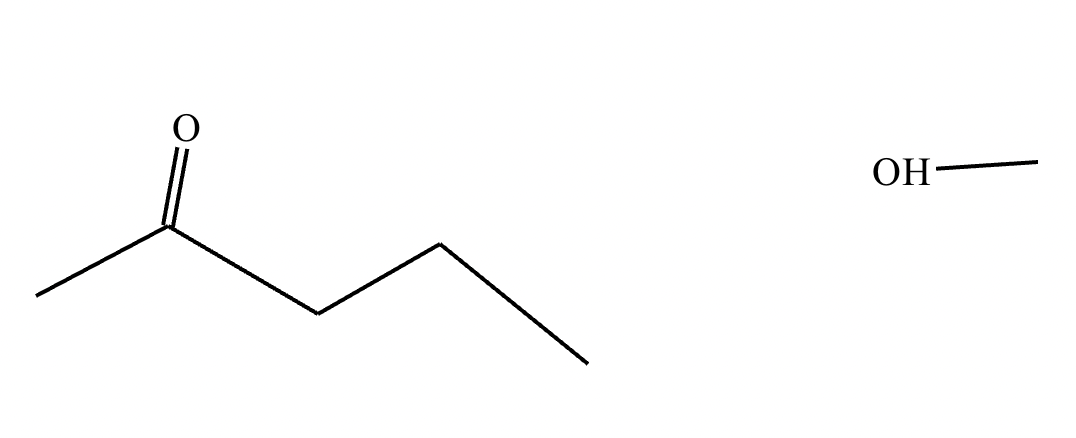
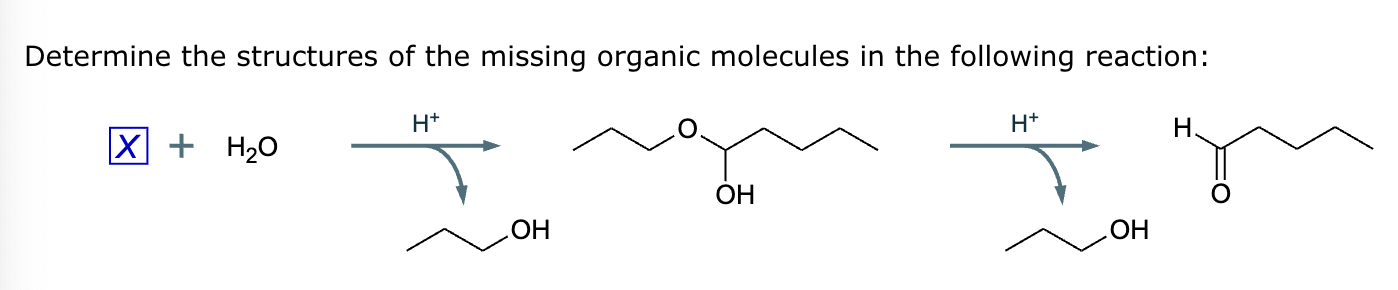
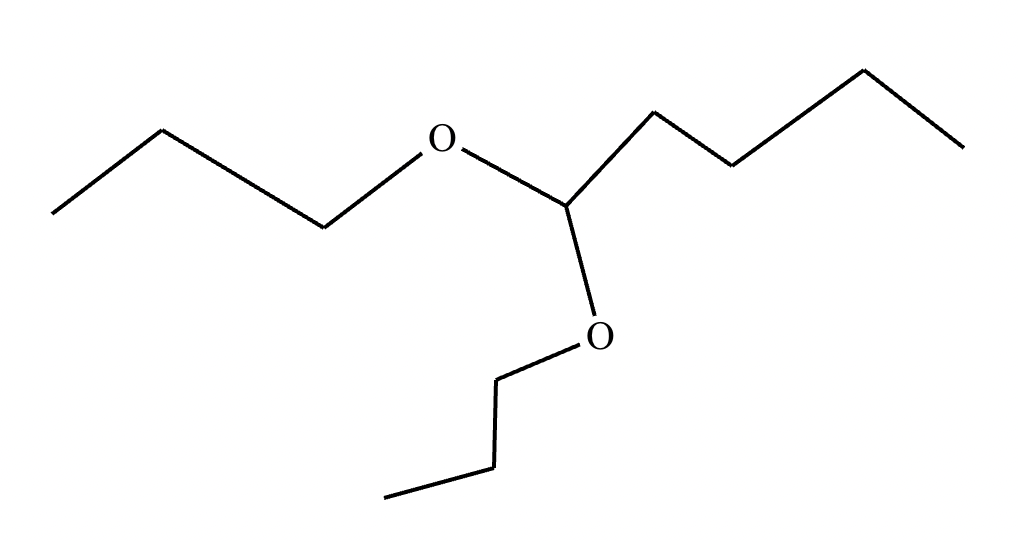
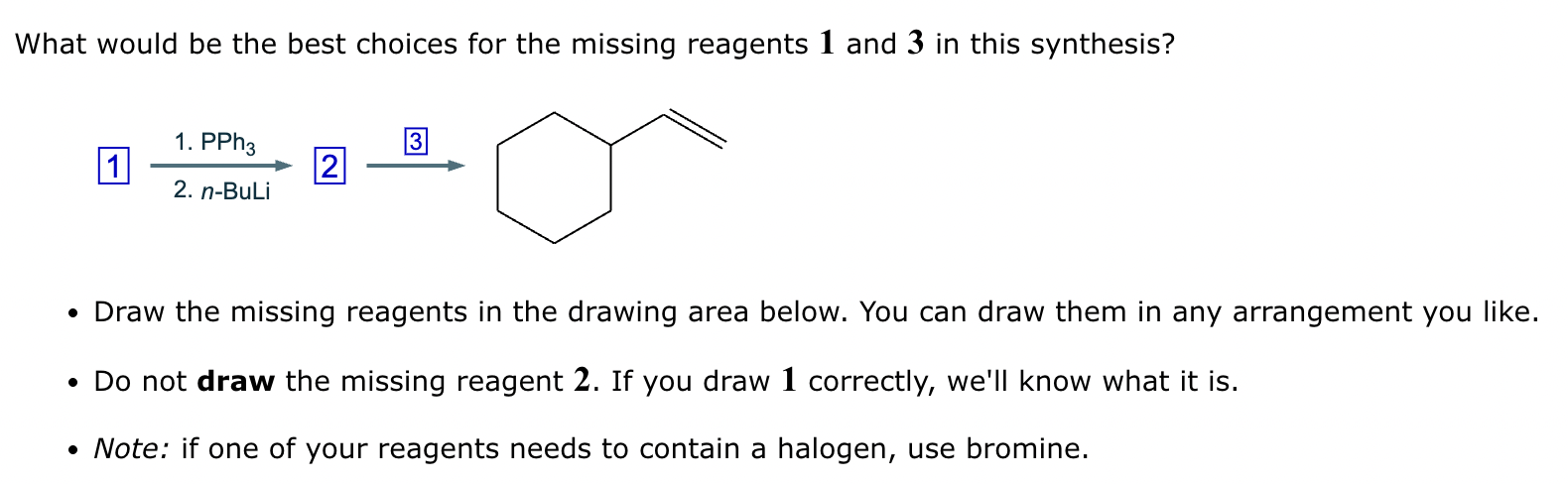
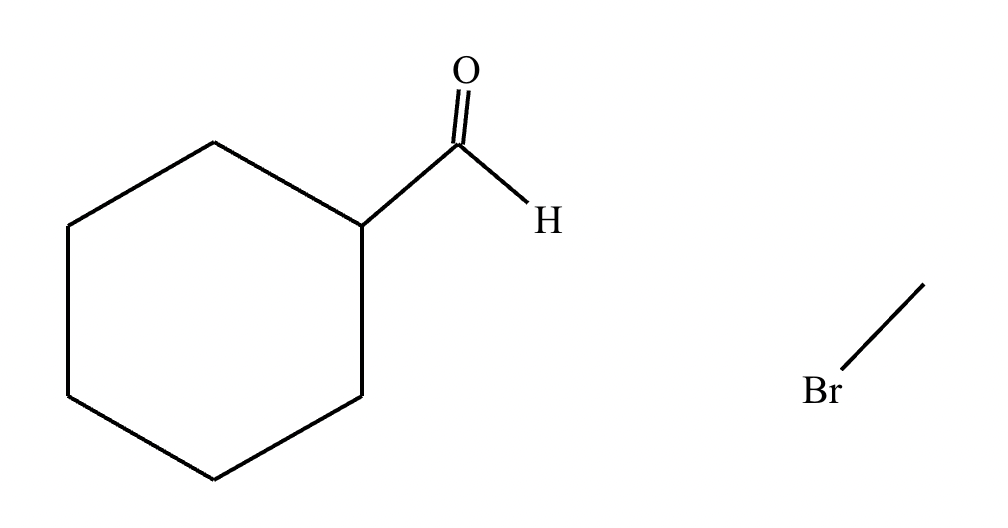
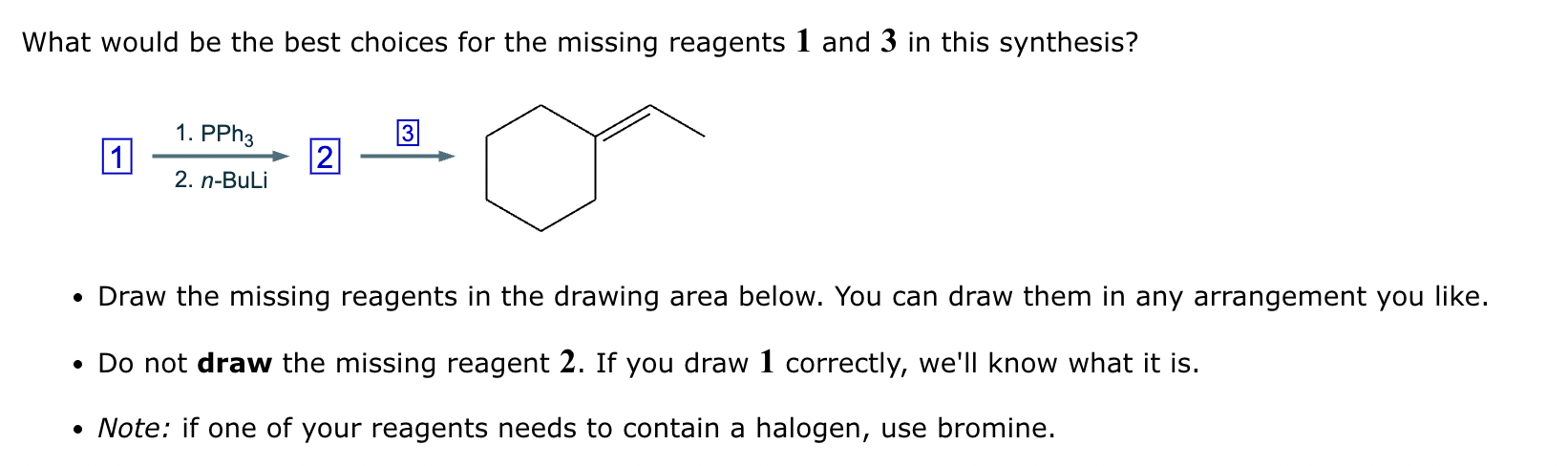
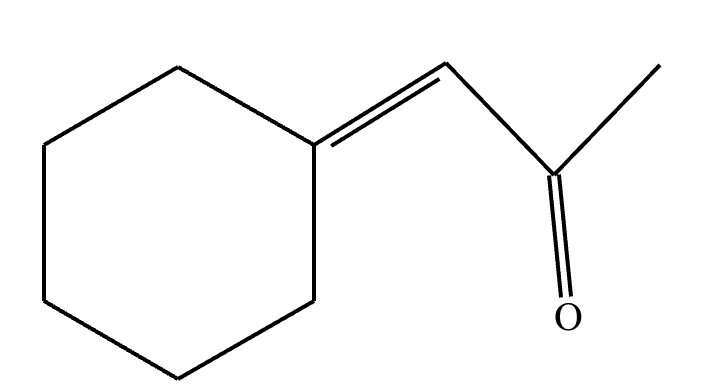
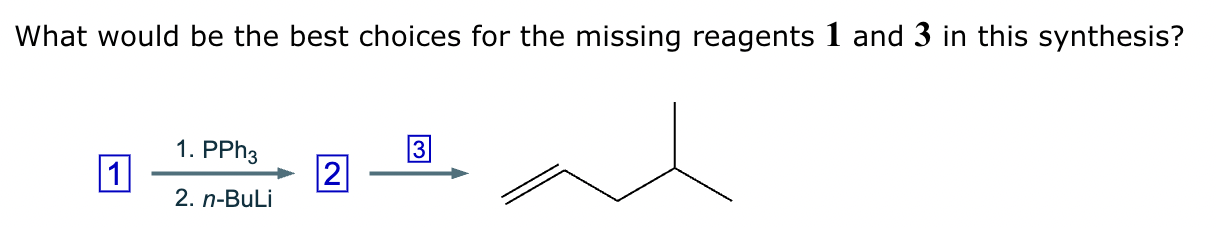
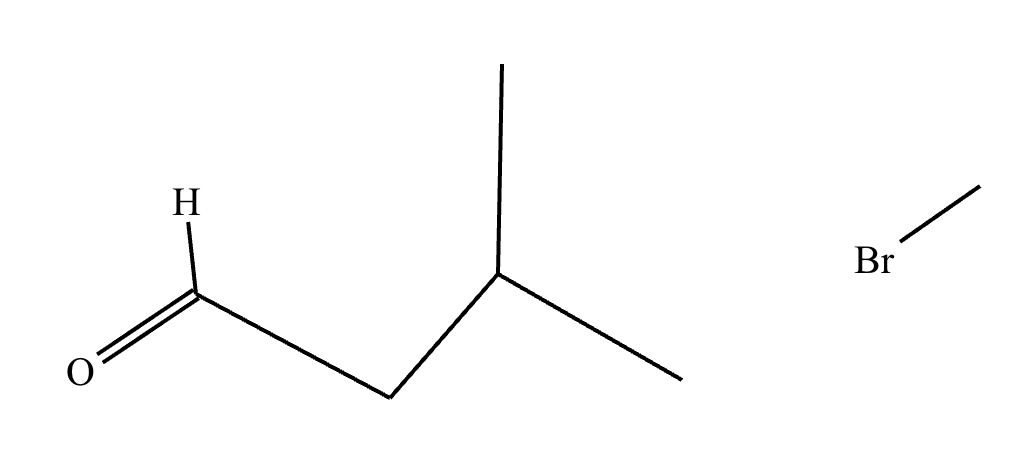
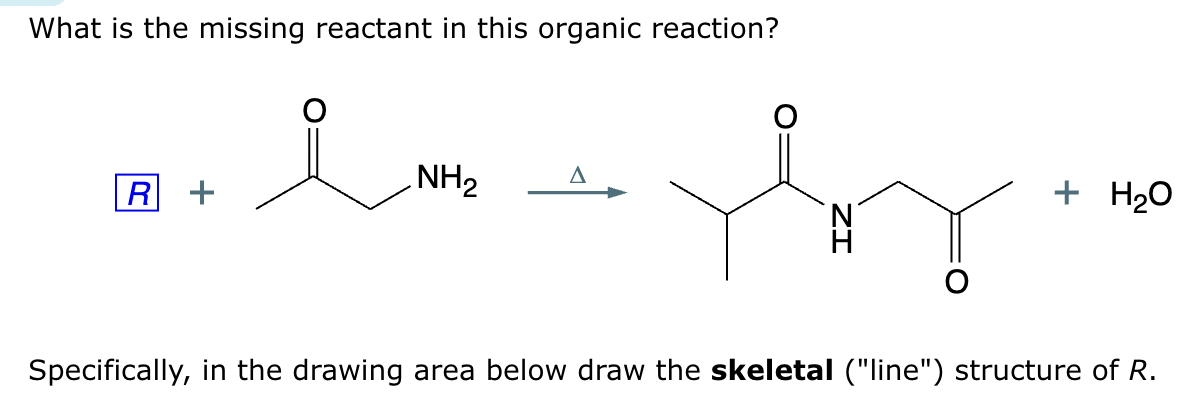
The product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below in any arrangement you’d like.
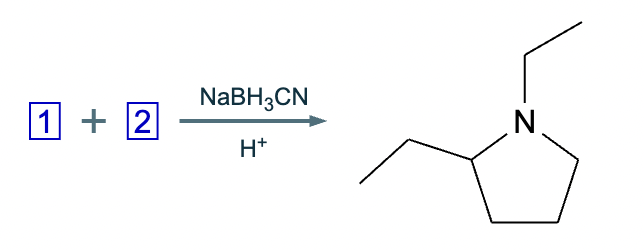
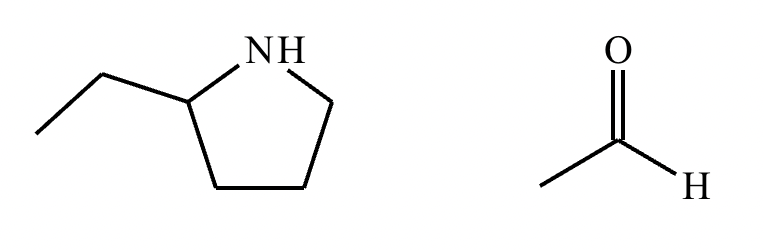
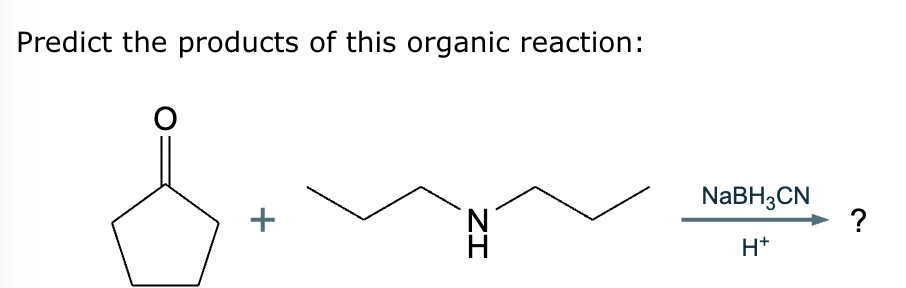
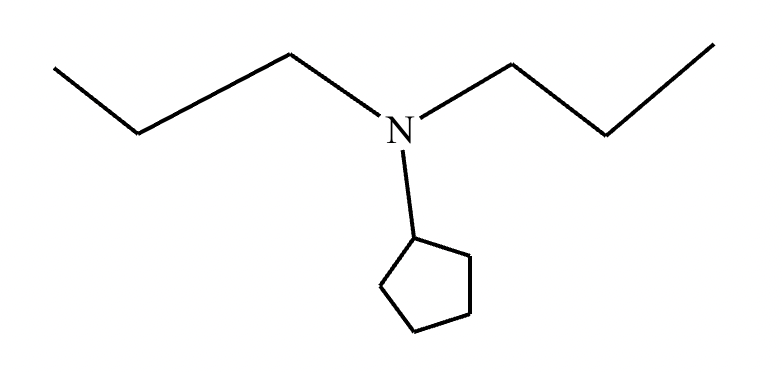
The product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below in any arrangement you’d like.
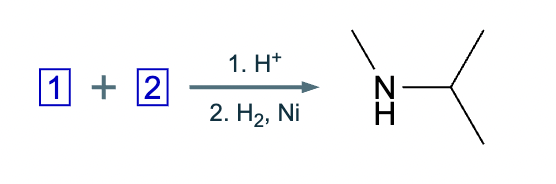
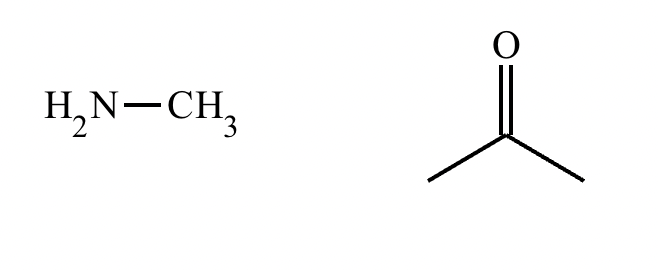
The product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below in any arrangement you’d like.
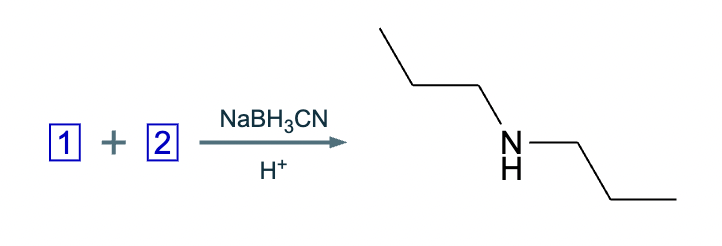
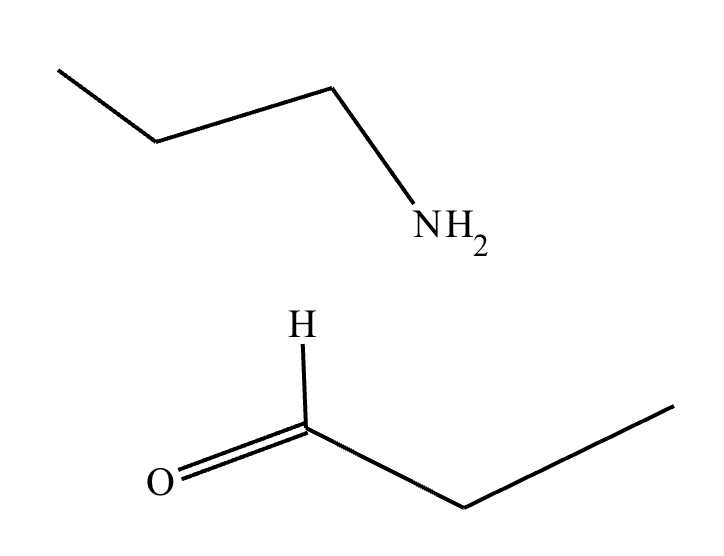
Under aqueous acidic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2:
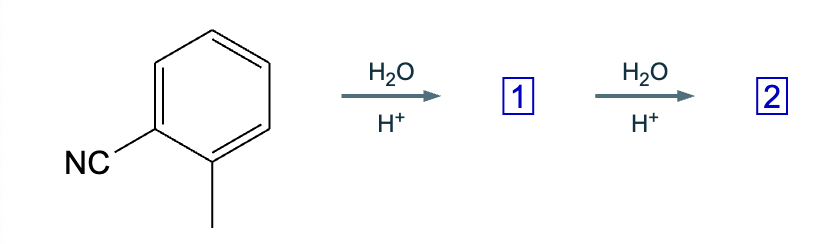
Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like.
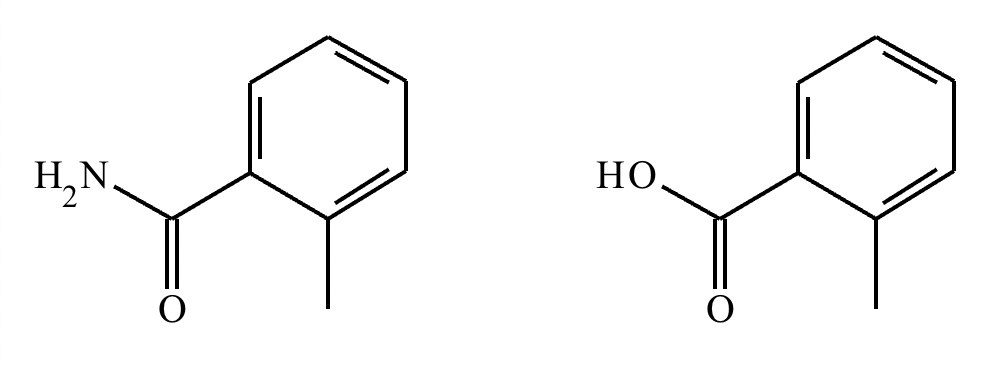
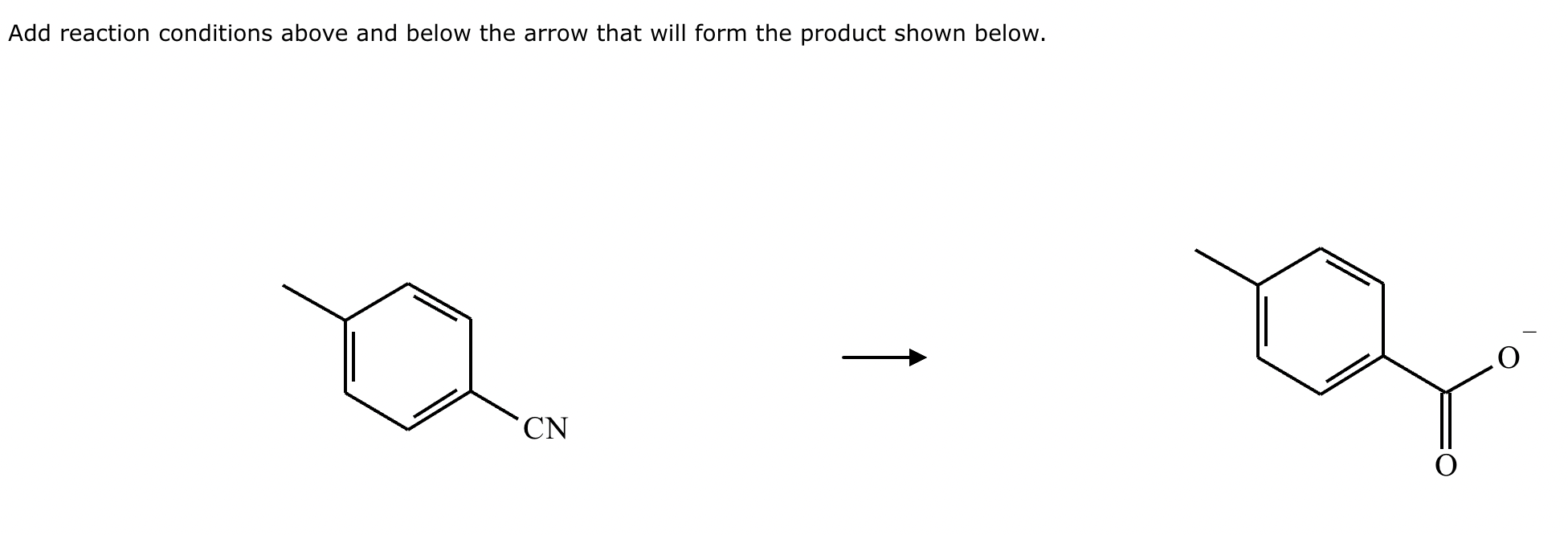
Under aqueous acidic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2:
Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like.
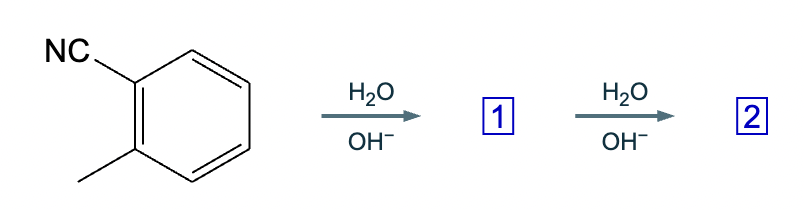
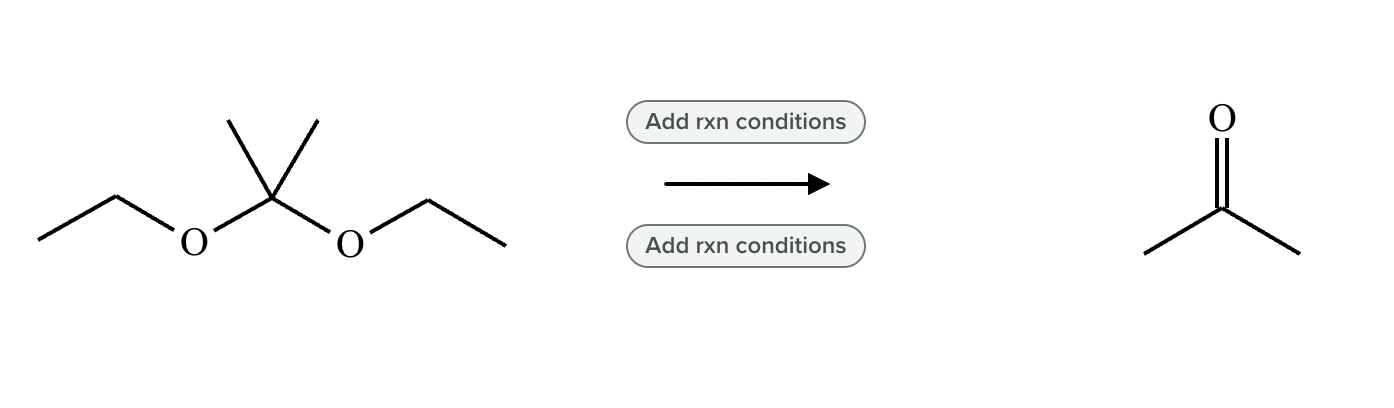
Add reaction conditions above and below the arrow that will form the product shown below.
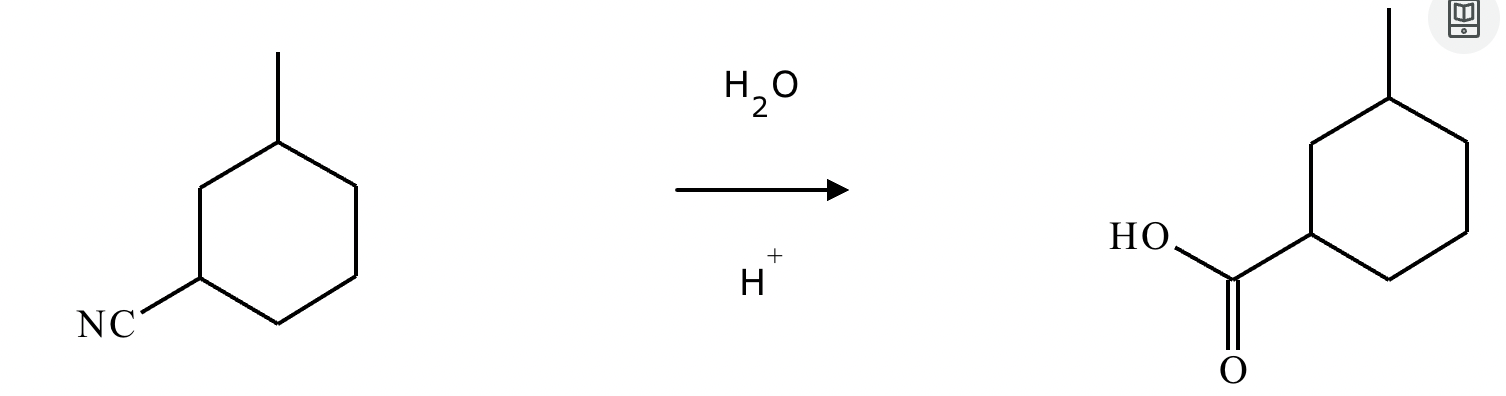
(Accidentally already put the answer)
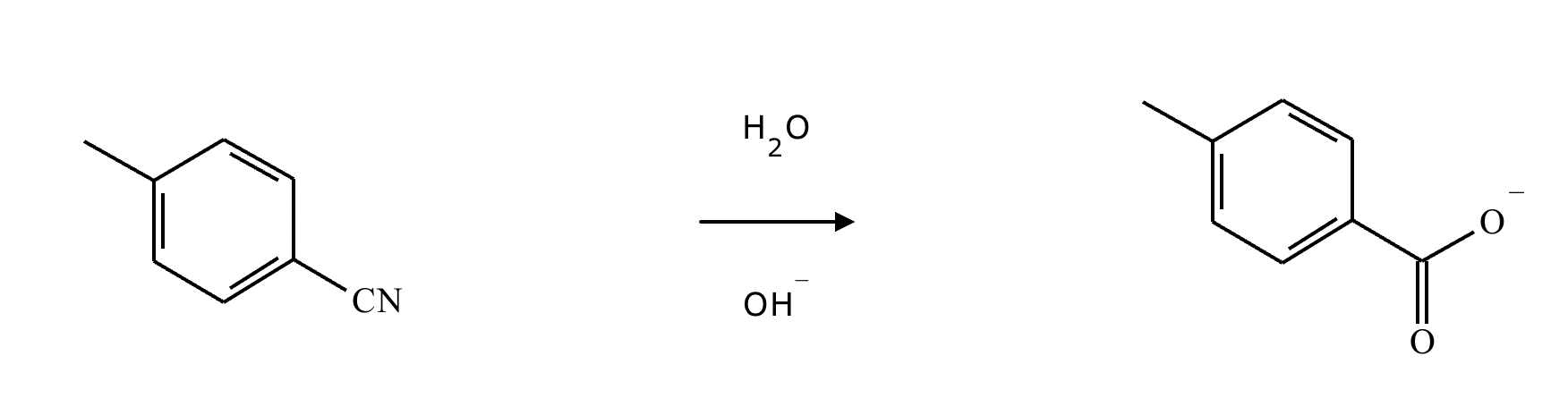
Under aqueous acidic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2:
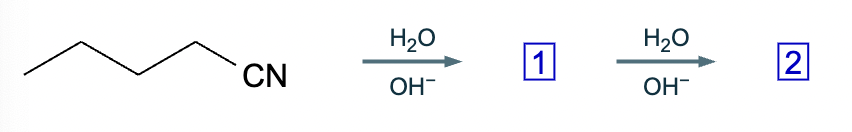
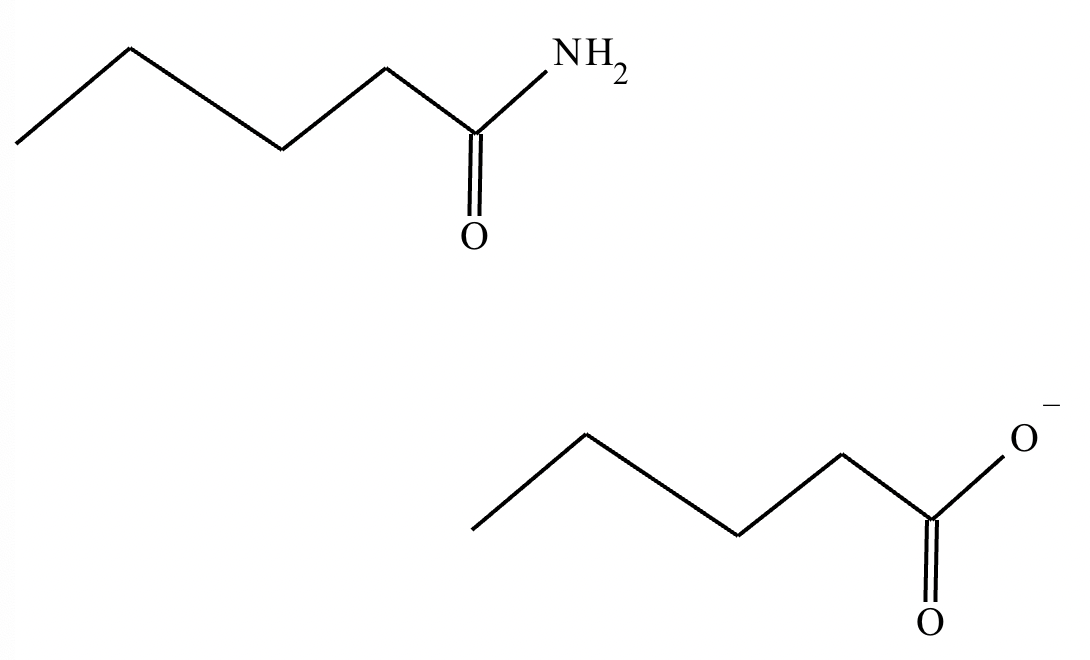
Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like.
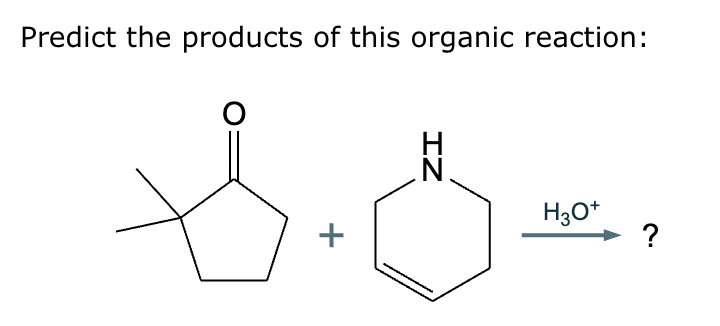
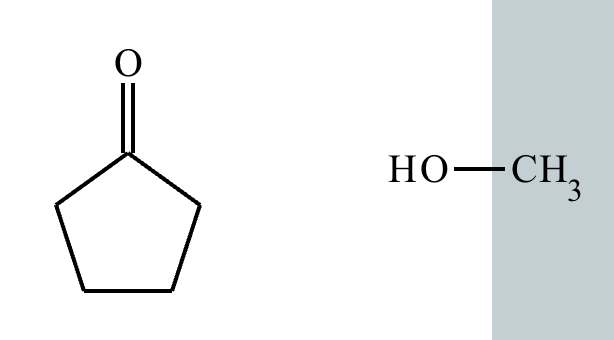
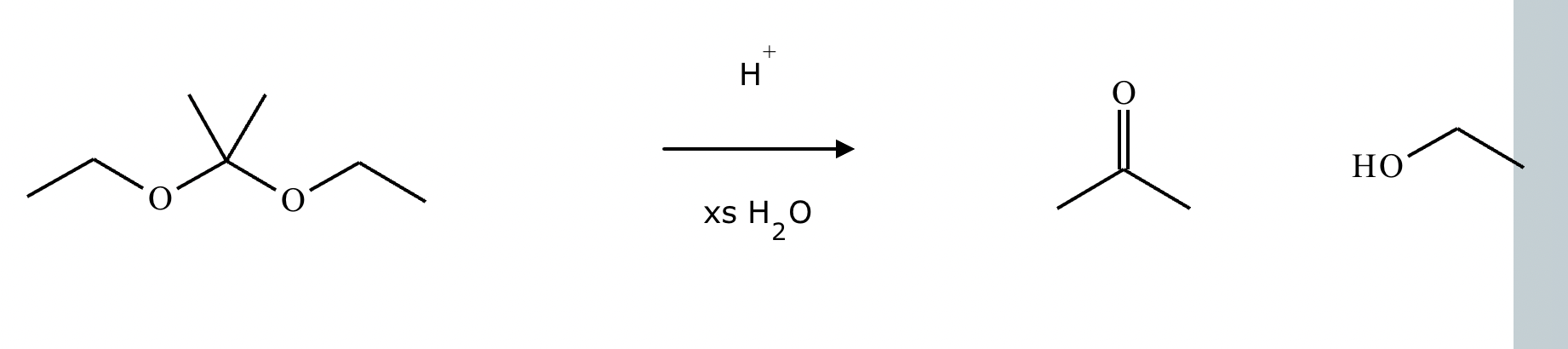
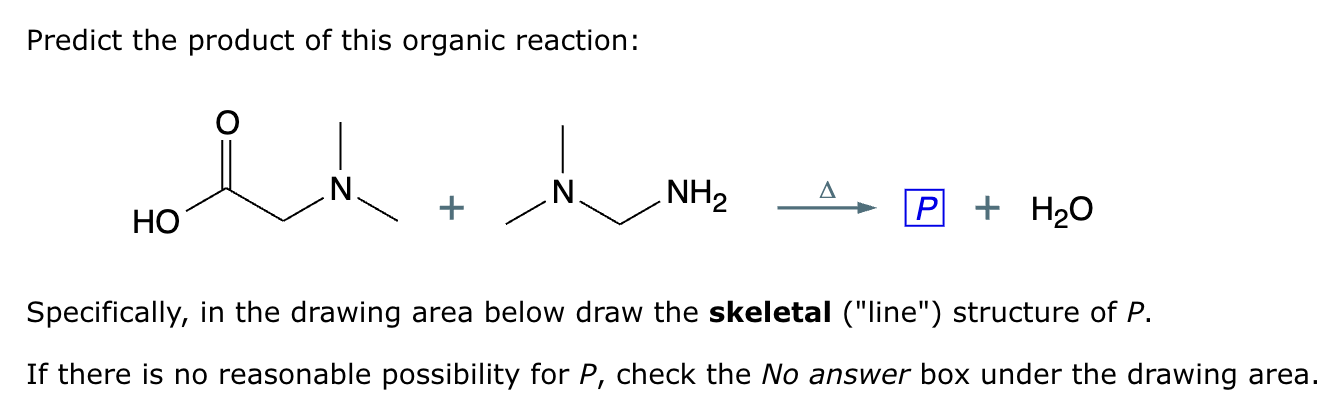
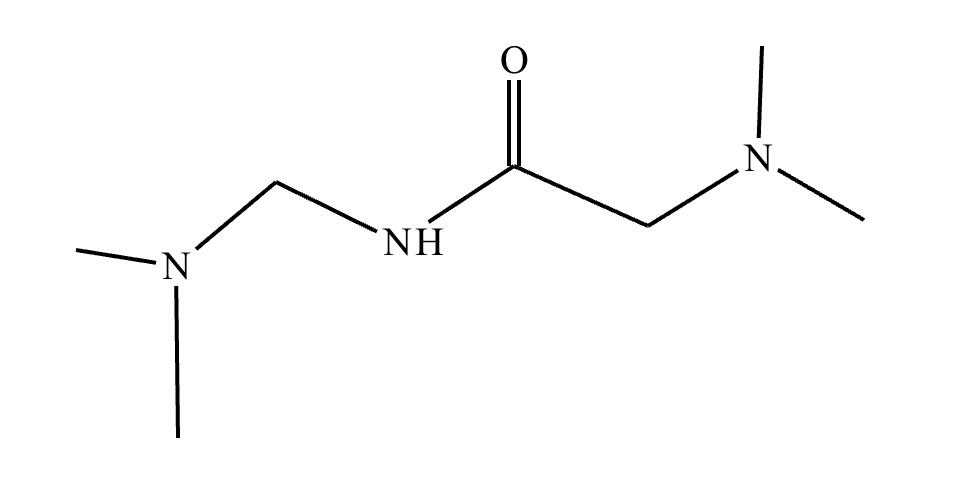
Predict the major products of this organic reaction.

Predict the major products of this organic reaction.
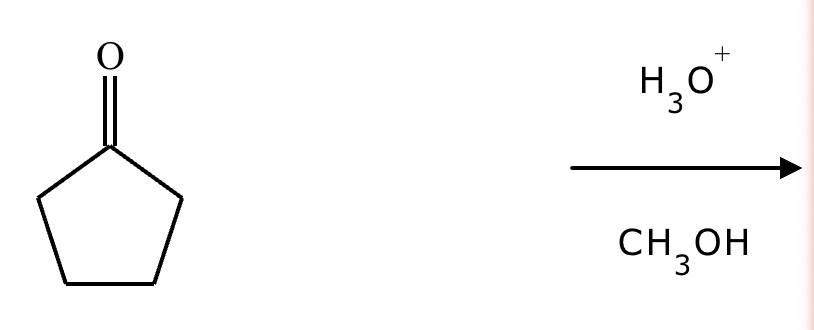
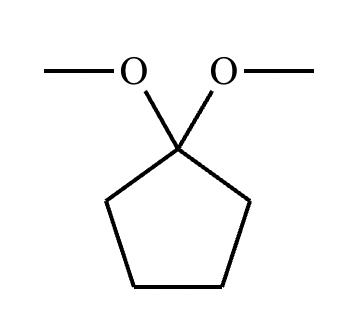
Predict the major products of this organic reaction.
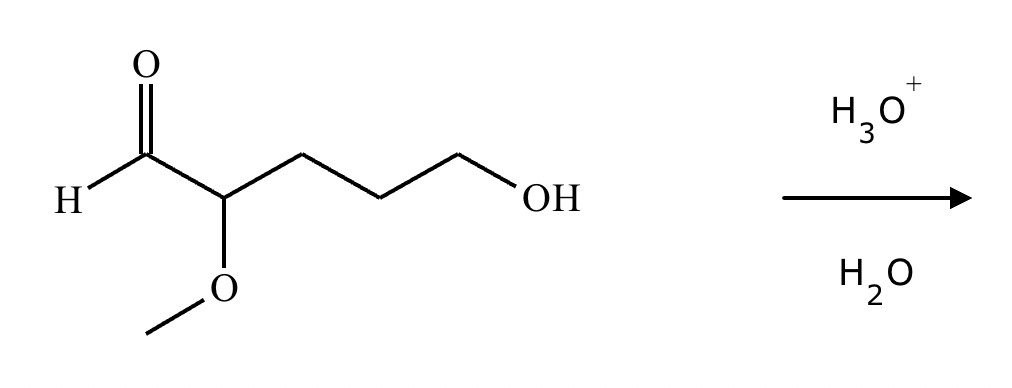
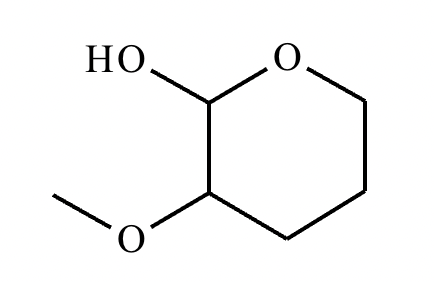
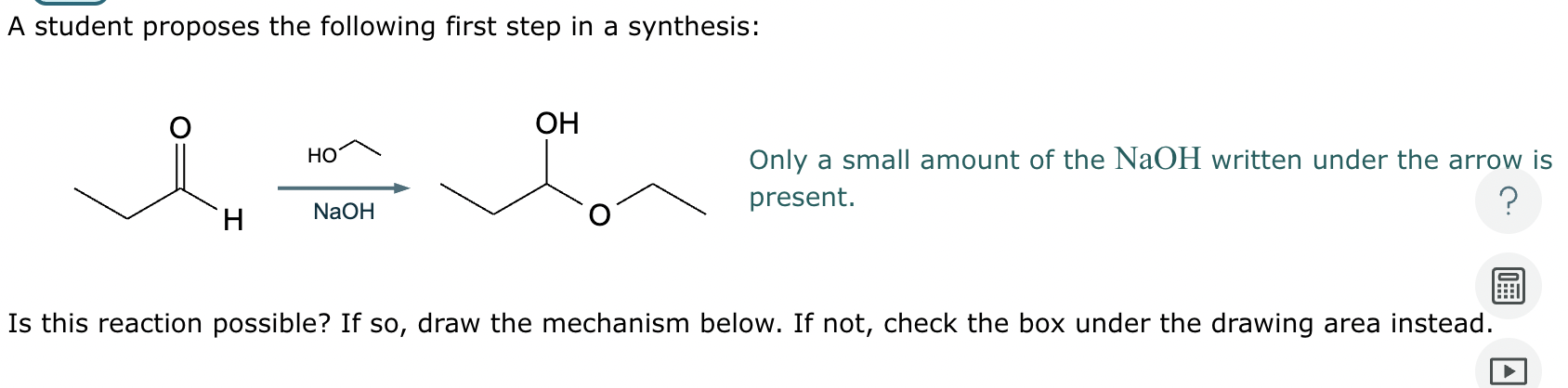
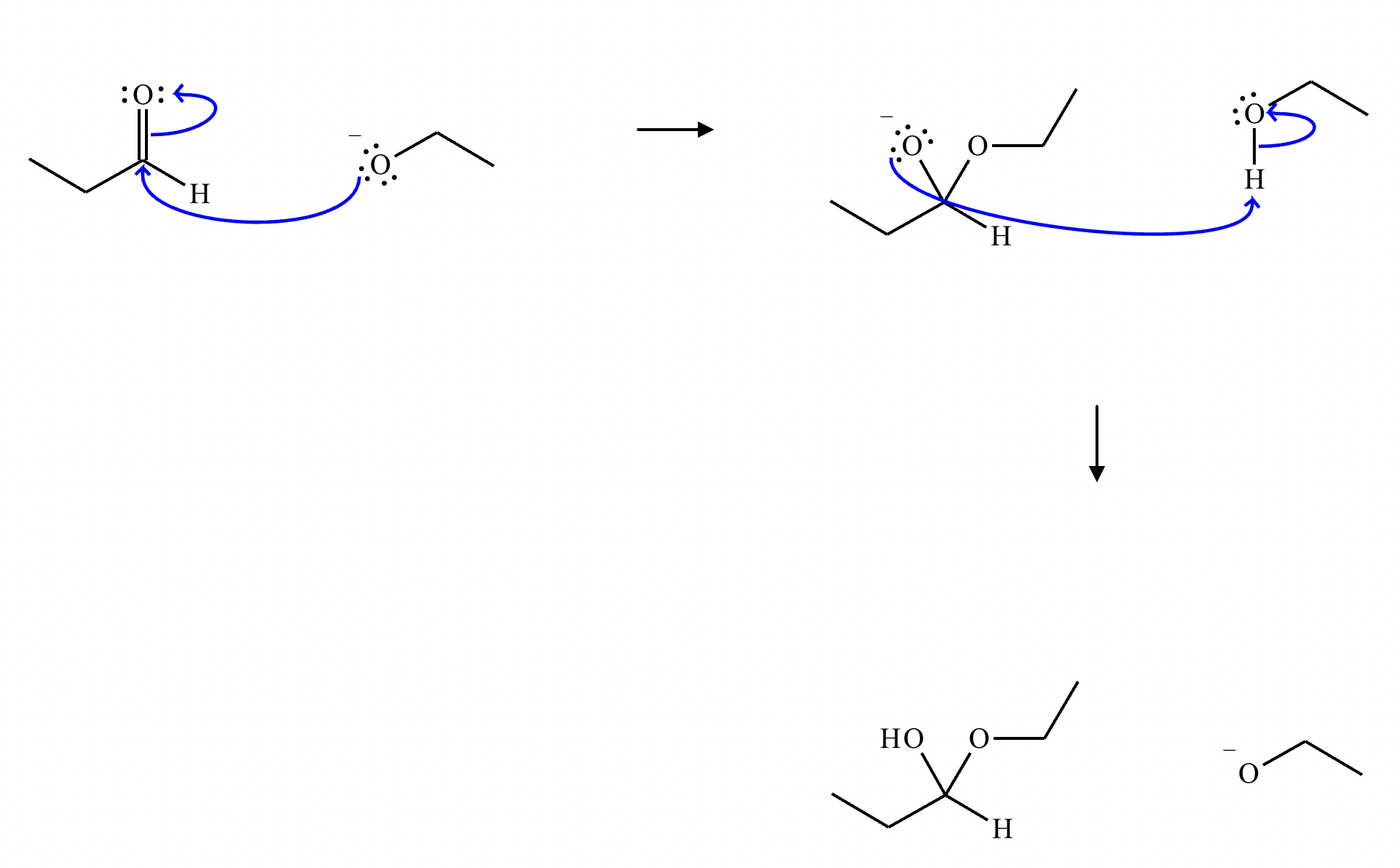

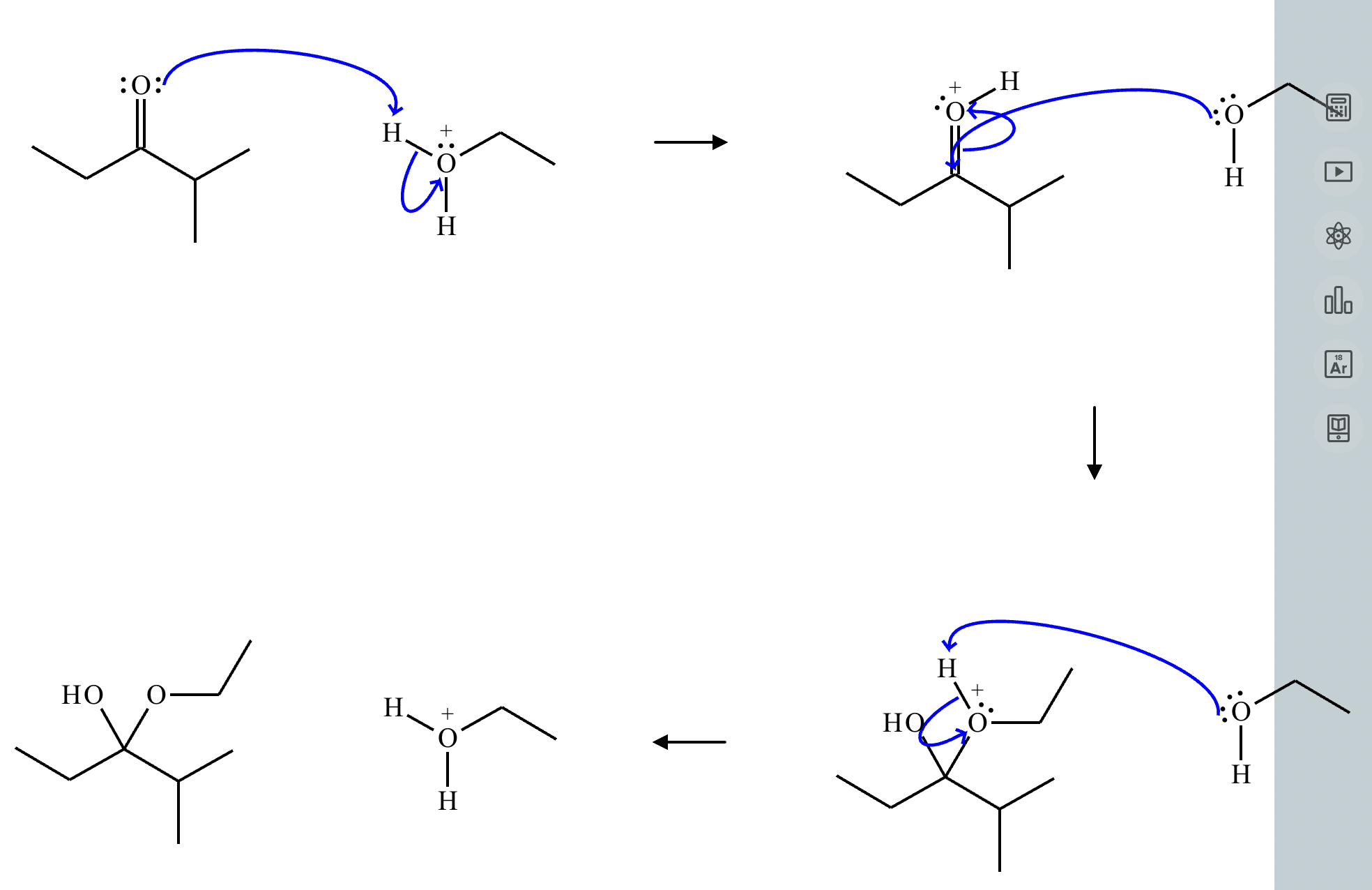
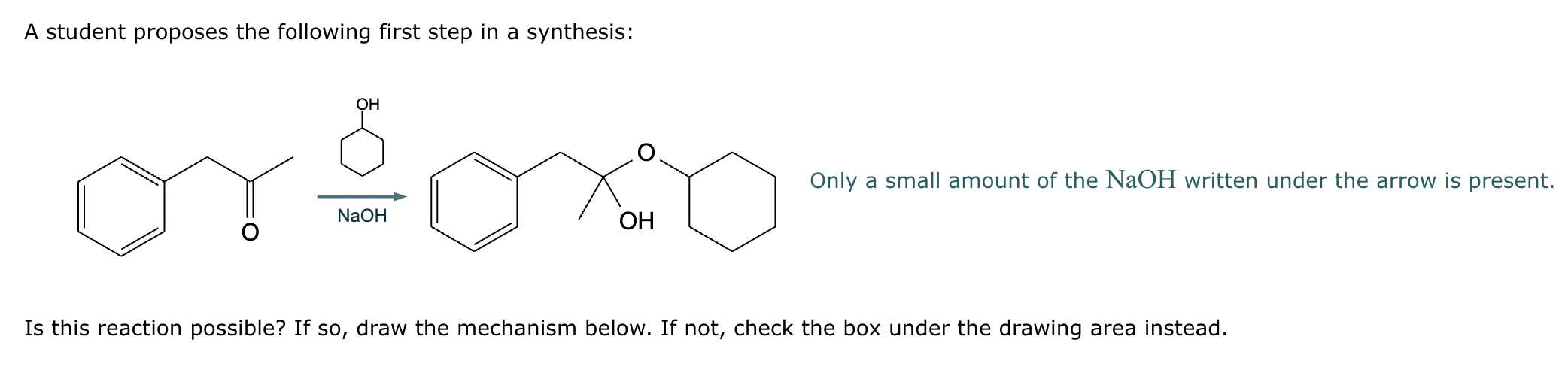
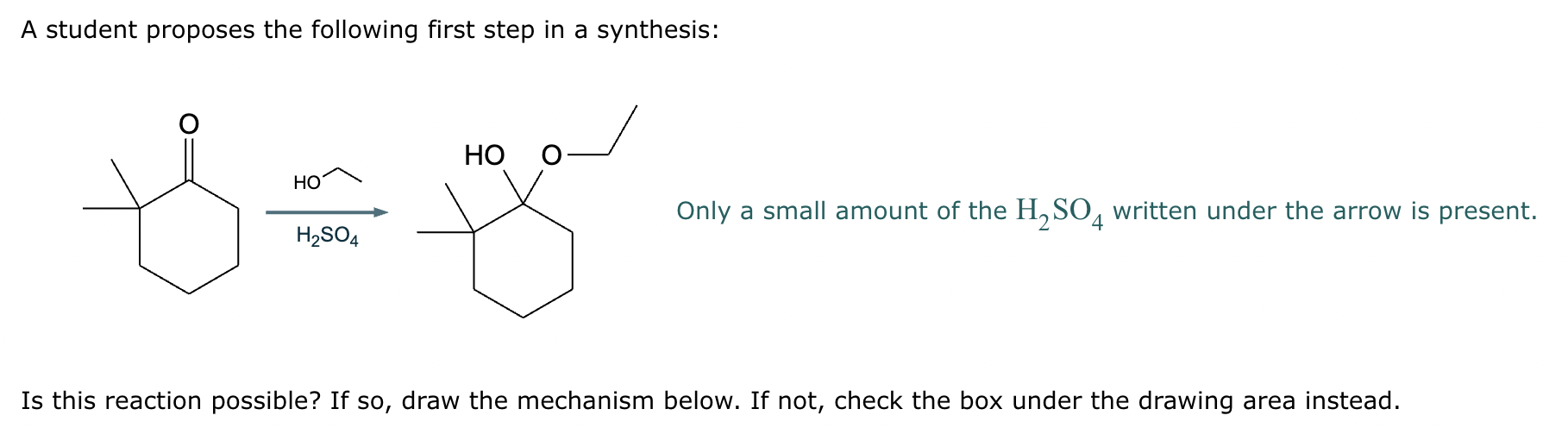
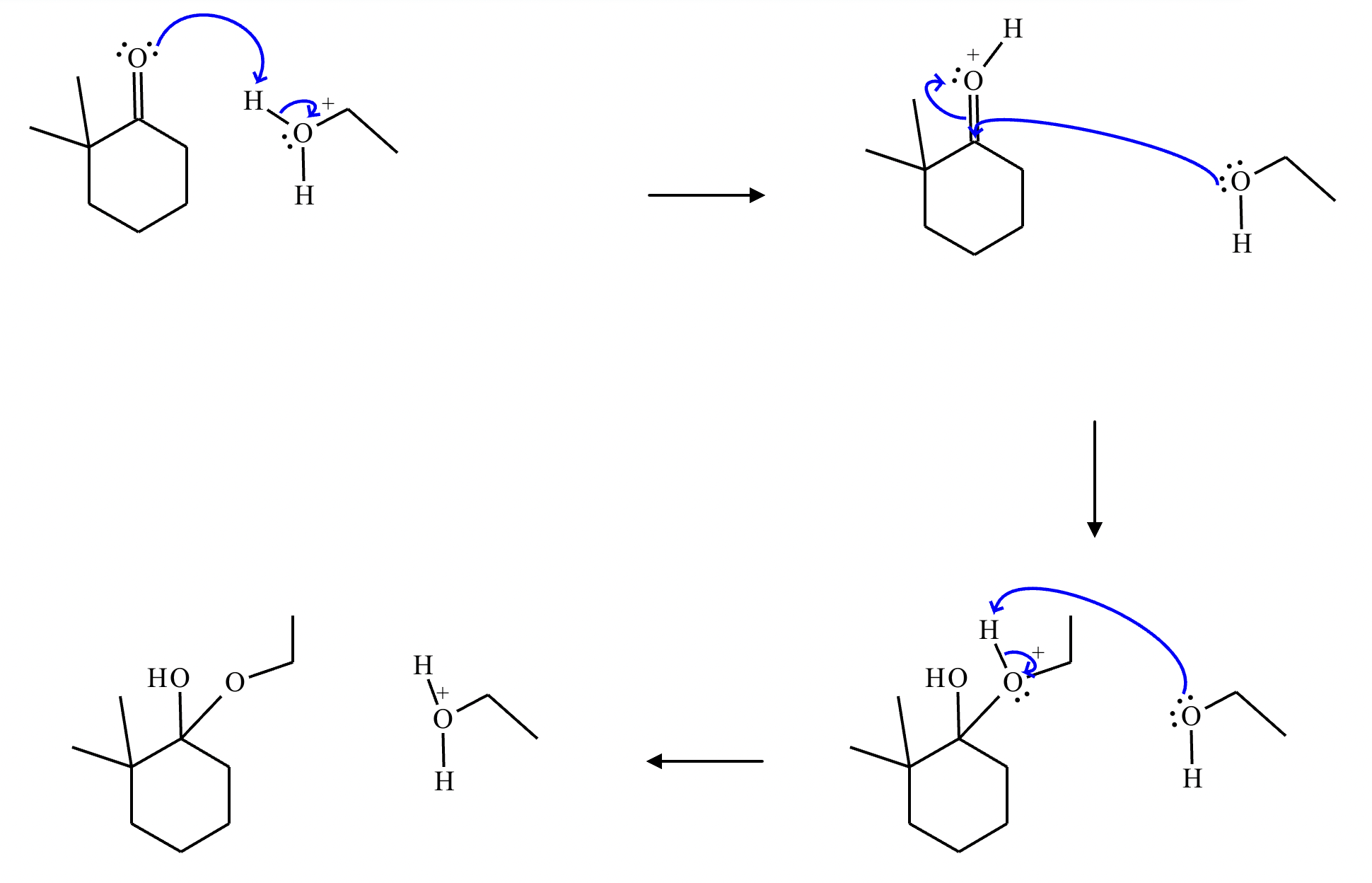
A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow.
Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area.
If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow.
You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown.
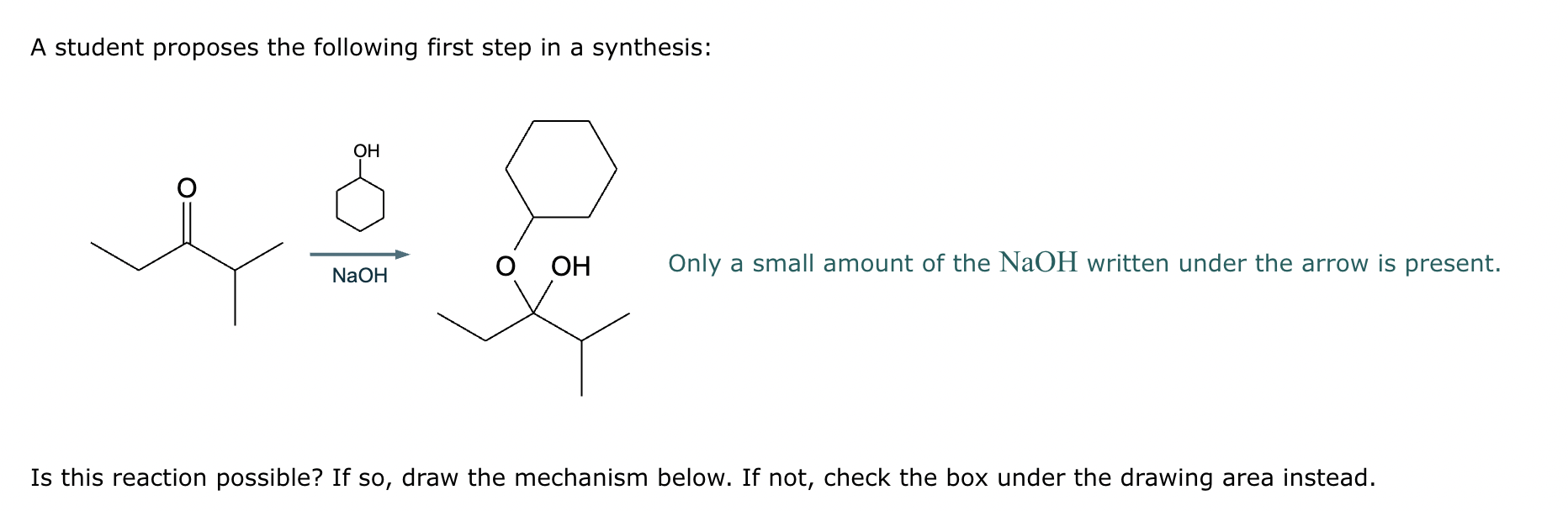
A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow.
Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area.
If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow.
You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown.
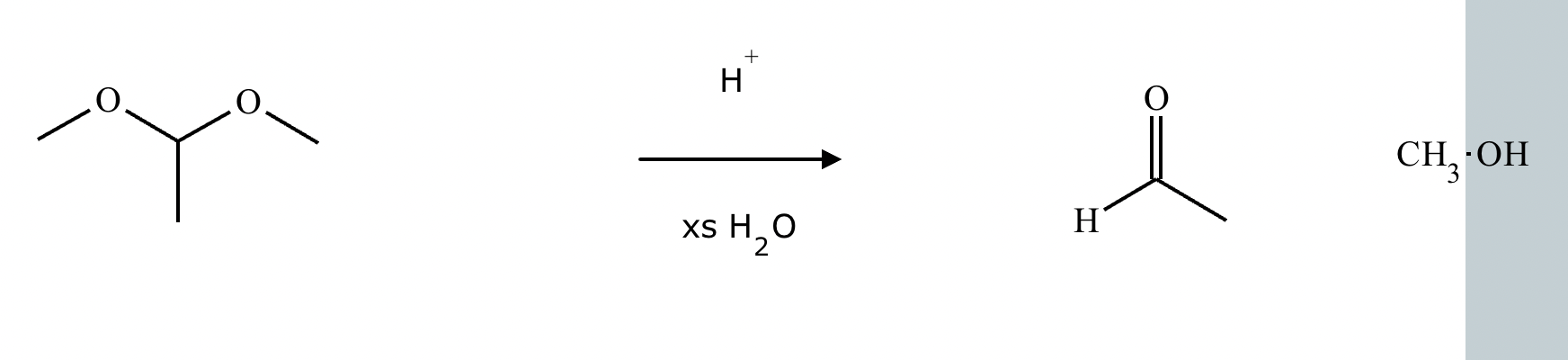
A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow.
Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area.
If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow.
You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown.
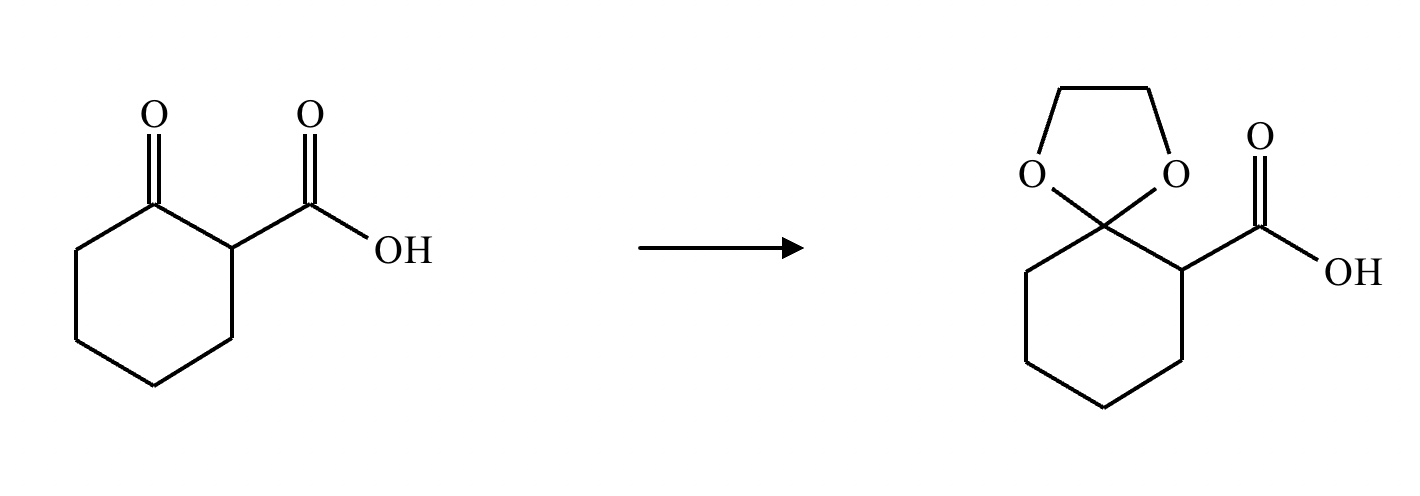
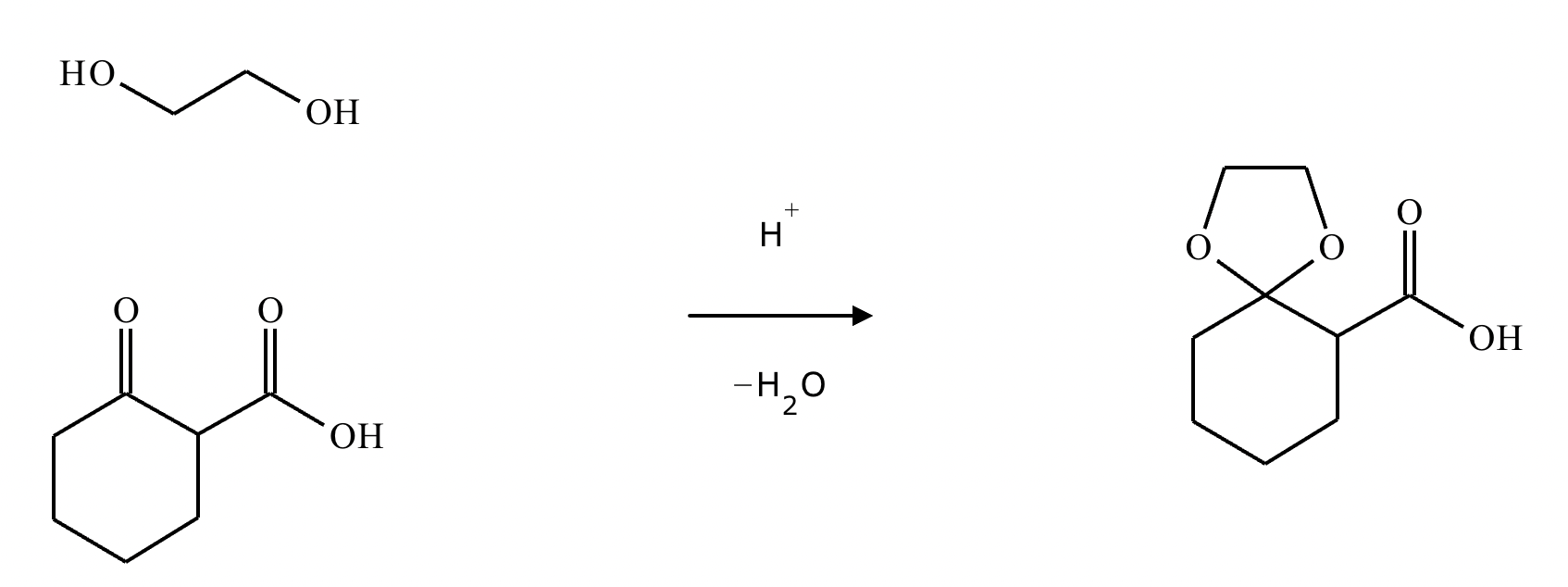
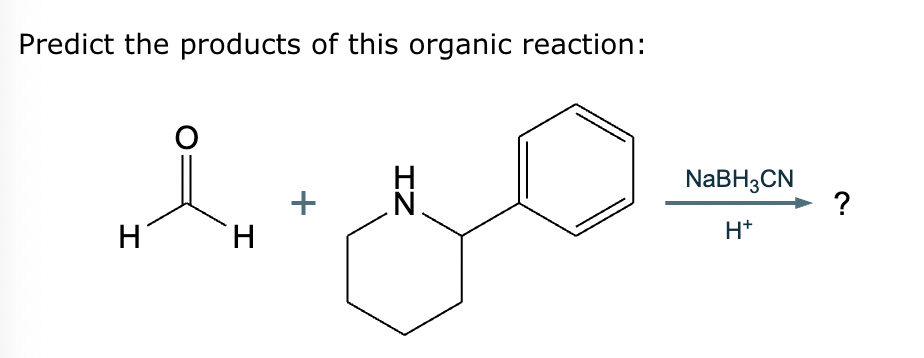
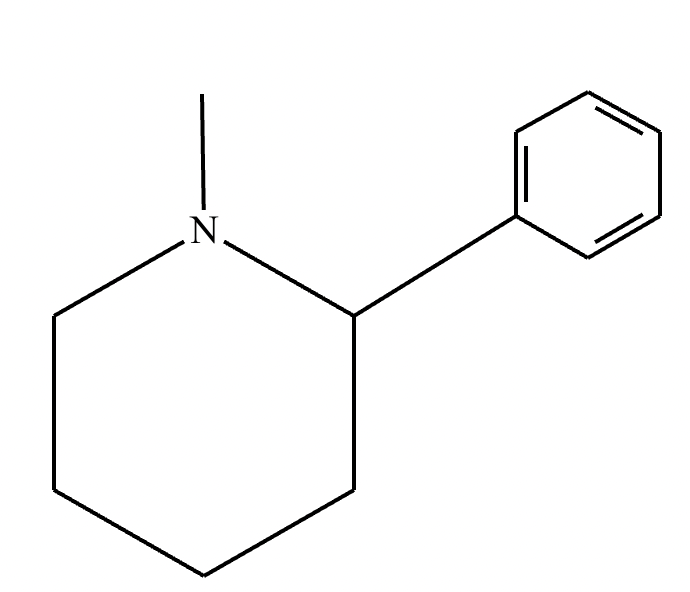
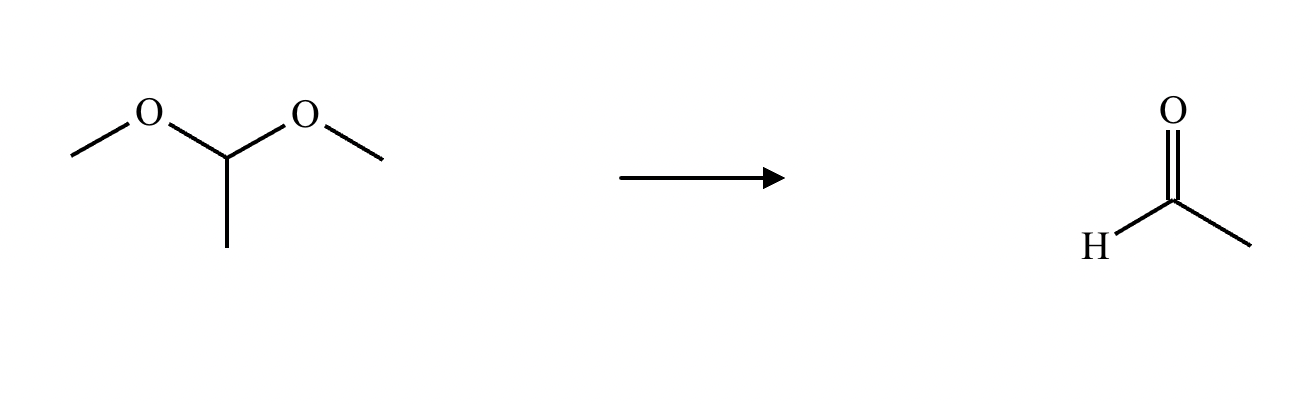
What’s the product of this reaction?
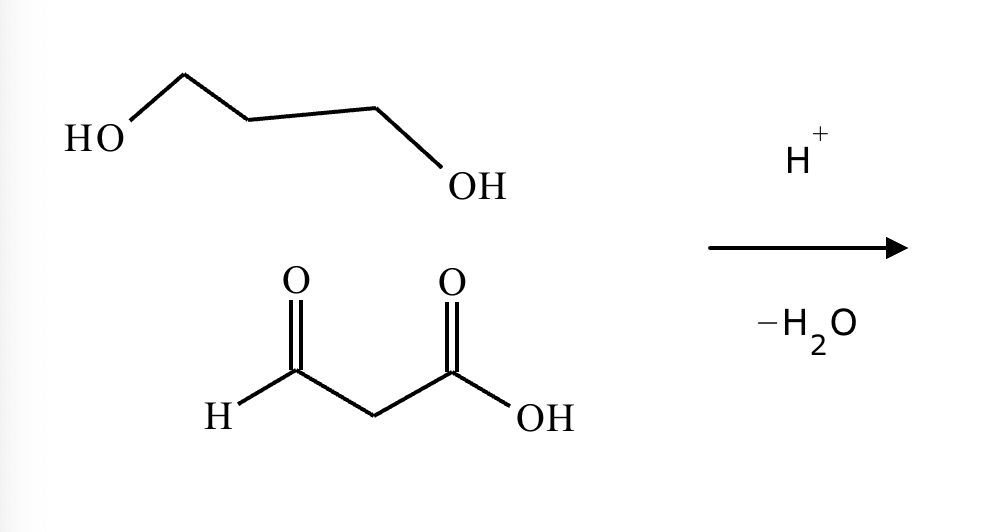
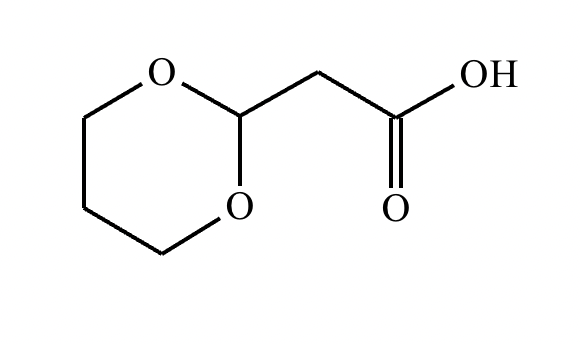
A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow.
Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area.
If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow.
You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown.
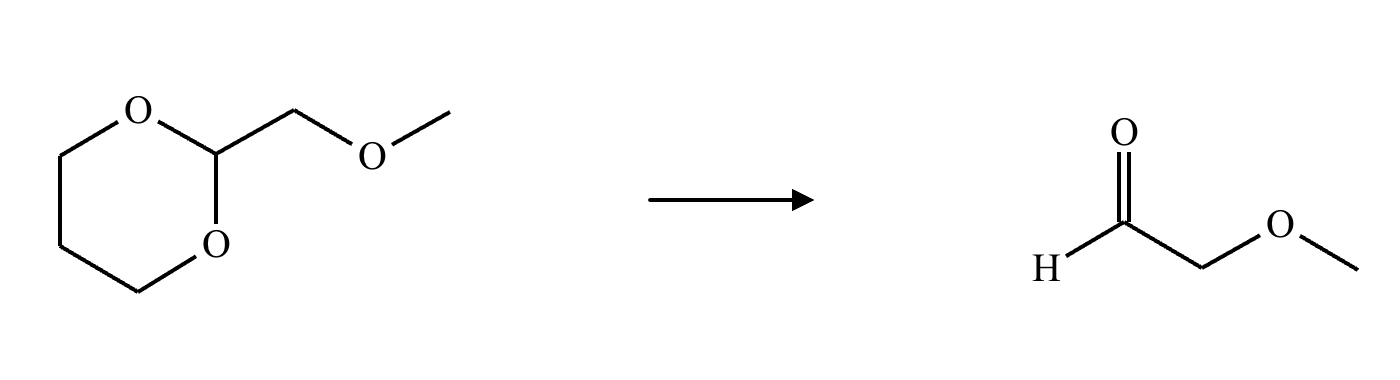
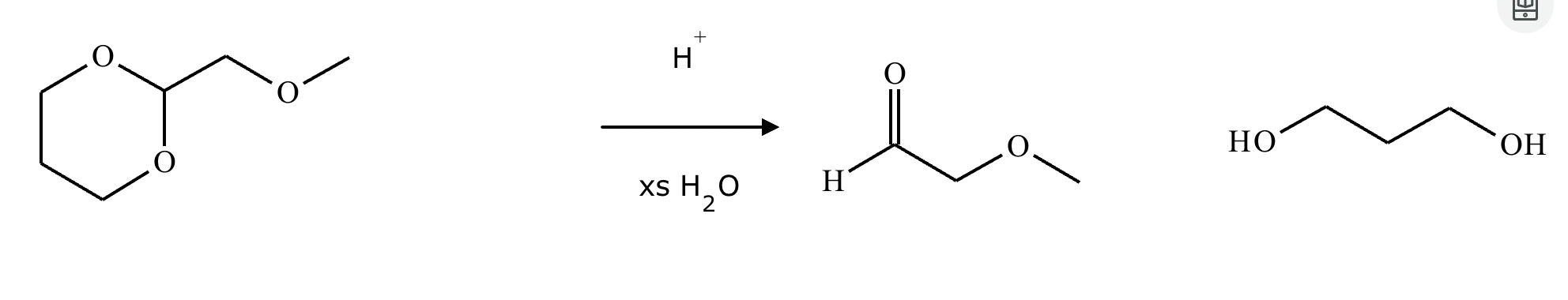
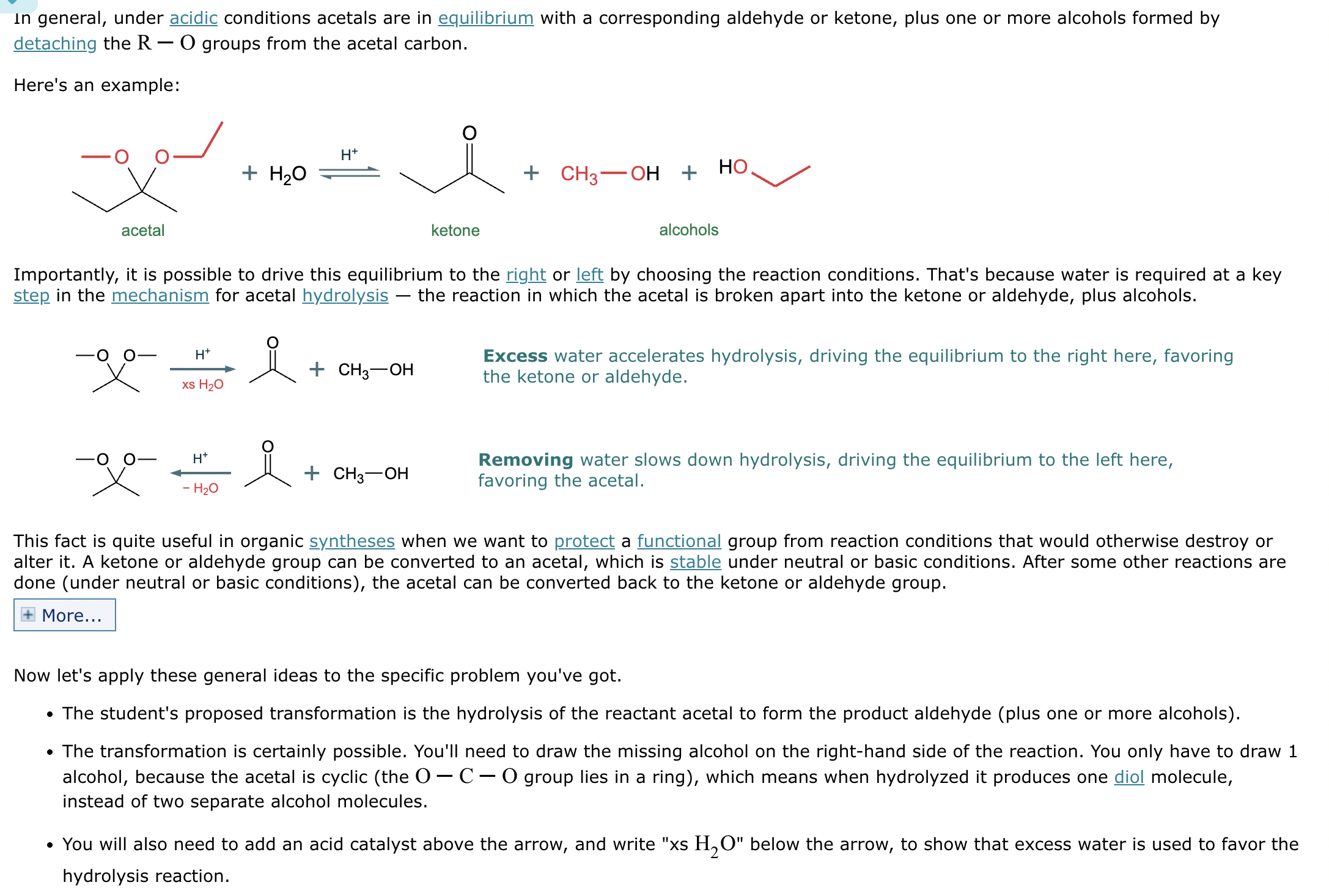
What’s the product of this reaction?
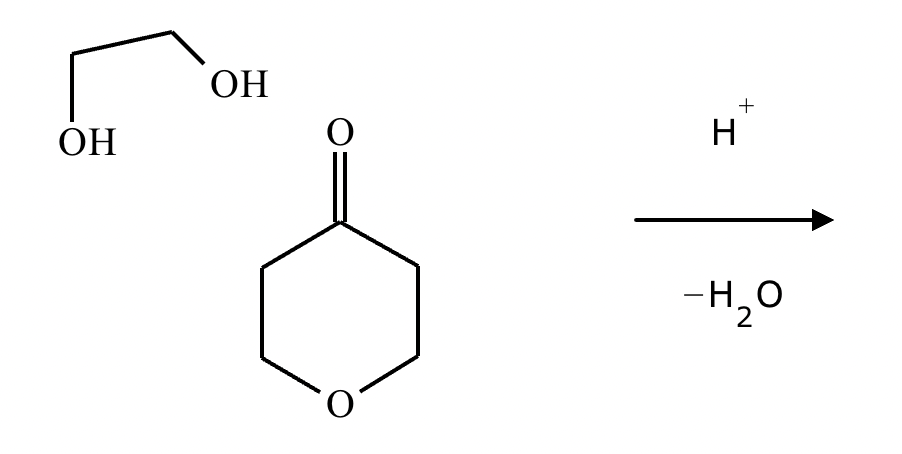
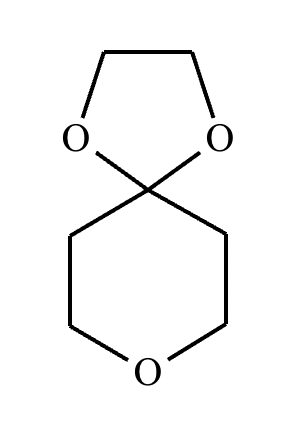
What are the products of this reaction?
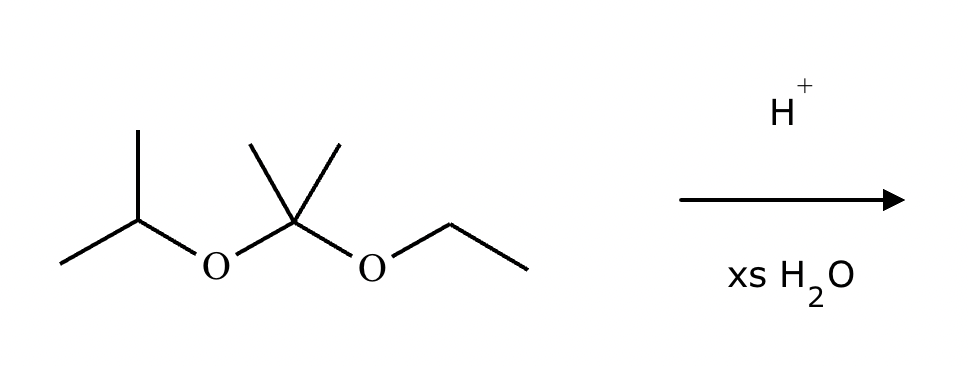
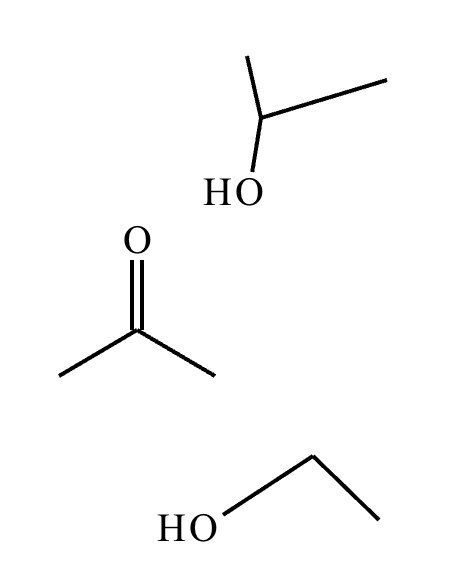
A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow.
Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area.
If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow.
You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown.
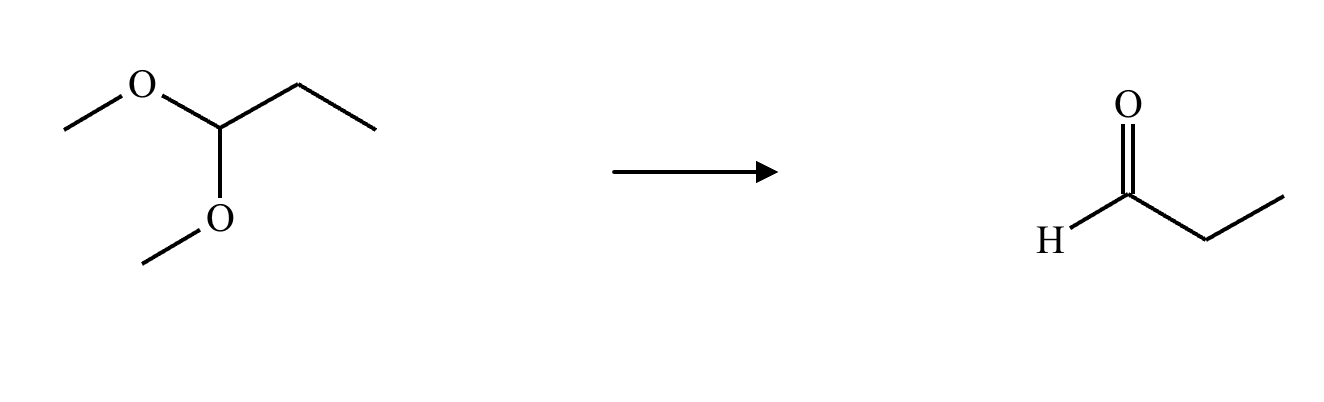
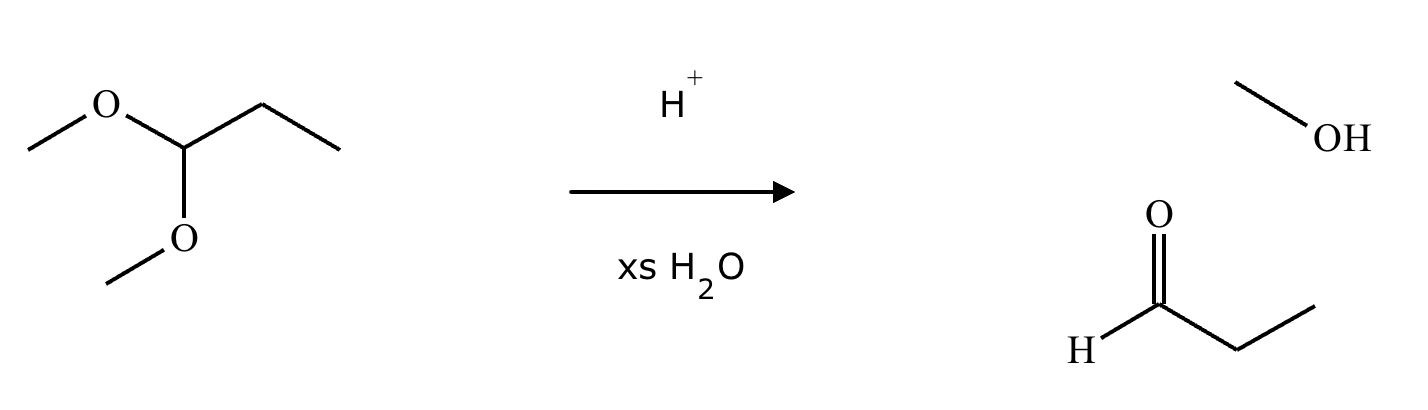
What’s the product of this reaction?
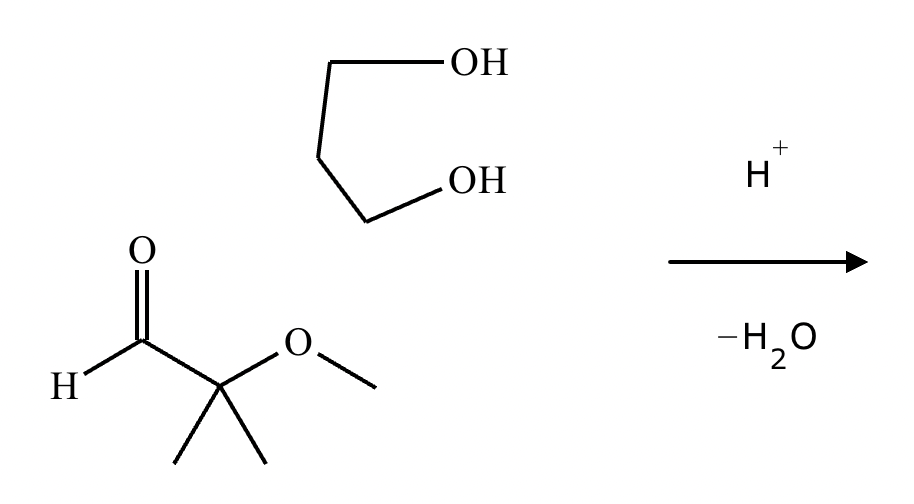
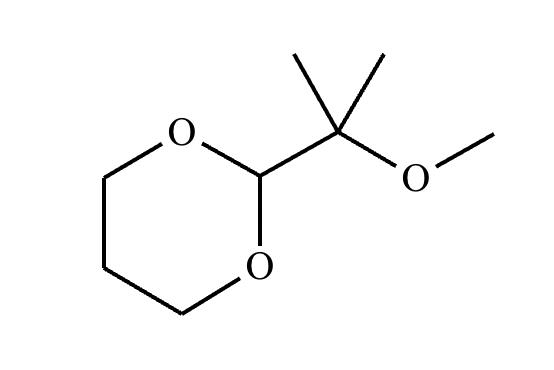
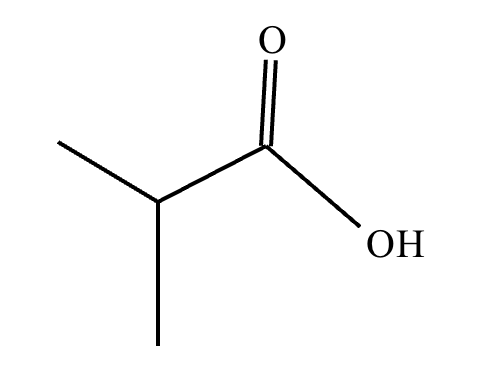
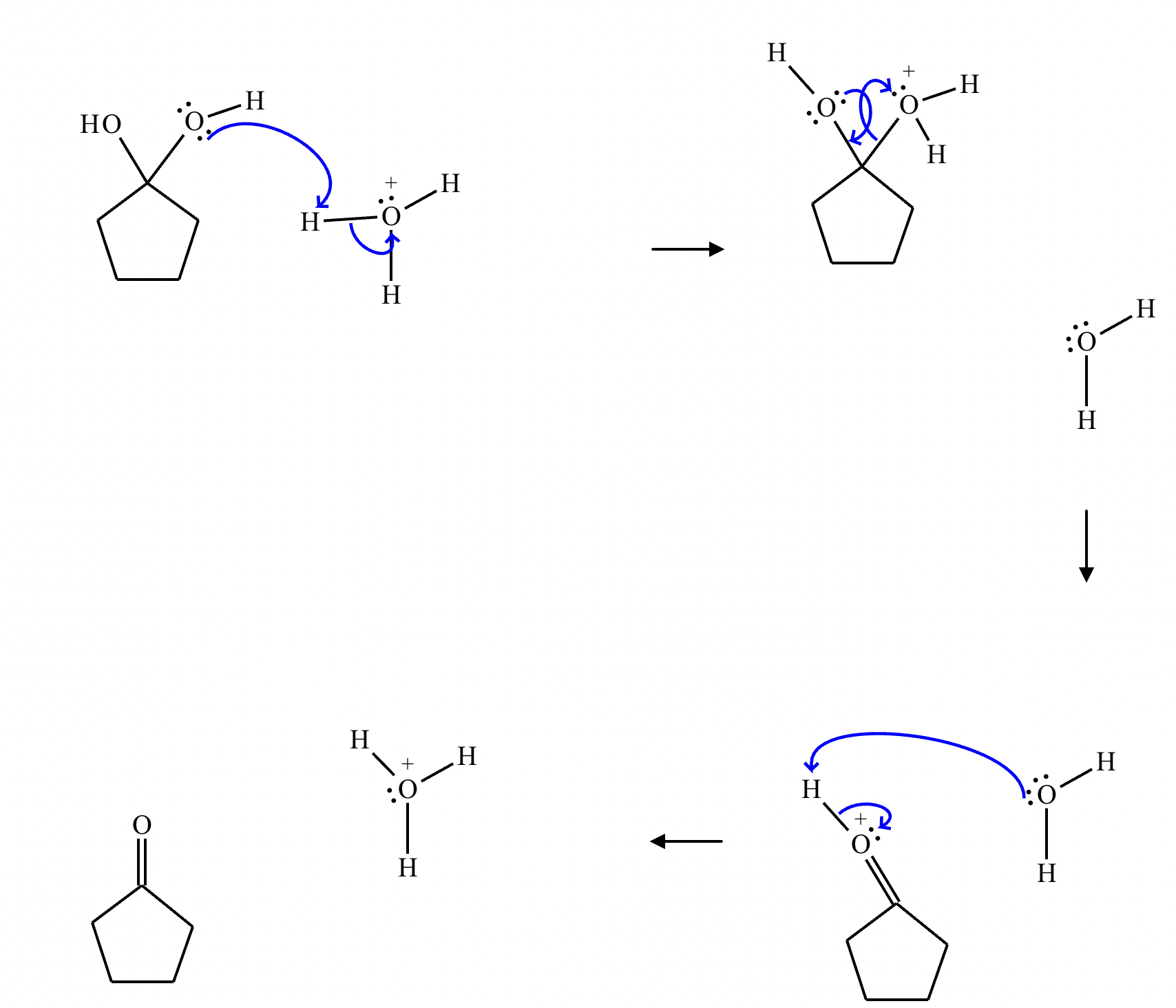
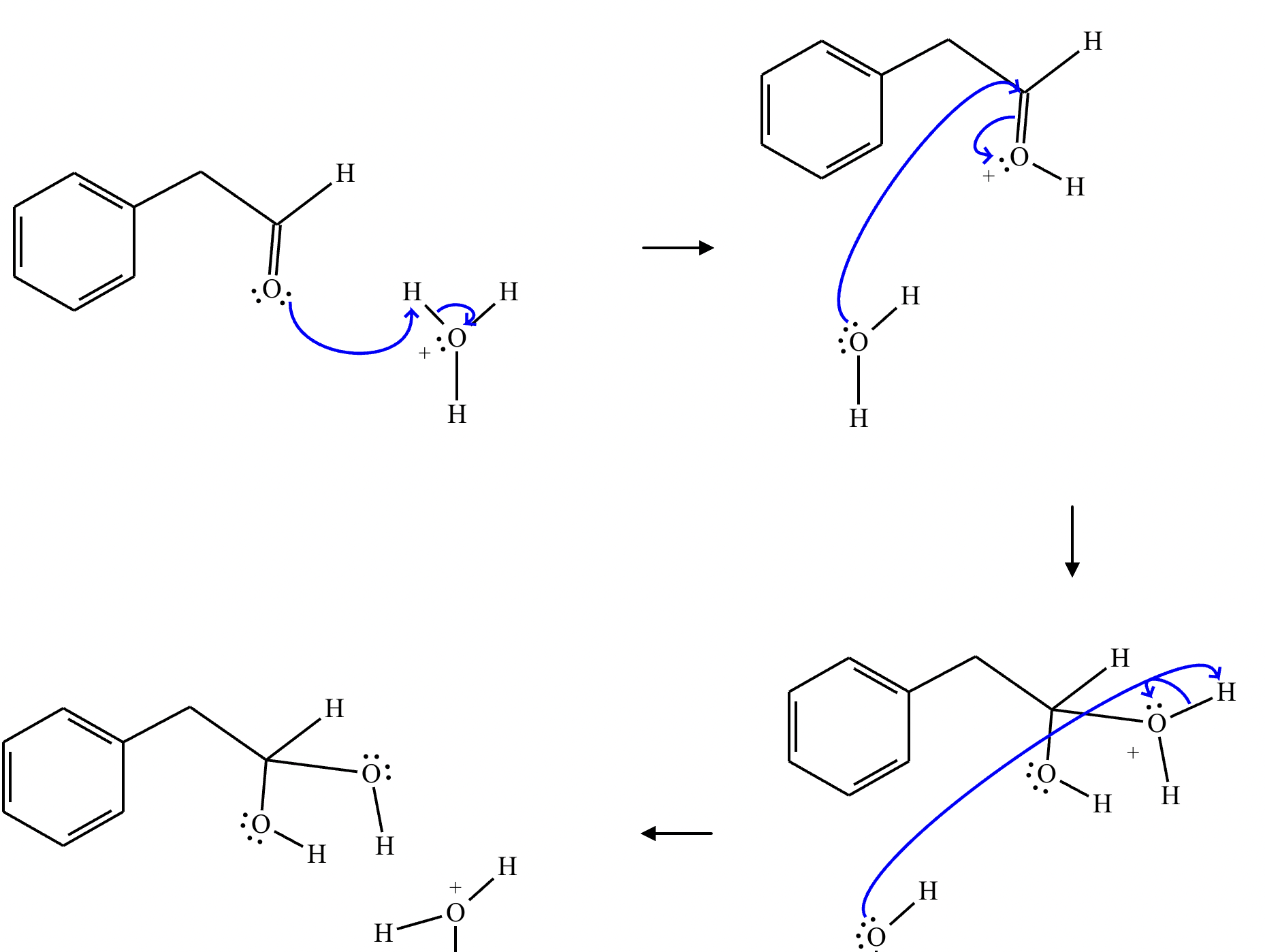
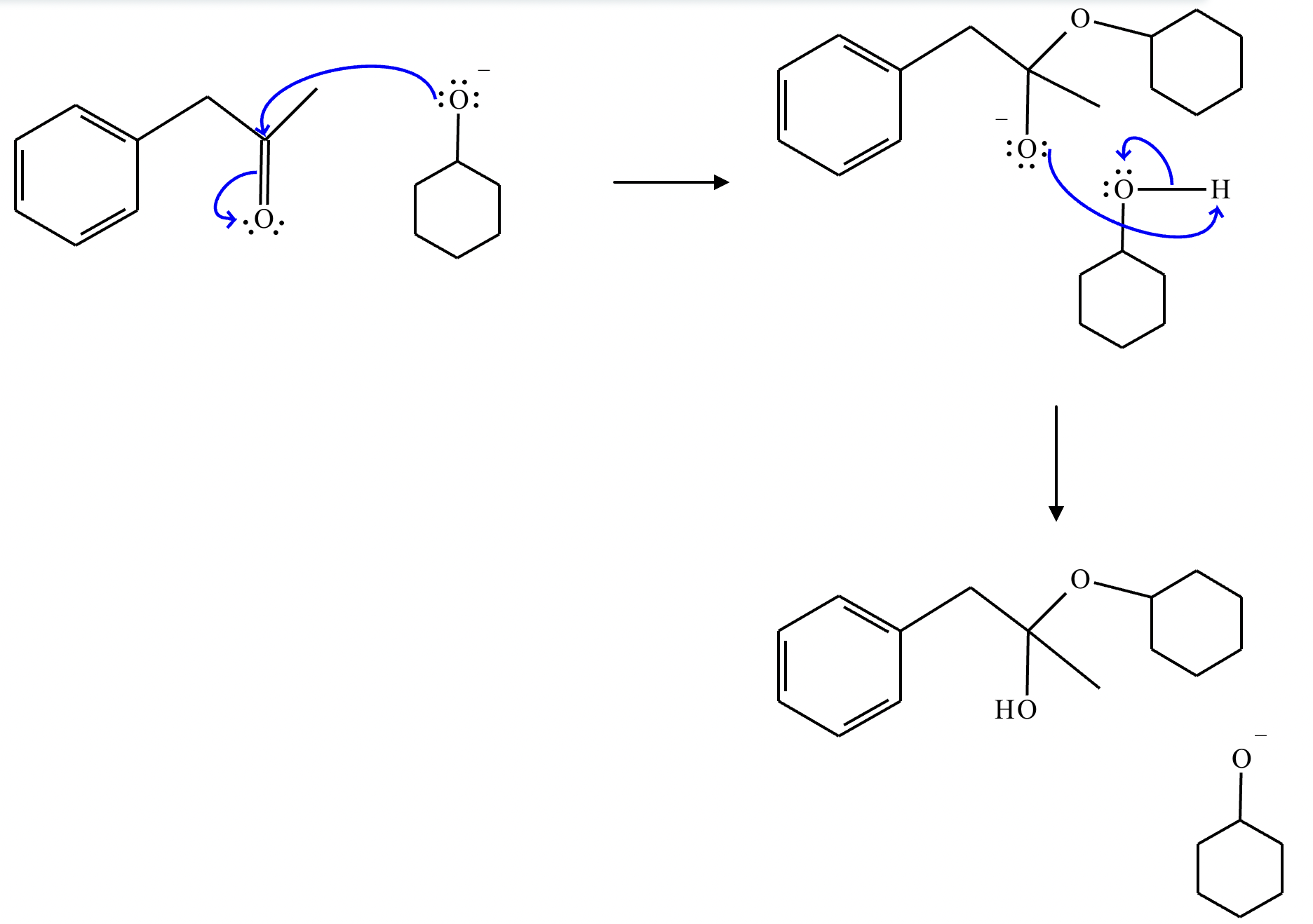
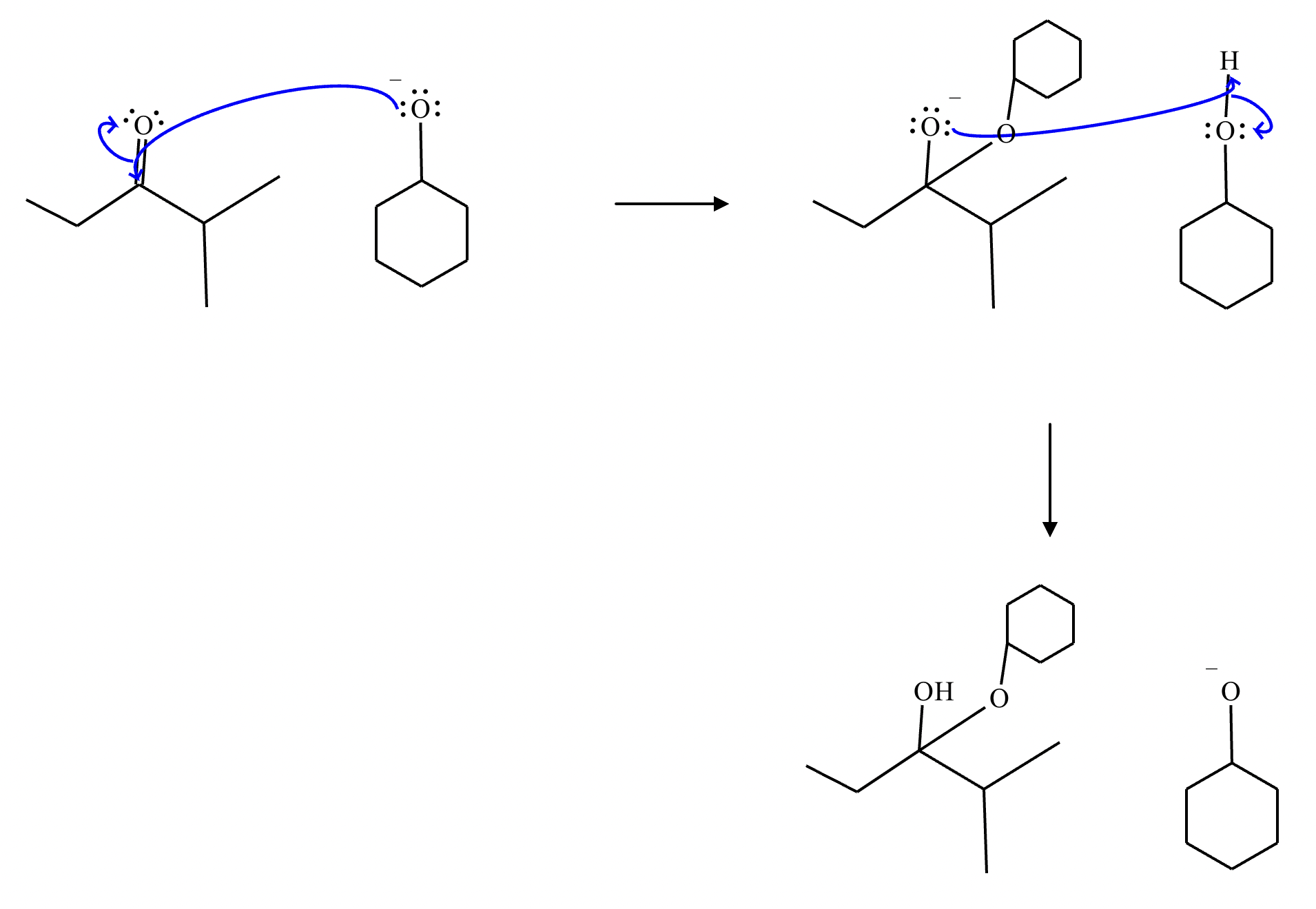
This organic molecule is dissolved in an acidic aqueous solution.
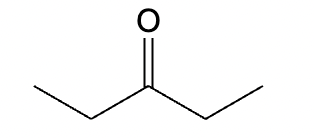
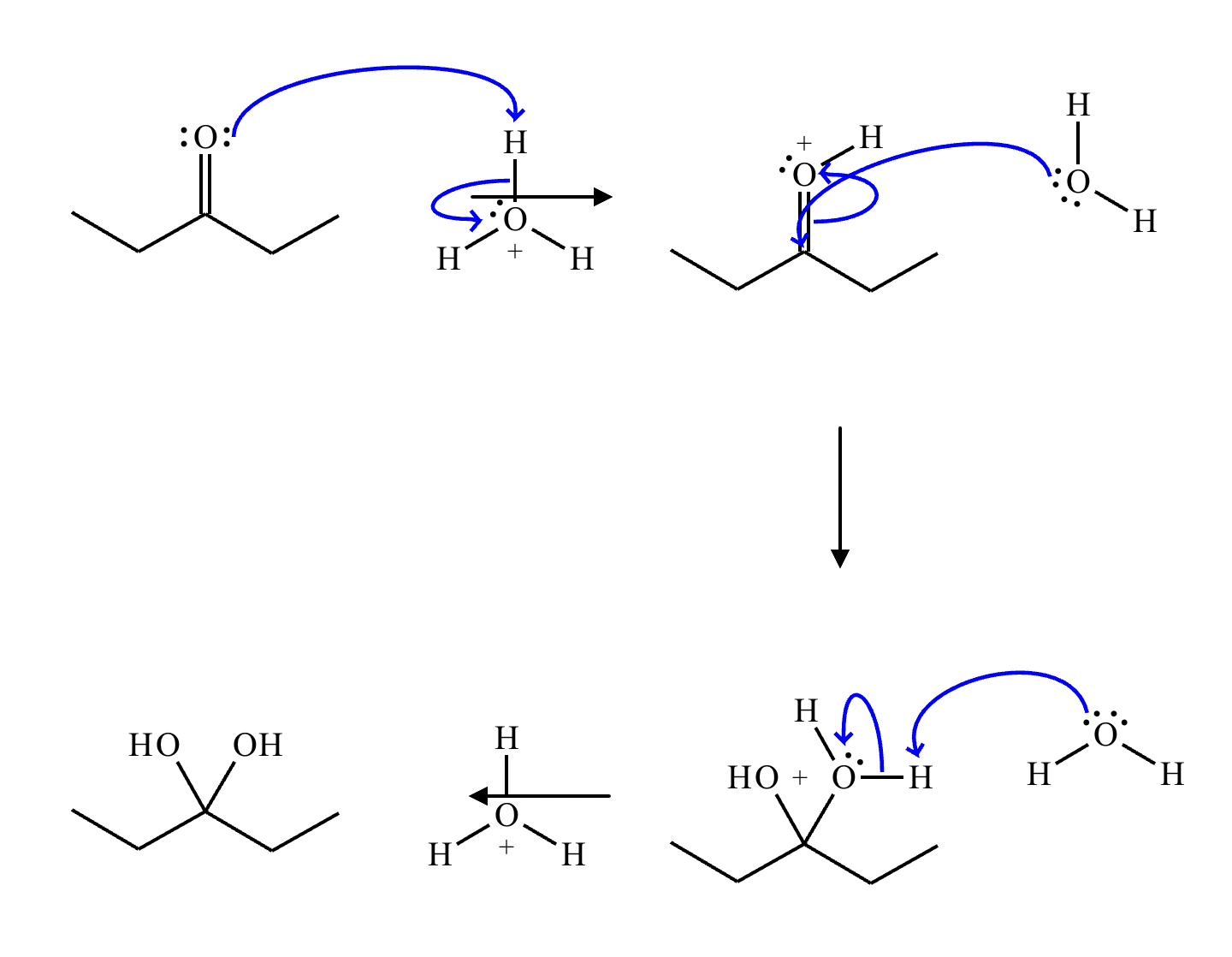
A short time later, sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C—OH stretch absorption. That is, there must now be a new molecule present with at least one C—OH bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule.
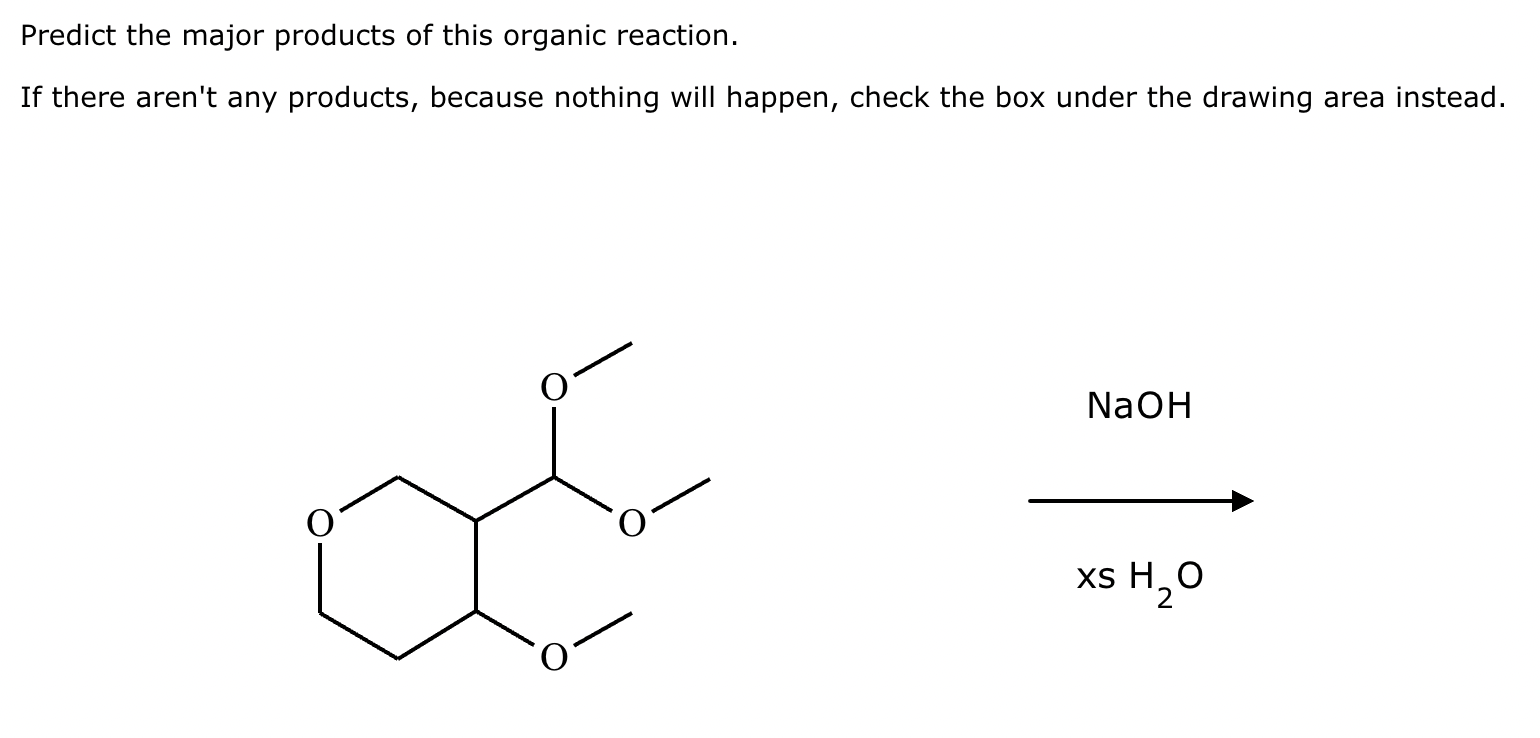
No reaction.

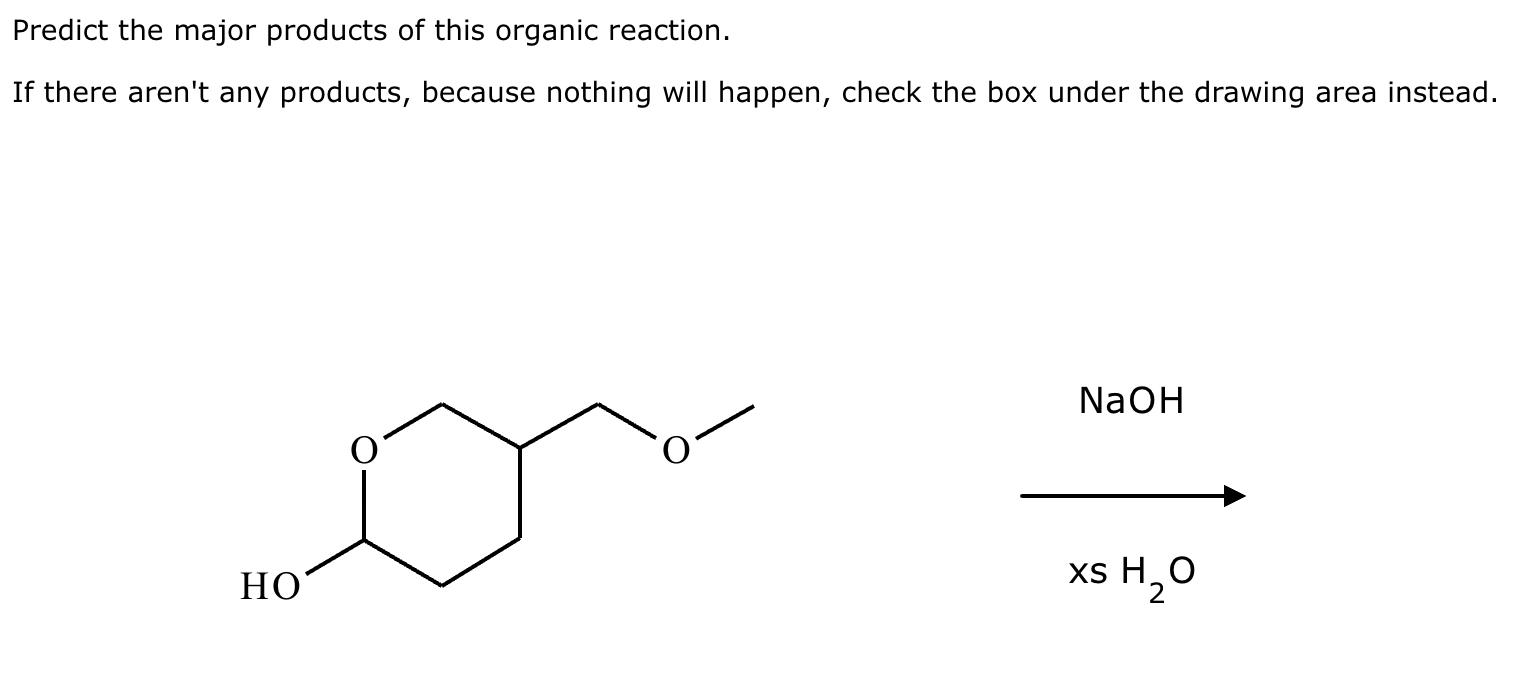
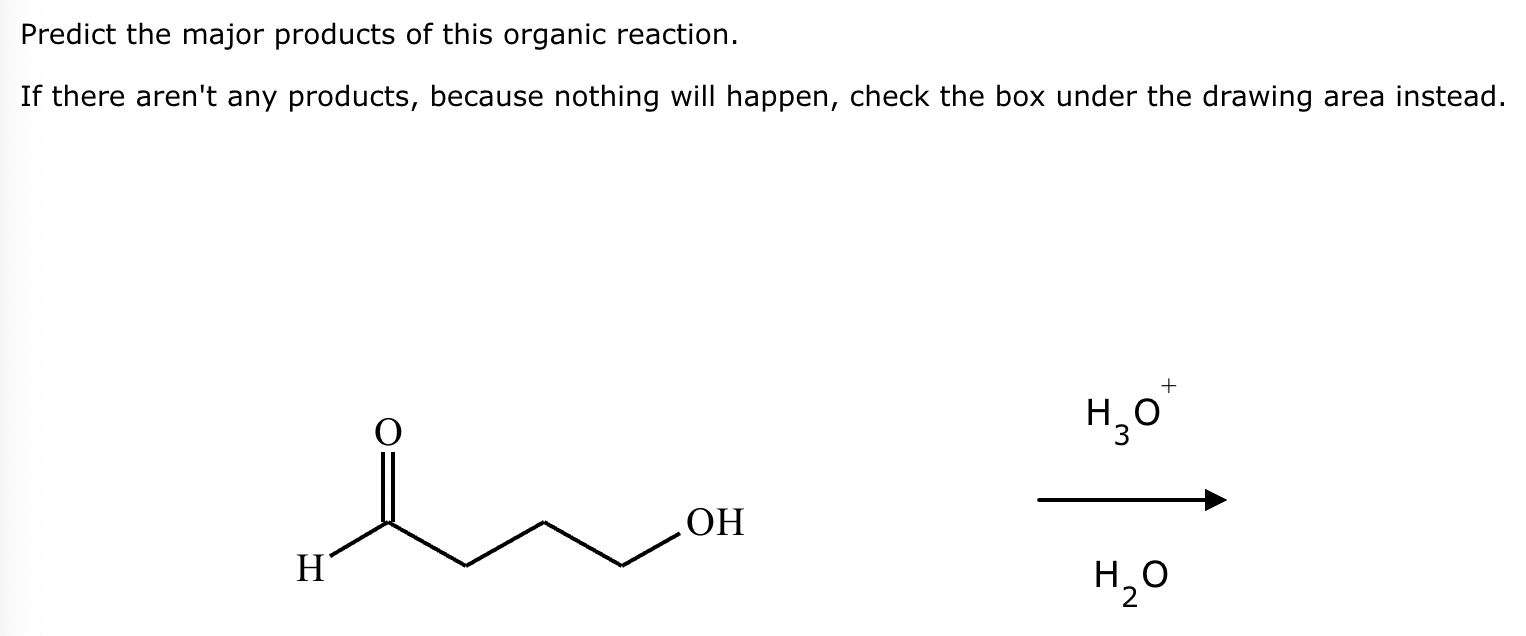
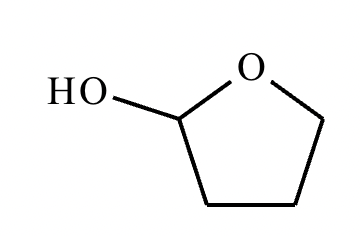
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
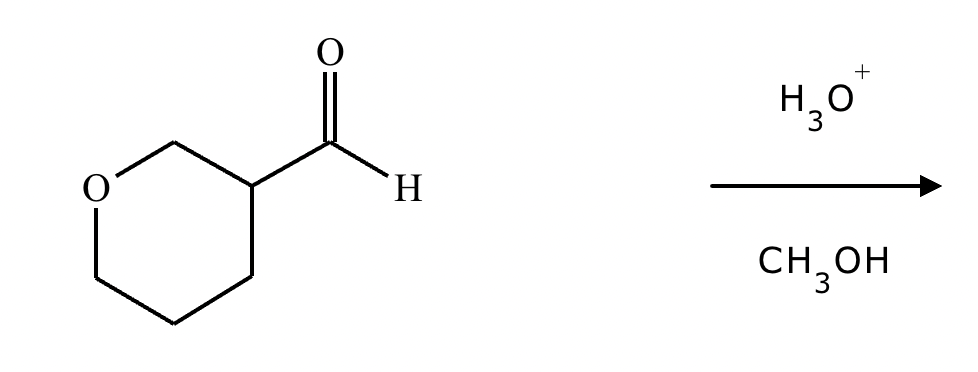
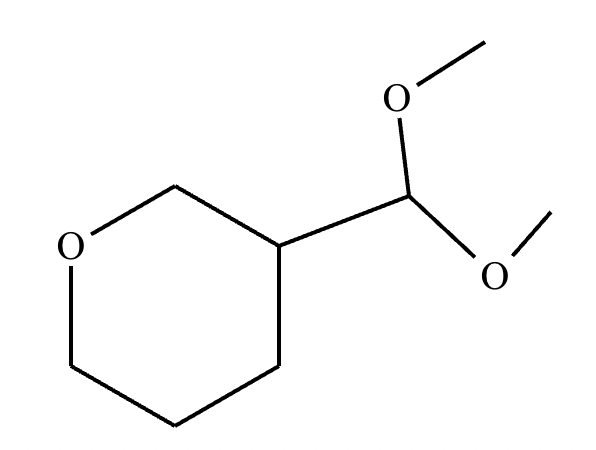
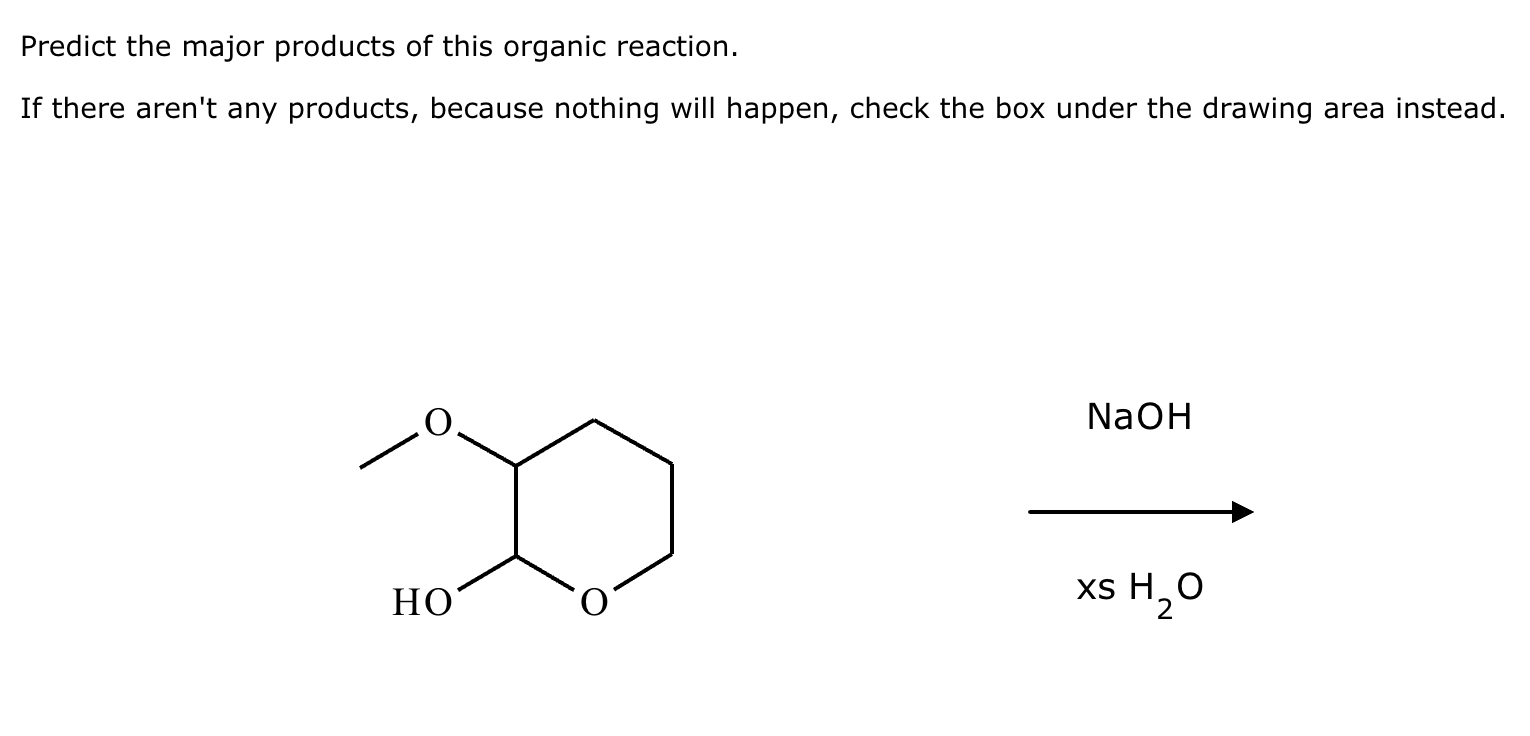
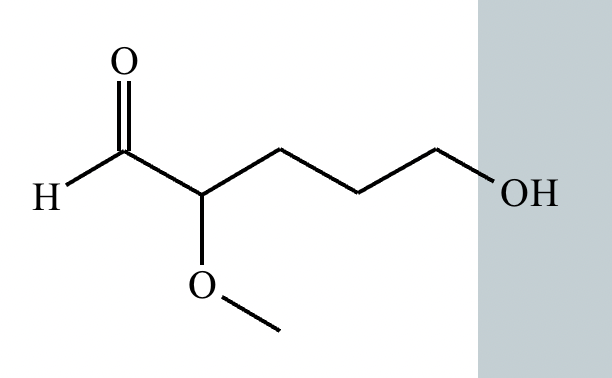
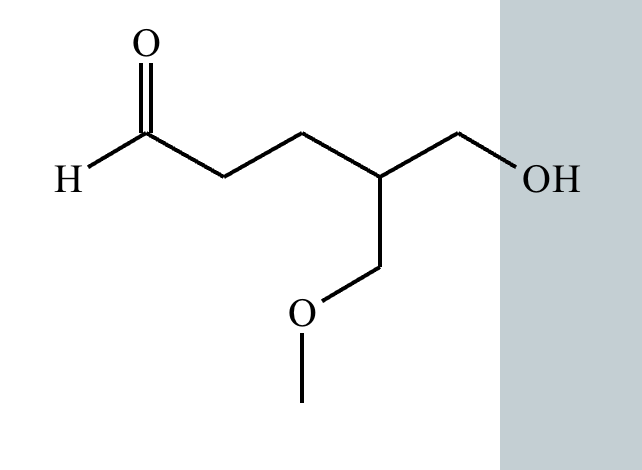
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.

No reaction. (Can’t be in basic conditions for acetals).
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
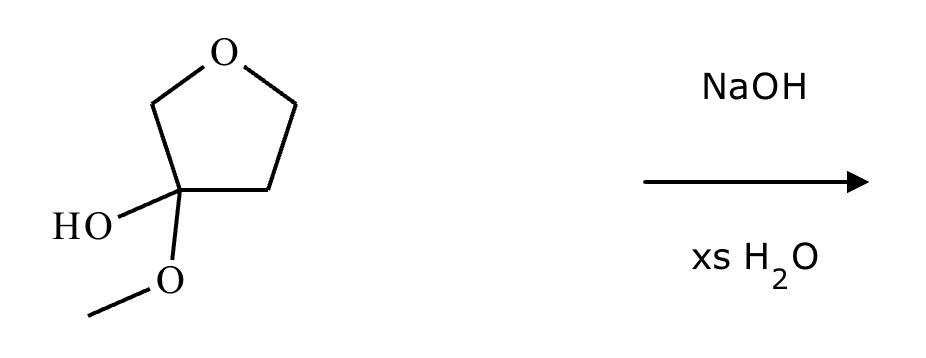
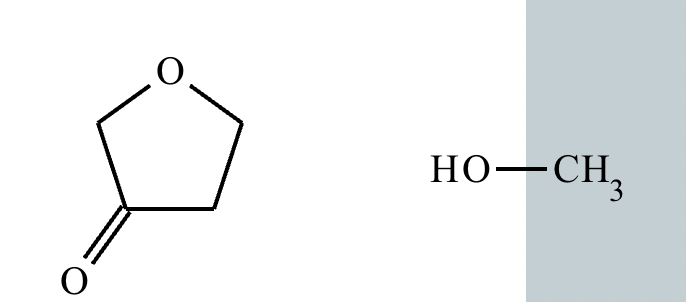
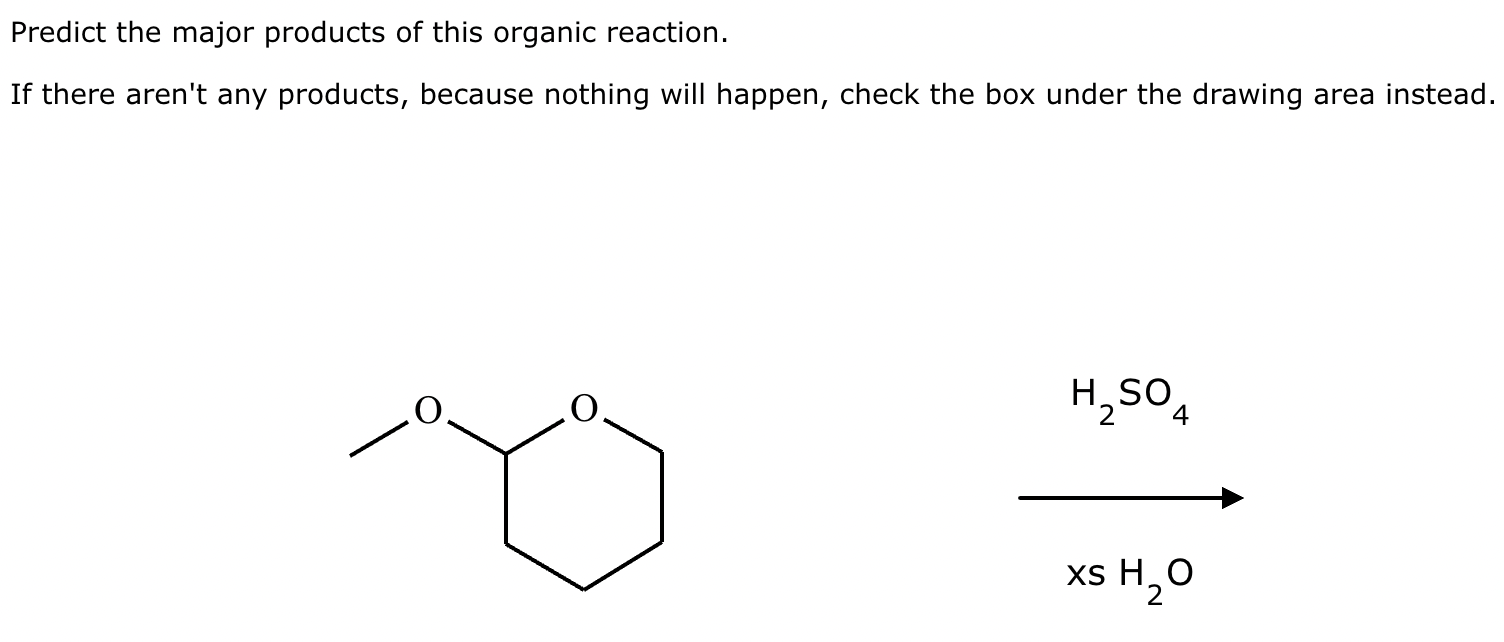
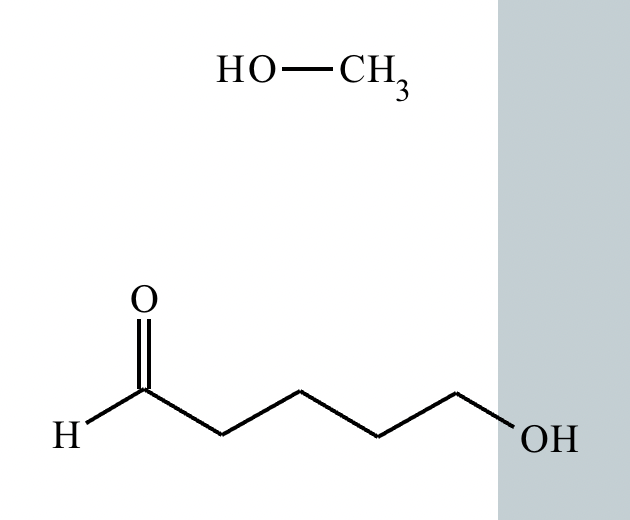
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
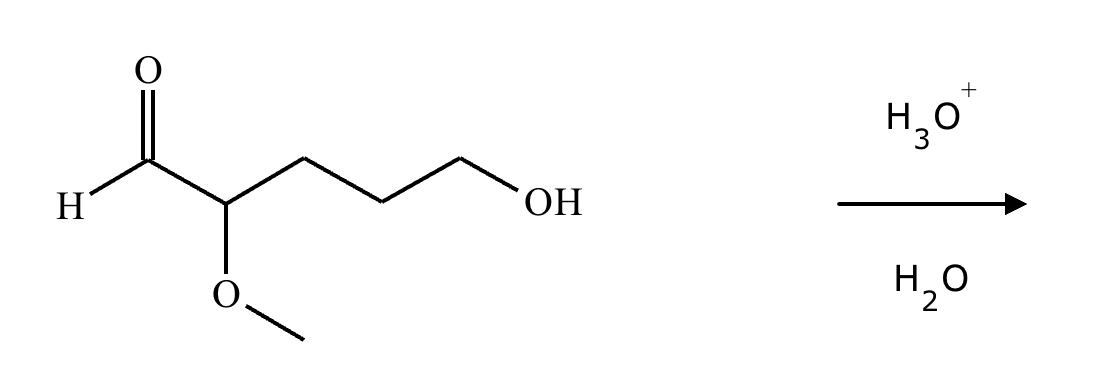
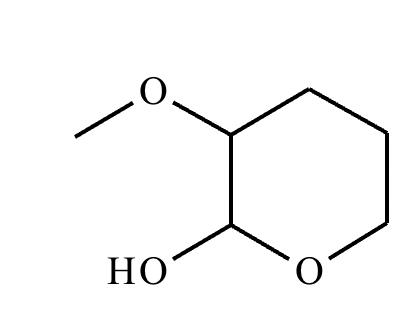
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
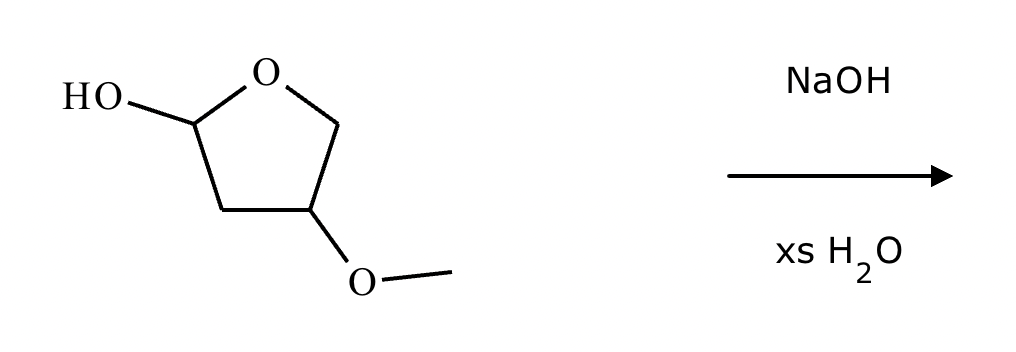
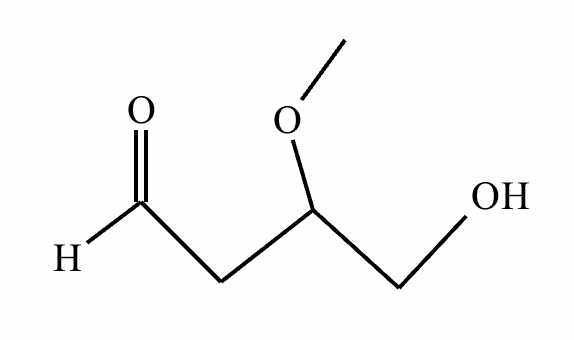
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
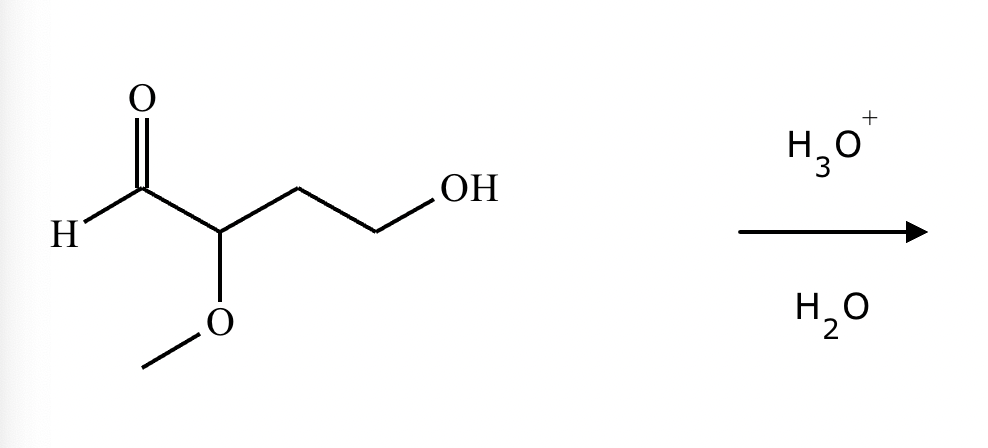
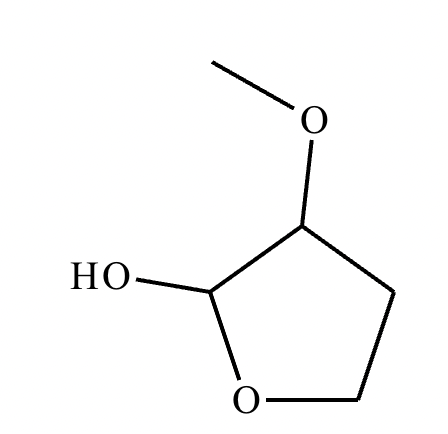
Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead.
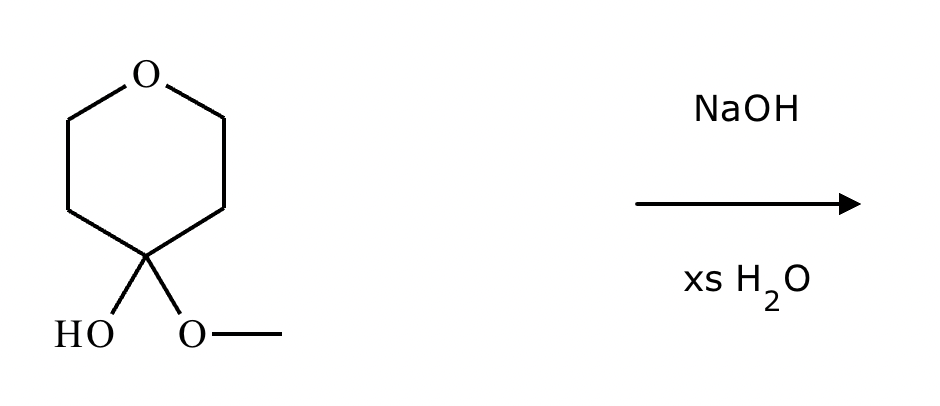
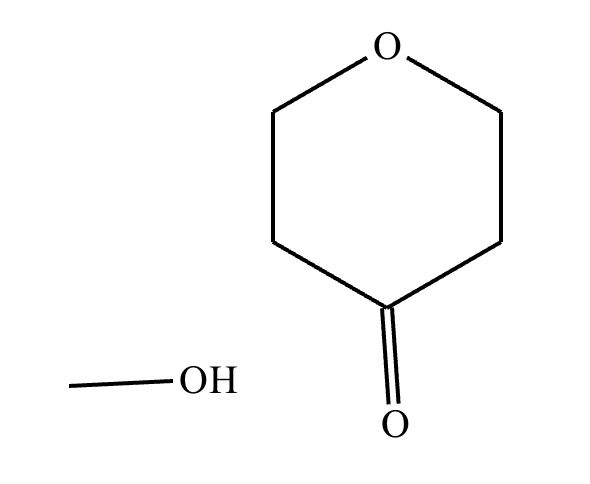
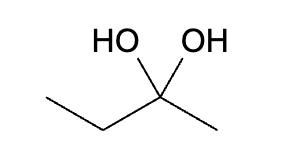
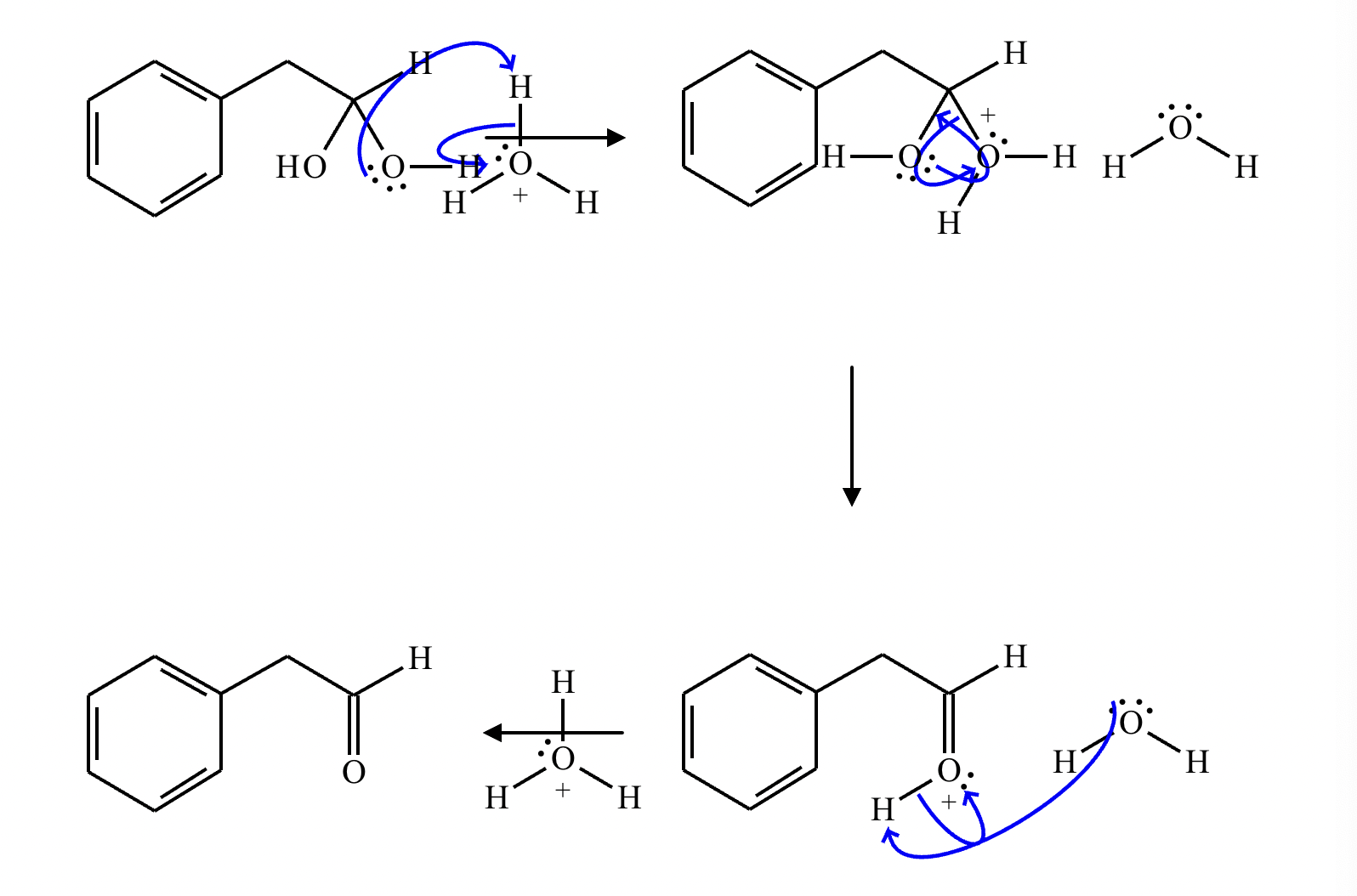
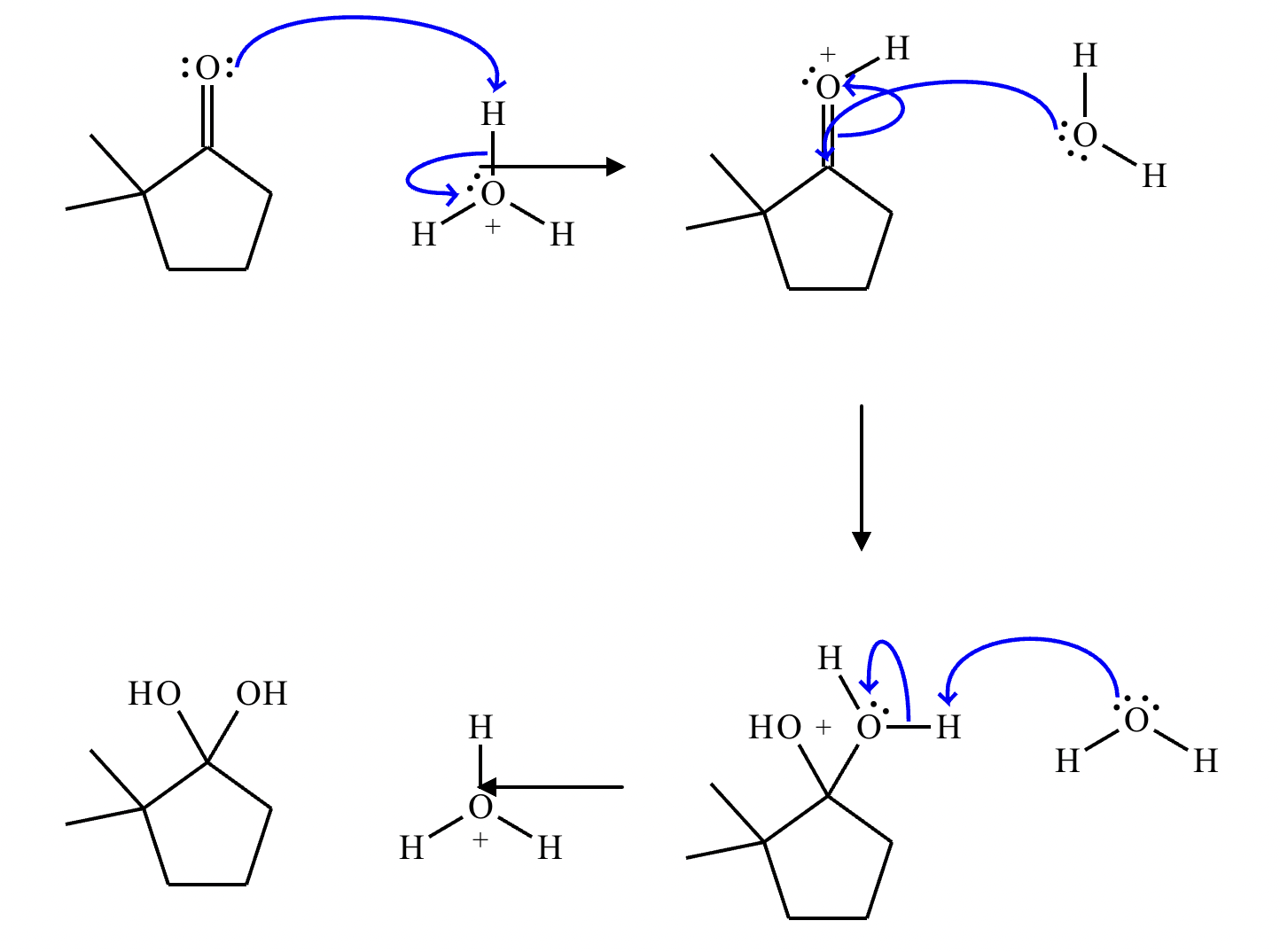
This organic molecule is dissolved in an acidic aqueous solution. A short time later, sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C=O stretch absorption. That is, there must now be a new molecule present with at least one C=O bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule.
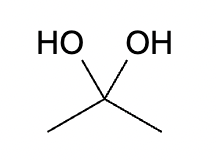
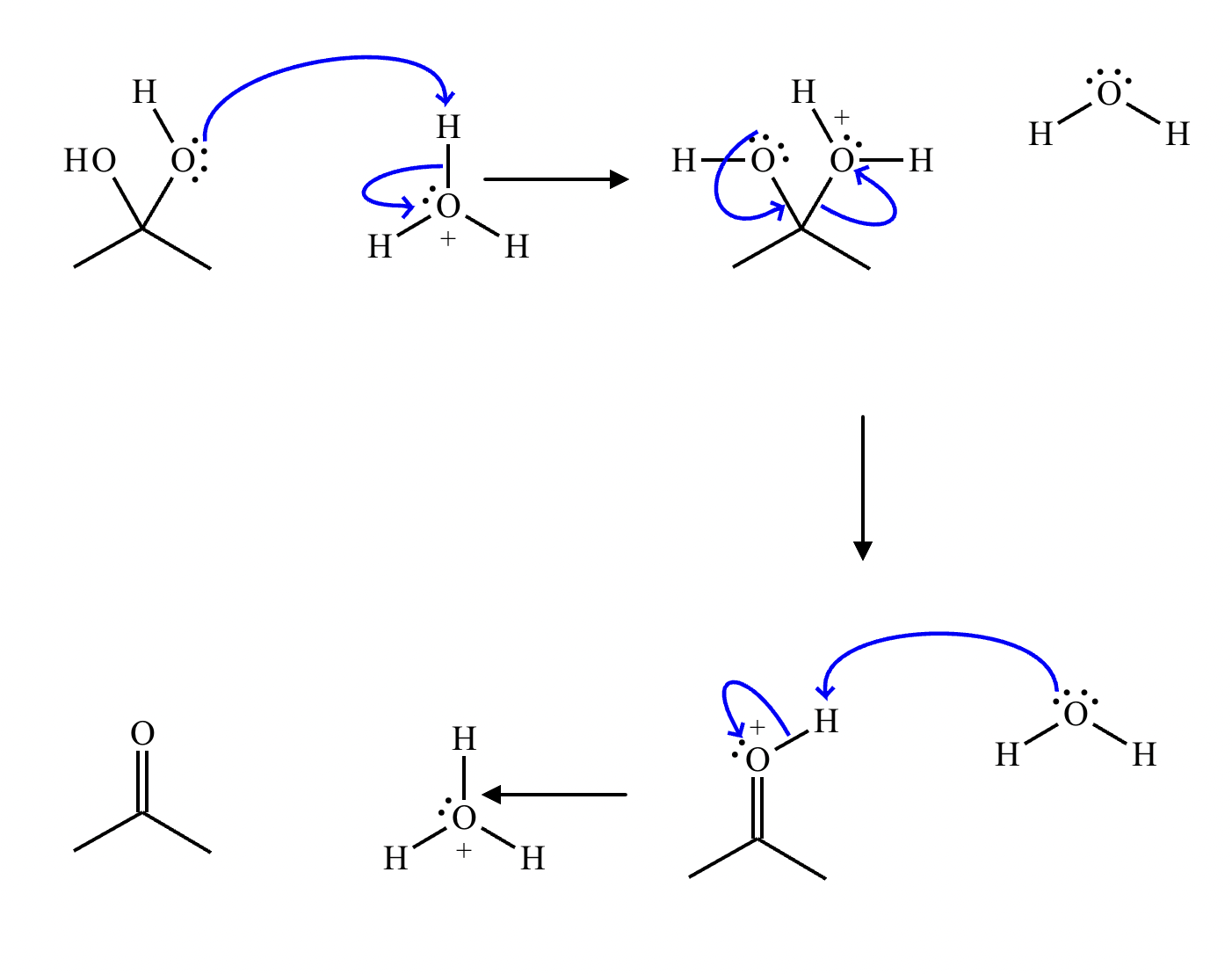
This organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution. A short time later, sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C—OH stretch absorption. That is, there must now be a new molecule present with at least one C—OH bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule.
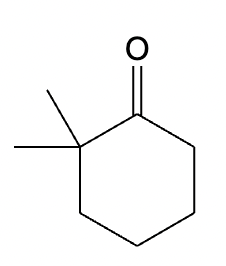
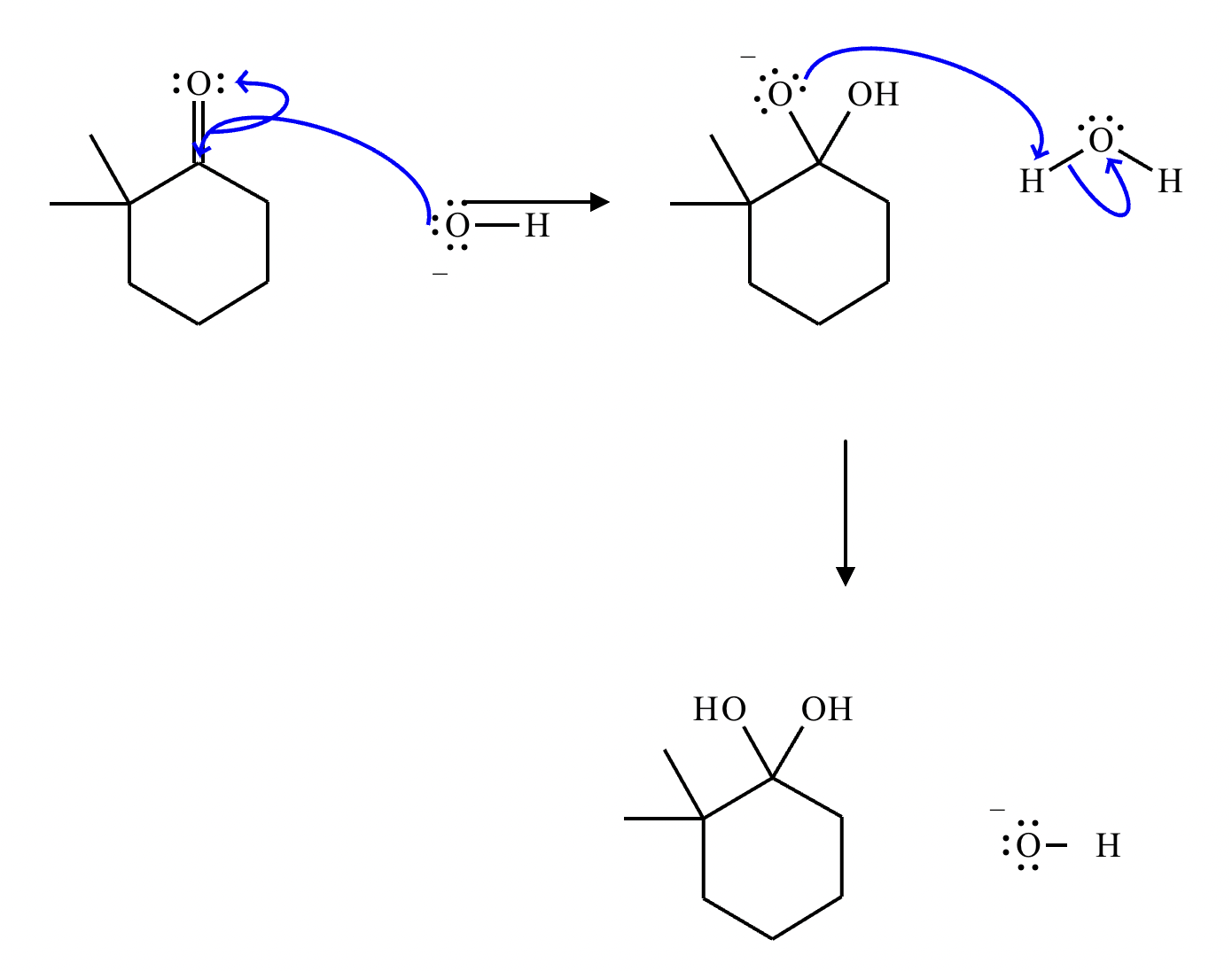
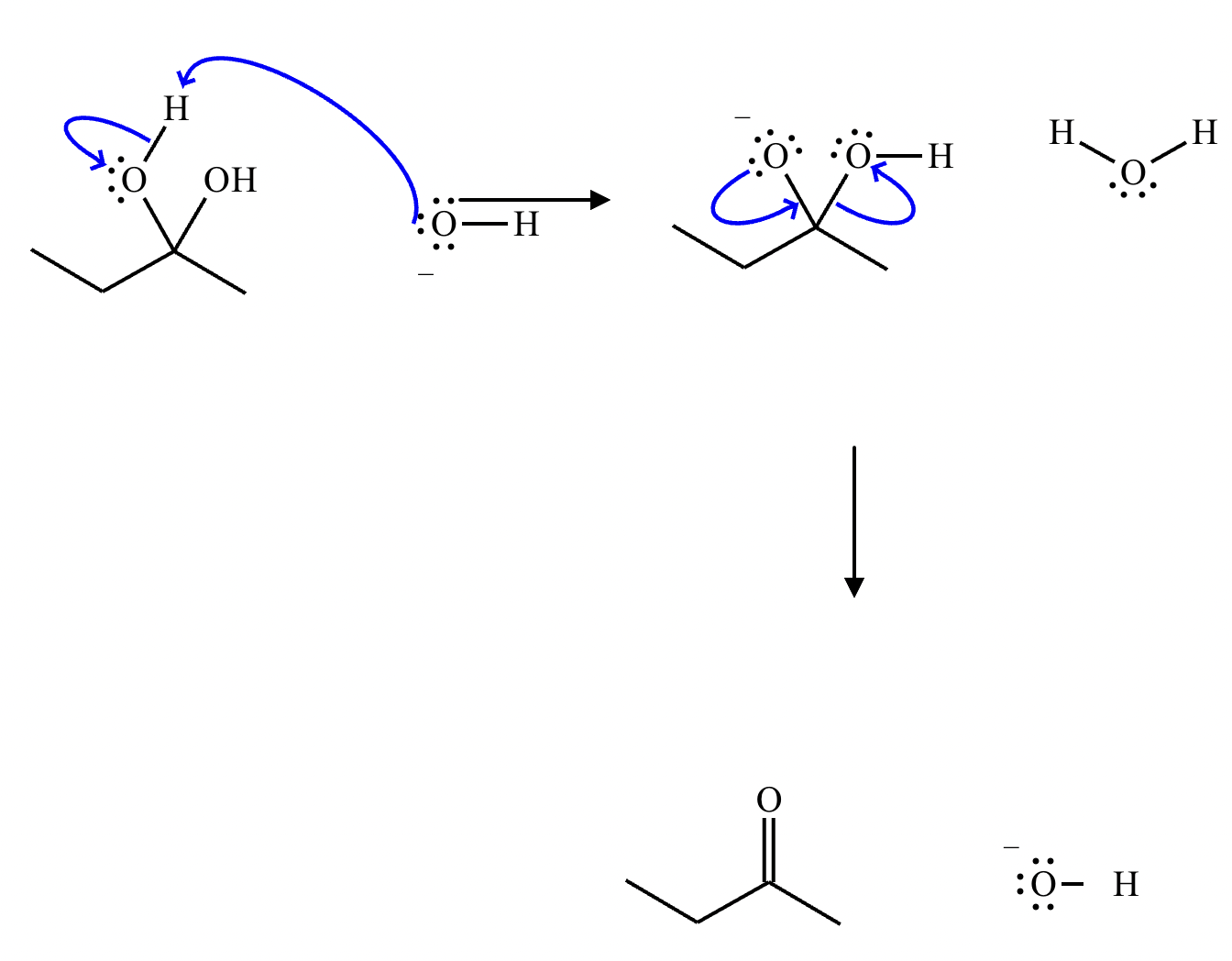
This organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution. A short time later, sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C=O stretch absorption. That is, there must now be a new molecule present with at least one C=O bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule.