H Chemistry - Unit 2 - All Sub-units
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
What are compounds containing only single carbon-carbon bonds described as?
Compounds containing only single carbon-carbon bonds are described as saturated
What are compounds containing double carbon-carbon bonds described as?
Compounds containing double carbon-carbon bonds are described as unsaturated
What happens in an addition reaction?
In an addition reaction, two molecules combine to form a single molecule
What is the test for saturation?
Unsaturated compounds rapidly decolourise bromine solution.
What are the 8 prefixes?
The 8 prefixes are;
Meth
Eth
Prop
But
Pent
Hex
Hept
Oct
What are isomers?
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae. They may belong to different homologous series and usually have different physical properties.
How can solubility, boiling point, and volatility of a compound be predicted?
Solubility, boiling point, and volatility of a compound can predicted by considering;
The presence of O-H or N-H bonds, which imply hydrogen bonding
The spatial arrangement of polar covalent bonds which could result in a molecule possessing a permanent dipole
Molecular size, which would affect London Dispersion Forces
The polarities of solute and solvent. Polar and ionic compounds tend to be soluble in polar solvents, non-polar compounds tend to be soluble in non-polar solvents.
What is volatility?
Volatility is how easily a molecule evaporates
What is an alcohol?
An alcohol is a molecule containing a hydroxyl functional group.
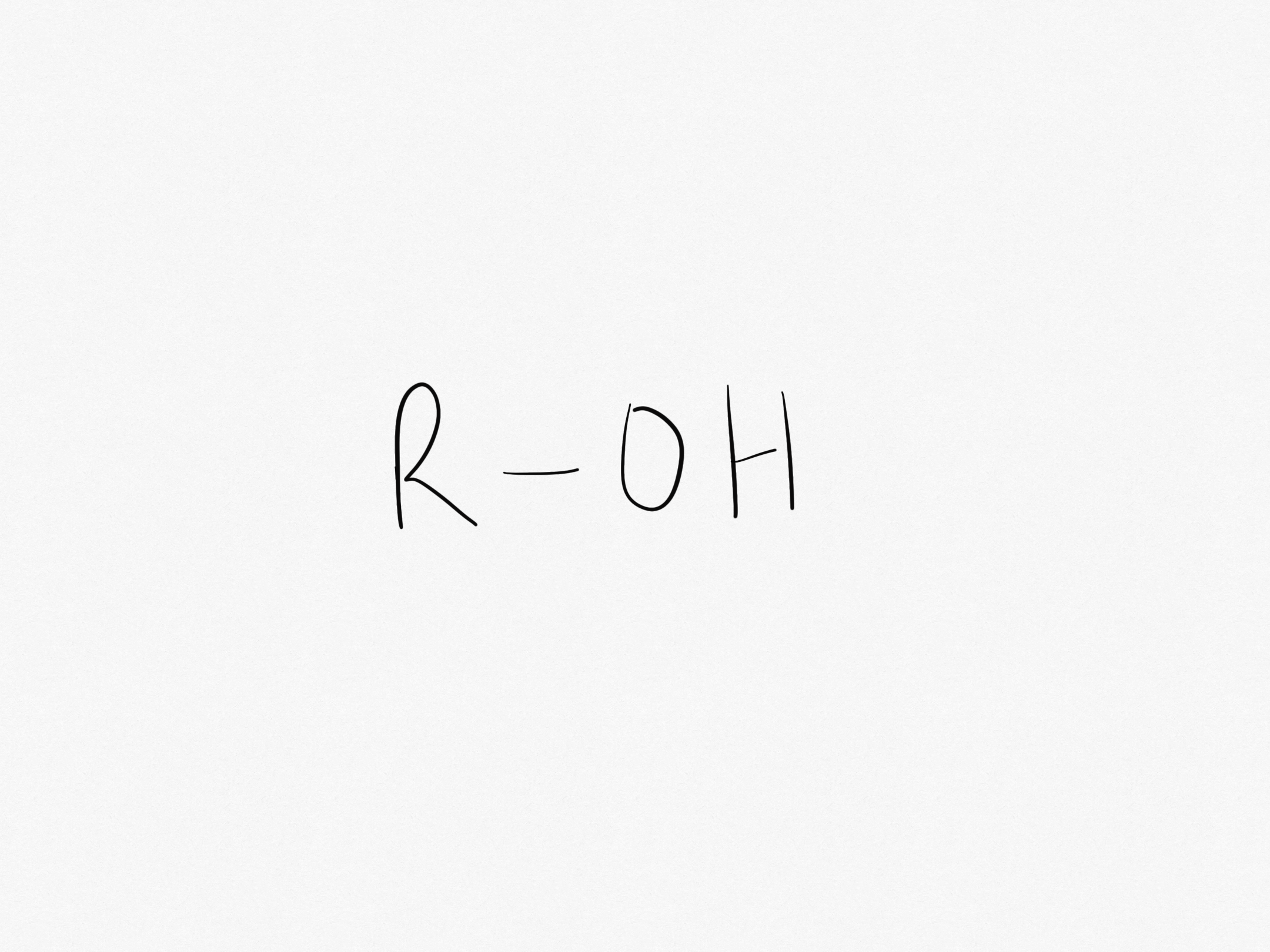
What is the hydroxyl functional group?
The hydroxyl functional group is -OH
What are the three classifications of alcohols?
The three classifications of alcohols are;
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
What is a primary alcohol?
A primary alcohol is an alcohol that’s hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that is attached to 1 or 0 other carbons.
What is a secondary alcohol?
A secondary alcohol is an alcohol that’s hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that is attached to two other carbons.
What is a tertiary alcohol?
A tertiary alcohol is an alcohol that’s hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that is attached to three other carbons.
What are alcohols containing two hydroxyl groups known as?
Alcohols with two hydroxyl groups are called diols.
What are alcohols containing three hydroxyl groups known as?
Alcohols with three hydroxyl groups are called triols.
What characteristic do hydroxyl groups give alcohols?
Hydroxyl groups make alcohols polar and this gives rise to hydrogen bonding.
What is a carboxylic acid?
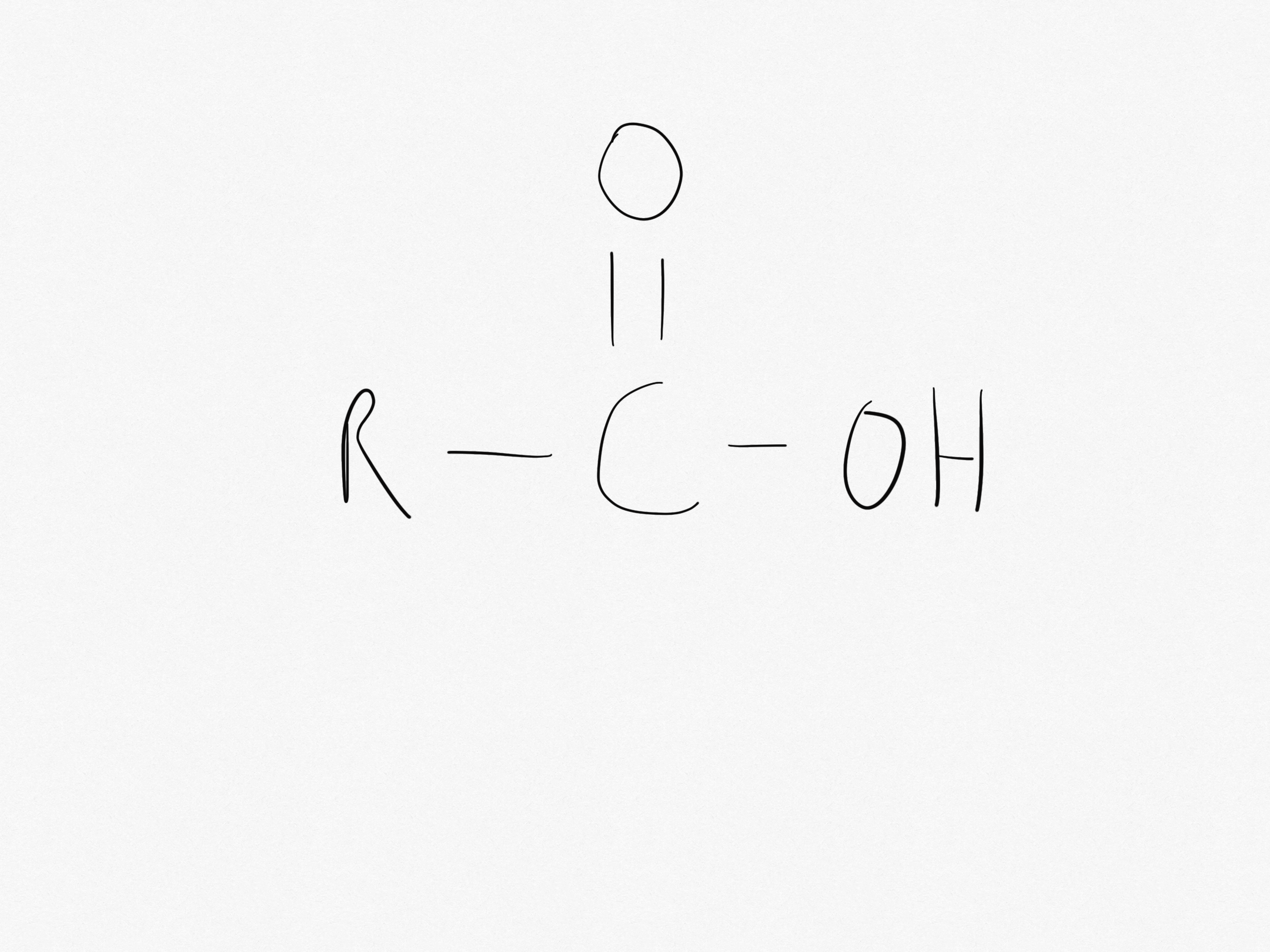
A carboxylic acid is a molecule containing the carboxyl functional group.
What is the carboxyl functional group?
The carboxyl functional group is -COOH
What are the different reactions with carboxylic acids?
The different reactions with carboxylic acids are;
A Metal Oxide + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + H2O
A Metal Hydroxide + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + H2O
A Metal Carbonate + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + H2O + CO2
What does the reaction of A Metal Oxide + A Carboxylic Acid produce?
A Metal Oxide + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + Water
What does the reaction of A Metal Hydroxide + A Carboxylic Acid produce?
A Metal Hydroxide + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + Water
What does the reaction A Metal Carbonate + A Carboxylic Acid produce?
A Metal Carbonate + A Carboxylic Acid —> A Salt + Water + CO2
What type of salt do carboxylic acids make?
Carboxylic acids make carboxylate salts
What is an ester?
An ester is a molecule containing an ester link
What is the ester link functional group?
The ester link functional group is -COO-
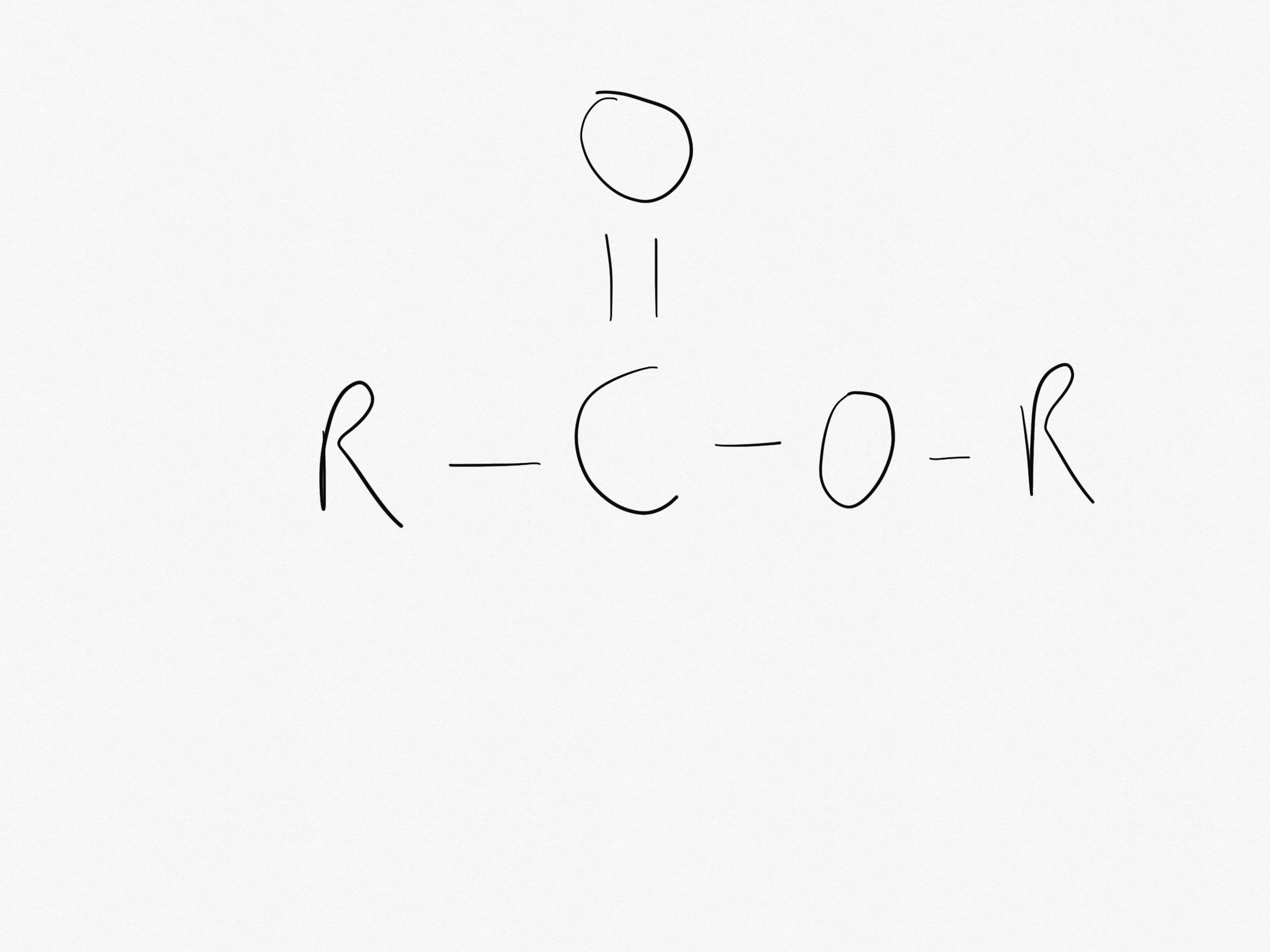
What side does the C=O part of COO lie on?
The C=O part of COO lies on the side of the carboxylic acid.
Where does an esters name come from?
The esters first name comes from the parent alcohol and the esters second name comes from the parent carboxylic acid
Where does an esters first name come from?
An esters first name comes from it’s parent alcohol
Where does an esters second name come from?
An esters second name comes from it’s parent carboxylic acid
What ester would ethanol and propanoic acid produce?
Ethanol and propanoic acid would produce Ethyl propanoate
What are esters used as?
Esters are used as;
Flavourings and fragrances because many have pleasant, fruity smells.
Solvents for non-polar compounds that do not dissolve in water
How are esters formed?
Esters are formed by a condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
What happens in a condensation reaction?
In a condensation reaction, two molecules are joined together with the elimination of a small molecule
What happens when an ester link is formed by the reaction between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group?
When an ester link is formed by the reaction between a hydroxyl group and carboxyl group, the small molecule eliminated is water.
What is the opposite of a condensation reaction?
The opposite of a condensation reaction is hydrolysis
What happens in a hydrolysis reaction?
In a hydrolysis reaction, a molecule reacts with water to break down into smaller molecules
What can esters be hydrolysed to produce?
Esters can be hydrolysed to produce an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
What are edible fats and edible oils formed from?
Edible fats and edible oils are esters formed from the condensation of glycerol and three carboxylic acid molecules.
What is the structure of an edible fat or edible oil?
The structure of an edible fat or edible oil;
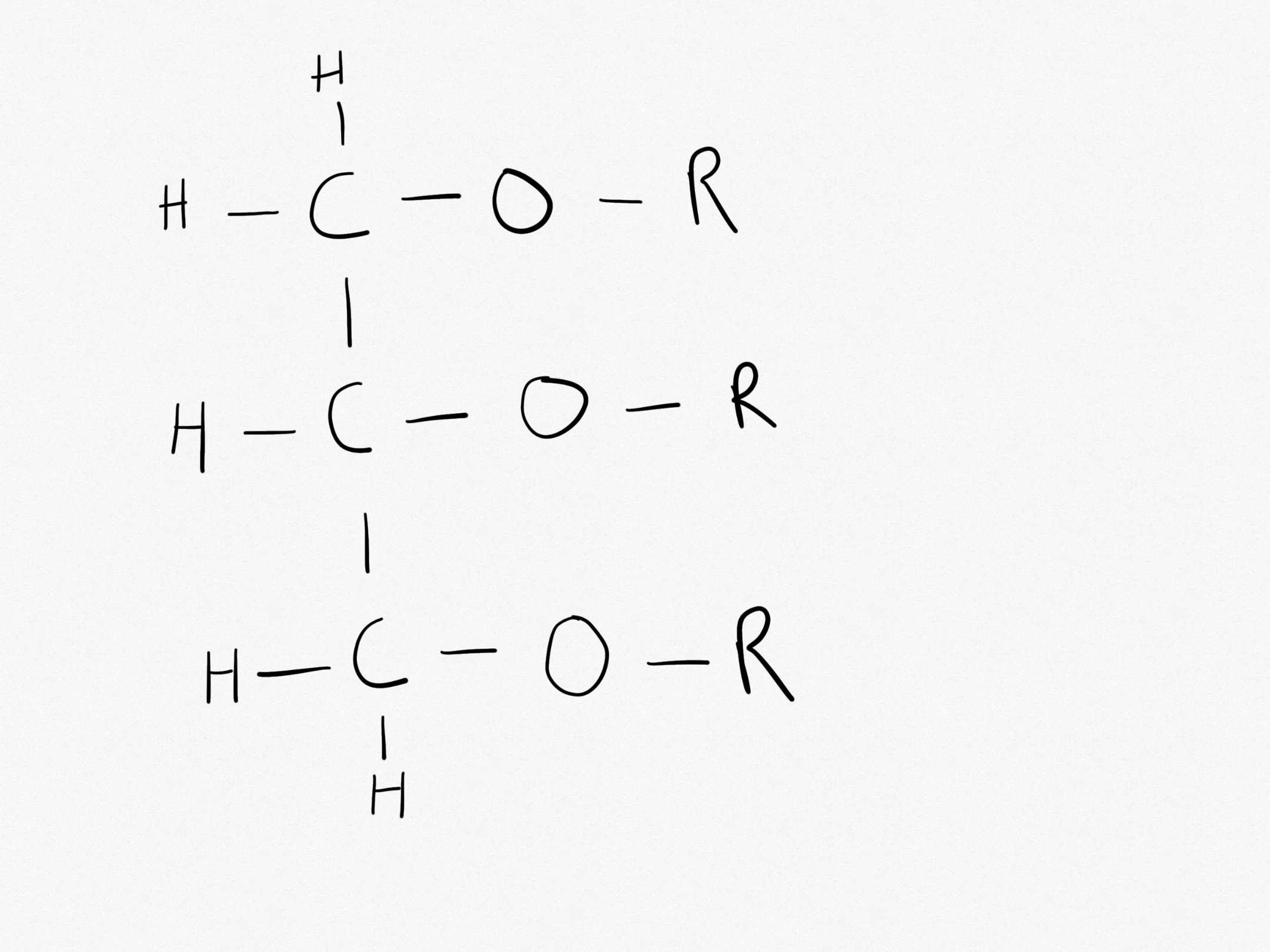
What is glycerol’s systematic name?
Glycerol’s systematic name is Propane-1,2,3-triol
What are the carboxylic acids that form edible fats and edible oils called?
The carboxylic acids that form edible fats and edible oils are called fatty acids
What are fatty acids?
Fatty acids are saturated or unsaturated straight chain carboxylic acids, usually with long chains of carbon atoms.
What is an example of a fatty acid?
An example of a fatty acid is stearic acid (C17H35COOH)
Which of the edible esters has a lower melting point?
Edible oils have a lower melting point than edible fats.
How do double bonds affect melting point of esters?
Double bonds in fatty acid chains prevent oil molecules from packing close together, so the greater the number of double bonds present, the weaker the van der Waals forces of attraction.
The greater the degree of unsaturation, the lower the melting point.
What do Bromine molecules do in an addition reaction?
In an addition reaction, the Bromine molecules add across the carbon-carbon double bond. The greater the number of double bonds present in a substance, the more bromine solution can be decolourised.
What are the functions of fats and oils?
The functions of fats and oils are;
They are a concentrated source of energy
They are essential for the transport and storage of fat-soluble vitamins in the body.
What is the ratio of glycerol molecules to fatty acid molecules in edible oils and fats?
The ratio of glycerol molecules to fatty acid molecules in edible oils and fats is 1:3
What are soaps?
Soaps are water soluble ionic salts of long chain fatty acids
How are soaps produced?
Soaps are produced by the alkaline hydrolysis of edible fats and edible oils.
The hydrolysis of edible oils and edible fats produces three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule.
The fatty acid molecules are neutralised by the alkali, forming water soluble, ionic salts called soaps.
What can soaps be used for?
Soaps can be used to remove non-polar substances such as oil and grease
What do soap ions have?
Soap ions have long non-polar tails that are readily soluble in non-polar compounds (hydrophobic) and ionic heads that are water soluble (hydrophilic).
How does the cleansing action of soap work?
The cleansing action of soap;
The hydrophobic tails dissolve in the oil or grease. The negatively charged hydrophilic heads remain in the surrounding water.
Agitation causes ball like structures to form. The negatively charged ball like structures repel each other and the oil or grease is kept suspended in the water.
What is hard water?
Hard water is a term used to describe water containing high levels of dissolved metal ions.
What happens when soap is used in hard water?
When soap is used in hard water, scum, an insoluble precipitate, is formed.
What are soapless detergents?
Soapless detergents are substances with non-polar hydrophobic tails and ionic hydrophilic heads. These remove oil and grease in the same way as soap.
Do soapless detergents form scum with hard water?
Soapless detergents do not form scum with hard water.
What can emulsifiers be used for?
Emulsifiers can be used to prevent non-polar and polar liquids separating into layers.
What does an emulsion contain?
An emulsion contains small droplets of one liquid dispersed in another liquid.
How can emulsifiers for use in food be made?
Emulsifiers for use in food be made by reacting edible oils with glycerol. In the molecules formed, only one or two fatty acid groups are linked to each glycerol backbone.
How do emulsifiers work?
How emulsifiers work;
The hydroxyl groups present in the emulsifier are hydrophilic whilst the fatty acid chains are hydrophobic.
The hydrophobic fatty acid chains dissolve in oil whilst the hydrophilic hydroxyl groups dissolve in water, forming a stable emulsion.
What are proteins?
Proteins are the major structural materials of animal tissue and are also involved in the maintenance and regulation of life processes.
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins which act as biological catalysts.
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are building blocks from which proteins are formed. They are relatively small molecules which all contain an amino group and carboxyl group.
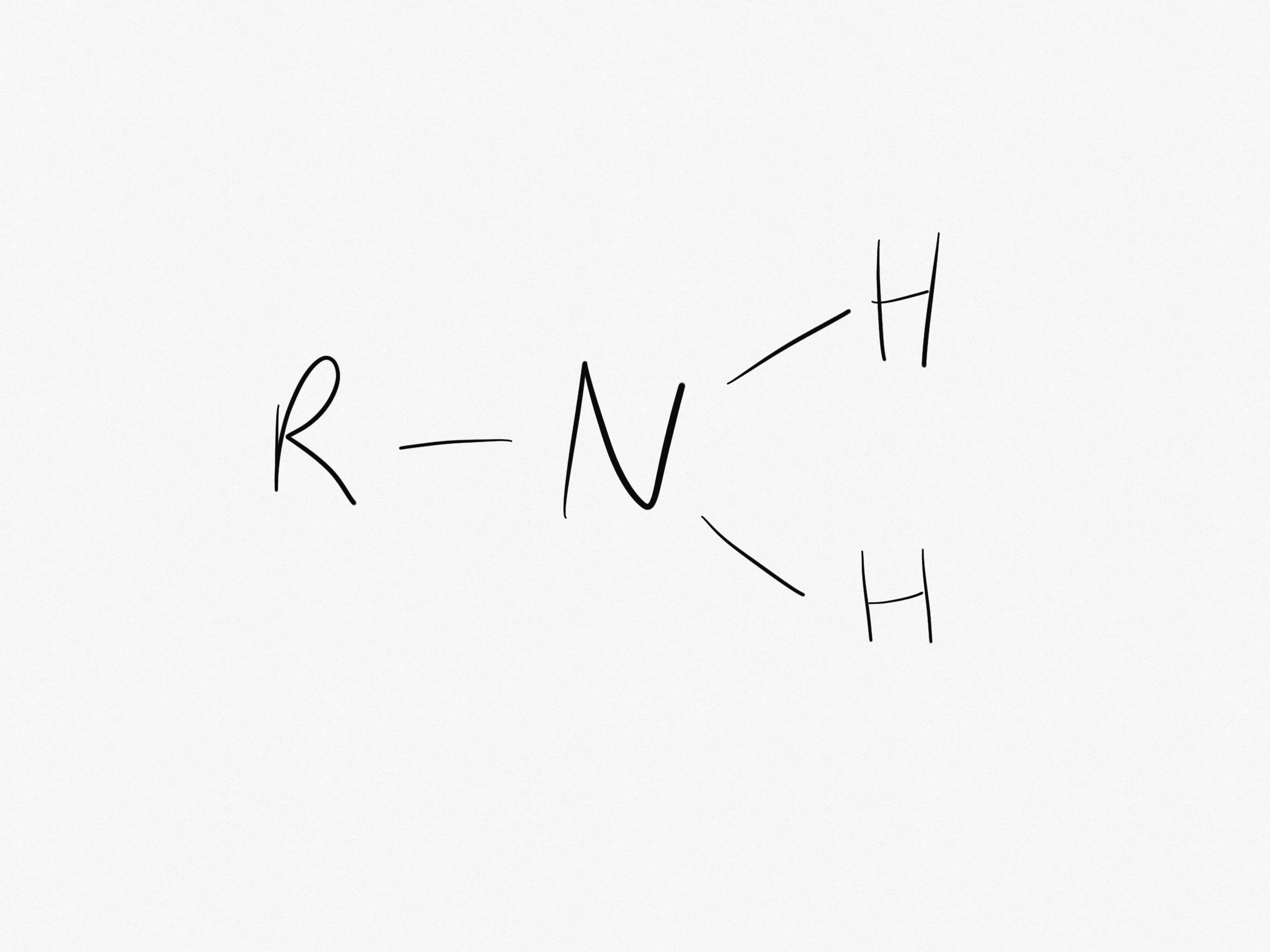
What is the amine group?
The amine group is NH2.
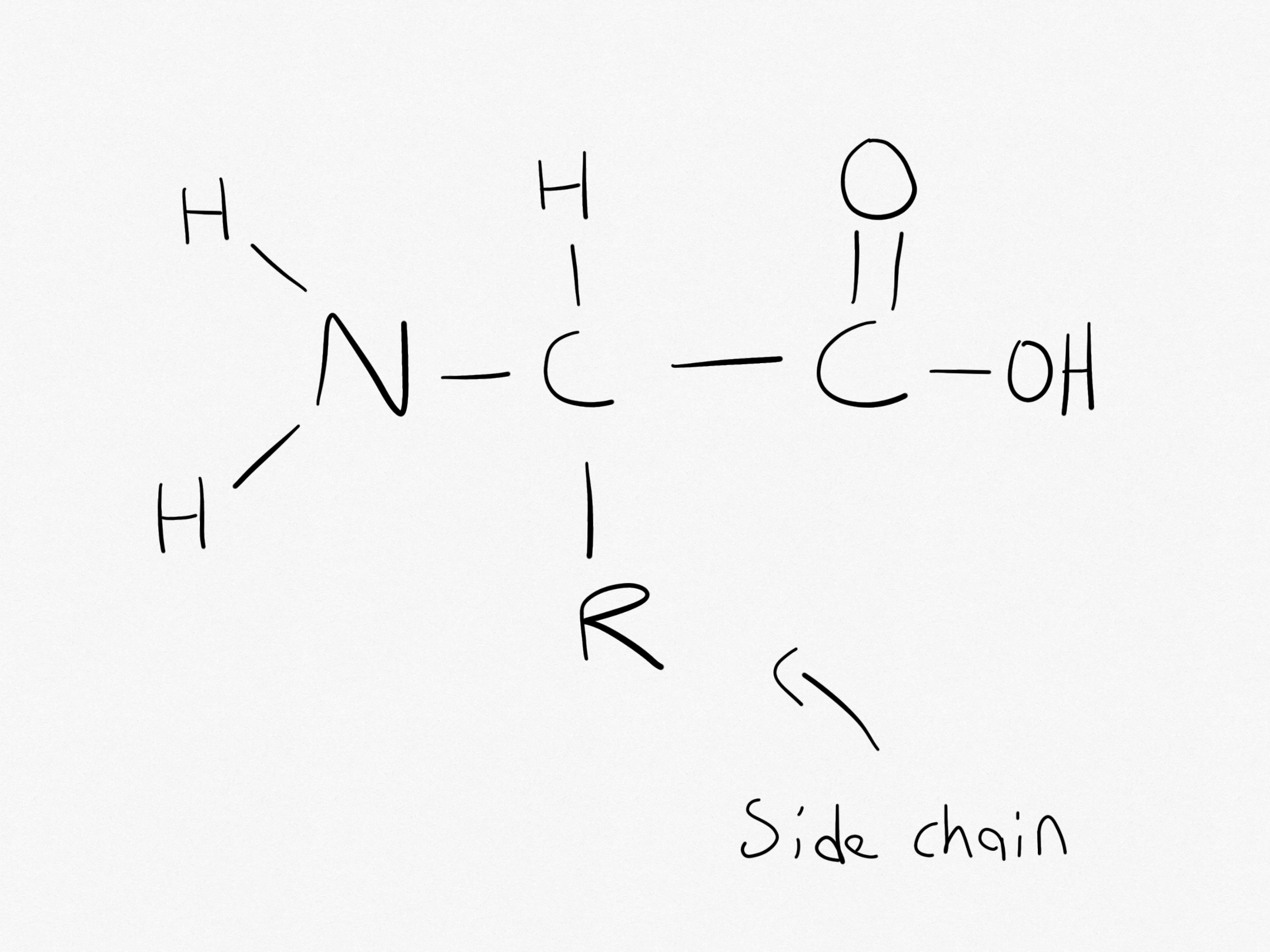
What is the structure of an amino acid?
The structure of an amino acid;
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made of many amino acid molecules linked together.
How are proteins formed?
Proteins are formed in condensation reactions where the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another amino acid join, with the elimination of water.
What is the link formed between two amino acids known as?
The link which forms between two amino acids is known as a peptide link or amide link
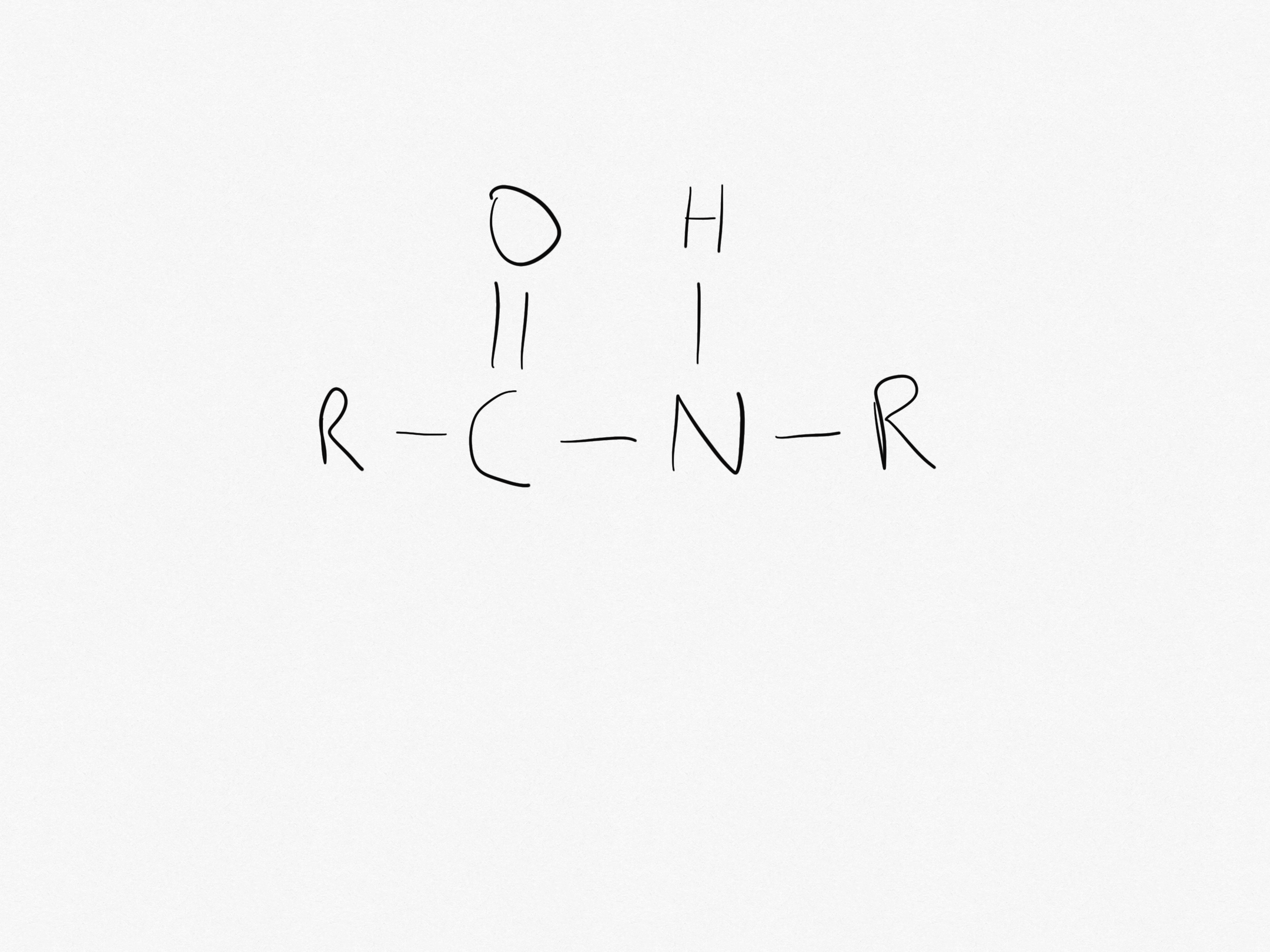
What is the peptide link?
The peptide link is -CONH-
How are proteins that fulfil different different roles formed?
Proteins which fulfil different roles in the body are formed by linking together differing sequences of amino acids.
What are essential acids?
Essential acids are amino acids that cannot be made by the body that must be acquired from the diet.
What happens to proteins during digestion?
During digestion, enzyme hydrolysis of protein produces amino acids
Within proteins, what do long chain molecules form?
Within proteins, the long chain molecules form spirals, sheets, or other complex shapes.
How are long chain molecules in proteins held in the form of spirals, sheets, or other complex shapes?
Long chain molecules in proteins are held in the form of spirals, sheets, or other complex shapes by intermolecular bonding between the side chains of constituent amino acids.
What happens when proteins are heated?
When proteins are heated, intermolecular forces between the side chains of constituent amino acids are broken, allowing proteins to change shape (denature).
What does the denaturing of proteins in foods cause?
The denaturing of proteins in foods causes the texture to change when it is cooked.
For carbon compounds, what is oxidation?
For carbon compounds, oxidation is an increase in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
For carbon compounds, what is reduction?
For carbon compounds, reduction is a decrease in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
What can hot copper oxide or acidified dichromate (VI) solutions be used to oxidise?
Hot copper oxide or acidified dichromate (VI) solutions can be used to oxidise;
Primary alcohols to aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
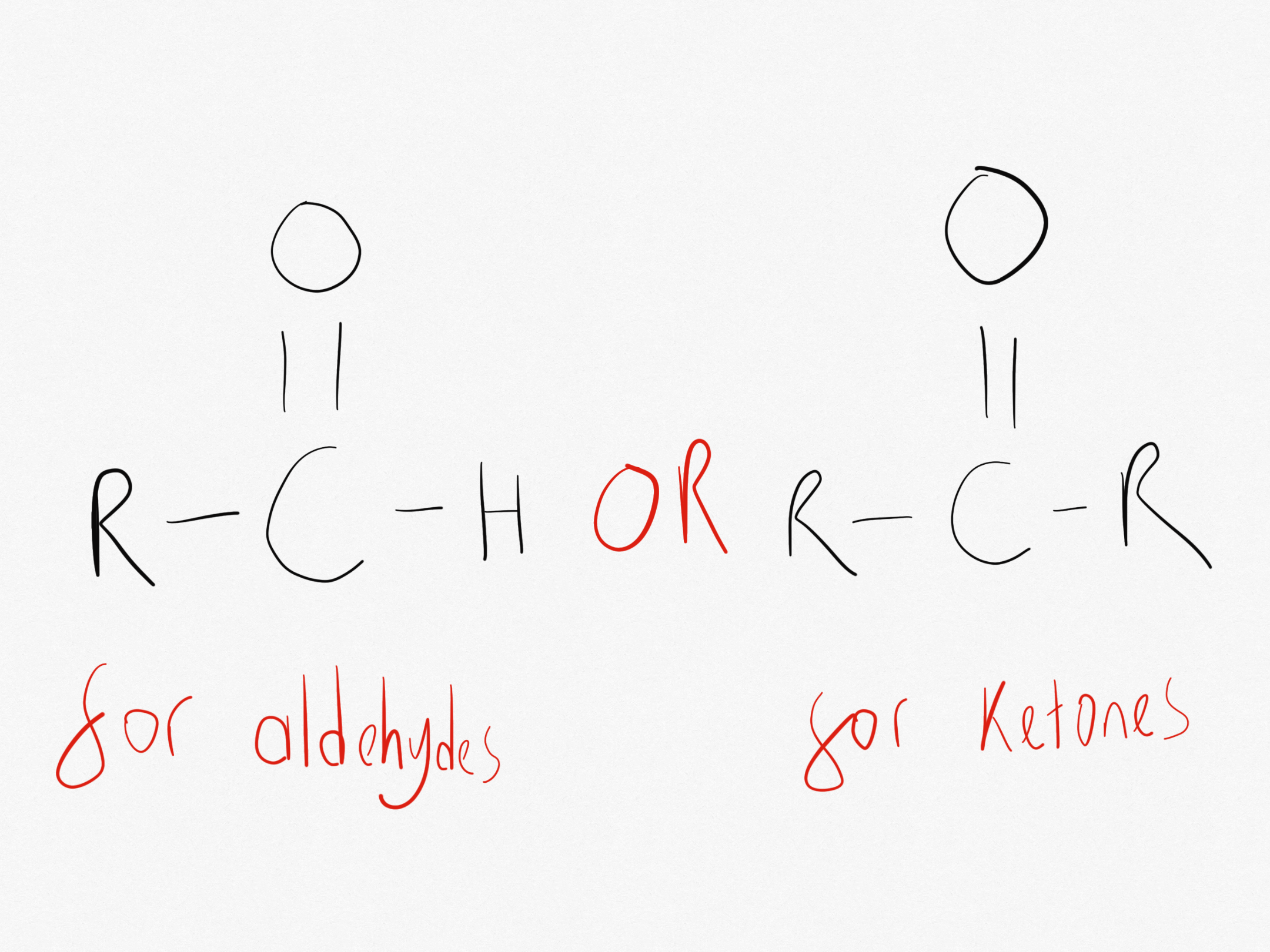
What are aldehydes and ketones?
Aldehydes and ketones are molecules containing a carbonyl functional group
What is the carbonyl functional group?
The carbonyl function group is C=O
What is the colour change when hot Copper (II) oxide oxidises something?
The colour change when hot Copper (II) oxide oxidises something is Black → Brown
What is the colour change when acidified dichromate oxidises something?
The colour change when hot Copper (II) oxide oxidises something is Orange → Green
What is the colour change when Fehling’s solution oxidises something?
The colour change when Fehling’s solution oxidises something is Blue → Brick Red
What is the colour change when Tollen’s reagent oxidises something?
The colour change when Tollen’s reagent oxidises something is Clear colourless → Silver mirror
What oxidising agent should you always use?
Youu should always use acidified dichromate (VI)
What is the oxidising pizza?
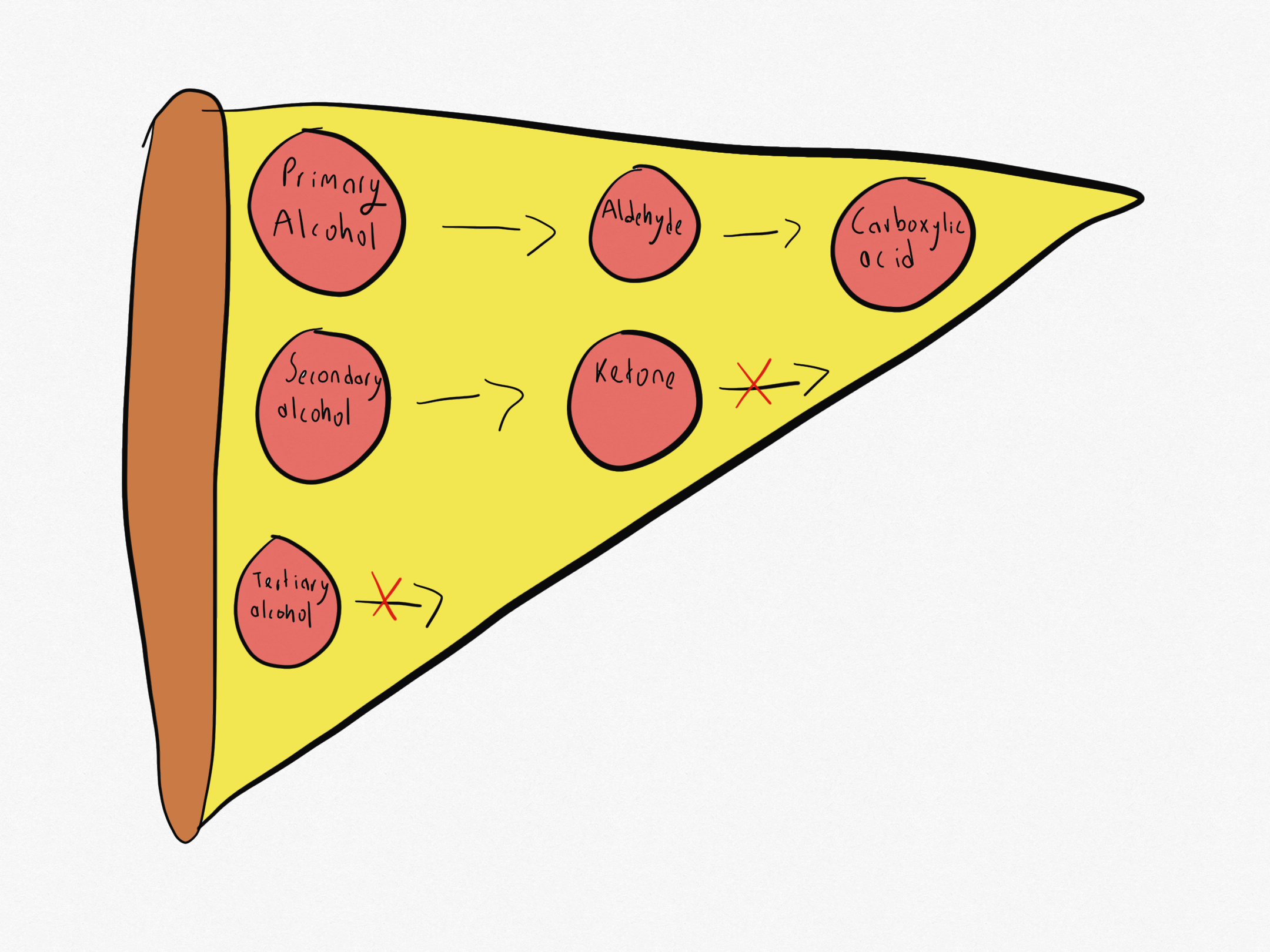
What can primary alcohols be oxidised to?
Primary alcohol → Aldehyde → Carboxylic acid
What can secondary alcohols be oxidised to?
Secondary alcohol → Ketone
What can tertiary alcohols be oxidised to?
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised
What type of molecule are many flavour and aroma molecules?
Many flavour and aroma molecules are aldehydes
What happens when food is exposed to oxygen?
When food is exposed to oxygen, oxygen from the air causes the oxidation of food. The oxidation of edible oils gives food a rancid flavour.
Where is the carbonyl group in an aldehyde?
In an aldehyde, the carbonyl group is on the end carbon
Where is the carbonyl group in a ketone?
In an ketone, the carbonyl group is located on a carbon between two other carbons
What is the ending of the name on an aldehyde?
The ending on an aldehyde is -al
What is the ending of the name on a ketone?
The ending on an ketone is -one
What are antioxidants?
Anti-oxidants are molecules that prevent unwanted oxidation reactions taking place. They are easily oxidised and oxidise in place of the compounds they have been added to protect.
What is an example of an antioxidant?
An example of an antioxidant is Vitamin C