Respiratory System I
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of vocabulary flashcards summarizing key terms and concepts related to the respiratory system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What do the Upper and Lower RT/Respiratory system include?
Upper RT: Nose, Nasal cavity, Sinuses, Pharynx
Lower RT: Larynx, Trachea, Bronchus, Bronchioles, Lungs, Alveoli.
Vital Lung Capacity
The maximum amount of air a person can exhale after maximum inhalation; generally larger in men than women.
Female < 4 L
Male > 4 L ~ difference about 1.5 L
What is lung size related to and which sex has larger vital lung capacities.
Lung size is related to body size and O2 demand for metabolism.
Men typically have larger vital lung capacities than women
Cardiac Notch
A concave space on the left lung which accommodates the heart.
How are the lobes structures in the lungs?
The right lung has 3 lobes but the left lung has 2 lobes: ~ different shapes due to the cardiac notch on the left.
Anatomy of Trachea and Bronchi
Hyoid bone
Sits above the larynx
Larynx
Connects pharynx to trachea
Trachea
Rigid air-conducting tube
Extends from larynx to carina
Tracheal cartilages
C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
Prevent tracheal collapse during inspiration
Why C-shaped? Open posteriorly to allow the oesophagus to expand during swallowing
Carina
Internal ridge where trachea divides
Very sensitive → triggers cough reflex
Primary bronchi
Right and left main bronchi
Conduct air into each lung
Difference:
Right bronchus = wider, shorter, more vertical
Left bronchus = narrower, longer (heart space)
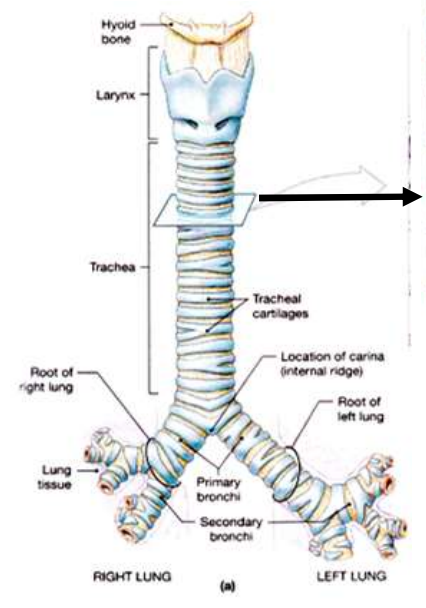
Trachea structure
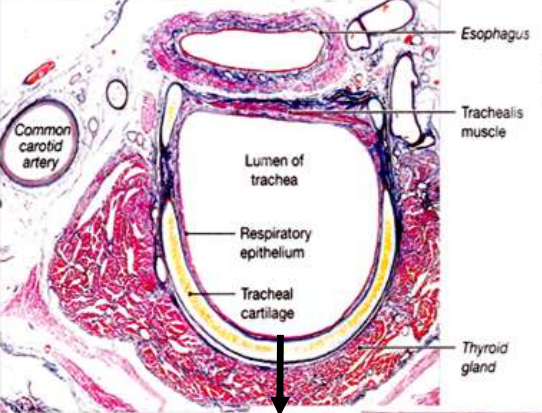
Lumen of trachea
Central open space
Where air flows
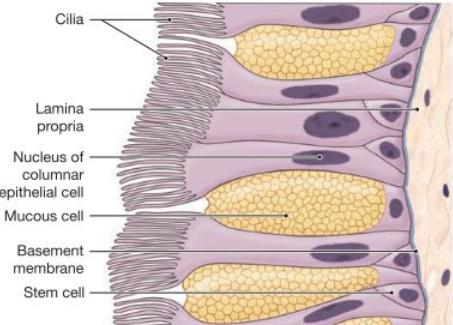
Respiratory epithelium
This is VERY important. Full name (learn this):
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Break it down:
Ciliated → move mucus
Goblet cells → secrete mucus
Columnar cells → tall cells for surface interaction
Function:
Traps particles and moves them OUT of the lungs
Trachealis muscle
Smooth muscle at the open end of cartilage rings
Contracts to:
Reduce tracheal diameter
Increase airflow velocity (e.g. coughing)
“The trachealis muscle allows flexibility and regulates airflow.”
Tracheal cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Prevents airway collapse
If you see cartilage → think airway support
Mucociliary Escalator
A mechanism in the respiratory system that moves debris from small bronchioles out of the lungs, to the top of the trachea to be swallowed.
Bronchial Tree
The structure formed by the branching airways from the trachea to the alveoli.
Describe the respiratory tree starting with Primary bronchi.
Primary bronchi branch into secondary bronchi, which further divide into tertiary bronchi and smaller bronchioles, until the terminal bronchioles which divide into respiratory bronchioles → supply air to alveolar ducts → supply air to alveoli.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
~ O2 is absorbed for cellular respiration (to form ATP)
~ CO2 is eliminated as a waste product of metabolism
Oxygen Absorption
The process in which oxygen is taken up by the blood from the alveoli.
Carbon Dioxide Elimination
The process of removing carbon dioxide from the blood, occurring in the alveoli.
Alveolar Epithelium
The thin layer of cells lining the alveoli, maximizing gas exchange.
How many alveoli sacs are the in the lungs and how wide are alveoli?
Lungs contains about 500 million tiny alveoli air sacs:
Alveoli are 250 µm wide and are surrounded by capillaries
How does the alveolar epithelium maximises gas exchange?
Large surface area (100 – 140 m2 ) ~
A thin cellular membrane (0.5 - 1 µm) ~
Excellent blood supply (5-25 l/min) ~ wet surface (alveolar fluid containing surfactant)
Surfactant
A substance secreted by Type II alveolar epithelial cells that reduces surface tension in the alveoli.
Alveolar epithelial cells and foetal development
• Lungs are not used for gas exchange during foetal life but must produce surfactant to be ready to breathe air at birth
• Alveolar epithelial Type II cells secrete surfactant to reduce surface tension
• Type-II cells mature fully in late pregnancy (wk 36)
• Premature babies can develop respiratory distress syndrome
• Alveolar epithelial Type I cells exchange gasses (02 and CO2 )
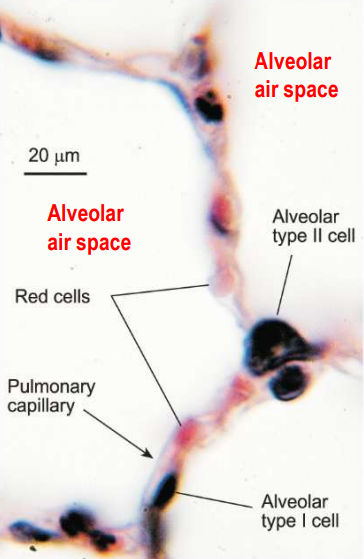
Type I Cells
Alveolar epithelial cells responsible for gas exchange. (O2 and CO2)
Type II Cells
Cells that secrete surfactant in the alveoli.
Inspiration
The active process of inhaling; involves diaphragm and intercostal muscle contraction. Air flows into lungs by negative pressure (-1 mmHg)
Expiration
The typically passive process of exhaling; involves relaxation of respiratory muscles. Air flows out of lungs by positive pressure ( +1 mmHg)
Negative Pressure
The pressure created in the thoracic cavity that helps draw air into the lungs during inhalation.
Positive Pressure
The pressure that pushes air out of the lungs during exhalation.
Chemoreceptors
Sensors in the body that detect changes in blood chemistry, influencing breathing rate.
Medulla Oblongata
The part of the brain that regulates autonomic functions, including breathing.
Pons
A part of the brain that regulates voluntary control and smooth transitions in breathing.
Respiratory Rate
The number of breaths taken per minute; influenced by CO2 and O2 levels.
Partial Pressure Gradient
The difference in pressure of gases in the alveoli and blood, driving gas exchange.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord, involved in monitoring blood pH and CO2 levels.
Proprioceptors
Sensory receptors in muscles and tendons that contribute to regulating breathing during movement.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome
A condition resulting from insufficient surfactant production, particularly in premature infants.
Gas Exchange
The process by which oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is removed in the alveoli.
Lung Surface Area
The area available for gas exchange, maximized by the presence of numerous alveoli.
Autonomic Nervous System
Part of the nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions, including breathing.
Respiratory Volumes
Measurements of the volume of air inhaled and exhaled during breathing.