3.6 & 3.7 proteins
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is the structure of amino acid
Central carbon (alpha carbon), four atoms or groups of atoms bonded to alpha Carbon NH2 (amino group), COOH (carboxyl group), H, R (side group)
what is the R group
Different in each amino acid, determines how the amino acid interacts and bonds with other amino acids in the polypeptide
what are the amino acids at each end of chain
N-terminal (amine terminal), C-terminal (carboxyl terminal)
what is a peptide bond
when two amino acids react together covalent bond, water is produced, called a dipeptide (condensation, hydrolysis to break peptide bond)
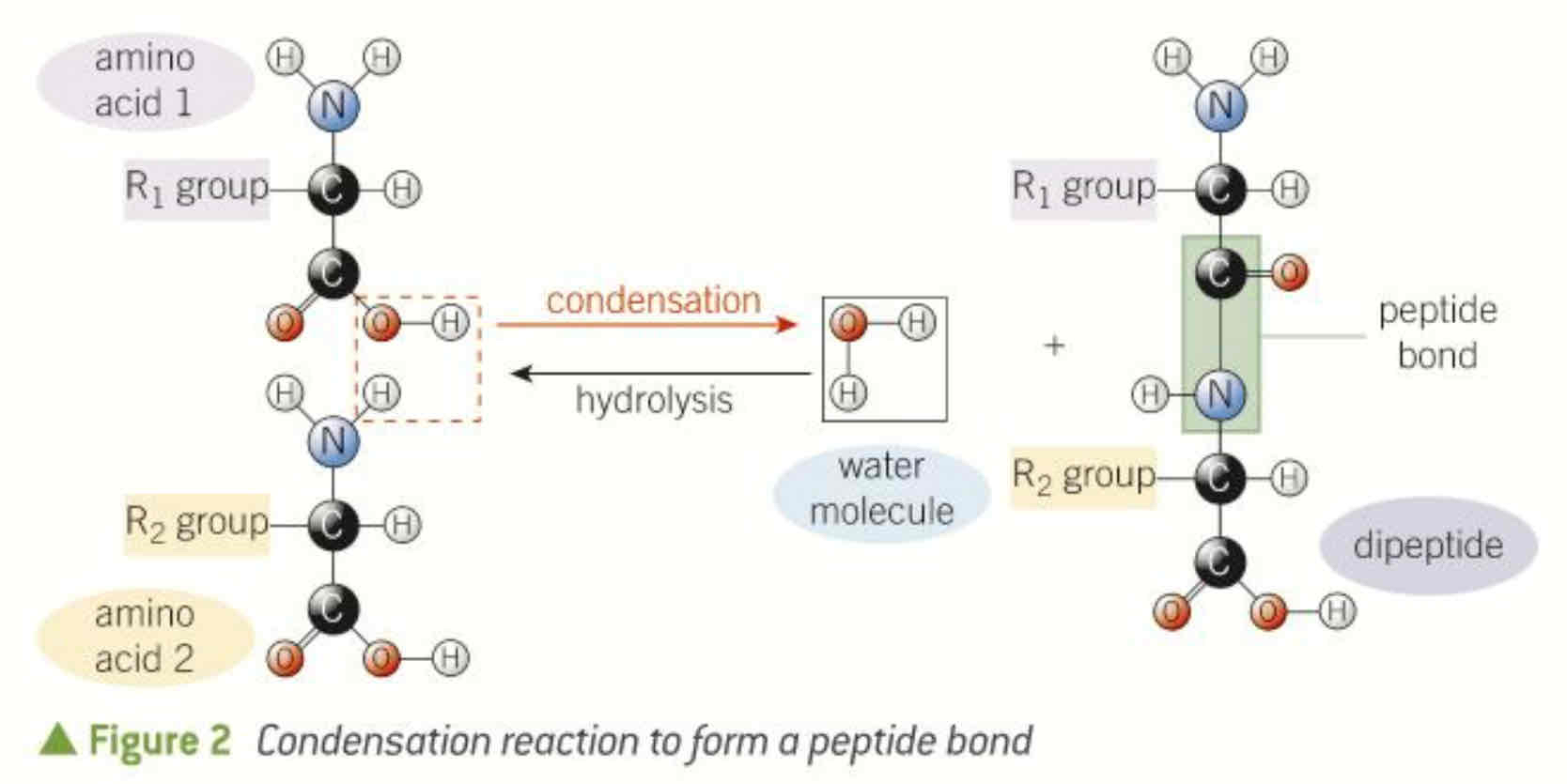
what is it called when many amino acids are joined by peptide bonds
polypeptide
what enzyme catalyses the joining of amino acids
peptidyl transferase ( in ribosomes)
what is the primary structure of protein
the sequence amino acids are joined, particular amino acids in sequence influence how polypeptide will fold give protein final shape, shape determines function, only bonds are peptide bonds
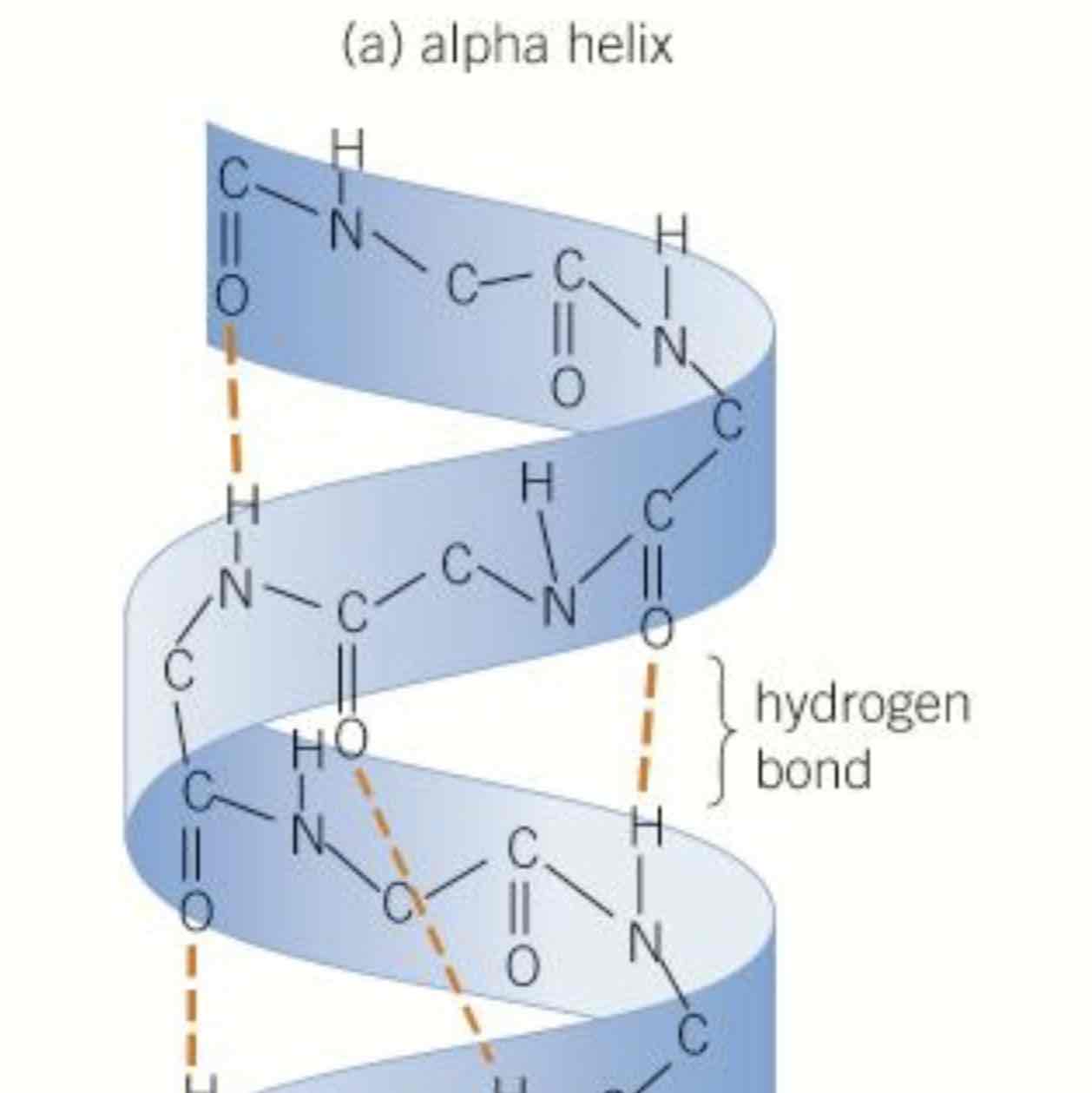
what is the secondary structure of protein
O, H and N atoms of repeating structure of amino acids interact, H bonds may form within amino acid chain, pull into a coil shape called an alpha helix
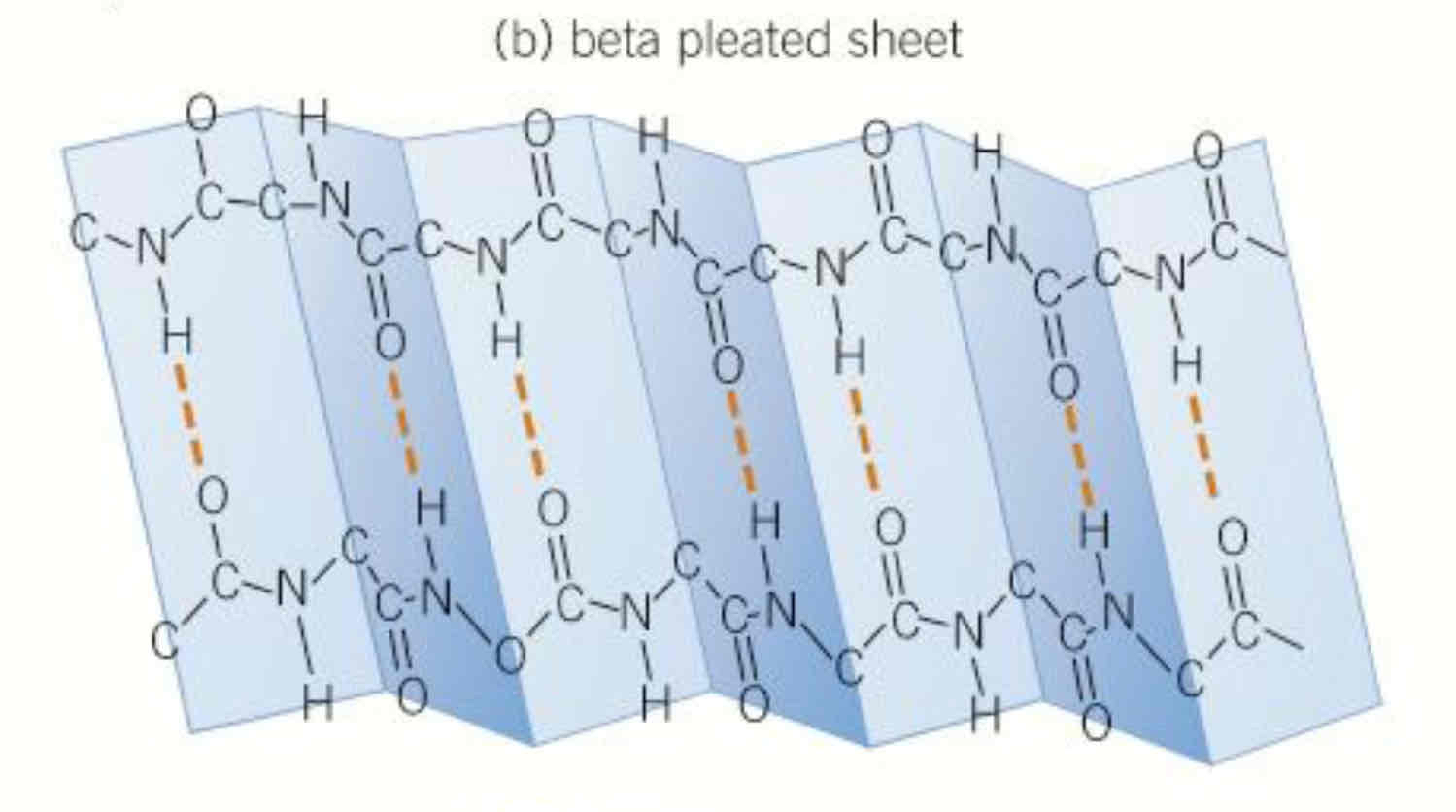
what is another secondary structure other than the alpha helix
polypeptide chains can also lie parallel to one another joined by h bonds, form sheet like structure, pattern formed by individual amino acids cause structure to appear pleated
tertiary structure of proteins
folding of a protein into final shape, includes sections of secondary structure, bring R-groups of different amino acids closer together to interact for further folding
what type of interactions with occur in tertiary structure
hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions (polar and non-polar R-groups), hydrogen bonds (weak), ionic bonds (stronger and form between oppositely changed R-groups), disulfide bonds (covalent and strongest, only between R-groups that contain sulfur atoms)
quarternary structure in proteins
association of two or more individual proteins called subunits, can be identical or different
how many subunits in enzymes
two identical subunits
how many subunits in insulin
two different subunits
how many subunits in haemoglobin
four (two sets of two identical subunits)
features of a globular protein
compact, water-soluble and usually roughly spherical in shape
how are globular proteins formed
proteins folds into tertiary structure, hydrophobic on inside, hydrophobic on outside, soluble
what is insulin role as a globular protein
hormone included in the regulation of blood glucose concentration, transported in bloodstream so need to be soluble, precise shapes to fit into specific receptors on plasma membranes
what is a conjugated protein
globular protein that contain a prosthetic group
different types of prosthetic groups
lipids or carbohydrates can combine with proteins forming lipoproteins or glycoproteins, metal ions and molecules derived from vitamins also form prosthetic groups
about the conjugated protein haemoglobin
quaternary protein made from four polypeptides, two alpha and two beta subunits, each subunits contain prosthetic haem group, iron II ions present able to combine reversibly with an oxygen molecule, transport oxygen around around body
conjugated protein catalase
enzyme, quaternary protein containing four haem prosthetic groups, presence of iron II ions allow catalase to interact with hydrogen peroxide and speed up break down
features of a fibrous protein
formed from long, insoluble molecules, high proportion of amino acids with hydrophobic R-groups in their primary structure, limited range off amino acids, repetitive and very organised, strong, long molecules
fibrous protein keratin
present in hair, skin and nails, large proportion of sulfur-containing amino acid (cysteine), many strong disulfide bonds (strong, inflexible and insoluble)
how does number of disulfude bonds affect flexibility
hair = fewer bonds = more flexible, nails = more bonds = less flexible
fibrous protein elastin
found in elastic fibres (and small protein), in the walls of blood vessels and in alveoli, gives structures flexibility to expand when needed and to return to normal size, quaternary structure made from tropoelastin
fibrous protein collagen
connective tissue found in skin, tensions, ligaments and nervous system, all different forms made out of three polypeptides wound together in long strong rope-like structure, has collagen