DSA03 - Short Stature and Tall Stature
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Familial Short Stature
Define Condition:
Dx of Exclusion
-Hx: (Nothing Remarkable)
> Short Height in Parents
-Sx/PE: Normal/Noncontributory, but consistently low height
-Dx:
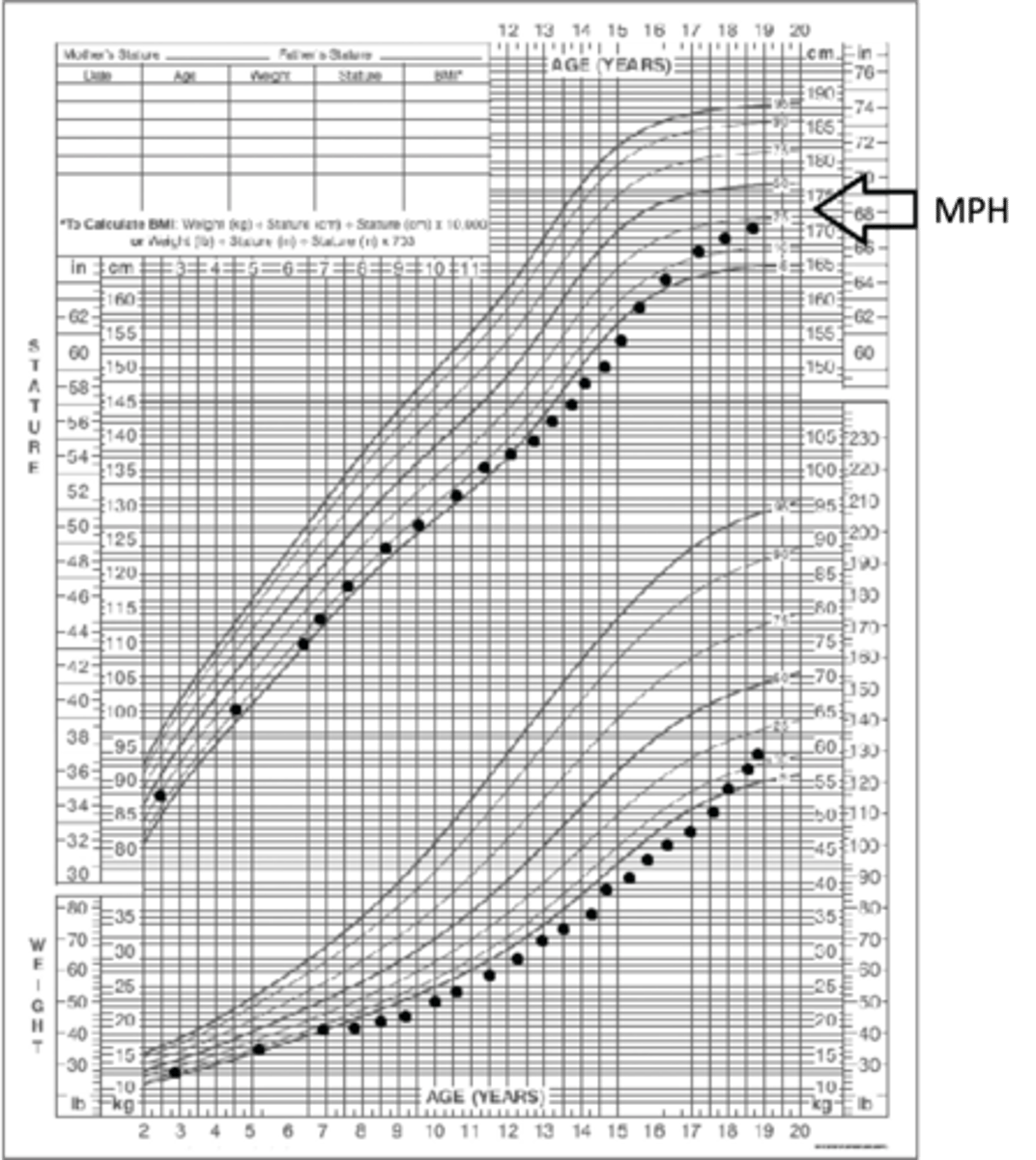
> Growth Chart Abnormality
> Mid-Parental Height/MPH (confirm child's height to family height) + Bone Age Film (CONFIRM - Lets clinician know how much vertical growth is remaining (can help calculate final adult height = Predicted Adult Height, or PAH) ==> If PAH/Final Height Prediction falls within MPH range --> CONFIRMS
-Tx:
> Reassurance
> Serial exams w/ height measurements to ensure continued normal growth/consider alternative diagnoses

[(Mom's height + 5 inches) + (dad's height)]/2 +/- 2.5"
How do you calculate Mid-Parental Height/MPH (aka target height) Range for a BOY?
[(Mom's height) + (dad's height - 5 inches)]/2 +/- 2.5"
How do you calculate Mid-Parental Height/MPH (aka target height) for a GIRL?
Constitutional Delay of Growth and Puberty (CDGP) - aka "Late Bloomer"
Define Condition:
When vertical growth is "behind schedule"; NOT PATHOLOGIC (Normal growth variant)
-Hx:
> Initially shorter than expected/shorter than peers
> Often FHx (ask parents when they went thru puberty)
-Path: Vertical growth spurt occurs later that in their peers --> Continue growing after peers stop growing
-Sx/PE:
> Pubertal exam = LESS MATURE for chronologic age
> Final Height will be within normal range of MPH
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
>> Height is low in prepubertal years, BUT parallel to standard lines
> Bone Age Film = Delayed Bone Age relative to chronologic age
> PAH --> Compare to MPH (PAH should be w/n MPH range)
-Tx:
> Reassurance (maybe brief Testosterone trial for boys - one injection every 30 days for 6 months)
> Continue Monitoring
-CBCd
-CMP
-ESR
-Celiac Screen
-Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs)
-Growth Factors (IGF-1 and IGFBP-3)
-Karyotype (if pt is girl)
What are suggested screening tests to assess for other causes of short stature?
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Define Condition:
Poor ve rtical growth d/t low GH secretion
-Hx:
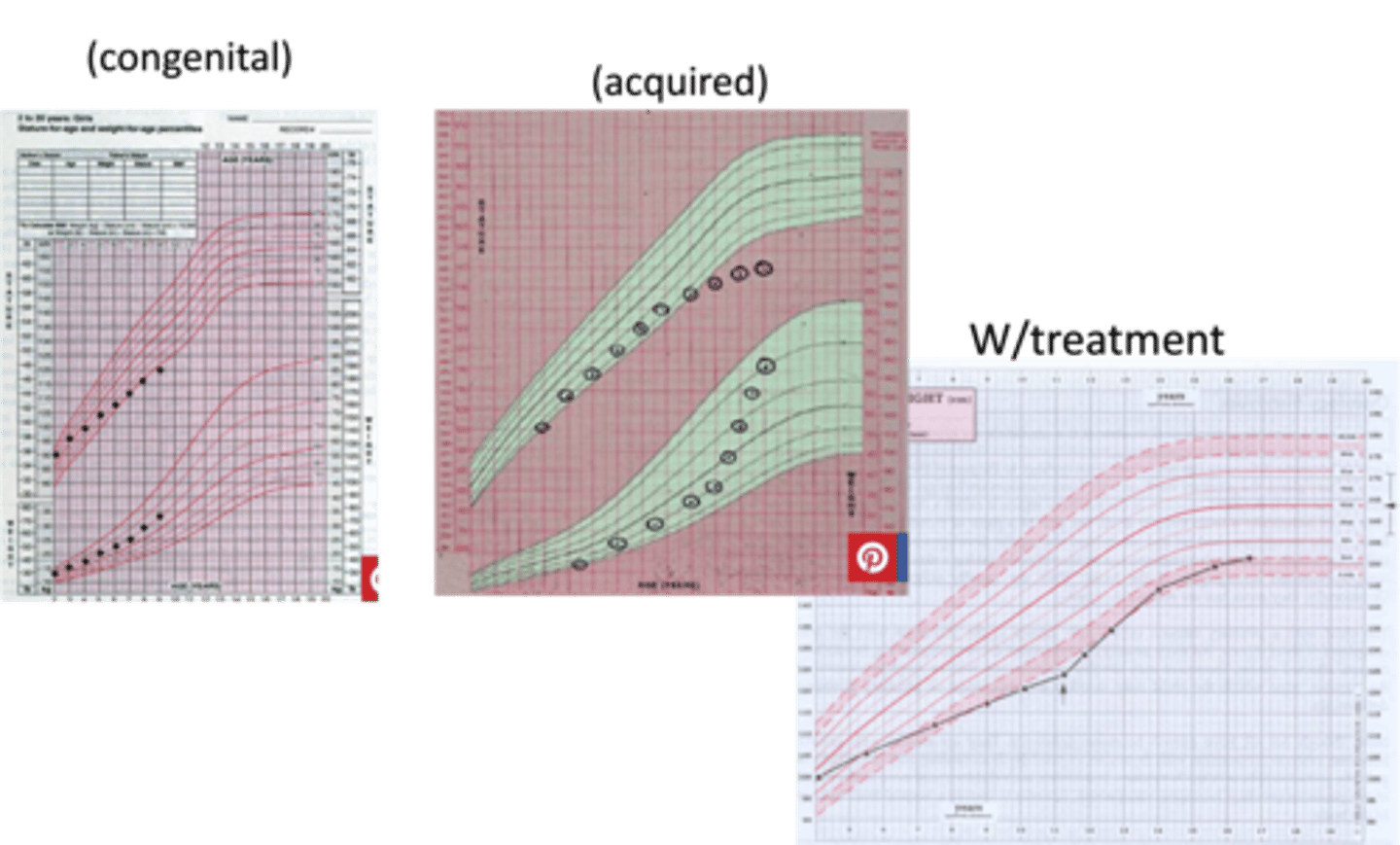
> Congenital = MCC IDIOPATHIC/SEVERE GENE MUTATIONS
>> Hx of Hypoglycemia in early newborn
>> Hx of Hyperbilirubinemia in early newborn
> Acquired
>> Trauma to Head
>> Radiation to brain
>> CNS Infex (Encephalitis, Meningitis)
>> Neurosurgical injury to pituitary
>> Sellar tumors
-Sx/PE:
> Normal + Short Stature
> Excess Adiposity (more lipolysis, more protein synthesis)
> Lack of Muscle Tissue (more lipolysis, more protein synthesis)
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
> Bone Age Film (DELAYED BONE AGE)
> PAH --> Compare to MPH (PAH BELOW MPH RANGE)
> PAH below <5th percentile
> Check IGF-1, IGFBP-3 (low levels)
> GH Stimulation Test
>> Usually via Arginine & Insulin
>> Levels drawn 8-10 times over time span of 2 hours after drug administration
>> GH peak > 10 ng/mL (Normal)
>> GH peak < 10 ng/mL --> DEFICIENCY
-Tx: Growth Hormone Injection (SQ)
> Nightly for years
> Continue visits to follow growth, assess compliance, optimize dose, and monitor S/Es
> D/C once vertical growth is nearly complete
-Stimulates linear growth by direct action on the epiphyseal plate
-Increases lipolysis
-Stimulates protein synthesis
-Antagonizes insulin action
What are the direct effects of GH on target tissues?
-Stimulates linear growth by action on the epiphyseal plate
-Balanced growth at other tissues
What are the indirect effects of GH (via IGF-1)?
Laron Syndrome (Not for Test, but BOARDS)
Define Condition:
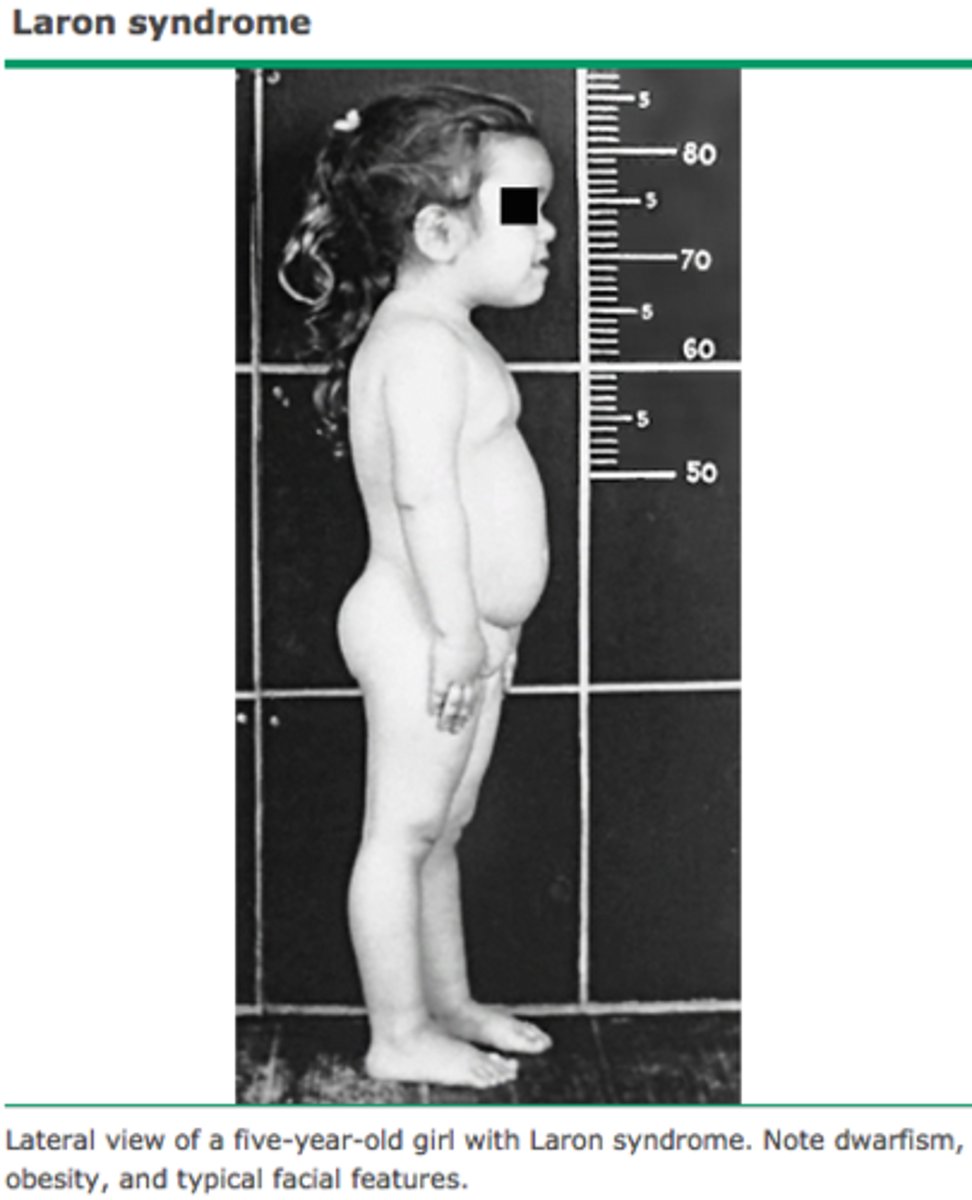
Autosomal RECESSIVE Disorder d/t LOSS OF FUNCTION mutation of GH receptor
-Path: FUNCTIONALLY deficient response to GH, but making enough
-Sx/PE: Lifelong, severe vertical growth failure
> Facial Dysmorphisms
> Short Limb Length compared to trunk length
> Intellectual development NORMAL (or only MINIMALLY IMPAIRED)
> Short Stature
> Excess Adiposity (more lipolysis, more protein synthesis)
> Lack of Muscle Tissue (more lipolysis, more protein synthesis)
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
> Bone Age Film (DELAYED BONE AGE)
> PAH --> Compare to MPH (PAH BELOW MPH RANGE)
> PAH below <5th percentile
> Check IGF-1, IGFBP-3 (low levels)
> GH Stimulation Test
>> Usually via Arginine & Insulin
>> Levels drawn 8-10 times over time span of 2 hours after drug administration
>> GH peak > 10 ng/mL (Normal)
-Tx: Recombinant IGF-1 (Mecasermin)
Hypothyroidism
Define Condition:
-Sx/PE: Poor Growth Velocity
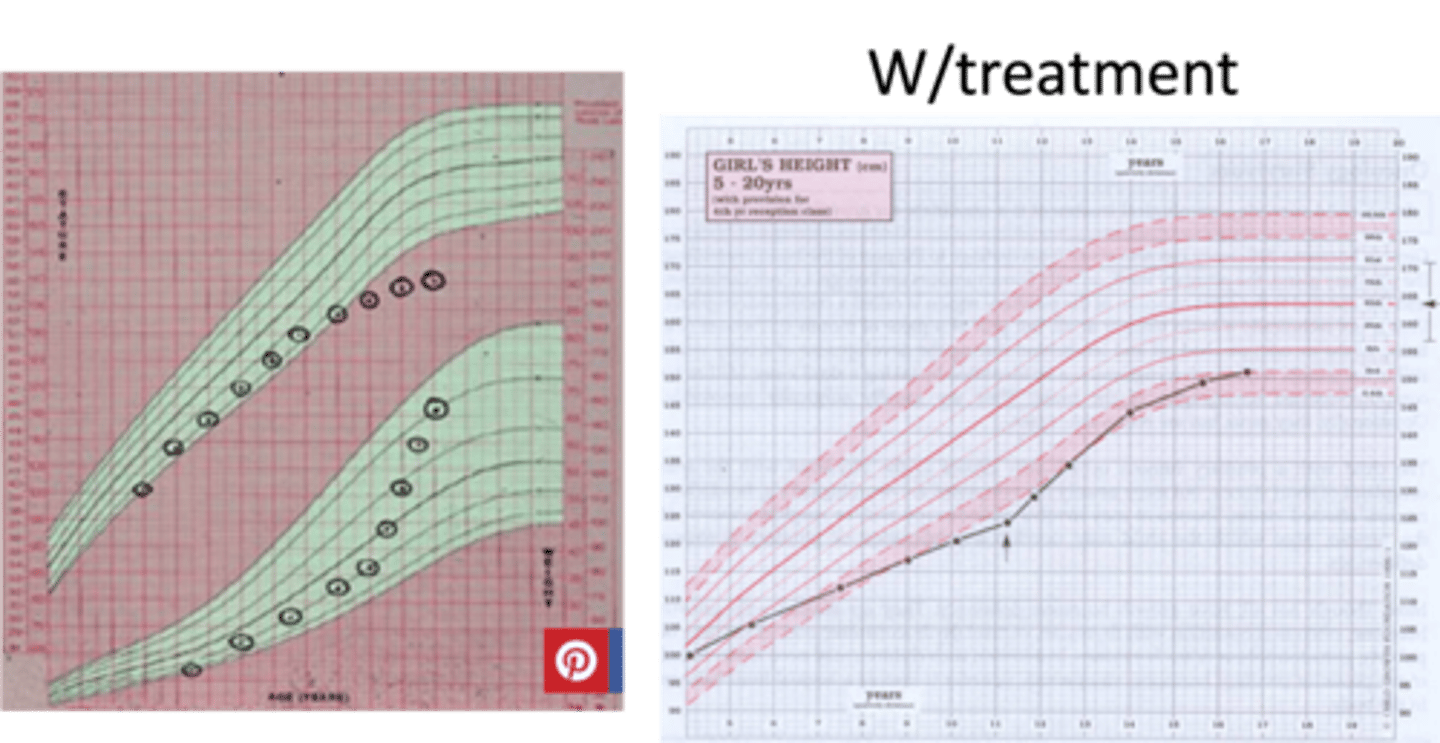
-Dx:
> Bone Age Film
>> Delayed Bone Age to relative to chronologic age
>> PAH may fall w/n MPP OR Below MPH
> Growth Chart
> TFTs
>> TSH & Free T4
-Tx: Thyroid Replacement Therapy
> Bone Age starts advancing
> May reach MPH target range
Cushing Syndrome
Define Condition:
Excess of glucocorticoids (for any reason - endogenous or exogenous) --> Impaired vertical growth
-Hx: Exposure to Glucocorticoid Therapy
> Asthma
> Inflammatory Diseases
> Transplant
> Leukemias
-Path: Vertical growth INHIBITION:
> Interfere w/ bone formation
> Disrupt collagen formation
> Nitrogen retention
> Impair GH secretion and action
-Sx/PE:
> Rapid Weight Gain
> Lower height for age group
-Dx:
> Growth chart
>> More striking plateau for vertical growth
>> MORE STRIKING INCREASE IN WEIGHT
> Cortisol Excess Stigmata
-Tx:
> Exogenous = Stop Offending agent (if possible)
> Endogenous (Cushing) = Tx Cushing
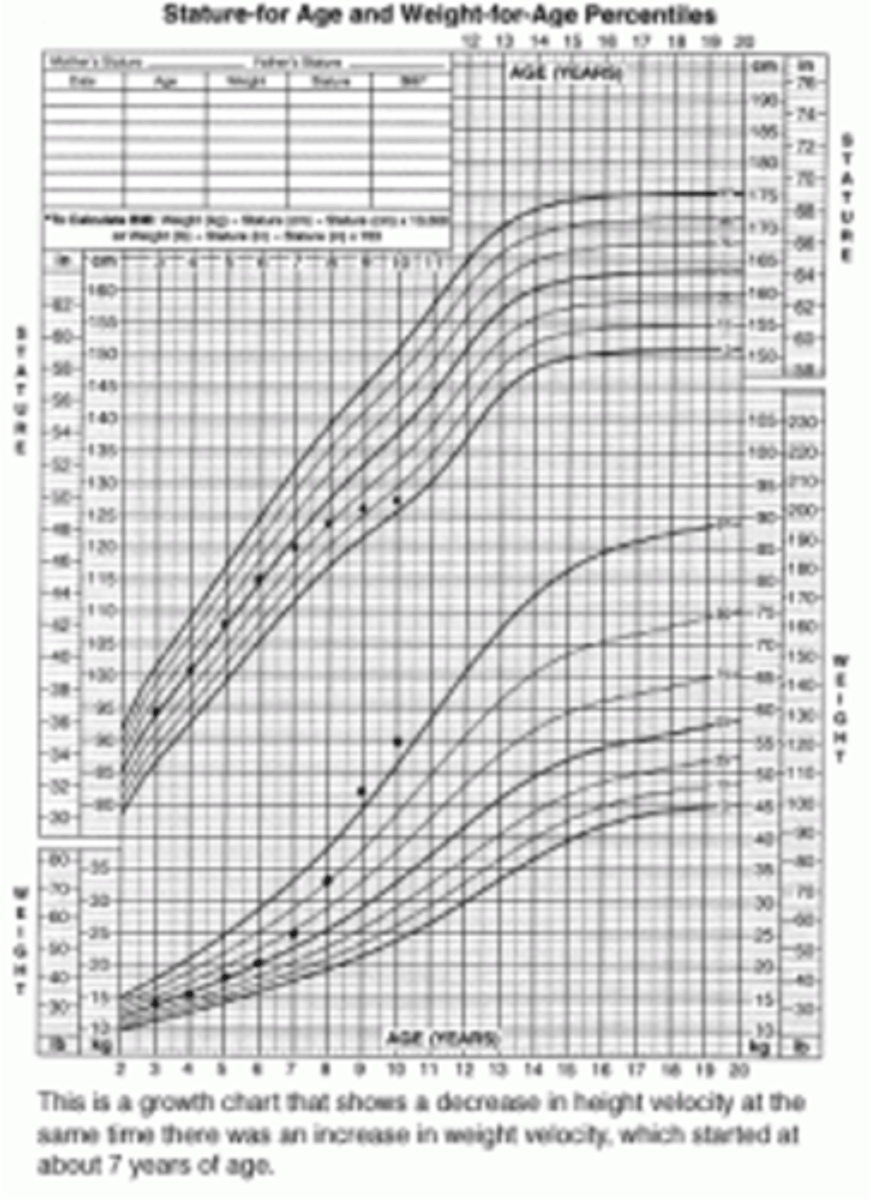
Undernutrition of Chronic Illness
Define Condition:
-Hx/Path:
> Inadequate nutrient intake (Swallowing dysfunction, Child neglect, Anorexia)
> Inadequate GI absorption (Celiac, IBD, CF)
> Increased metabolic demand (Chronic infex, Chronic Resp Fail)
> Inadequate metabolic utilization of nutrients (Inborn metabolism error, DM2)
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
>> Weight affected FIRST --> Vertical growth affected (less than weight)
>> Infant = Head circumference compromised
> Screening Labs for Systemic Illness
>> CBCd
>> CMP
>> ESR
>> Celiac
>> U/A
>> HbA1c
-Tx: Tx Underlying cause + Utilize other professionals (dietitians, social workers, therapists)
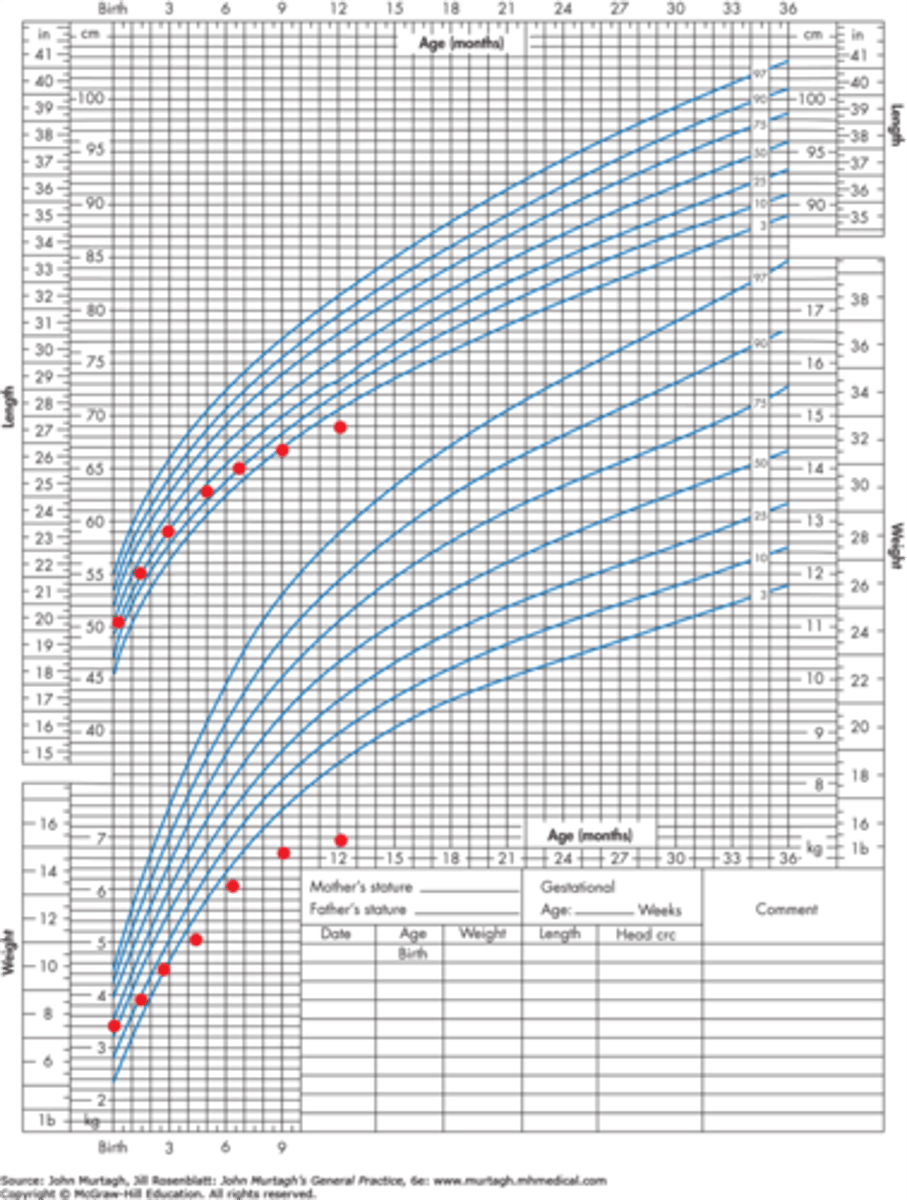
Genetic Syndromes causing SHORT STATURE
Define Cause of Stature Issue:
-Hx/Path:
> Conditions:
>> Trisomy 21
>> Turner Syndrome
>> Noonan Syndrome
>> Prader Willi Syndrome
> General Features:
>> Hx of delayed developmental milestones/intellectual disability
>> Multiple/unrelated health issues affecting disparate organ systems
-Sx/PE:
> Trisomy 21 = Epicanthal Folds
> Turner = Low posterior hairline
-Dx:
> Growth chart
> Check karyotypes in all girls (esp for TURNER)
> Focused genetic testing
-Tx:
> Turner = GH
> Noonan = GH
> Trisomy = None
Familial Tall Stature
Define Condition:
When pt is tall b/c parents are tall (normal growth pattern) - not pathologic
-Hx:
> Unremarkable Hx
> FHx of Tall Stature
-Sx/PE: Normal
-Dx:
> Growth Chart = Height AND Weight consistently elevated
> Bone Age FIlm
>> Calculate PAH ---> Compare to MPH (PAH should fall within MPH range)
-Tx:
> Reassurance
> Tall girls may get estrogen (facilitates closure on growth plates, but not common d/t S/Es)
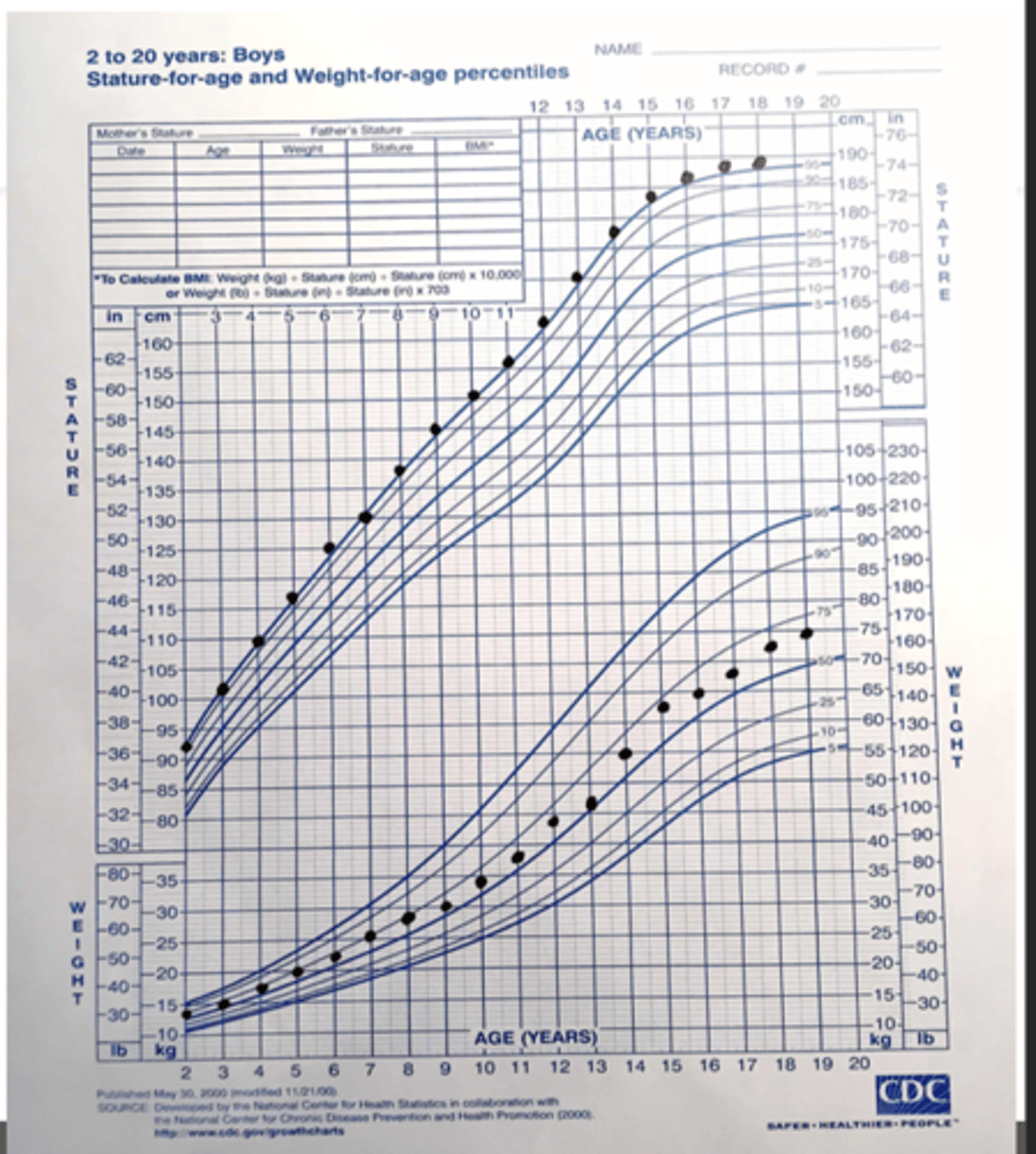
Precocious Puberty
Define Condition:
When pt is tall d/t early puberty (natural vertical growth acceleration of puberty BEFORE other children) - normal growth variant (not pathologic)
-Sx/PE: Early Pubertal Features (more mature for chronologic age)
> Early Acne
> Axillary hair
> Pubic hair
> Breast development
> Menses
-Dx:
> Growth Chart = Increase in the speed of weight gain at the same time as the vertical growth acceleration
> Bone Age Film = PAH --> Compare to MPH
>> Bone age will be ADVANCED to chronologic age, but concordant w/ pubertal status
>> PAH is LOWER than MPH (Completes puberty EARLY --> cease vertical growth early)
> Labs
>> Boys = HIGH Testosterone
>> Girls = HIGH Estradiol
> Height Velocity Chart = Velocity INCREASES SIGNIFICANTLY in puberty (acceleration begins early)
-Prog: If appropriate Tx, PAH will be normal
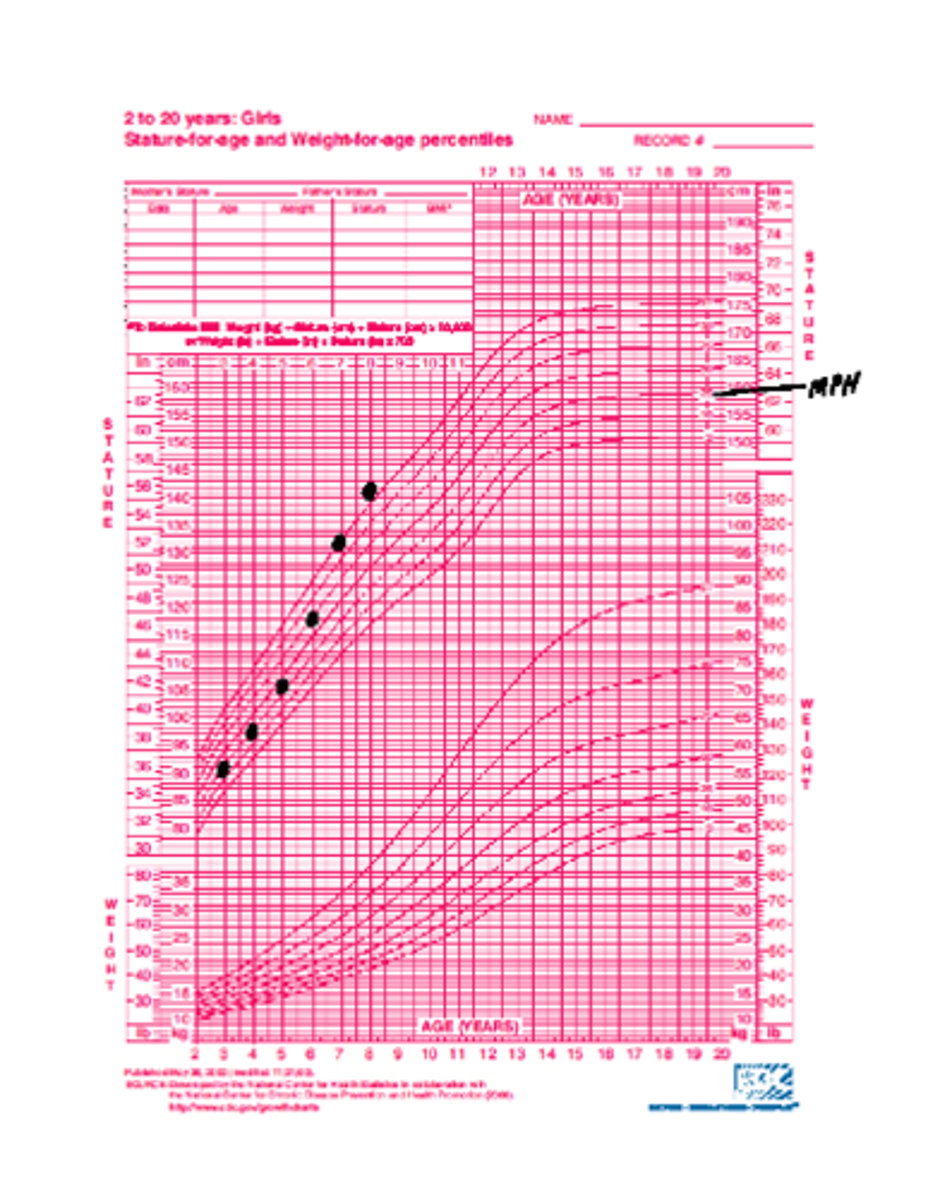
Excessive caloric intake
Define Condition:
Children w/ too much intake have BRISK vertical growth
-Hx:
> High caloric Intake
> Inactivity
-Sx/PE: Unremarkable, besides tall stature & obesity
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
>> Weight Gain BEFORE brisk vertical growth
>> Rate/Magnitude of Weight Gain is MORE STRIKING than rate of vertical growth
-Tx:
> Reassurance
> Address intake
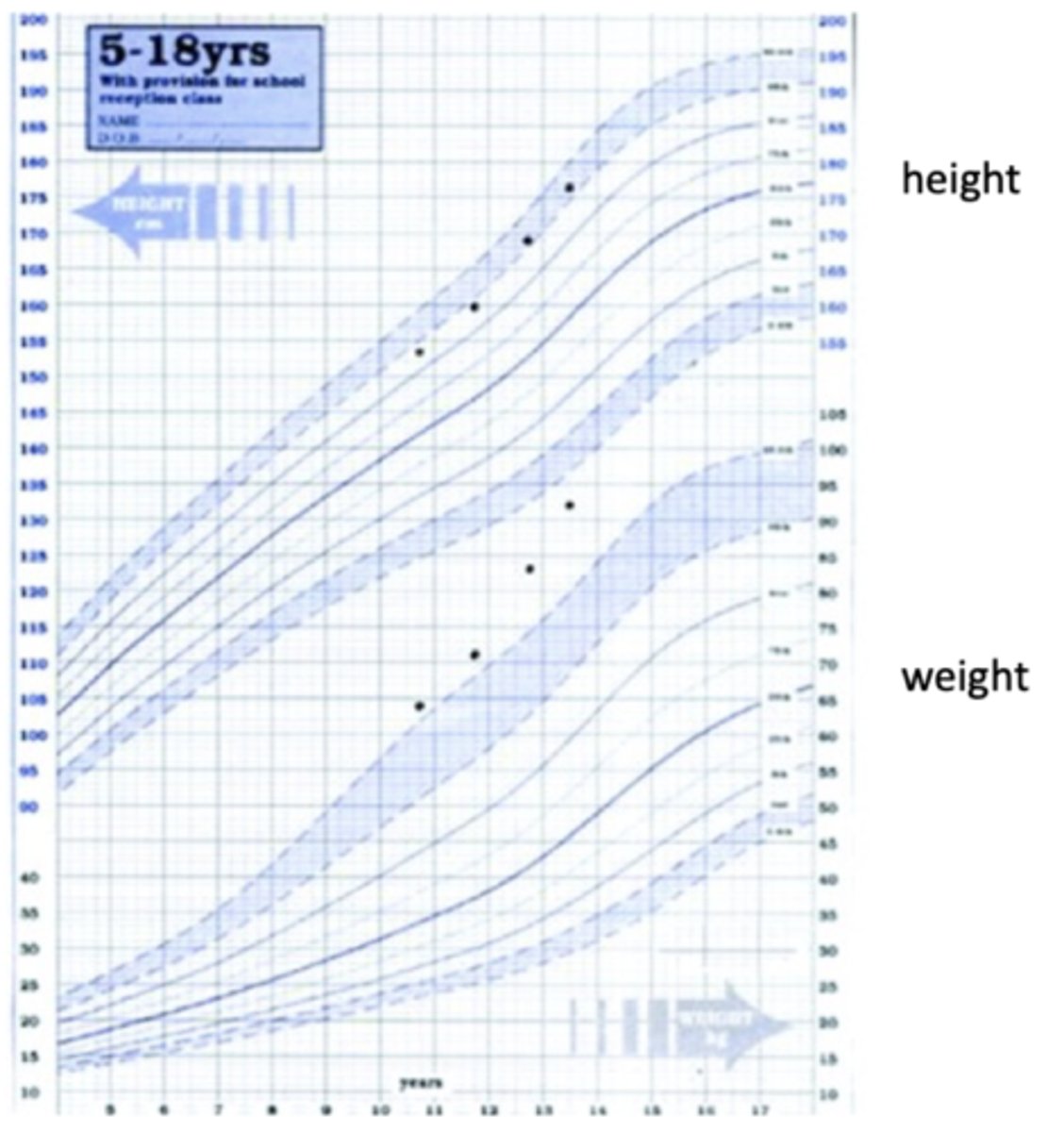
Pituitary Gigantism
Define Condition:
Pituitary adenoma secretes excessive GH when BEFORE growth plates have closed
-Sx/PE:
> Excessive Linear Growth
> Significant weight gain (begins with height acceleration)
-Dx:
> Growth Chart
>> Vertical Growth is MORE STRIKING than weight gain
> Check IGF-1 + GH Suppression:
>> First ELEVATED
>> THEN GH Suppression via 75 g Oral Glucose Load, then check after 2 hrs -->
>>> if < 1 ng/mL = Normal
>>> if > 1 ng/mL = GH Excess
> MRI (Pituitary) if GH Supression is Abnormal
-Tx:
> 1st = Transphenoidal Surgery (complete tumor resection)
> 2nd = Pharmacotherapy (if unfit for surgery, tumor too complicated, no relief from surgery)
>> Somatostatin Analog ("-tide")
>> GH receptor antagonist (Pegvisomant)
>> D2 Agonist (Cabergoline, Bromocriptine)
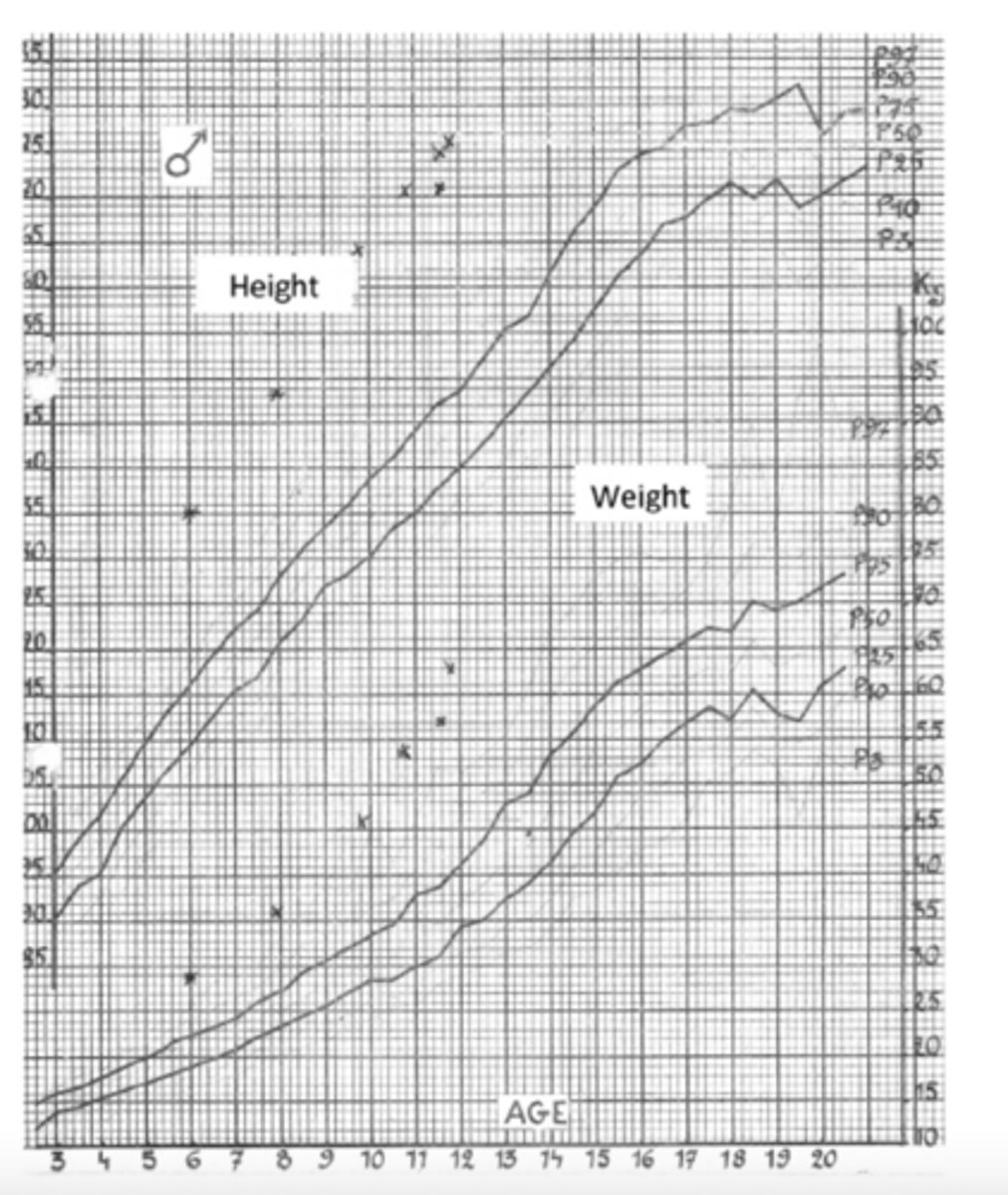
Acromegaly
Define Condition:
Pituitary adenoma secretes excessive GH when growth plates have closed - MC than pituitary gigantism
-Hx:
> Insidious onset (but slow progression)
> Dx in 40s
> A/w...
>> OSA
>> T2DM
>> Carpal Tunnel
>> Joint Pain
>> CVD
-Sx/PE:
> Macrognathia (enlarged hands/feet, coarse facial features, widened spaces btwn teeth, macroglossia)
> Secondary to Adenoma = HA, Visual Field Defects
-Dx:
> Check IGF-1 + GH Suppression:
>> First ELEVATED
>> THEN GH Suppression via 75 g Oral Glucose Load, then check after 2 hrs -->
>>> if < 1 ng/mL = Normal
>>> if > 1 ng/mL = GH Excess
> MRI (Pituitary) if GH Supression is Abnormal
-Tx:
> 1st = Transphenoidal Surgery (complete tumor resection)
> 2nd = Pharmacotherapy (if unfit for surgery, tumor too complicated, no relief from surgery)
>> Somatostatin Analog ("-tide")
>> GH receptor antagonist (Pegvisomant)
>> D2 Agonist (Cabergoline, Bromocriptine)
Genetic Syndromes causing TALL STATURE
Define Condition:
-Hx/Path:
> Marfan Syndrome
> Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
> Homocystinuria
-Sx/PE:
> Height OUT OF PROPORTION to family height
-Dx:
> Bone Age Film = PAH out of MPH range
> Labs:
>> Kline = Karyotype
-Tx: Genetics referral