CDC Fascioliasis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The trematodes Fasciola hepatica (also known as the ____or the __)
common liver fluke,sheep liver fluke
Fasciola gigantica are large liver flukes (F. hepatica: up to __
30 mm by 15 mm
F. gigantica up to ____
75 mm by 15 mm
Fasciola primarily found in__ (their main definitive hosts) but also are causal agents of fascioliasis in humans.
domestic and wild ruminants
F. hepatica and F. gigantica are distinct species, “intermediate forms” that are thought to represent hybrids of the two species have been found in parts of _ where both species are endemic.
Asia and Africa
Immature eggs are discharged in the __ and passed in the stool
biliary ducts
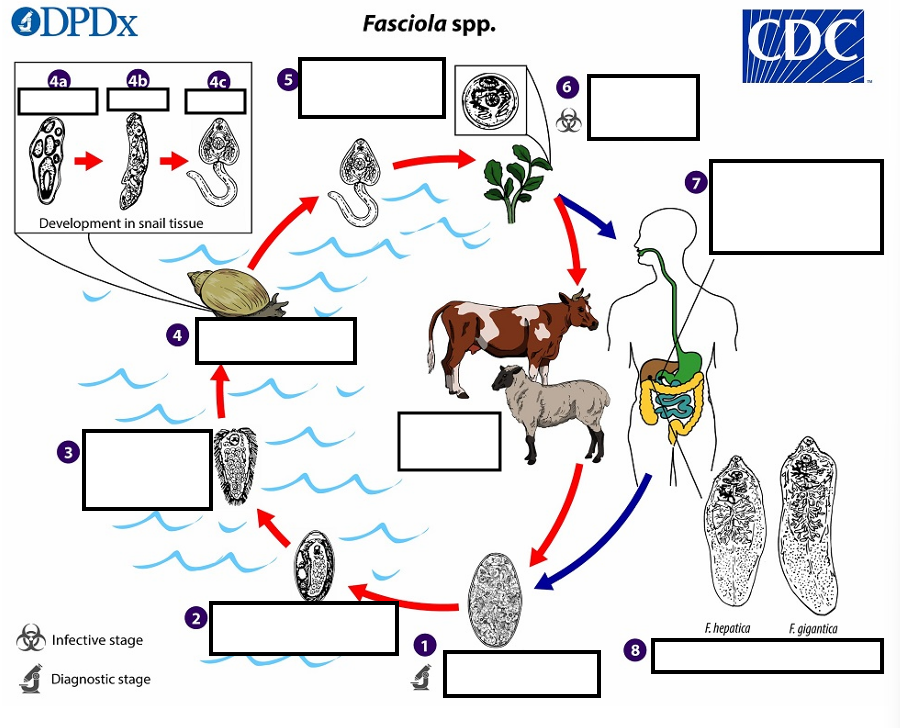
1 Eggs become embryonated in freshwater over ~_____, which invade a suitable snail intermediate host
2 weeks
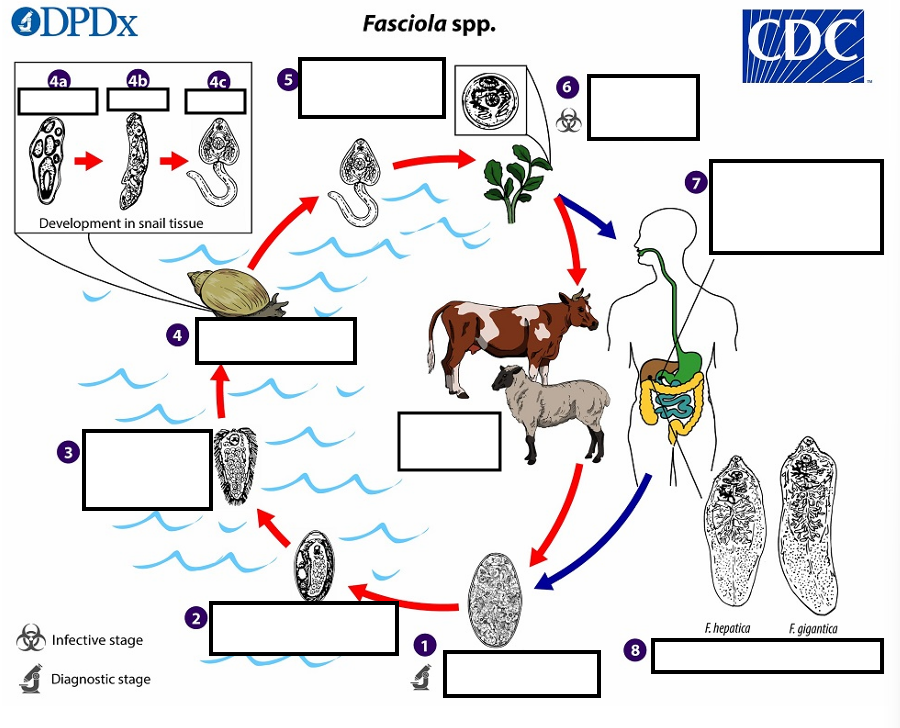
2 embryonated eggs release_____________
miracidia
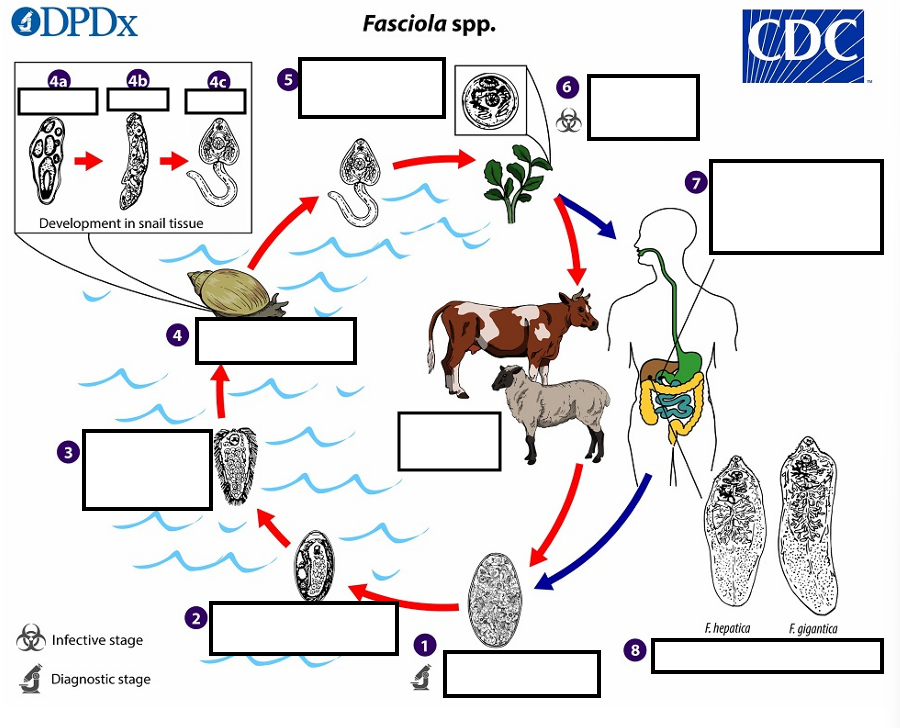
3 which invade a suitable snail ____________
intermediate host
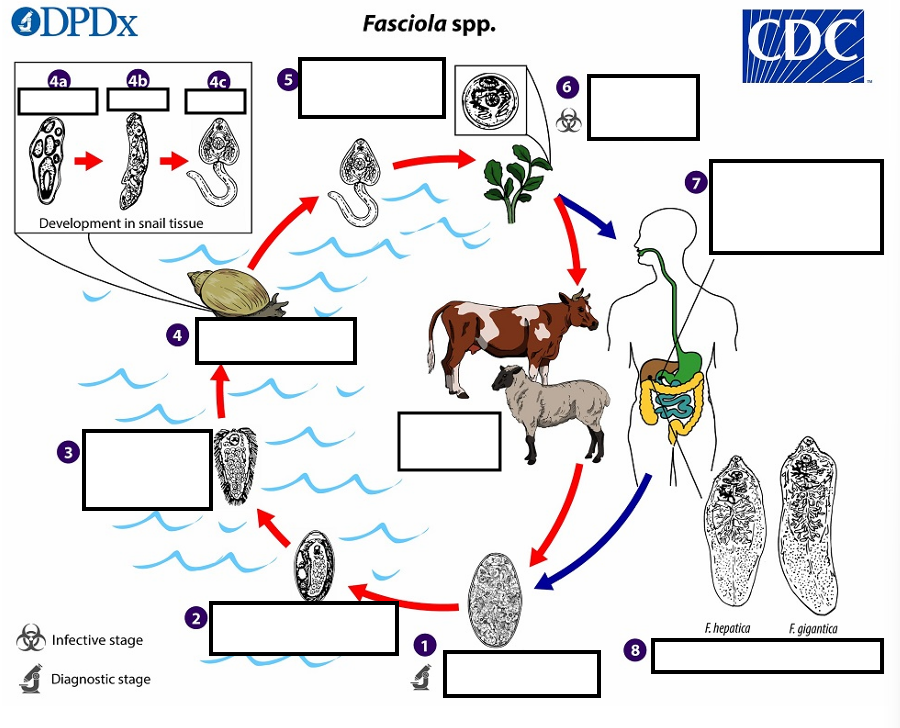
(4) In the snail, unundergo several developmental stages (sporocysts, rediae , and cercariae . The cercariae are released from the snail (5) and encyst as__ on aquatic vegetation or other substrates.
metacercariae
(5) Humans and other mammals become infected by ingesting __ (e.g., watercress) duodenum
metacercariae-contaminated vegetation
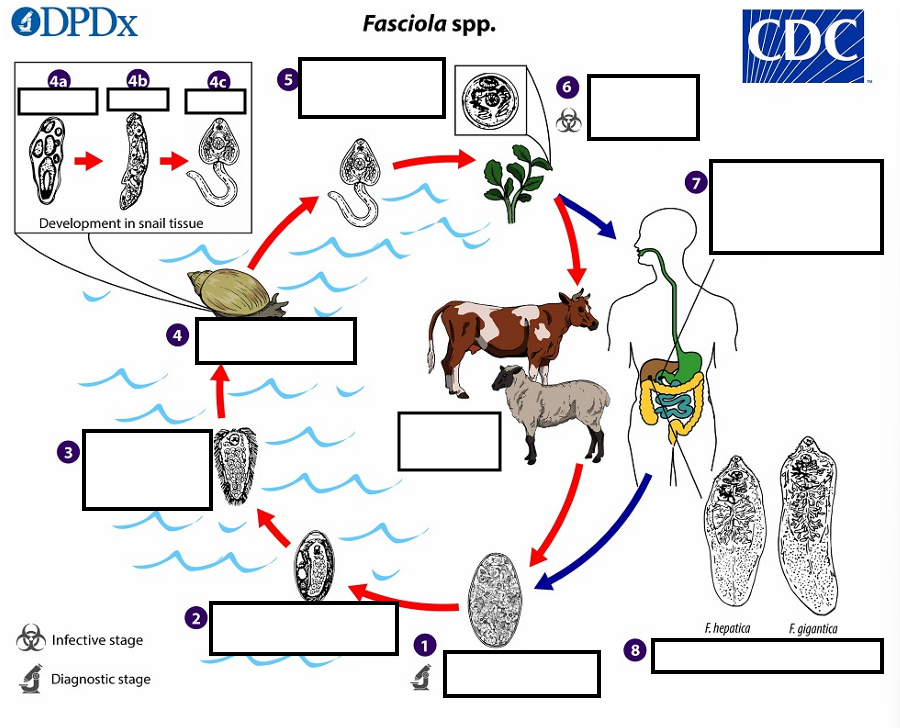
(6) After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the_______
duodenum
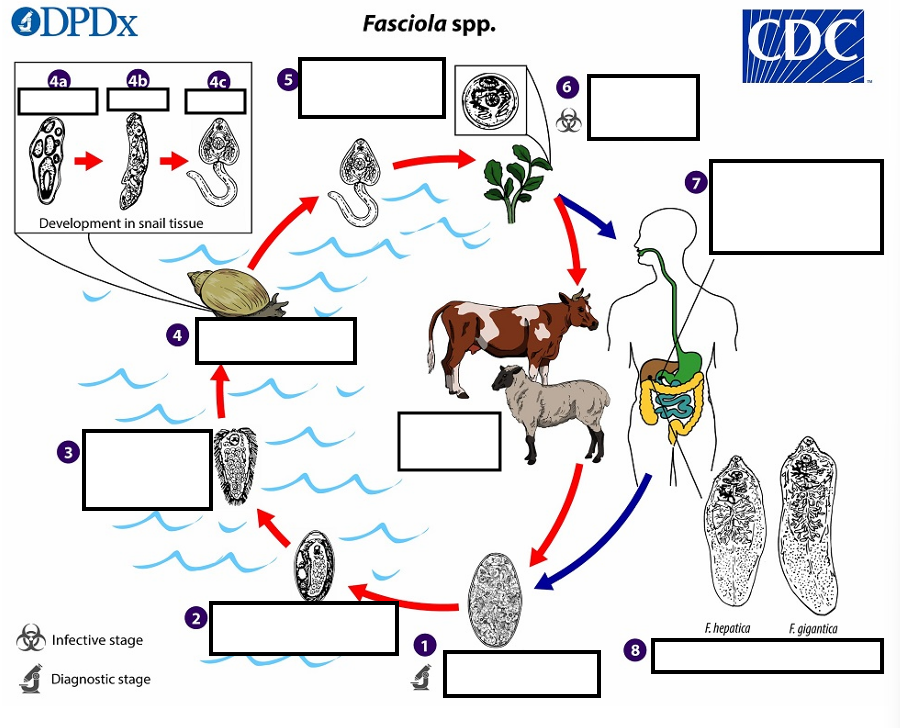
7 and penetrate through the intestinal wall into the ______________.
peritoneal cavity
7 The immature flukes then migrate through the liver parenchyma into ___, where they mature into adult flukes and produce eggs
biliary ducts
8 In humans, maturation from metacercariae into adult flukes usually takes about development of F. gigantica may take somewhat longer than F. hepatica
3–4 months
At least _ species have been identified as intermediate hosts for one or more Fasciola spp
20 snai
Fasciola hepatica is found on all inhabited continents, in more than __ countries, particularly where _ are raised. 70, sheep or cattle
“Intermediate forms” have been reported from areas, particularly in Asia, where both ___ are endemic.
F. hepatica and F. gigantica
However, other ________with unusual ploidy and morphology occasionally have been reported in areas where the two species are not sympatric (e.g., the United Kingdom), which underscores the need for more research into atypical forms
non-sperm-producing forms
Eggs of Fasciola spp. are broadly ellipsoidal, are operculated, measure 130–150 µm long by______wide, and are passed unembryonated in feces.
60–90 µm
During the early phase of the infection (usually referred to as the acute phase also, the migratory, invasive, hepatic, parenchymal, or larval phase), the period when the larval fluke is migrating from the intestines and through the liver parenchyma, larval migration can be associated with __.
inflammation, tissue destruction, and toxic/allergic reactions
Nonspecific symptoms/signs
(e.g., a_) and laboratory abnormalities (e.g., peripheral
eosinophilia, elevated transaminase levels) may develop.
bdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, hepatomegaly, malaise, fever, cough

Adult of F. hepatica stained with carmine