Cranial Nerves and Parasympathetic Pathways
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Where are the cell bodies of the preganglionic parasympathetic neurons located?
In the midbrain, pons, or medulla.
What are the locations of the ganglia for the parasympathetic nerves of CN III, VII, and IX?
In the orbit, pterygopalatine fossa, or infratemporal fossa.
What type of cell body is found in the ganglia for the parasympathetic nerves of CN III, VII, and IX?
Postganglionic cell body.
What do the parasympathetic fibers of CN III, VII, and IX travel with to reach their target organs?
A branch of the trigeminal nerve providing sensation.
What types of glands are innervated by the parasympathetic fibers of CN VII and IX?
Salivary glands and mucous glands (not sweat glands).
What structures do the parasympathetic fibers of CN III affect?
Glands, pupils, and lens.
What is the role of the preganglionic cell body in the parasympathetic pathway?
It initiates the parasympathetic response before synapsing at the ganglion.
What is the significance of the location of the ganglia for CN III, VII, and IX?
They are strategically located to efficiently innervate nearby target organs.
What is the general model followed by the parasympathetics of CN III, VII, and IX?
They all share a similar pathway involving preganglionic and postganglionic cell bodies and specific ganglion locations.
What are the cranial nerves involved in the parasympathetic division of the ANS?
Cranial nerves III (Oculomotor), VII (Facial), IX (Glossopharyngeal), and X (Vagus).
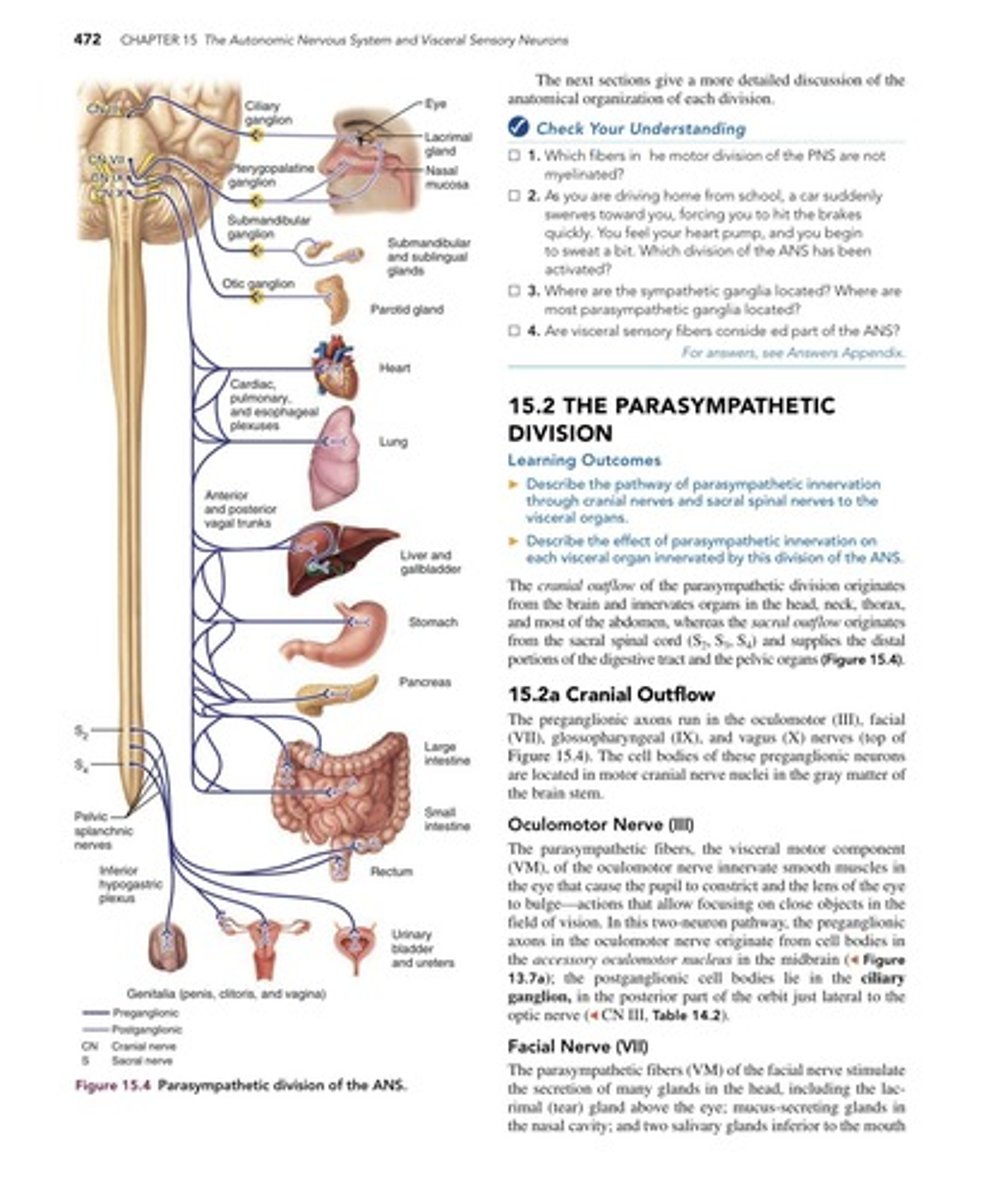
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve (CN III) in the parasympathetic division?
It innervates smooth muscles in the eye, causing pupil constriction and lens bulging for focusing on close objects.
Where do the preganglionic axons of the oculomotor nerve originate?
From cell bodies in the accessory oculomotor nucleus in the midbrain.
Where are the postganglionic cell bodies for the oculomotor nerve located?
In the ciliary ganglion, located in the posterior part of the orbit.
What glands are stimulated by the facial nerve (CN VII) in the parasympathetic division?
The lacrimal gland, mucus-secreting glands in the nasal cavity, and submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
Where do the preganglionic neurons for the facial nerve originate?
In the lacrimal nucleus in the pons.
What is the pathway for the facial nerve to the lacrimal and nasal glands?
Preganglionic neurons synapse with postganglionic neurons in the pterygopalatine ganglion.
What is the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) in the parasympathetic division?
It stimulates secretion from the parotid gland.
Where do the preganglionic neurons of the glossopharyngeal nerve originate?
In the inferior salivatory nucleus in the medulla.
Where do the postganglionic neurons of the glossopharyngeal nerve synapse?
In the otic ganglion, located inferior to the foramen ovale of the skull.
What is the role of the vagus nerve (CN X) in the parasympathetic division?
It innervates organs in the thorax and most of the abdomen.
What is the sacral outflow in the parasympathetic division?
It originates from the sacral spinal cord (S2, S3, S4) and supplies the distal portions of the digestive tract and pelvic organs.
What is the effect of parasympathetic innervation on visceral organs?
It generally promotes functions such as digestion and energy conservation.
What is the location of sympathetic ganglia compared to parasympathetic ganglia?
Sympathetic ganglia are located near the spinal cord, while most parasympathetic ganglia are located near or within the target organs.
Which fibers in the motor division of the PNS are not myelinated?
Postganglionic fibers.
What happens to the body during a stressful situation in terms of the ANS?
The sympathetic division is activated, causing increased heart rate and sweating.
What is the function of the pelvic splanchnic nerves?
They provide parasympathetic innervation to the pelvic organs.
What is the inferior hypogastric plexus?
A network of nerves that innervates pelvic organs.
What is the significance of the ciliary ganglion?
It is the site where postganglionic neurons for the oculomotor nerve synapse.
What does the term 'visceral motor component' refer to?
The part of the autonomic nervous system that controls involuntary functions of internal organs.
What are the effects of parasympathetic innervation on the heart?
It decreases heart rate.
What are the effects of parasympathetic innervation on the digestive system?
It stimulates digestion and increases glandular secretions.
How does the parasympathetic division affect the urinary bladder?
It promotes contraction of the bladder for urination.
What is the primary function of the vagus nerve (X)?
To innervate the visceral organs of the thorax and most of the abdomen, facilitating rest-and-digest activities.
What percentage of preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body are contained in the vagus nerve?
Nearly 90%.
What are the effects of vagal stimulation on the digestive system?
It stimulates digestion by increasing secretion of digestive glands and motility of the smooth muscle in the digestive tract.
Where are the preganglionic cell bodies of the vagus nerve located?
In the dorsal motor nucleus of vagus in the medulla.
What is the significance of intramural ganglia in the vagus nerve's function?
Most postganglionic neurons are confined within the walls of the organs being innervated, forming intramural ganglia.
What organs does the vagus nerve innervate through the cardiac plexus?
The heart.
What organs does the vagus nerve innervate through the pulmonary plexus?
The lungs.
What organs does the vagus nerve innervate through the esophageal plexus?
The esophagus and stomach.
What organs does the vagus nerve innervate through the celiac plexus?
The intestines, liver, pancreas, and other abdominal organs.
What spinal segments give rise to the sacral outflow of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Segments S2-S4 of the spinal cord.
What organs are innervated by the sacral parasympathetic outflow?
The distal half of the large intestine, bladder, uterus, and erectile tissues of the external genitalia.
What are the effects of parasympathetic innervation on the bladder?
Stimulation of voiding of urine.
What are the effects of parasympathetic innervation on the reproductive organs?
Stimulation of erection.
What is the pathway of preganglionic axons from the sacral parasympathetic region to the pelvic organs?
They run in the ventral roots to the ventral rami, branching to form pelvic splanchnic nerves.
What is the role of the inferior hypogastric plexus?
It contains fibers from both divisions of the ANS and helps innervate pelvic organs.
What is the basic organization of the sympathetic division?
It exits from the thoracic and superior lumbar parts of the spinal cord, from segments T1 to L2.
What is the function of the adrenal medulla in the sympathetic nervous system?
To release hormones that enhance the body's fight-or-flight response.
What is the significance of the trigeminal nerve (V) in the autonomic nervous system?
It has the widest distribution within the face and is involved in the routing of postganglionic axons.
What is the effect of sympathetic innervation on the heart?
It increases heart rate.
What is the effect of sympathetic innervation on the digestive system?
It inhibits digestion and reduces motility.
What is the effect of sympathetic innervation on the bronchi in the lungs?
It causes dilation of the bronchi.
Which cranial nerves carry preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
Cranial nerves III (oculomotor), VII (facial), and IX (glossopharyngeal).
Where do the preganglionic cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system lie?
In the visceral motor region of the spinal gray matter, forming the lateral gray horn.
What is the primary function of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
To innervate visceral organs in internal body cavities and superficial regions, including sweat glands and blood vessels.
What are the effects of the parasympathetic division on the eye's iris?
Stimulates constrictor muscles, constricting eye pupils.
How does the parasympathetic division affect the heart rate?
Decreases rate; slows and steadies the heart.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on the heart muscle?
Increases rate and force of heartbeat.
What happens to the bronchioles under parasympathetic stimulation?
Constricts bronchioles.
What effect does the sympathetic division have on the digestive tract organs?
Decreases activity of glands and muscles, constricts sphincters, and causes vasoconstriction.
What is the role of the vagus nerve in the autonomic nervous system?
It carries parasympathetic fibers to various organs, including the heart and digestive tract.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on sweat glands?
Stimulates copious sweating.
How does the parasympathetic division affect the gallbladder?
Stimulates activity, causing the gallbladder to contract and expel bile.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on blood vessels?
Constricts most vessels and increases blood pressure.
What happens to the bladder under parasympathetic stimulation?
Causes contraction of smooth muscle of bladder wall and relaxes urethral sphincter, promoting voiding.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on the liver?
Epinephrine stimulates the liver to release glucose into the blood.
What is the effect of the parasympathetic division on the ciliary muscle of the eye?
Stimulates ciliary muscles, resulting in bulging of the lens for accommodation and close vision.
How does the sympathetic division affect the adrenal medulla?
Stimulates medulla cells to secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream.
What is the role of the sympathetic trunk ganglia?
They are part of the sympathetic nervous system and relay signals to various organs.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on the uterus?
Stimulates contraction of smooth muscle of the uterine wall and causes vasoconstriction of vessels.
What is the effect of the parasympathetic division on the penis?
Causes erection through vasodilation.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on mental activity?
Increases alertness.
What is the effect of the sympathetic division on adipose tissue?
Stimulates lipolysis (fat breakdown).
What is the difference in complexity between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions?
The sympathetic division is more complex, innervating more organs and structures.
What is the effect of the parasympathetic division on blood vessels?
Little or no effect.
What happens to the kidney under sympathetic stimulation?
Causes vasoconstriction and decreases urine output.