Chapter 2 - Bones and Fascia of Lower Limb
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Describe the divisions of the skeleton
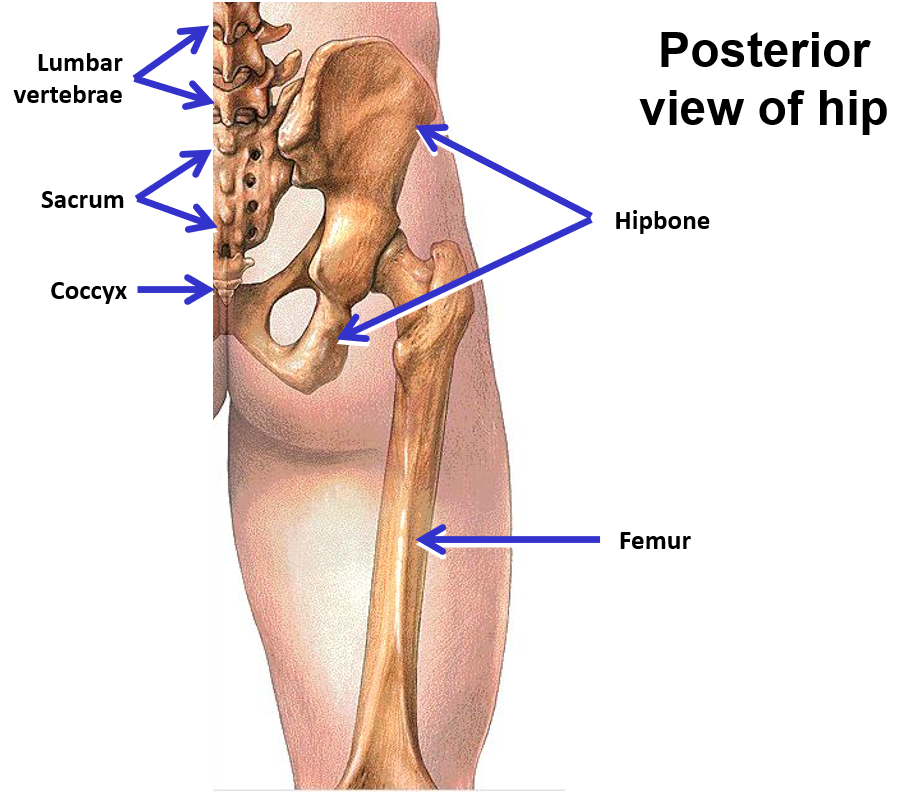
Axial skeleton - forms central axis of body
Appendicular skeleton - bones of the limbs and girdles
What comprises the Axial skeleton
Axial skeleton - forms central axis of body
–Skull
–Rib cage - 12 pairs of ribs + sternum
–Vertebral column
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum - formed by fusion of 5 embryonic vertebrae
Coccyx - formed by fusion of 4 embryonic vertebrae
Intervertebral discs – fibrocartilage discs that unite adjacent vertebrae
What comprises the Appendicular skeleton
Appendicular skeleton - bones of the limbs and the girdle bones that unite limbs to axial skeleton
Lower limb:
Hipbone - single bone that forms pelvic girdle; attaches lower limb to sacrum (part of axial skeleton)
Femur - bone of the thigh
Tibia and fibula - bones of the leg
Tarsal, metatarsal, and phalanx bones - bones of the foot
Upper limb:
Scapula and clavicle - form pectoral girdle; attach upper limb to sternum (part of the axial skeleton)
List and describe the regional names of the lower limb
Gluteal region - buttocks (posterior to hip joint)
Covered by gluteal fascia (deep investing fascia)
Thigh - from hip to knee
Surrounded by fascia lata (deep investing fascia of the thigh)
Contains femur
Popliteal fossa - diamond-shaped depression of posterior knee joint
*fossa = depression
Leg - from knee to ankle
Contains tibia (medial side) and fibula (lateral side)
Surrounded by crural fascia (deep investing fascia of leg)
Foot
Dorsum = top of foot; covered by thin dorsal fascia (deep investing fascia on top of foot)
Plantar = bottom of foot; covered by thick plantar fascia (deep investing fascia of plantar foot)
Digits are numbered: big toe = #1; little toe = #5
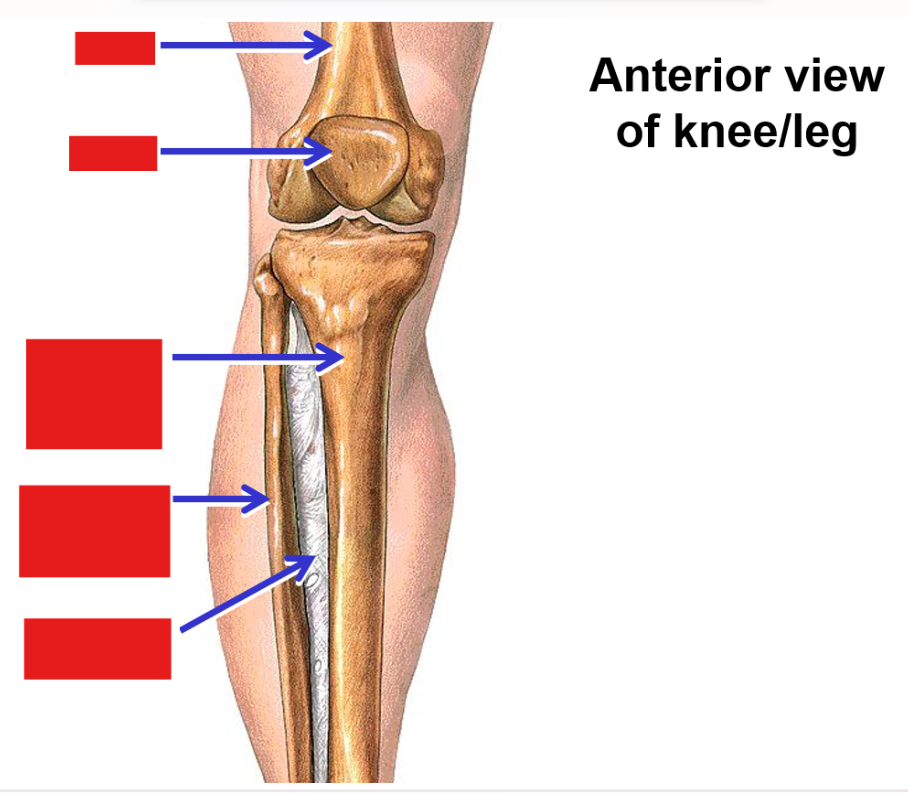
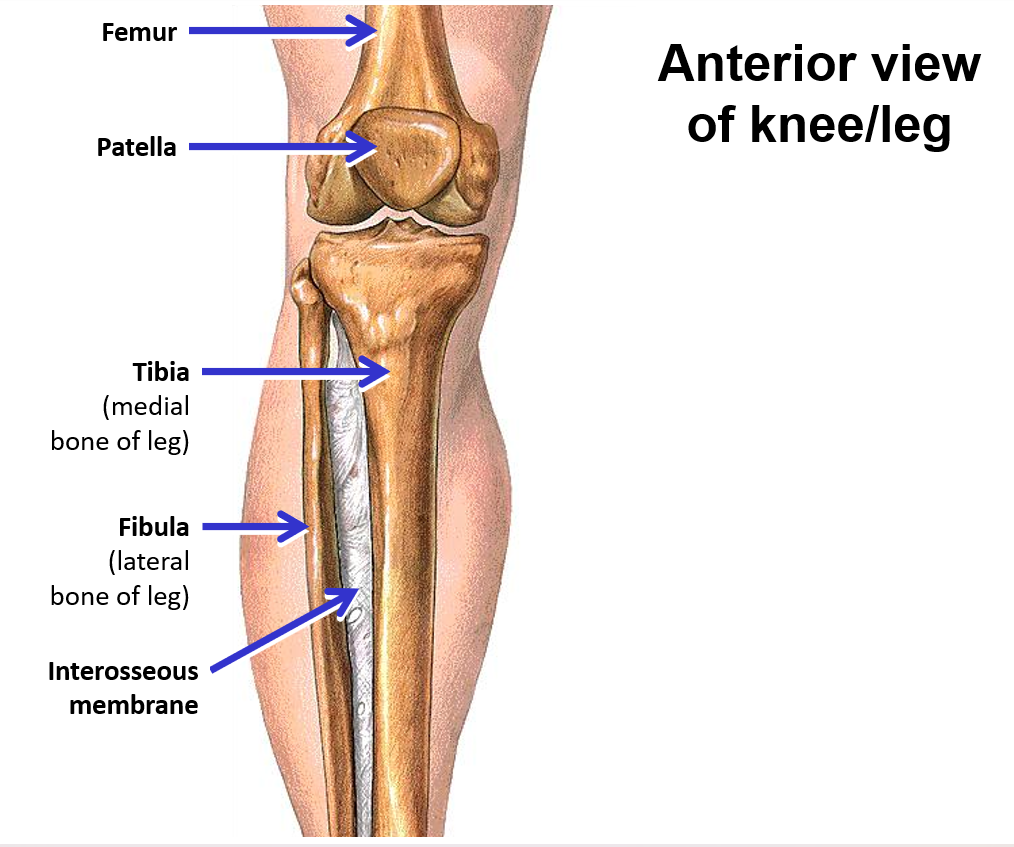
List and describe the bones of the lower limb
Pelvis - consists of 2 hipbones + sacrum
Hipbone - single bone in adult; formed by fusion of 3 bony parts (ilium, ischium, and pubis)
Right and left hipbones united to each other anteriorly
Posteriorly each hipbone is attached to the sacrum
Femur - single bone of the thigh
Knee joint - articulation between femur of thigh and tibia and fibula of leg; also includes patella
Patella - a sesamoid bone (‘floating’ bone located within a muscle tendon) (knee cap)
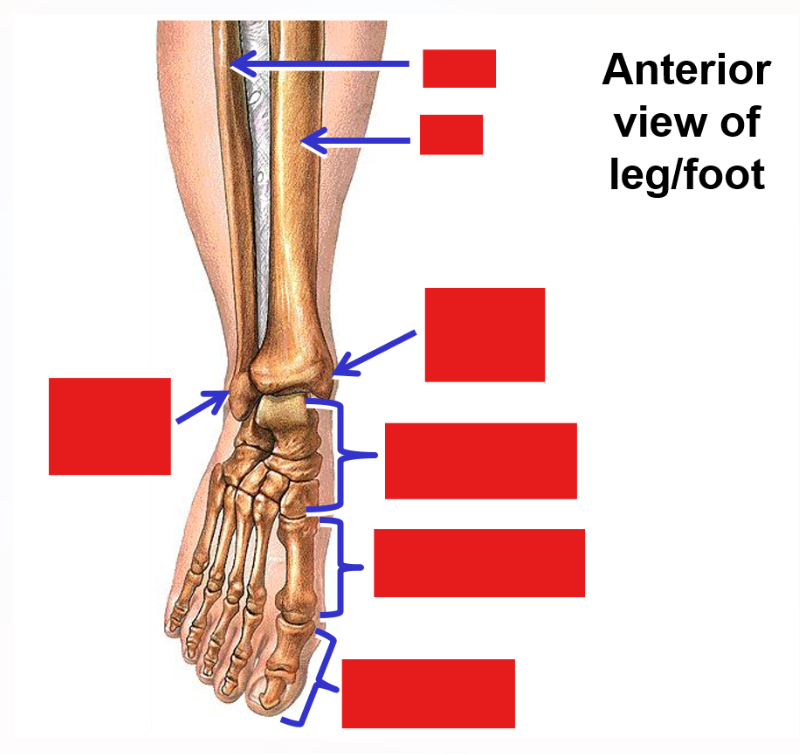
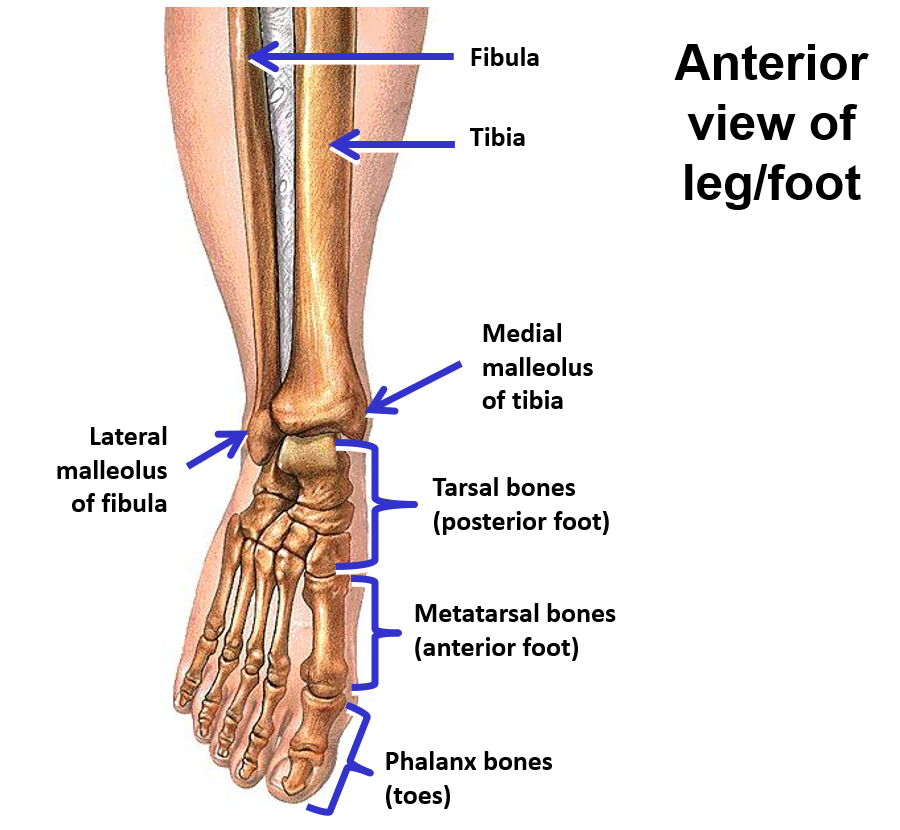
Tibia - weight bearing bone on medial side of leg (triangular bone)
Medial malleolus - at distal end of tibia
Fibula - thin bone on lateral side of leg
Lateral malleolus - at distal end of fibula
Ankle joint - articulation between tibia and fibula of leg and talus bone (tarsals) of foot
Tibia and fibula strongly united along their length by interosseous membrane (layer of dense connective tissue) (in between bone)
No movement between tibia and fibula (provides stability for weight-bearing support
Foot
Tarsal bones - 7 irregular-shaped bones that form posterior ½ of foot
—» Talus bone - contributes to ankle joint
—» Calcaneus bone - forms heel
Metatarsal bones - 5 elongated bones that form anterior ½ of foot
—» Metatarsal bones numbered 1-5, starting on medial side of foot
Phalanx bones (phalanges) - bones that form the digits
—» Big toe (toe #1): has proximal and distal phalanx bones
—» Digits #2-5: have proximal, middle, and distal phalanx bones
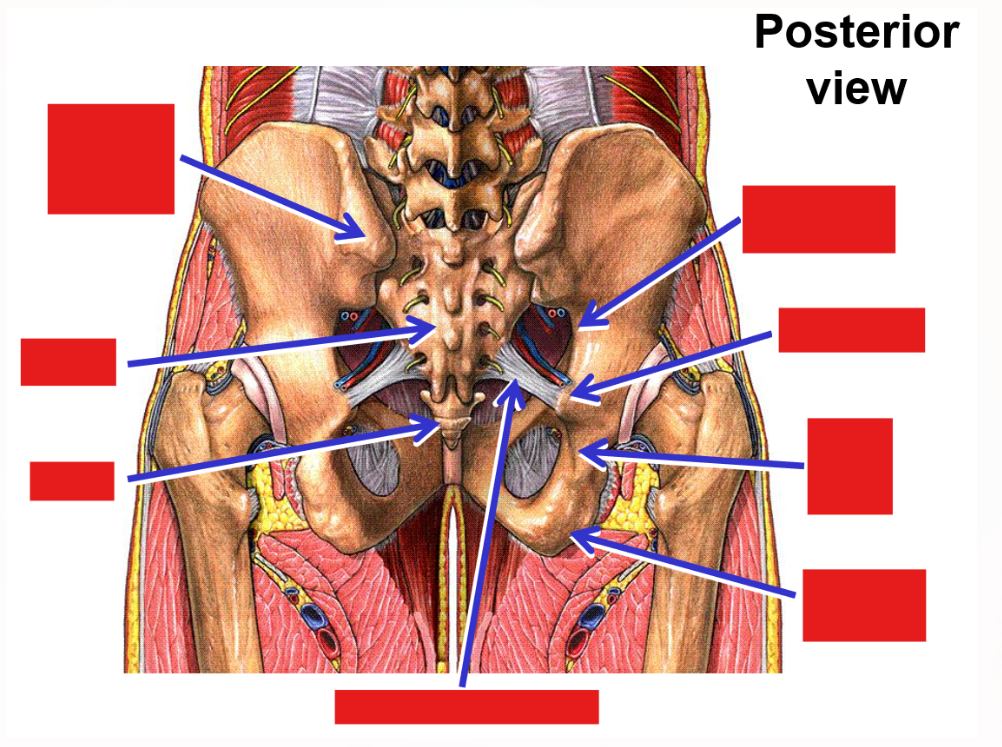
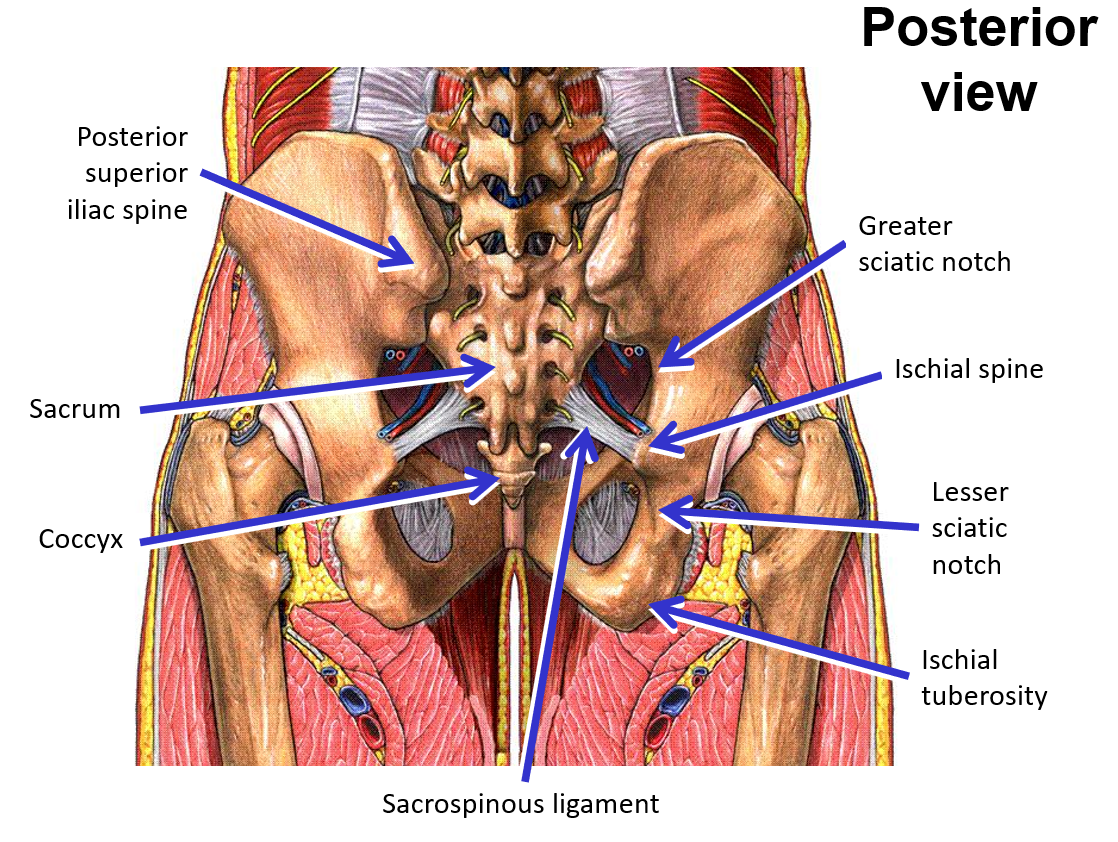
List and describe the bony landmarks of the Pelvis
Pelvis consists of 2 hipbones and the sacrum
Hipbone formed by fusion of pubis, ischium, and ilium
Pubis - anterior, inferior portion of hipbone
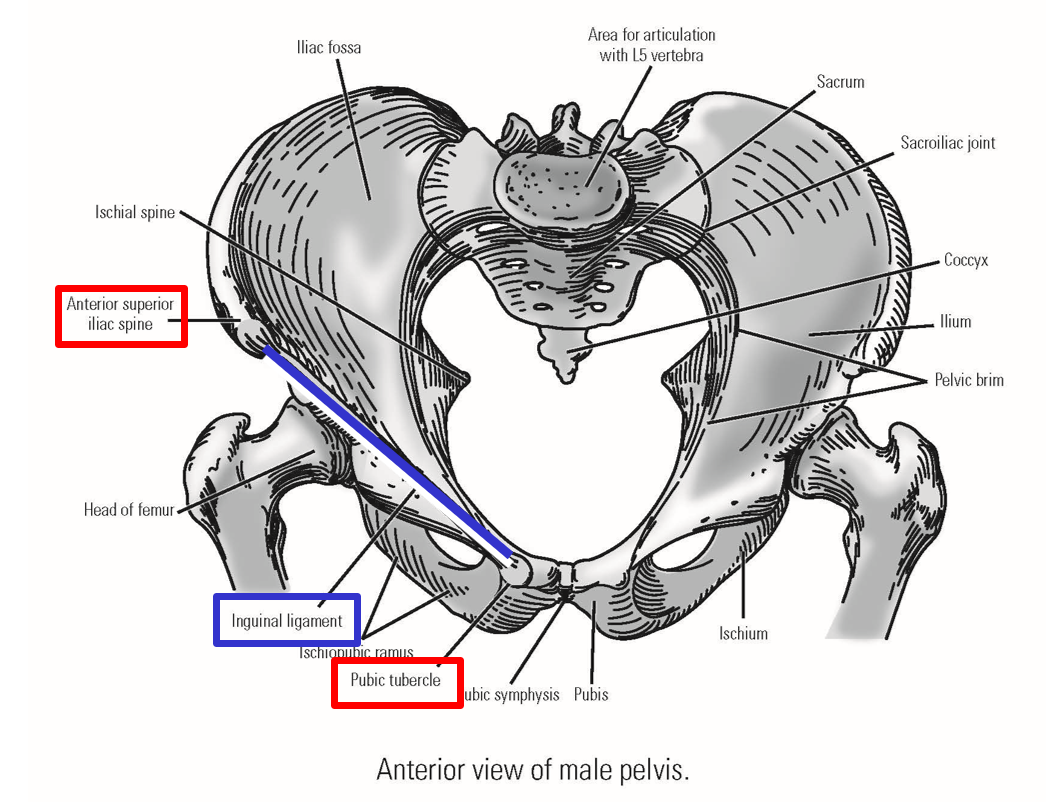
Pubic tubercle
Pubic symphysis - joint that unites right & left hipbones
Ischium - posterior, inferior portion of hipbone
Ischial tuberosity
Ischial spine
Ilium - superior portion of hipbone
Iliac crest
Iliac fossa
Anterior superior iliac spine
Anterior inferior iliac spine
Posterior superior iliac spine
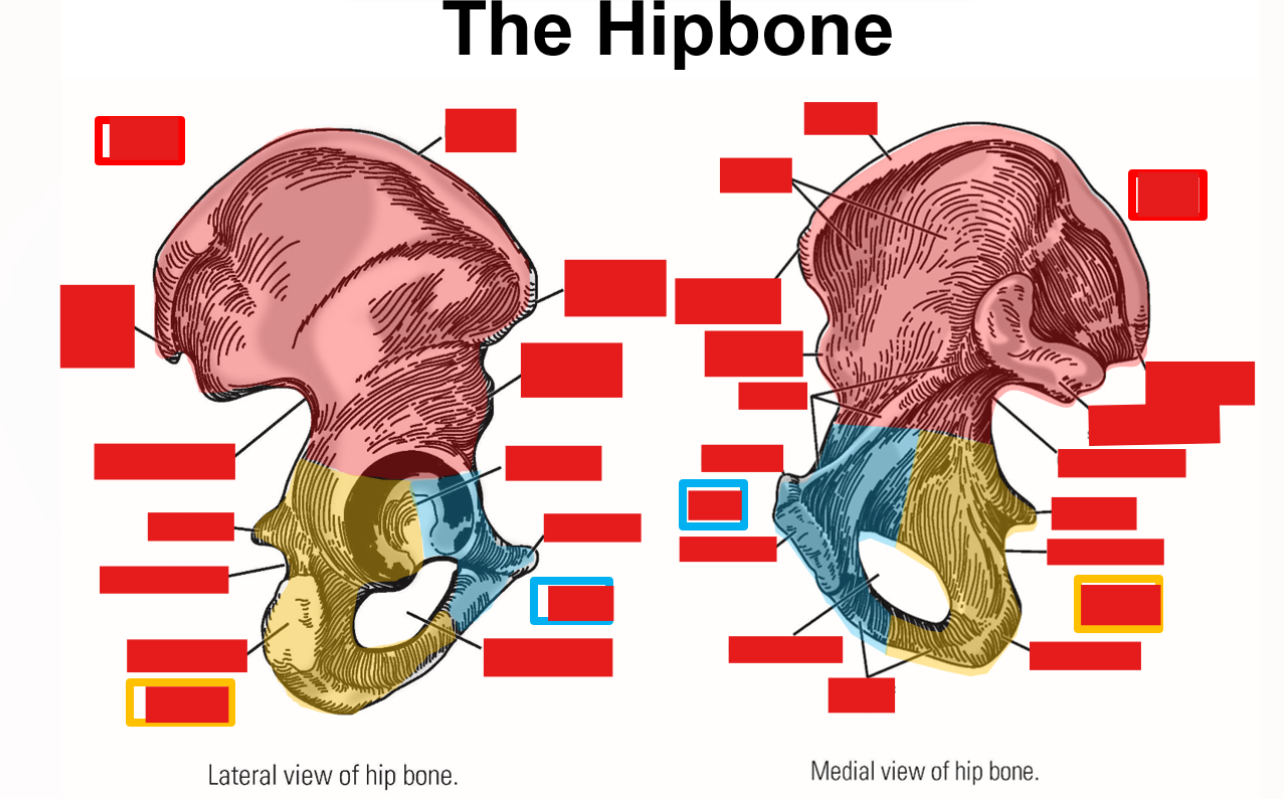
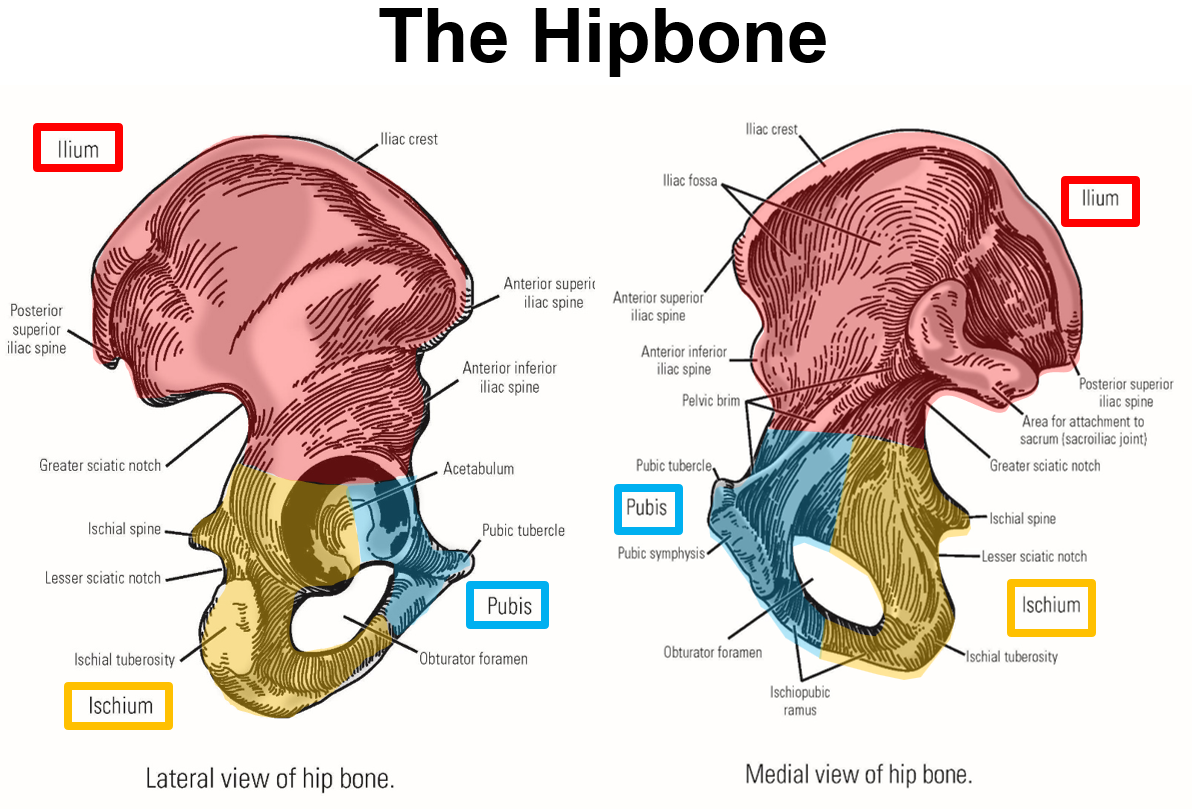
Describe what consists of the hip bone
Pelvis
Acetabulum - socket portion of hip joint
Ischiopubic ramus (bare of bone)
Greater sciatic notch; Lesser sciatic notch
—» Notches are separated by ischial spine
Obturator foramen
Sacroiliac joints - join sacrum to ilium portion of hipbone
Pelvic ligaments
Sacrospinous ligament - sacrum to ischial spine
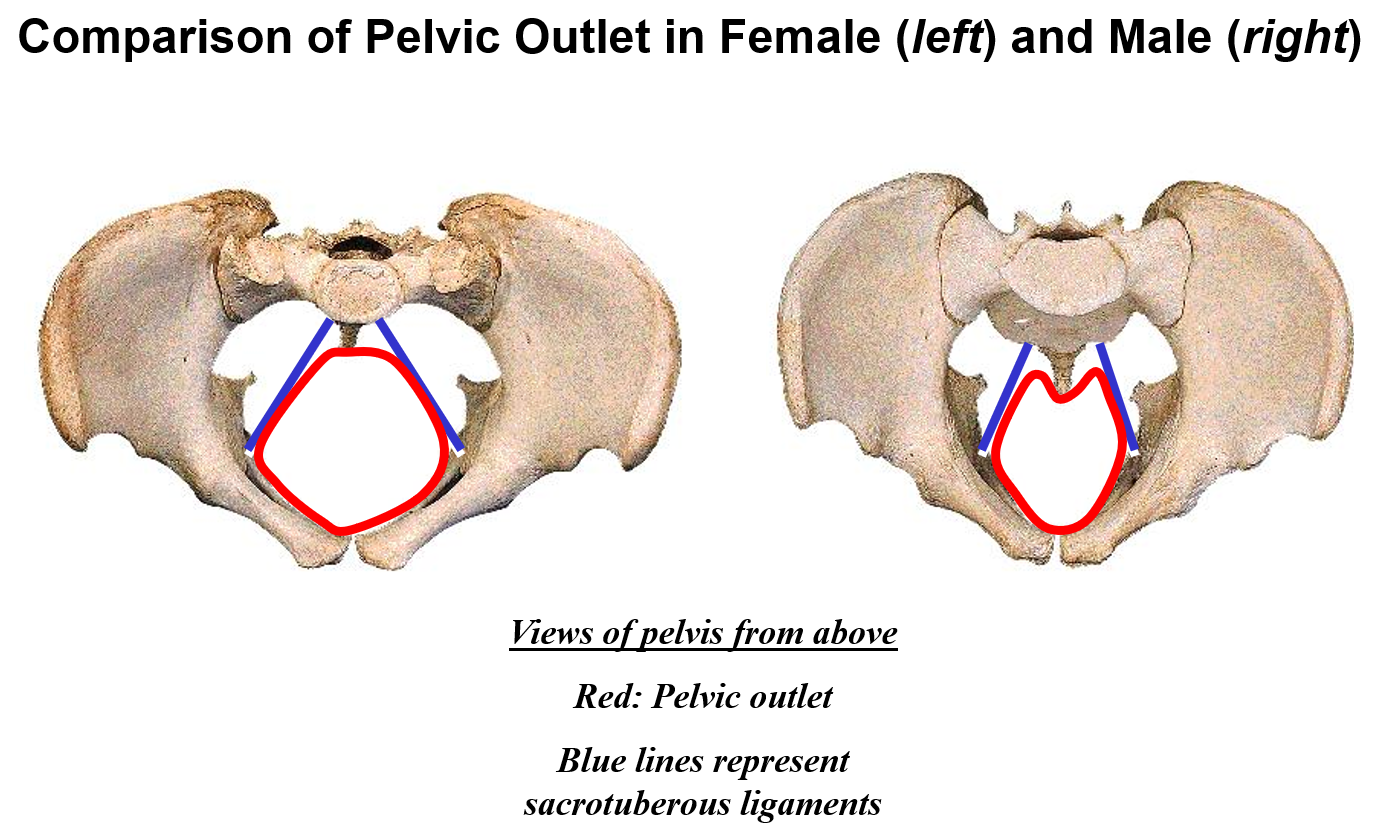
Sacrotuberous ligament - sacrum to ischial tuberosity
Addition of these ligaments converts greater and lesser sciatic notches into greater sciatic foramen and lesser sciatic foramen
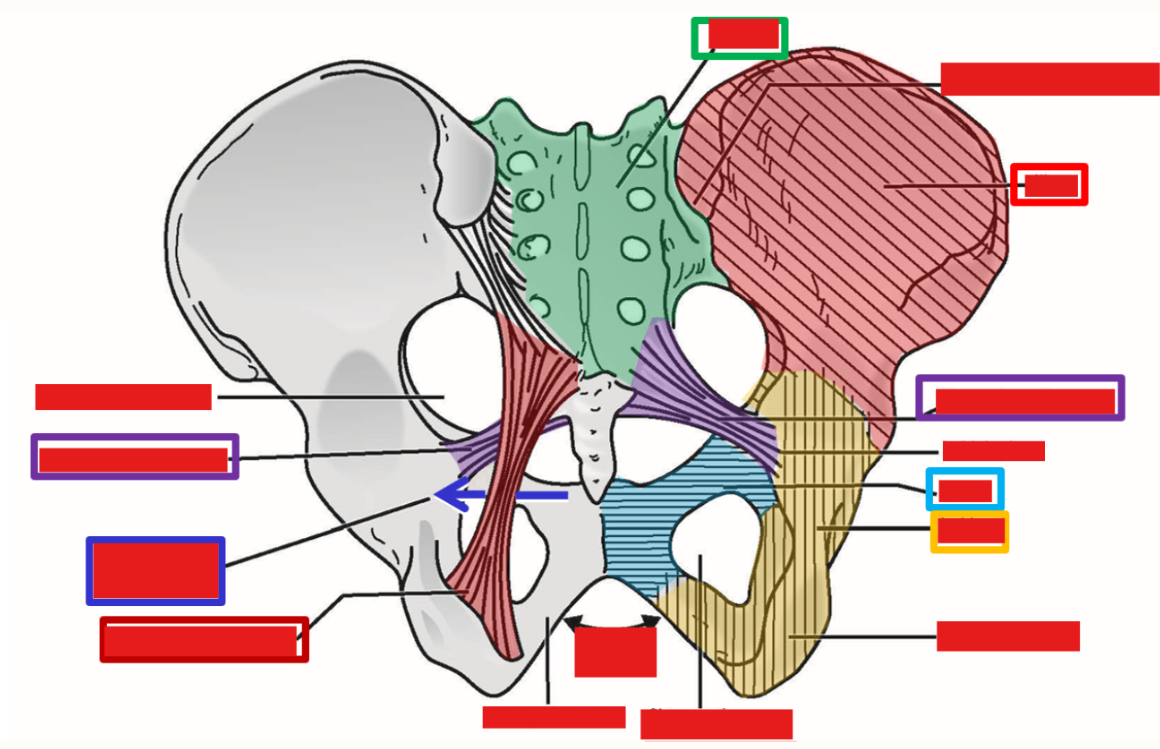
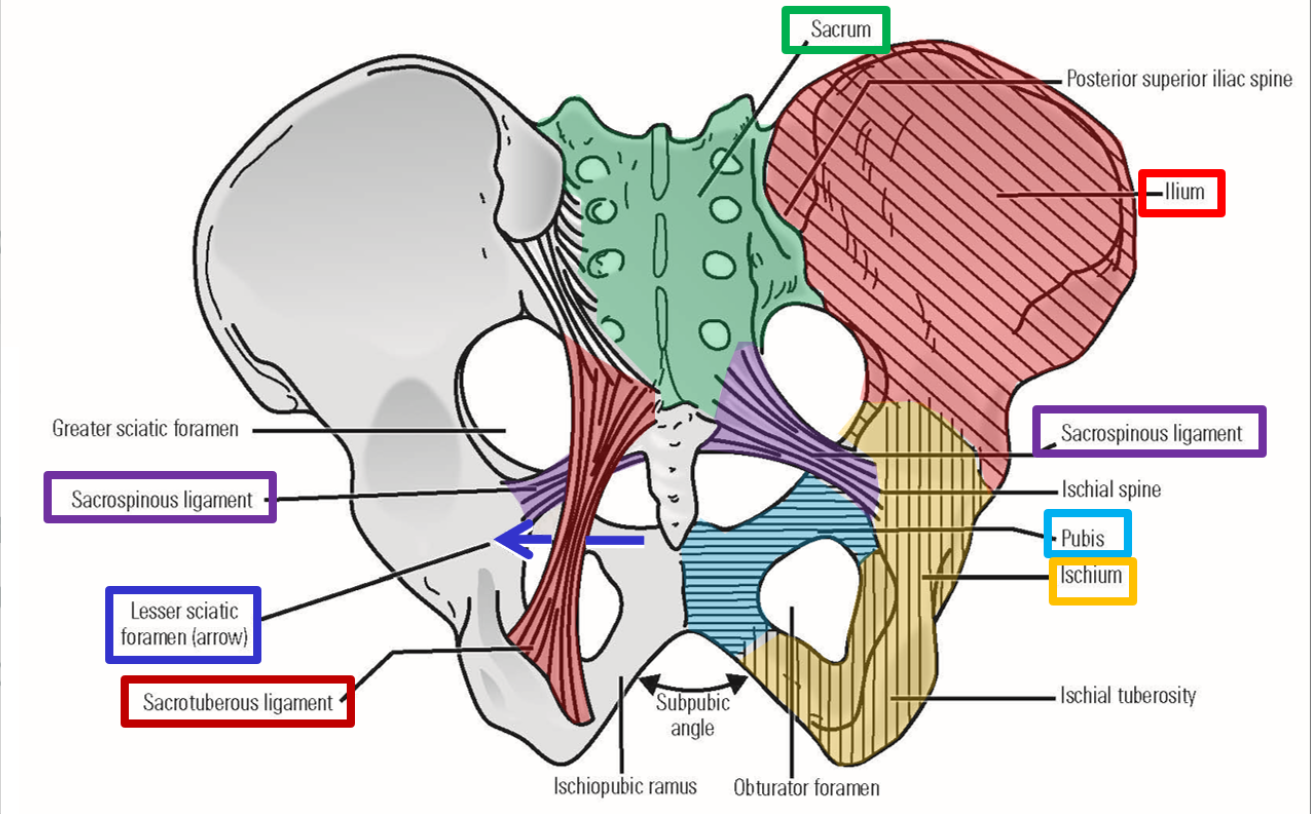
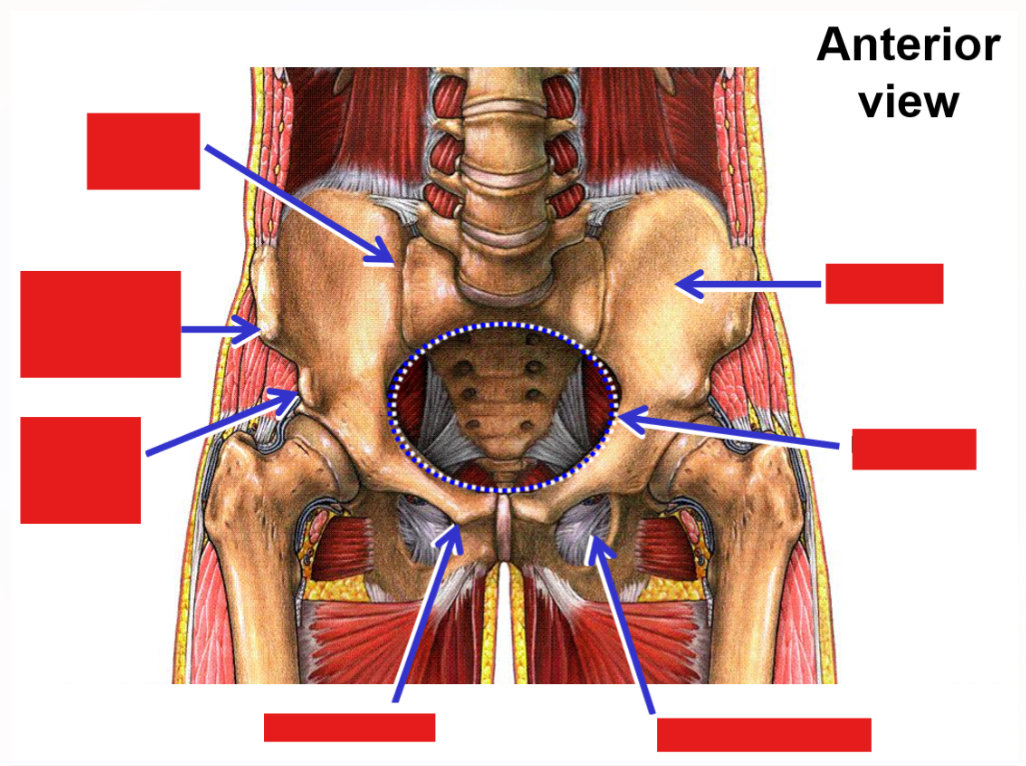
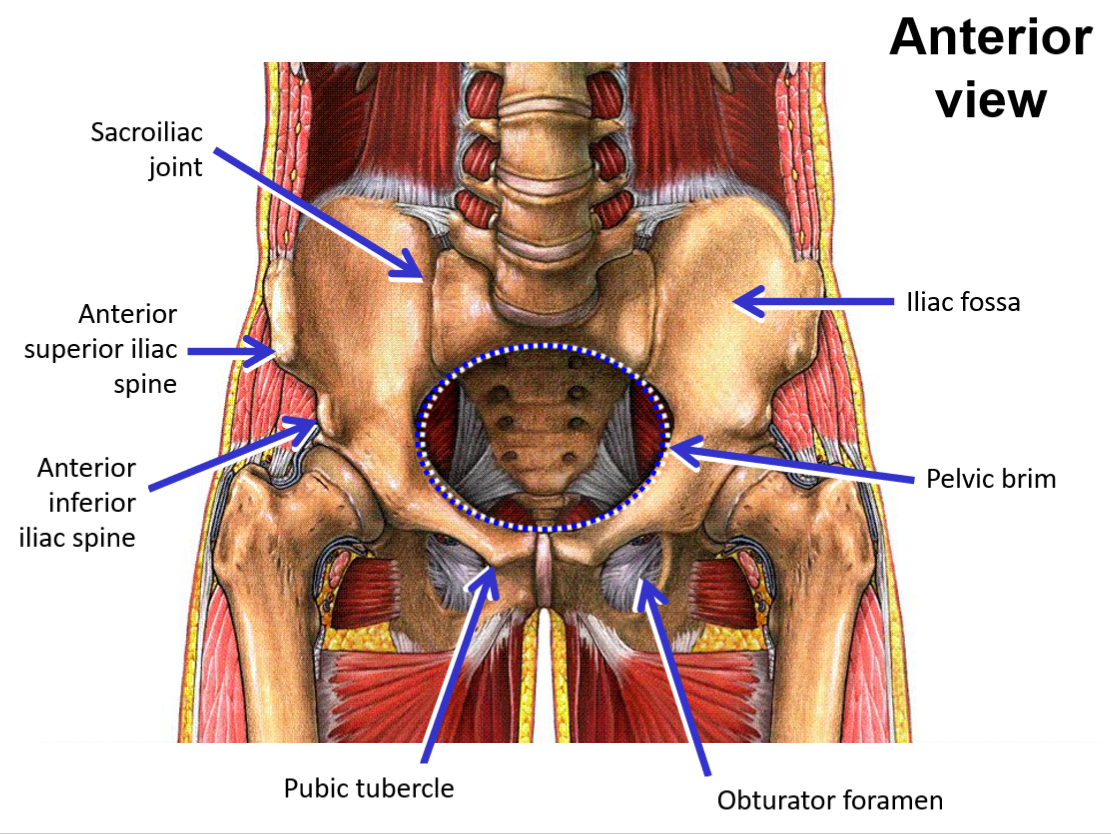
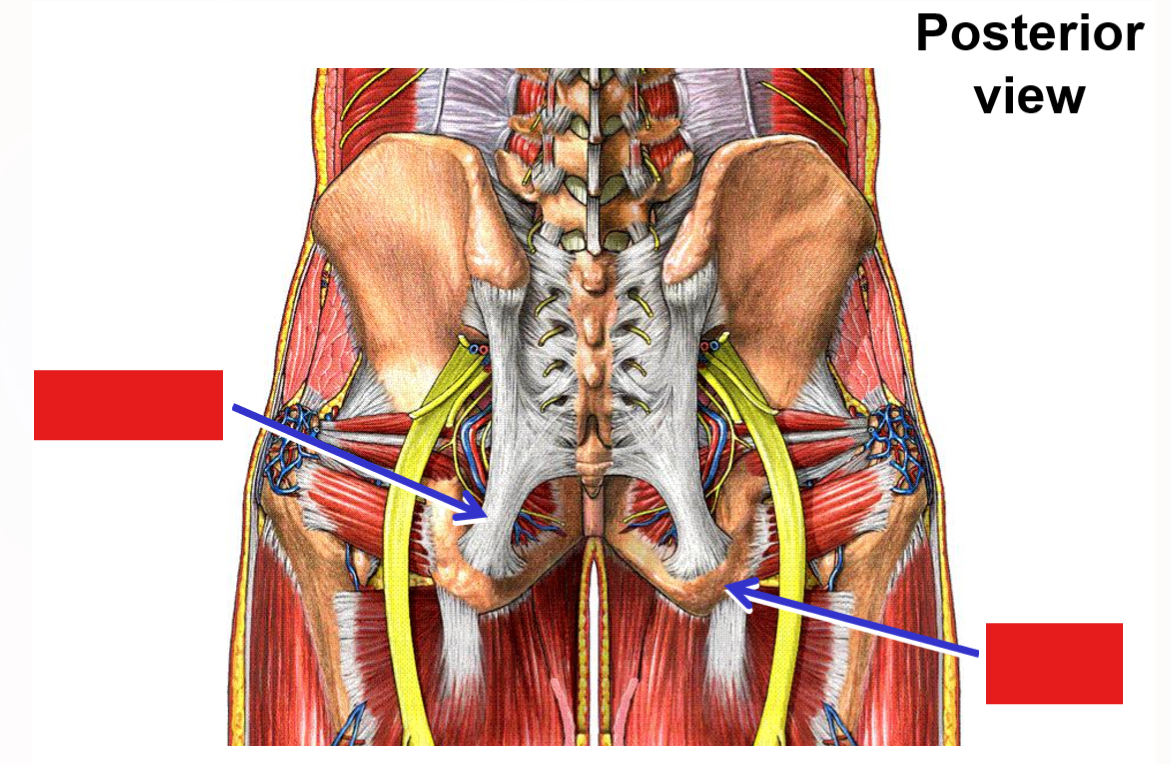
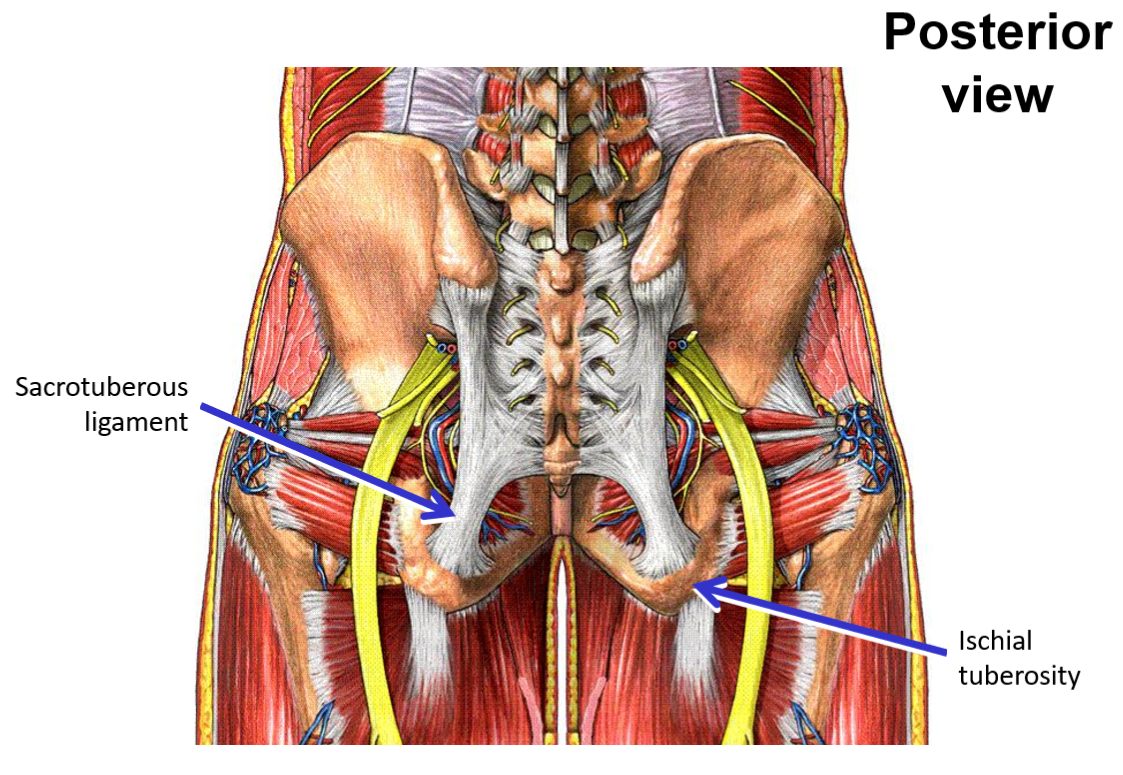
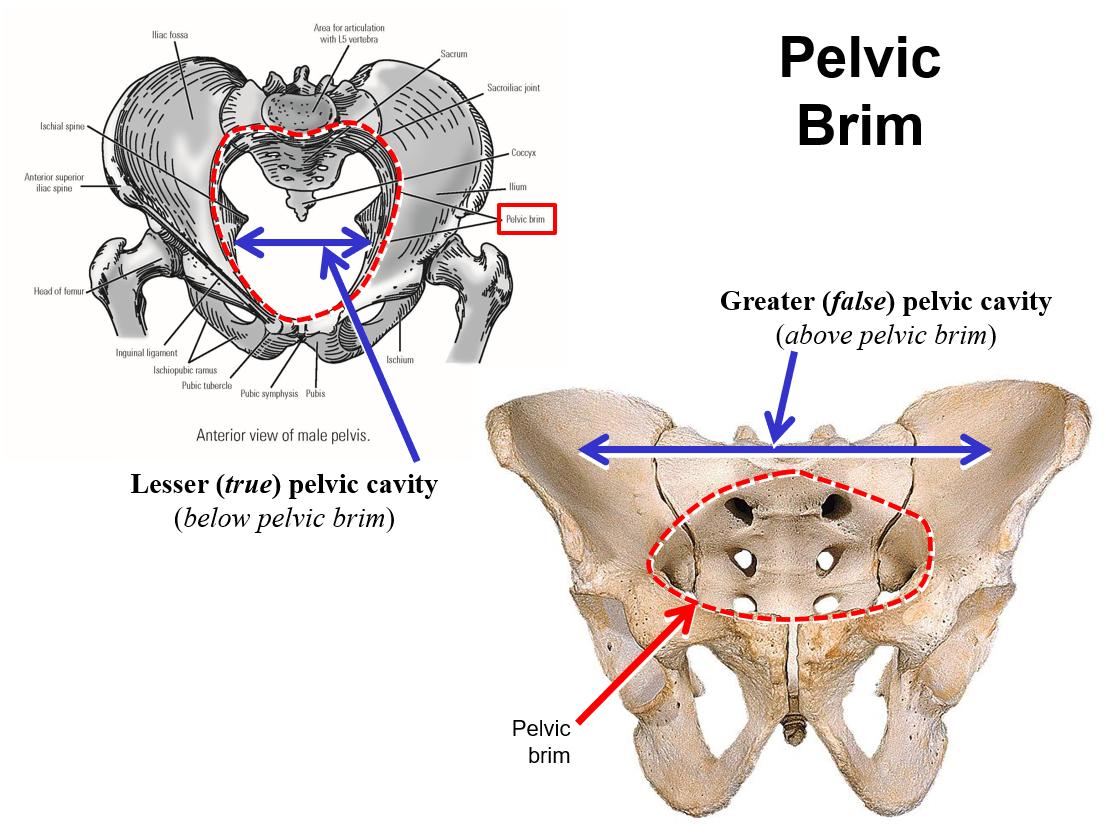
Describe the pelvic brim
Bony line formed by superior margin of pubis, inferior margin of iliac fossa, and superior margin of sacrum
Greater (false) pelvic cavity - broad space located above level of pelvic brim (between iliac fossae)
Lesser (true) pelvic cavity - narrow space located below level of pelvic brim
Describe the pelvic outlet. What is it defined by?
Pelvic outlet - inferior opening of pelvis
Defined by pubic symphysis, ischiopubic rami, ischial tuberosities, sacrotuberous ligaments, and coccyx
Outlet is wider and rounder in females; narrow in males
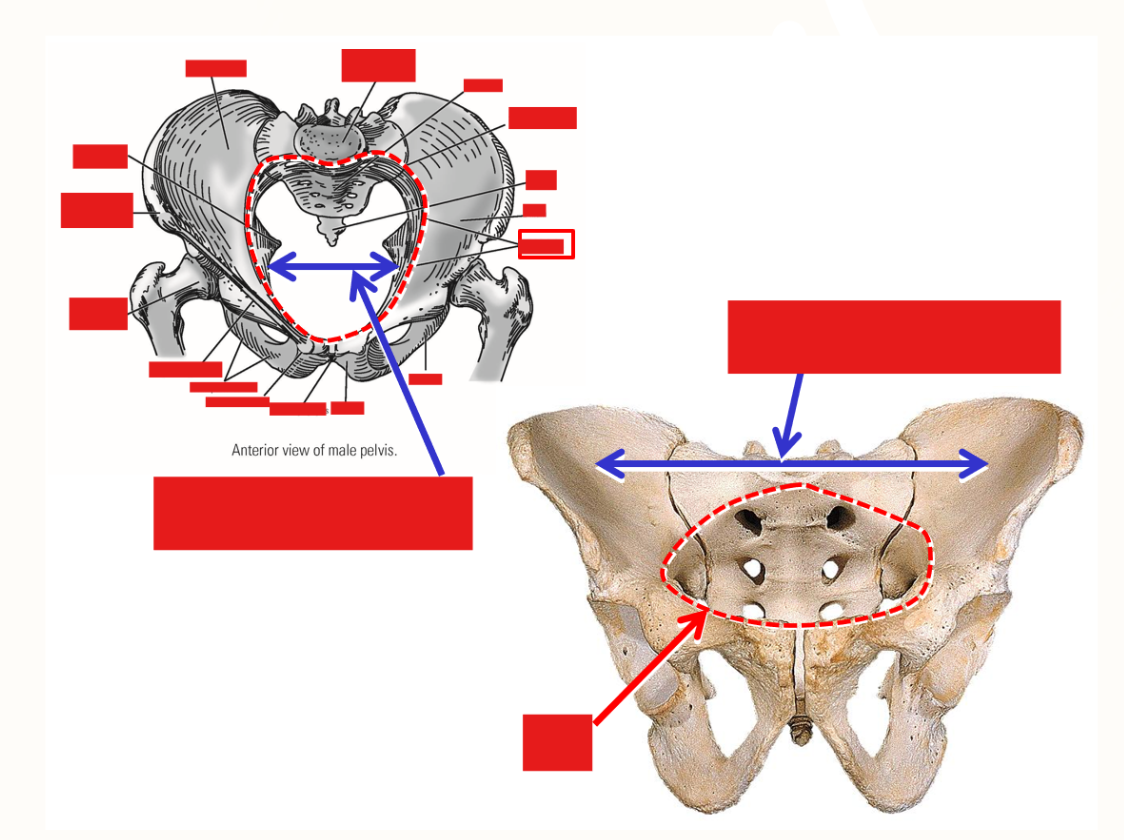
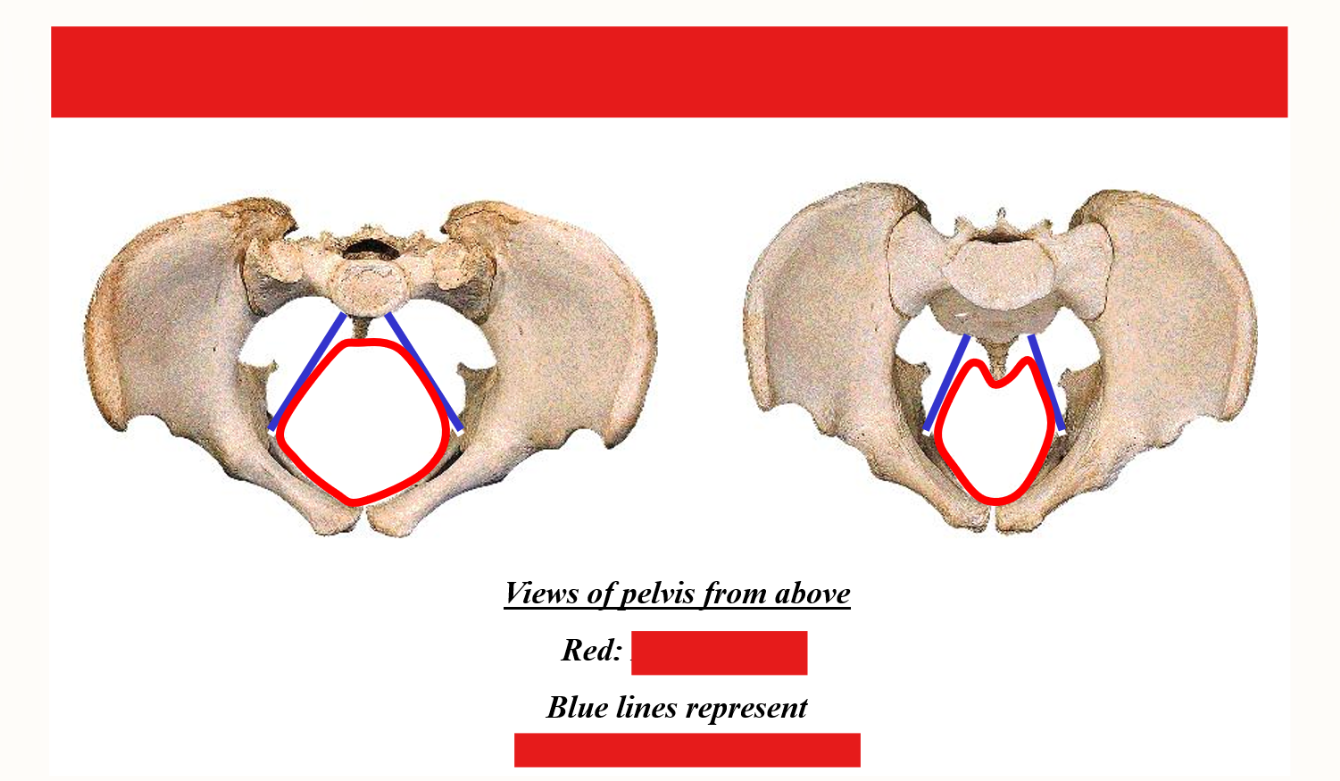
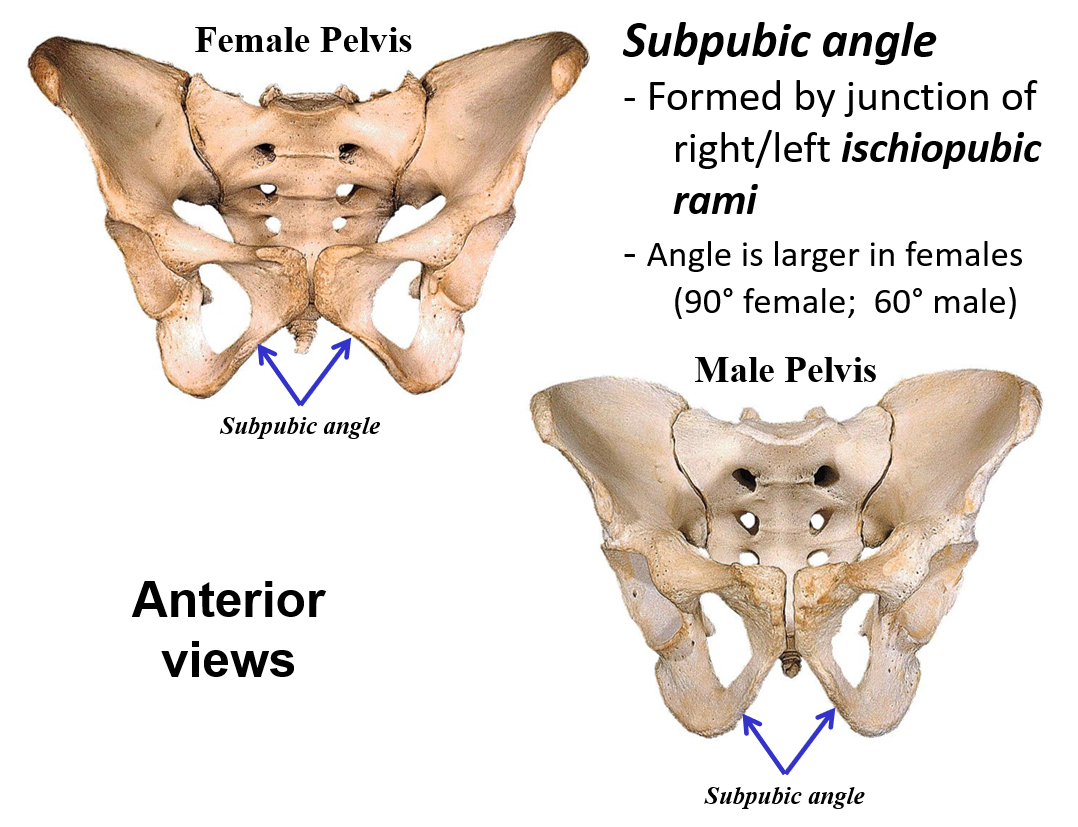
Describe the Subpubic angle
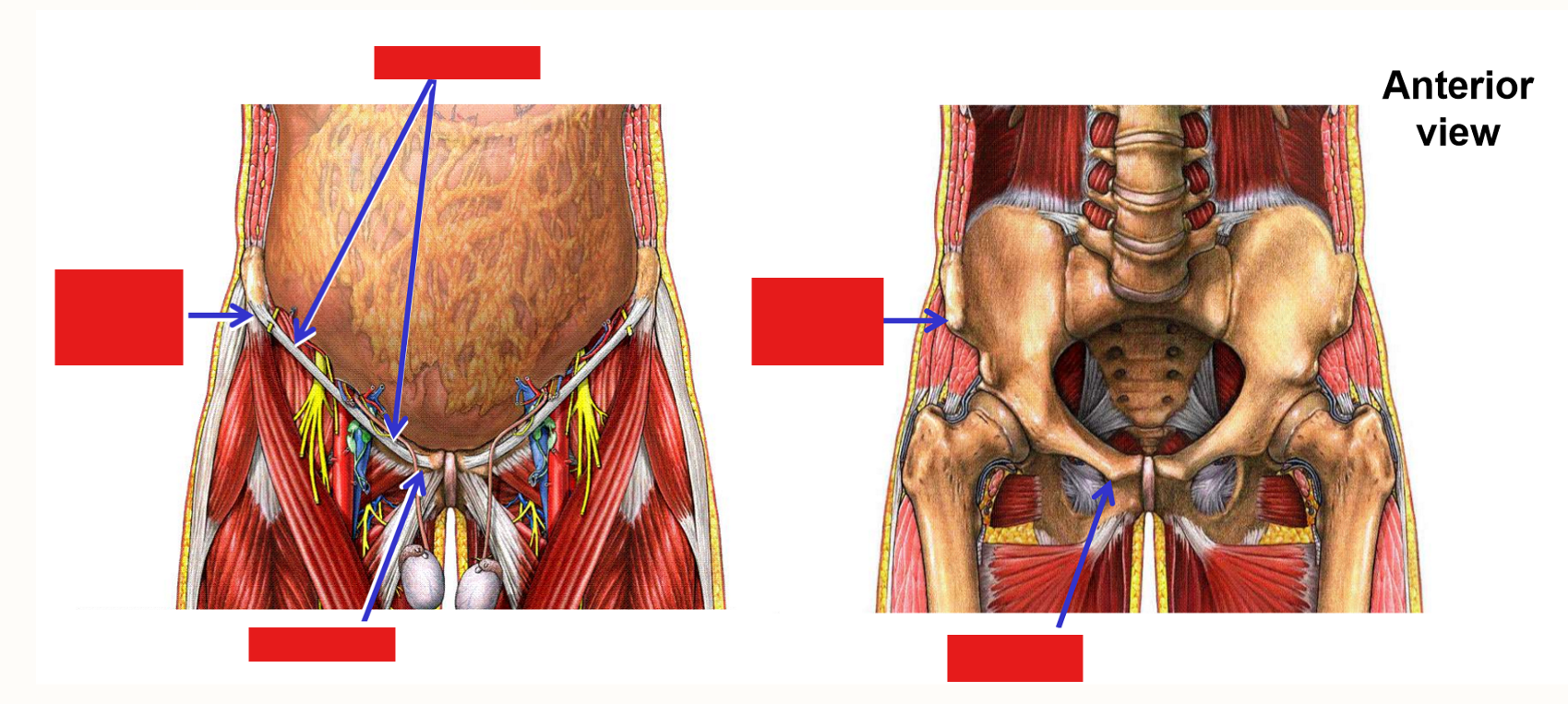
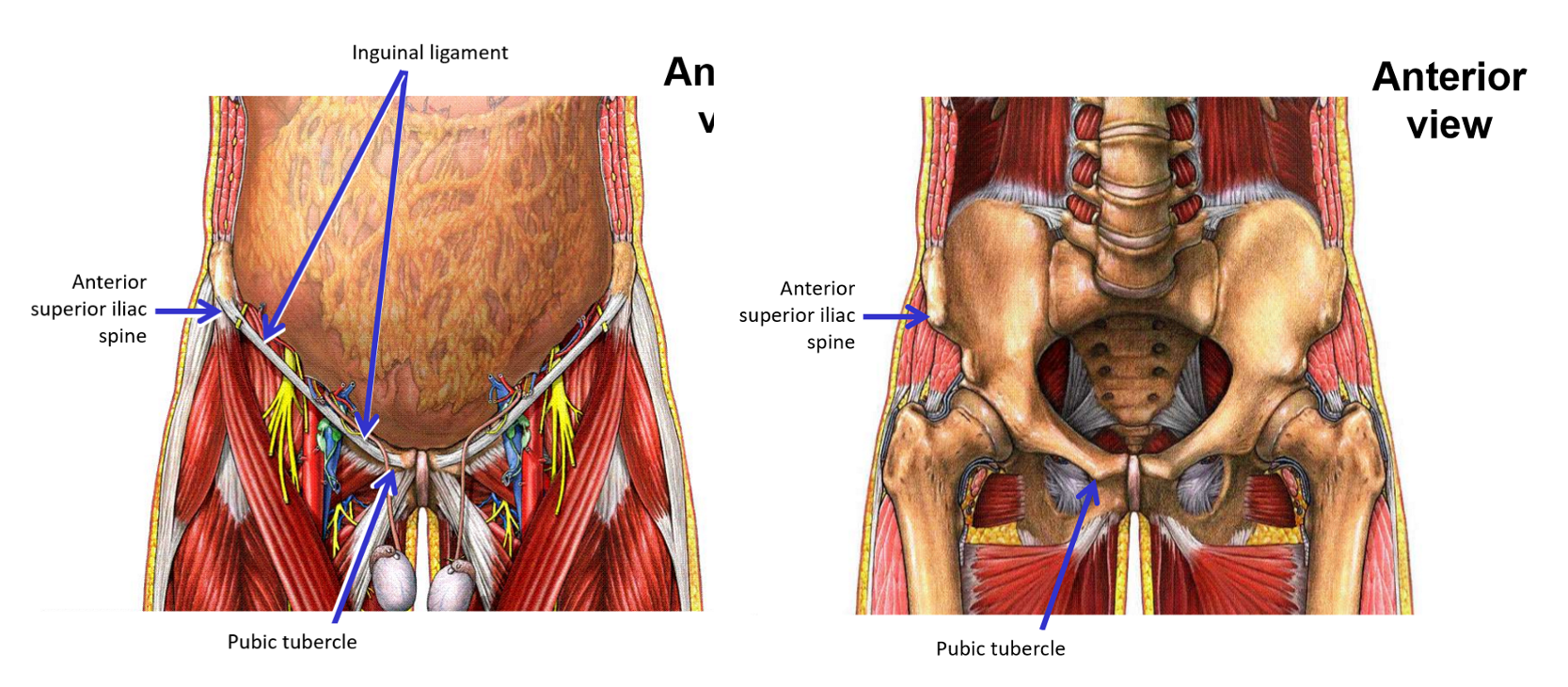
Describe the Inguinal Ligament
Inguinal ligament - dividing line between trunk of body and lower limb
Bony attachments:
Anterior superior iliac spine - lateral attachment
Pubic tubercle - medial attachment
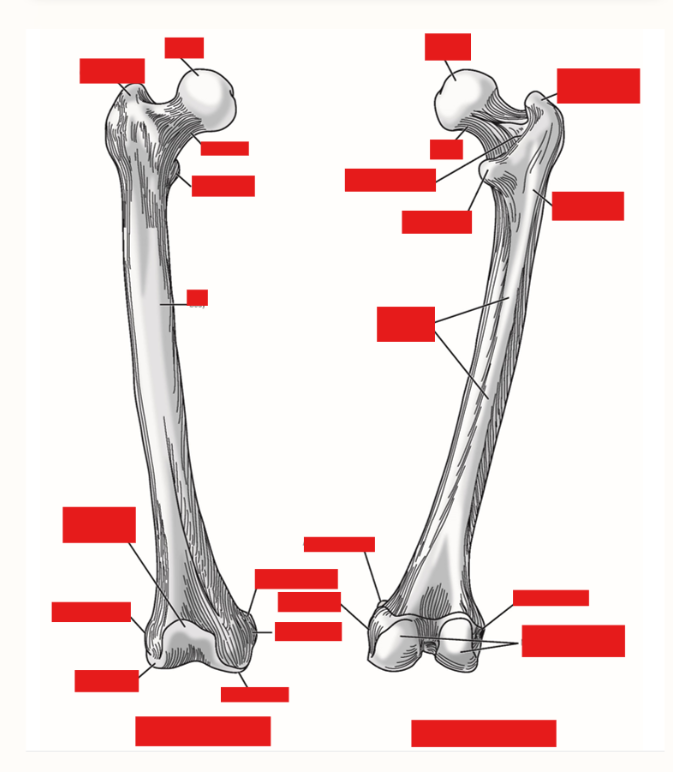
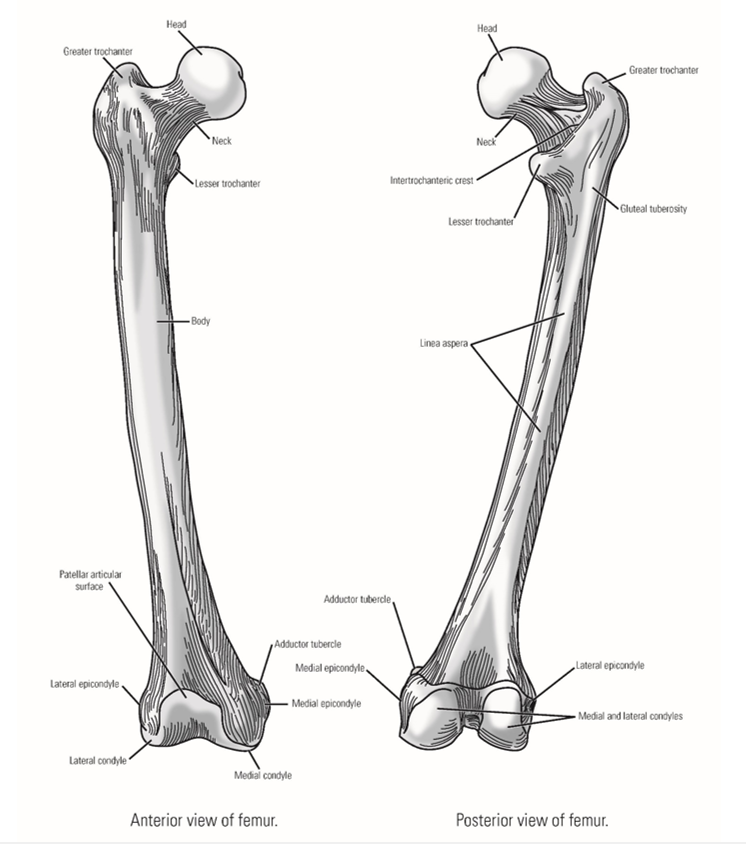
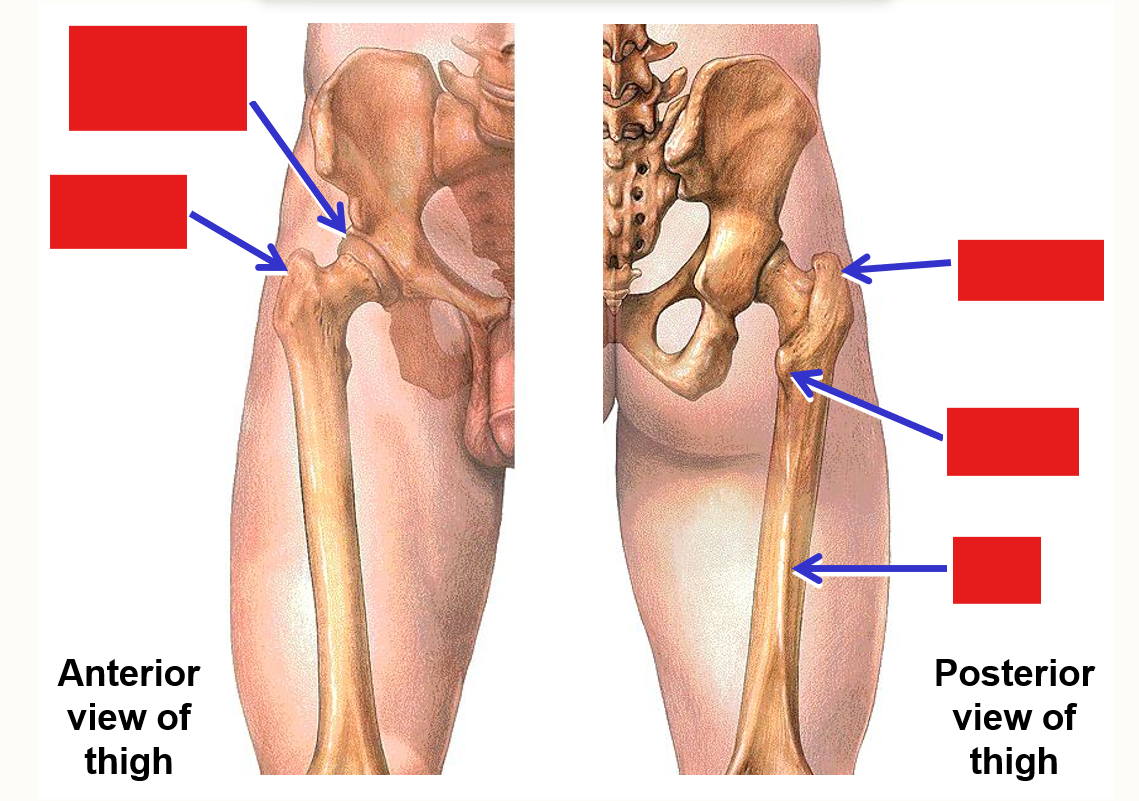
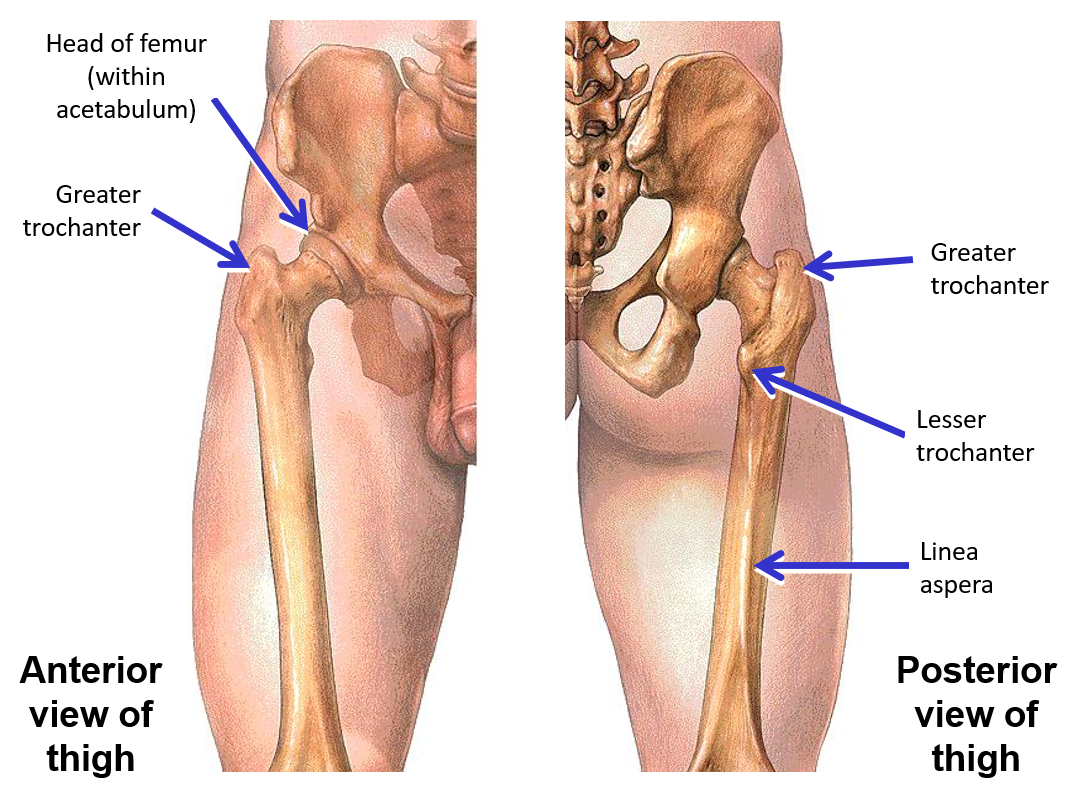
List the Bony Landmarks of Proximal Femur
Head - forms ball portion of ball & socket hip joint
Neck
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Gluteal tuberosity
Shaft
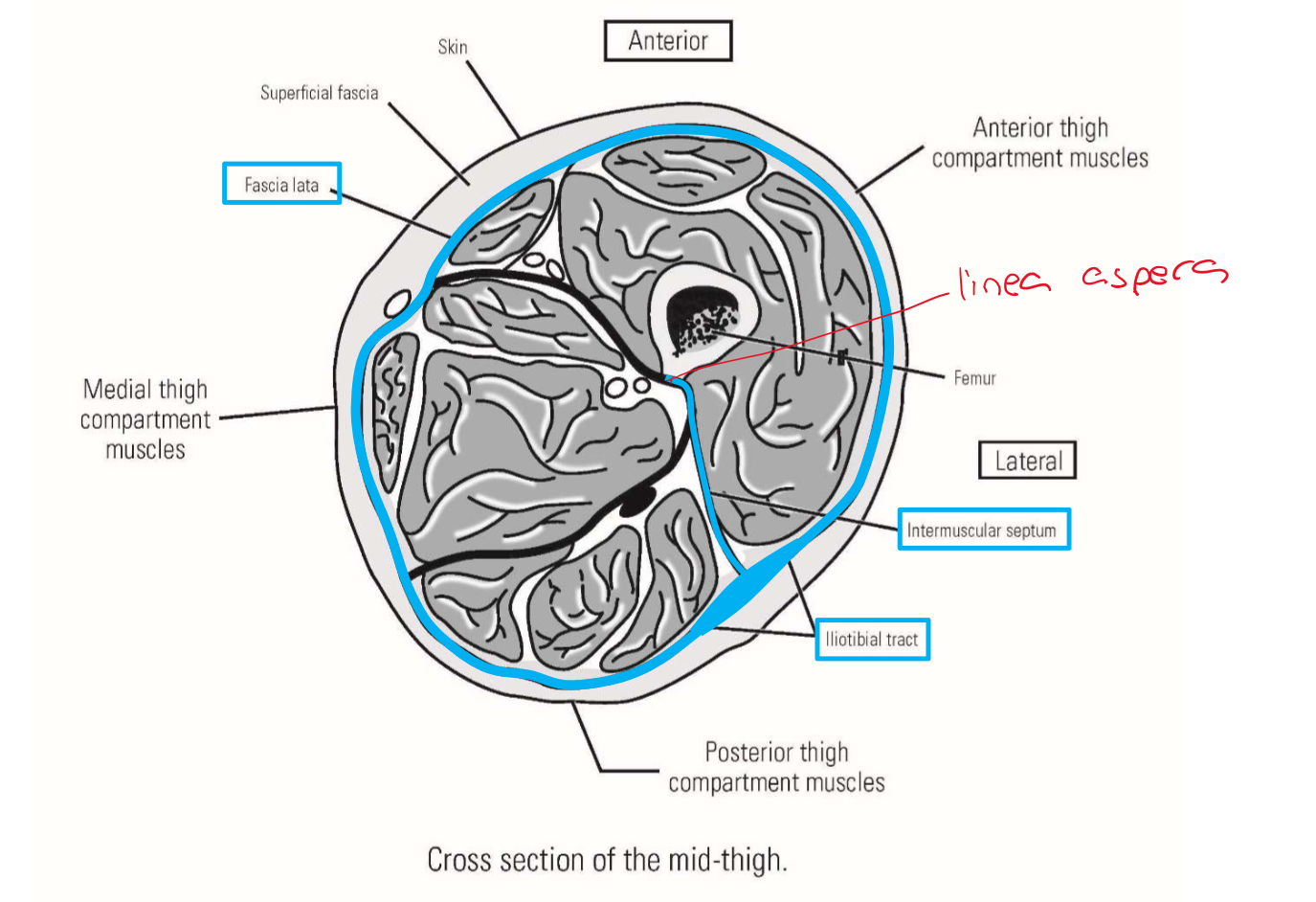
Linea aspera - bony ridge on posterior side of shaft
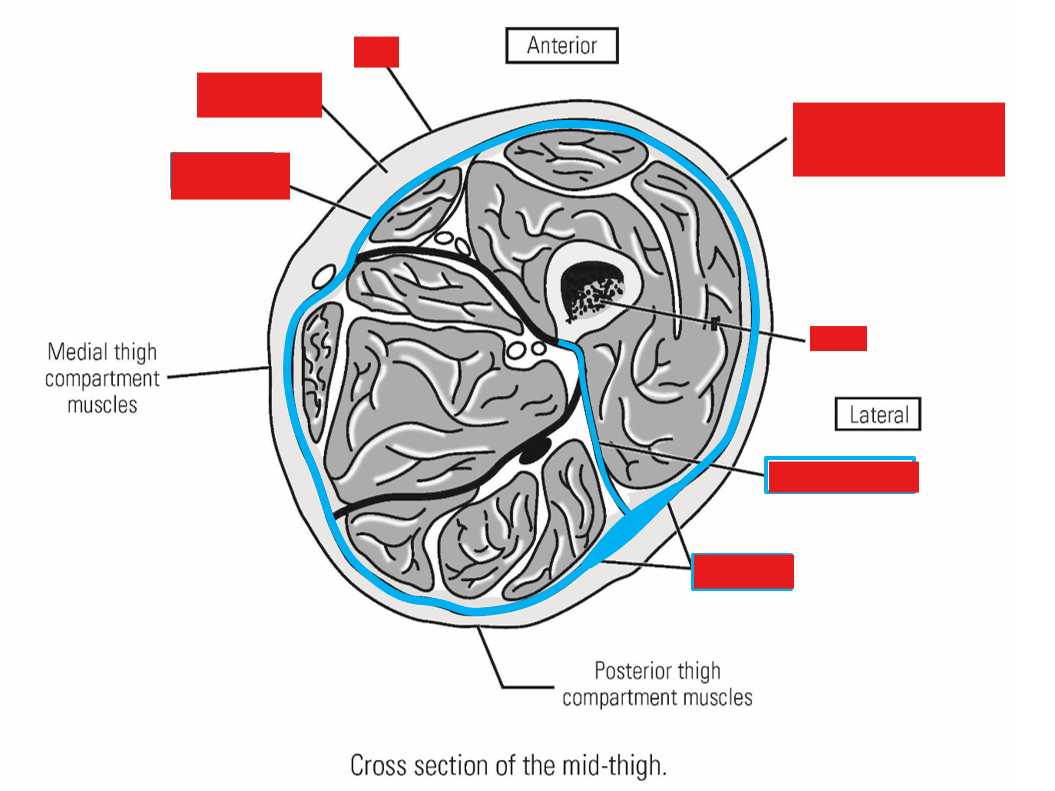
Describe the Deep Investing Fascia of Thigh
Fascia lata
Surrounds entire thigh
Anchored to linea aspera of femur by three intermuscular septa (lateral septum most important)
—» Intermuscular septa divide thigh into 3 compartments
Iliotibial tract - much thicker, lateral portion of fascia lata
Runs down lateral side of thigh - anchored to femur by lateral intermuscular septum
Attached superiorly to iliac crest of pelvis
Attached inferiorly to proximal, lateral tibia