Seawater Properties and Ocean Tectonics: Key Concepts and Evidence
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What are the major properties of water that influence its behavior in the ocean?
High specific heat, high latent heats, incredible solvent properties, high surface tension, high viscosity, and a strange temperature-density relationship.
What is the specific heat of water?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C.
How does water's high specific heat affect climate?
It allows oceans to act as a massive global climate buffer by resisting changes in temperature.
What is the structure of a water molecule?
One oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms, with a bond angle of 104.5°.
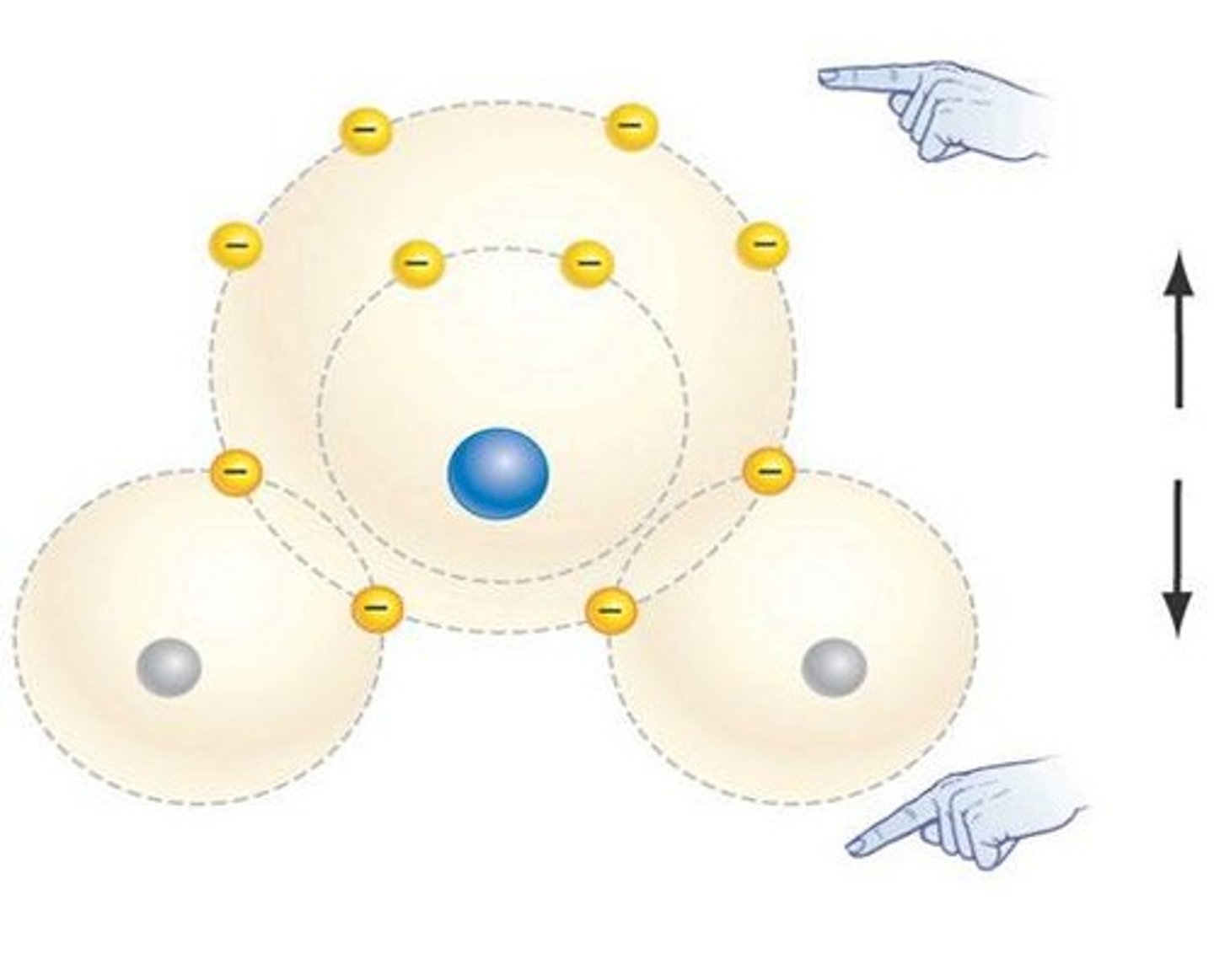
What is the polarity of a water molecule?
Water has a slight negative charge on oxygen (δ−) and slight positive charges on hydrogen (δ+).
What is the consequence of water's strange temperature-density relationship?
It leads to unique behaviors in aquatic environments, such as the stratification of water layers.
What is salinity in seawater?
The total amount of dissolved salts in seawater, typically measured in Practical Salinity Units (PSU).
What is the global average salinity of seawater?
Approximately 35 PSU, with a range of 32-38 PSU in the open ocean.
What factors increase surface salinity in the ocean?
Evaporation and sea ice formation.
What factors decrease surface salinity in the ocean?
Precipitation, river runoff, and ice melt.
What is the Rule of Constant Proportions?
The principle that the relative proportions of major ions in seawater remain virtually constant, despite variations in total salinity.
What is the composition of seawater?
On average, seawater is 96.5% pure water (H₂O) and 3.5% dissolved substances, primarily salts.
What are the consequences of water being a powerful solvent?
It allows oceans to act as receptacles for various substances, including particulate mineral matter, dissolved salts, and organic matter.
What is the significance of vertical differences in salinity and temperature in the ocean?
They can structure the water column and lead to density stratification, affecting marine life and ocean currents.
What happens to water's density as temperature changes?
Water exhibits a strange temperature-density relationship, where its density decreases as it approaches 0°C from below 4°C.
What is the boiling and freezing point of water?
Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
What is the role of hydrogen bonding in water's properties?
Hydrogen bonds contribute to water's high specific heat, surface tension, and solvent capabilities.
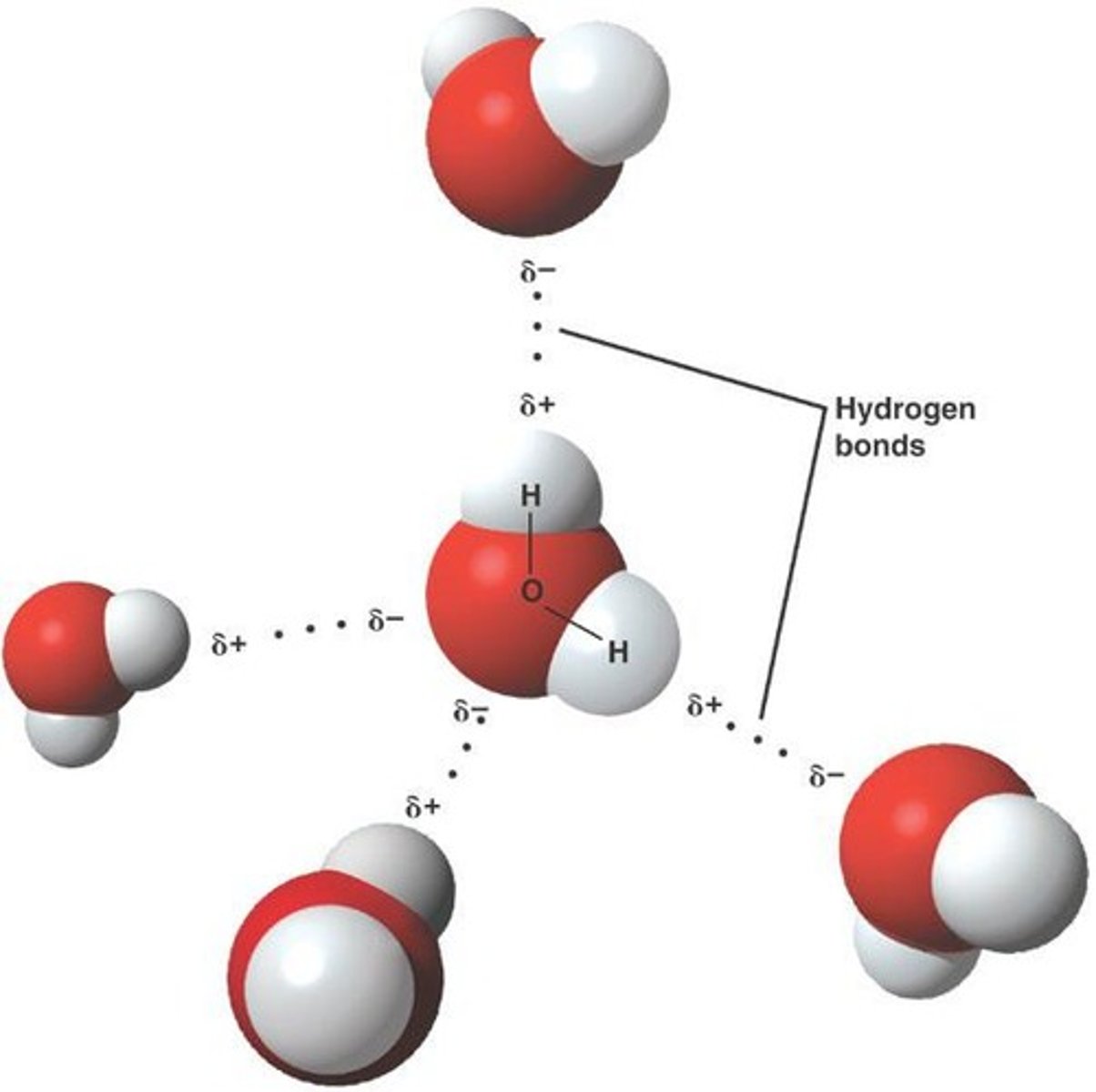
What is the impact of ocean water not being 'pure'?
It means that ocean water contains various dissolved substances and particulate matter, affecting its chemical and physical properties.
How does the temperature of water affect its density?
As water cools, it becomes denser until it reaches 4°C; below this temperature, it becomes less dense, which is unusual for most substances.

What is the residence time of major ions in the ocean compared to the mixing time of the ocean?
The residence times of major ions are much longer than the mixing time of the ocean, which is about 1000 years.
What characterizes the Mediterranean Sea?
It is a semi-enclosed sea with a restricted connection to the Atlantic Ocean at the Strait of Gibraltar and has a hot, dry regional climate.
What is the salinity of Mediterranean water compared to Atlantic water?
Mediterranean water has a salinity of 38.5 PSU, while Atlantic water has a salinity of 36 PSU.
Which gases are biologically important in seawater?
Oxygen (O₂) is essential for respiration, and Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) is essential for photosynthesis.
How does high surface tension affect gas diffusion in seawater?
High surface tension enhances gas diffusion as bubbles can form in agitated waters and persist, increasing oxygen uptake.
What factors cause dissolved gas concentration to vary with depth in the ocean?
Dissolved gas concentration varies with depth due to diffusion, photosynthesis, and pressure.
What is the significance of the Southern Ocean regarding CO₂?
The Southern Ocean is a major sink for atmospheric CO₂, absorbing approximately 40% of the annual global ocean uptake of anthropogenic CO₂.
What is ocean acidification and its impact on marine organisms?
Ocean acidification occurs when pH drops due to increased CO₂, reducing carbonate ion availability, which affects organisms that build shells from calcium carbonate.
What are pteropods and why are they vulnerable to ocean acidification?
Pteropods, or 'sea butterflies,' are tiny swimming snails whose shells dissolve in more acidic conditions, impacting their survival and the food web.
What is the relationship between temperature, salinity, and density in seawater?
Density increases as temperature decreases, salinity increases, and pressure increases; cold, salty water is denser.
What are the three distinct layers of the ocean based on density?
The three layers are the Surface Mixed Layer, the Pycnocline, and Deep Water.
What is the thermocline?
The thermocline is a zone of rapid temperature change in the ocean.
How does salinity vary in the ocean?
Salinity varies with excess evaporation over precipitation in mid-latitudes and excess precipitation over evaporation at the equator.
What are some important properties of water?
Water has a strange temperature-density relationship, high specific heat, high latent heats, is an incredible solvent, has high surface tension, and high viscosity.
What is the Gibraltar Exchange?
The Gibraltar Exchange refers to the flow of water between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean at the Strait of Gibraltar, influenced by salinity differences.
What is bathymetry?
The study of underwater depth of ocean floors.
What is the principle of isostasy?
The equilibrium between Earth's crust and the denser mantle beneath it.
What are the three major types of plate boundaries?
Divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries.
What technology was used for early seafloor mapping?
Lead lines, which provided a single depth point at one location.
How does single-beam sonar work?
A ship transmits a sound ping, measuring the time for the echo to return to calculate depth.
Who created the first comprehensive map of the ocean floor?
Marie Tharp and Bruce Heezen in the 1950s-70s.
What is multibeam sonar?
A technology that sends out a wide swath of sound beams to create high-resolution maps of the seafloor.

What is satellite altimetry?
A method using satellites to measure the height of the sea surface to map large-scale seafloor topography.
What are AUVs?
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles that create ultra-high-resolution maps of the seafloor.
What are ROVs?
Remotely Operated Vehicles that are tethered to a ship for real-time piloting and inspection.
What is the average depth of the oceans?
Approximately 3,600 meters, with 84% deeper than 2000 meters.
What is the greatest depth recorded in the oceans?
About 11,000 meters in the Mariana Trench.
What are the two ways to define Earth's layers?
By composition (chemical) and by physical properties.
What is the lithosphere?
The rigid outer layer of the Earth, including the crust and uppermost mantle.
What is the asthenosphere?
A hot, weak layer of the mantle that flows slowly beneath the lithosphere.
What is the difference between continental and oceanic crust?
Continental crust is thicker and less dense, while oceanic crust is thinner and more dense.
What is the theory of plate tectonics?
The theory that Earth's lithosphere is fractured into tectonic plates that move slowly.
What evidence supports the theory of continental drift?
Fit of continents, fossil distribution, rock correlation, and glacial evidence.
What is paleomagnetism?
The study of the magnetic properties of rocks to understand historical plate movements.
What is a divergent boundary?
A plate boundary where tectonic plates move apart, leading to seafloor spreading.
What occurs at convergent boundaries?
Plates collide, leading to the destruction of old oceanic crust.
What is a transform boundary?
A plate boundary where plates slide horizontally past one another.
What are the three types of plate boundaries based on the crust involved?
Oceanic-Continental, Oceanic-Oceanic, and Continental-Continental.
What geological process occurs when a dense oceanic plate collides with a continental plate?
Subduction, where the oceanic plate sinks into the mantle.
What forms at the site of subduction?
A deep ocean trench and volcanic mountains.
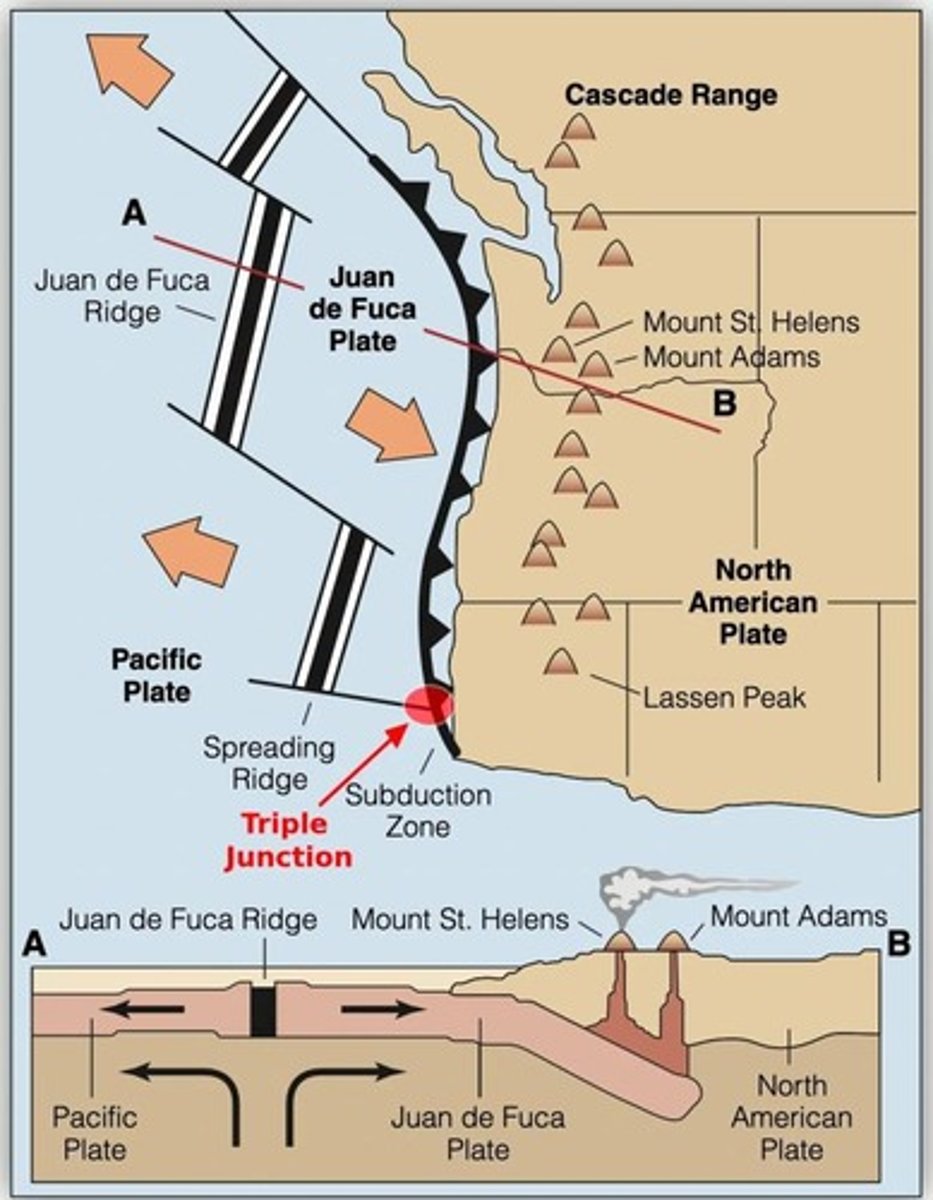
What is the Cascadia Subduction Zone?
A boundary where the Juan de Fuca Plate subducts beneath the North American Plate, creating the Cascade Range of volcanoes.
What is the potential consequence of the Cascadia Subduction Zone rupturing?
It could cause a magnitude 9+ megathrust earthquake.
What is the average depth of ocean trenches?
6-11 km deep, with an average of 3.5 - 5 km.
What characterizes Oceanic-Oceanic convergence?
It involves the subduction of one oceanic plate beneath another.
What is a transform fault?
A boundary where plates slide past each other in opposite directions.
What is the Blanco Fracture Zone?
A major transform fault system separating the Juan de Fuca Ridge from the Gorda Ridge.
What are the three main parts of the Continental Margin?
Continental Shelf, Continental Slope, and Continental Rise.
What is the typical slope of the Continental Shelf?
0.1°.
What distinguishes an Active Margin from a Passive Margin?
Active Margins are tectonically active with narrow shelves, while Passive Margins are tectonically quiet with wide shelves.
What are Submarine Canyons?
Deep, V-shaped valleys incised into the continental slope and shelf, formed by turbidity currents.
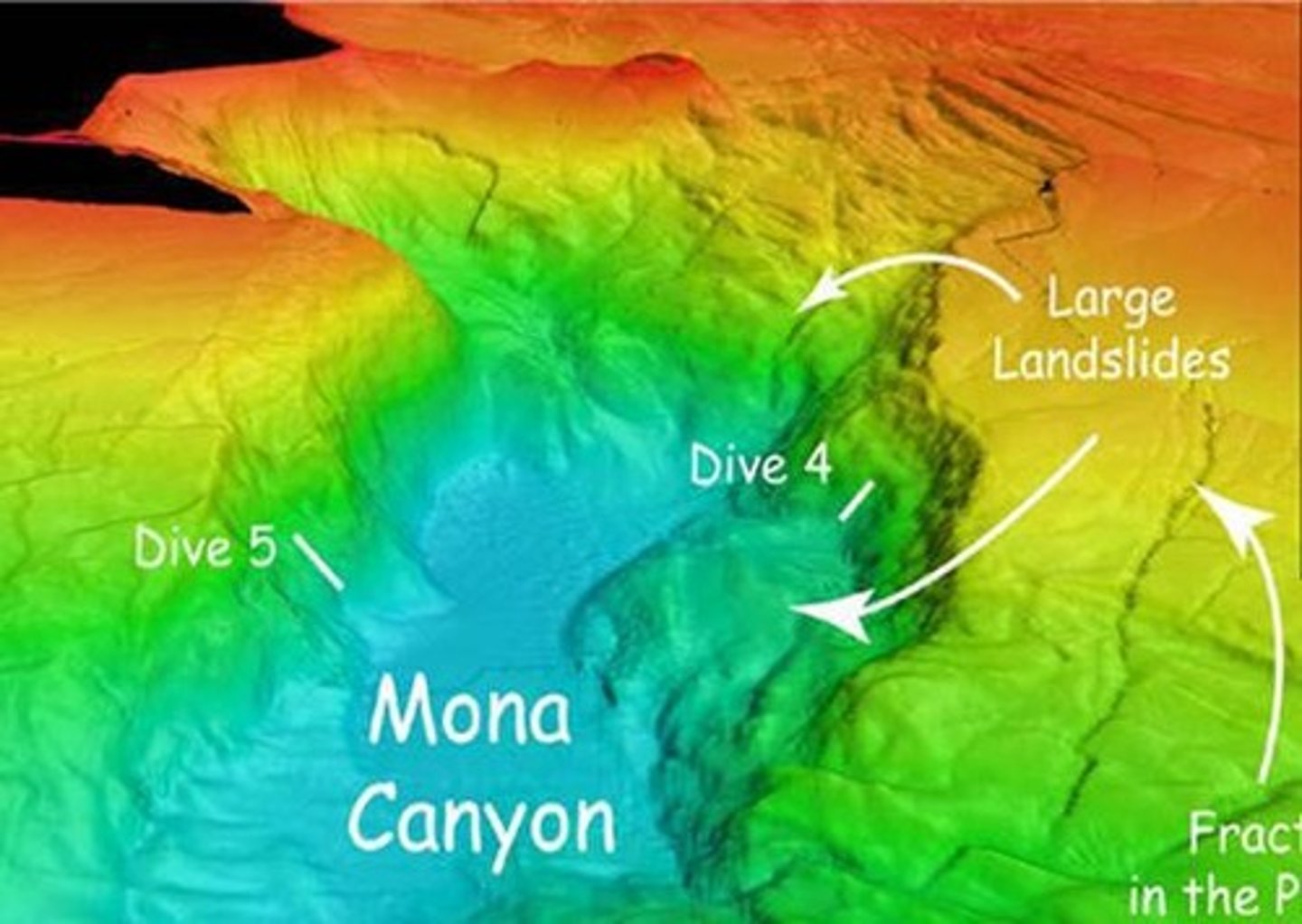
What is Monterey Canyon known for?
It is one of the deepest and largest submarine canyons, funneling sediment and organic matter into the deep sea.
What are Abyssal Plains?
Vast, flat, and deep areas of the ocean floor, typically between 3,000 and 6,000 m deep.
Why are abyssal plains more developed in the Atlantic Ocean than in the Pacific Ocean?
The Atlantic is bordered by passive margins, while the Pacific is lined with trenches that trap sediment.
What is the average width of a Continental Slope?
Around 20 km.
What geological features are formed by divergent boundaries?
Seamounts and Guyots.
What is the significance of hot spots in geology?
They reveal plate movement.
What is the average slope of the Continental Rise?
1°.
What happens to the sediment in the Cascadia Trench?
It is largely filled in by sediment eroding from the North American continent.
What is the average slope of the Continental Slope?
4° to 25°.
What is the role of turbidity currents in submarine canyons?
They carve the canyons, not rivers.
What is the average width of the Coastal Shelf?
Approximately 70 km, but can be wider in some areas.
What is the primary characteristic of a Passive Margin?
It is located far from a plate boundary and is tectonically quiet.
What geological feature is formed by the collision of two continental plates?
Mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas.