HEARING AND BALANCE
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what structures make up the outer ear
auricle/lobule
external acoustic meatus
tympanic membrane
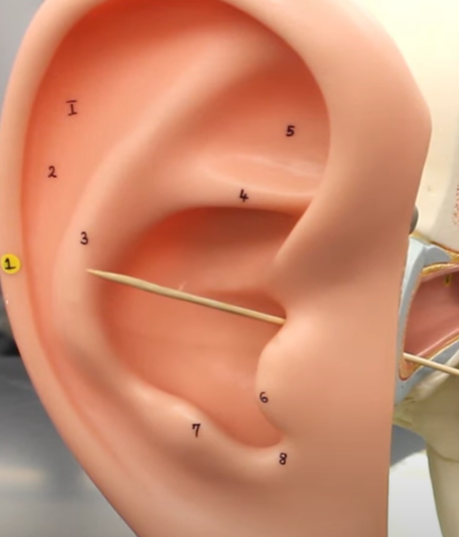
what is this region
auricle
what does the auricle
collects and directs soundwaves into the external acoustic meatus
what completes the formation of the auricle
lobule
what does this do
transmit soundwaves to the eardrum
what is this
tympanic membrane
what does the tympanic separate
outer and inner ear
what does the tympanic membrane do
what structure equalizes pressure in order for the tympanic membrane to vibrate properly
pharyngotympanic tube
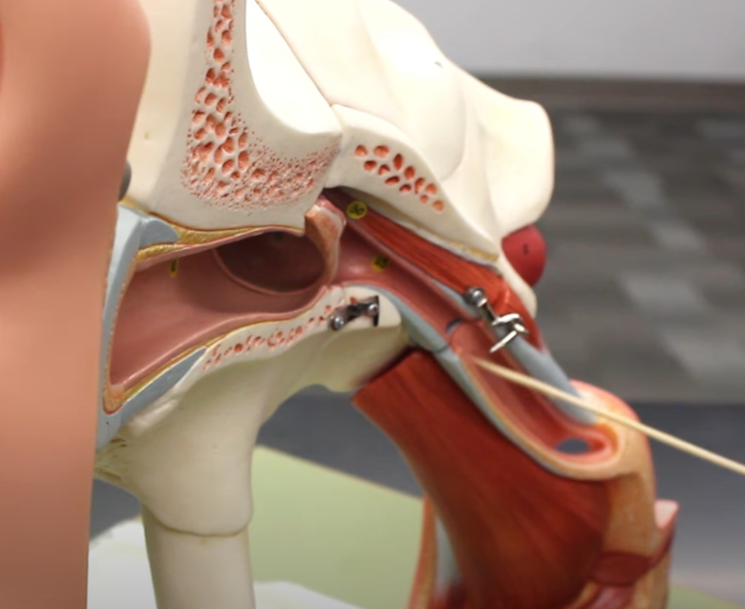
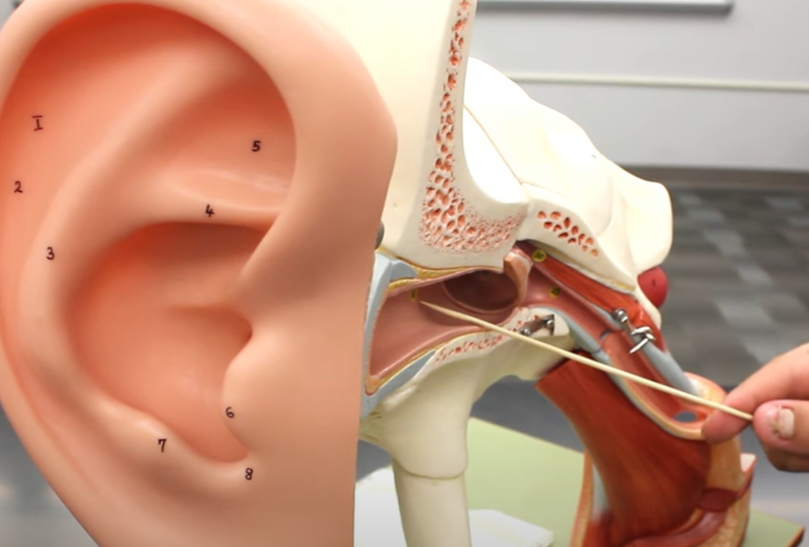
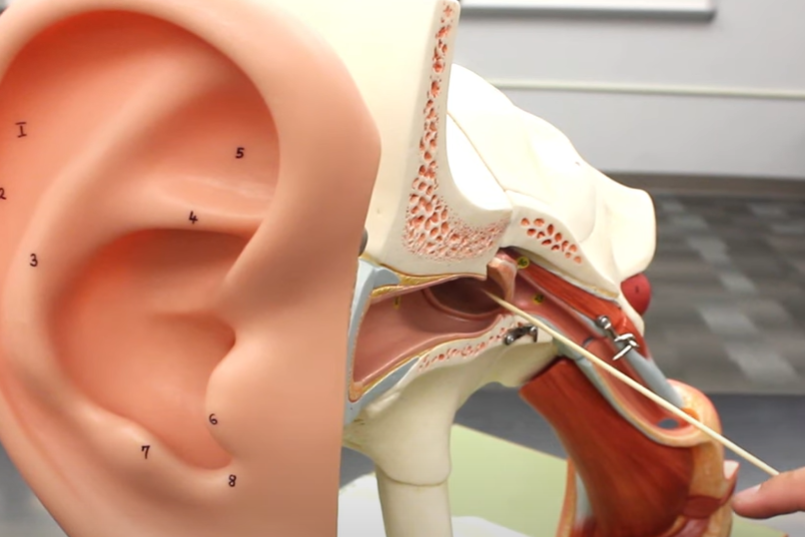
true or false: this is the pharyngotympanic tube
true
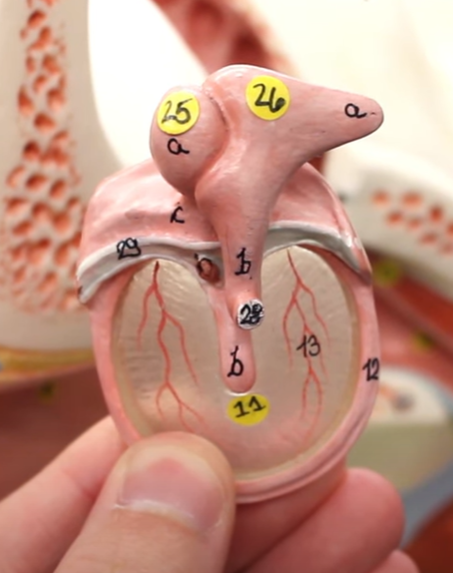
25=
malleus
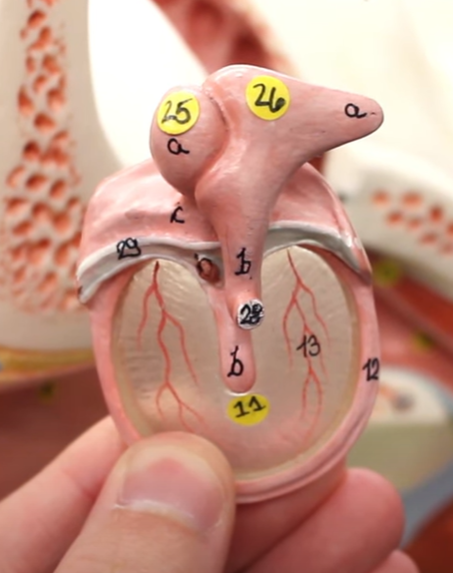
26=
incus
which ossicle connects to the oval window
stapes
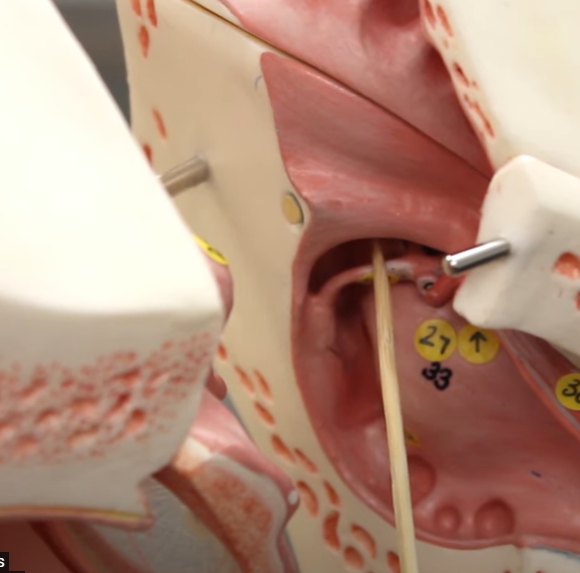
what is this
stapedius muscle
what do the semicircular canals do
rotate during dynamic activity
when a ballerina spins in place, what semicircular canal activates
posterior
when a child does a summersault in gymnastics, what semicircular canal activates
anterior
when a child does a cartwheel, what semicircular canal is activated
lateral
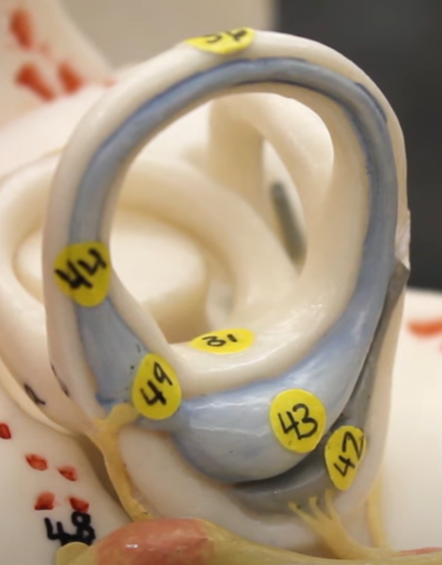
#31
vestibule
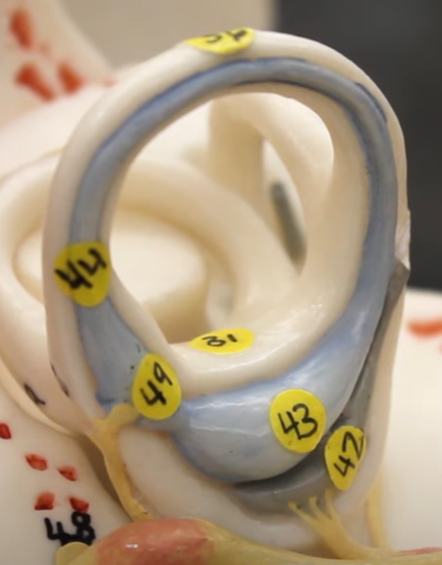
#43
utricle
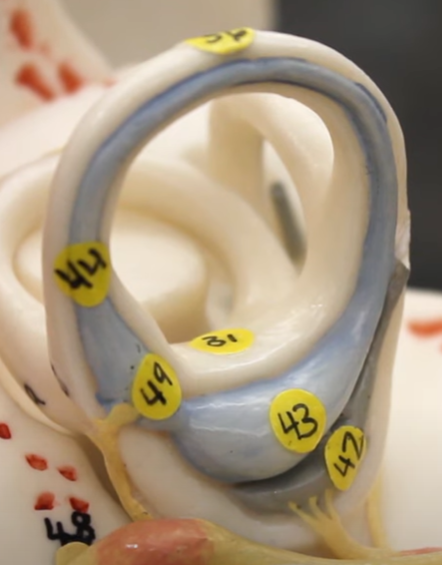
#42
saccule
balance nerves fuse with cochlear nerve that form
CN VIII
larger hair structure=
kinocilia
smaller hair structure=
stereocilia
kinocilia moving towards stereocilia causes
hyperpolarization
when stereocilia goes towards kino cilia, what happens
hair cells depolarize and send signals to brain
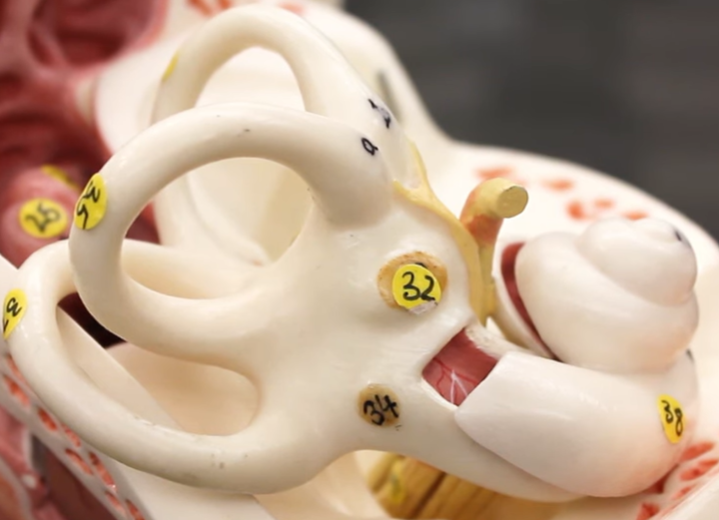
32
oval window
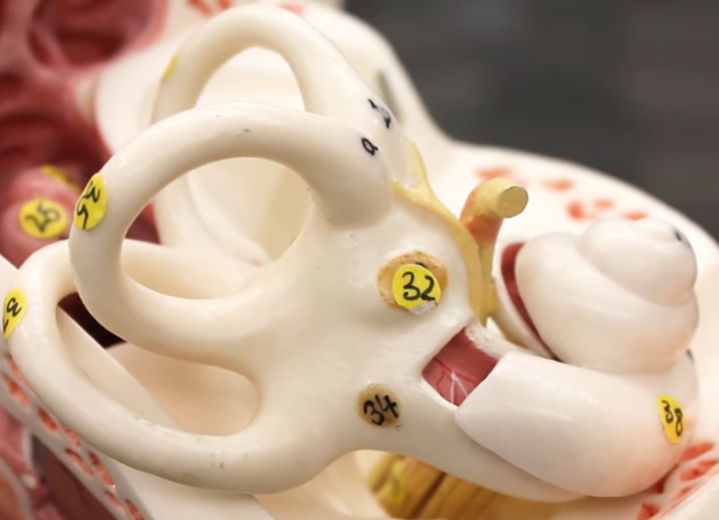
34
round window
what does the round window do
prevent the scattering of vibrational impulses
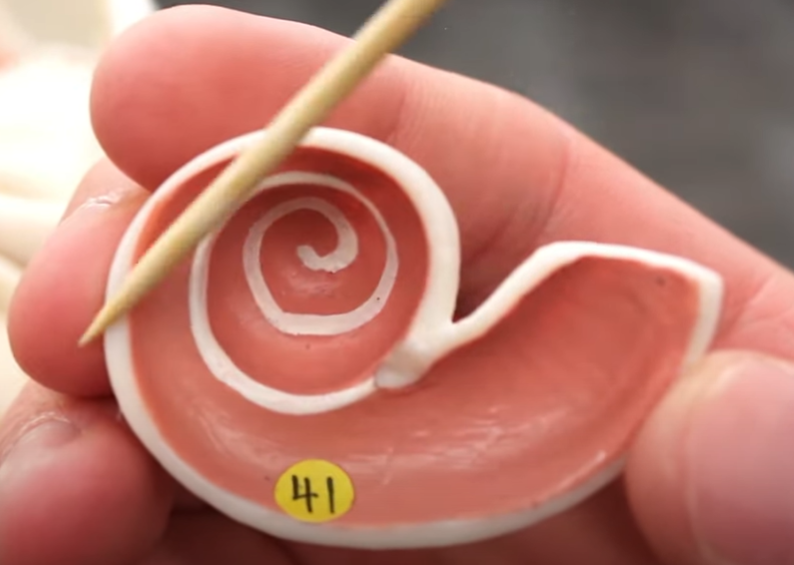
41
scala vestibule
what does the spiral organ of corti do
pick up soundwaves
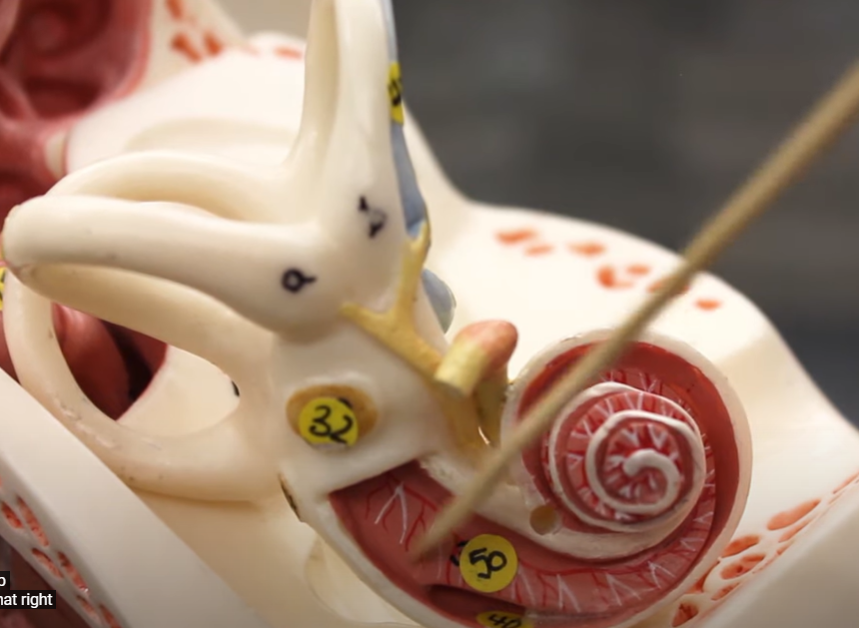
what is 40
scala tympani
what does a pressure difference in the cochlea do
cause the basilar membrane to vibrate
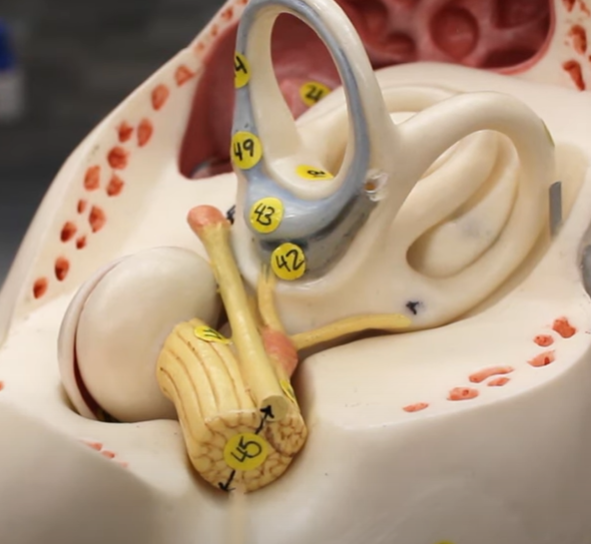
45
vestibular nerve
what is the cochlea associated with
soundwaves
what is the stapes’ relationships with the oval window
after receiving vibrations from the malleus and incus, the stapes and oval window convert the mechanical vibration into fluid-filled vibrations
what membrane separates the scala vestibule from the scala media
vestibular membrane
what membrane separates the scala media from the scala tympani
basilar membrane
what does the basilar membrane detect
different sound frequencies/pitches
true or false: low frequencies do not sitmulate the basal layer
true
what frequency stimulates the basilar membrane, which causes the cilia to move
high
what structure modulates sounds
inner hairs
what is the cochlear duct called
scala media
what causes the hair cells to move
endolymph rushing in-between the hair cells and techorial membrane when the basilar membrane is vibrating
what is the large stereocilium called
kinocilium
what does the organ of corti consist of
techorial membran and hair cilia
what does the organ of corti do
transform vibrational waves into electrical sound waves for the primary auditory cortex to interpret
what structure transfers information from the organ of corti to the primary auditory cortex
cochlear branch of CN VIII
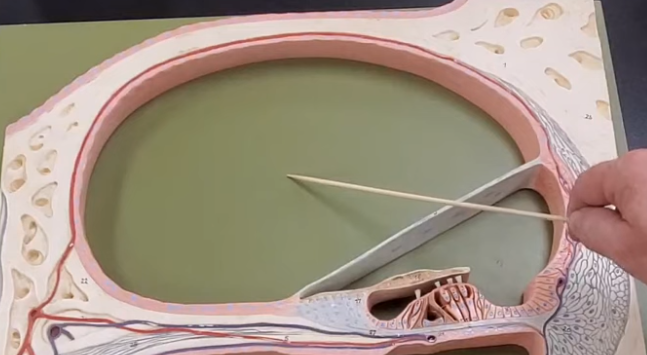
what is this
scala vestibuli
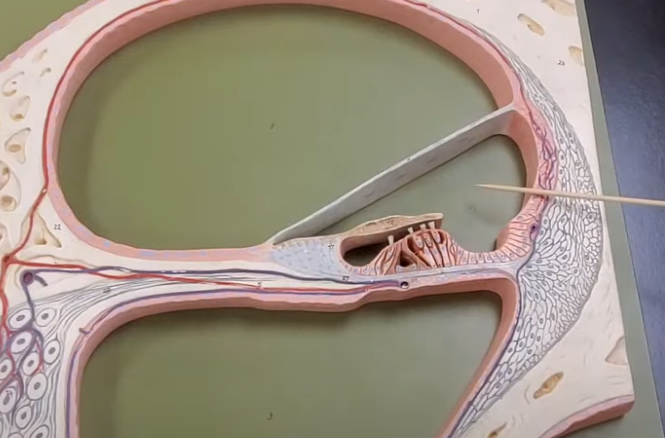
what is this
scala media
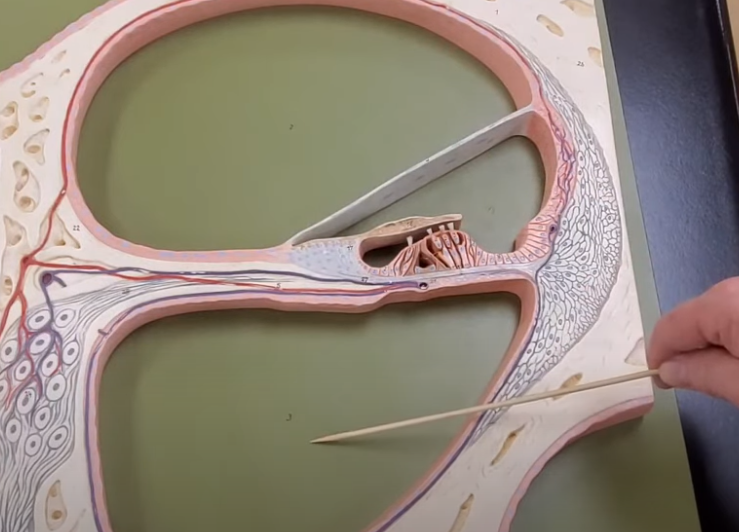
what is this
scala tympani
what separates the vestibular and cochlear ducts
vestibular membrane
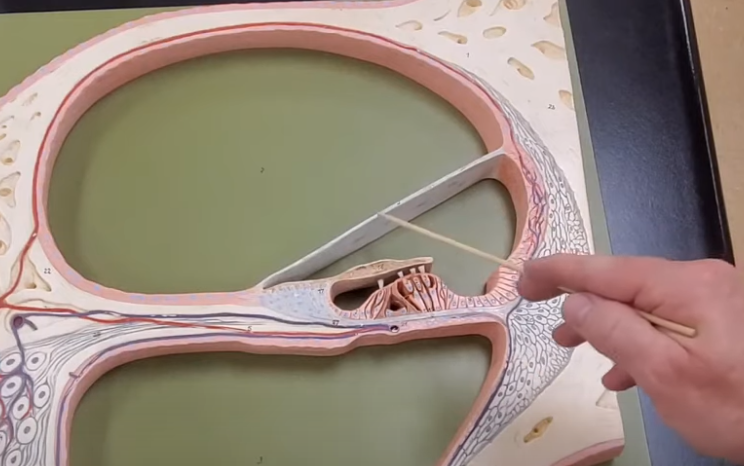
what are the vestibules responsible for
static movement