Comprehensive Overview of Nutrition and Health
1/502
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
503 Terms
Macronutrients
Nutrients providing energy: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids.

Carbohydrates
Organic macronutrient; 4 calories per gram.
Water
Inorganic nutrient; essential for biochemical processes.
Minerals
Micronutrients; major and trace elements essential for health.
Proteins
Organic macronutrient; contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen.
Vitamins
Micronutrients; organic compounds vital for body functions.
Lipids
Organic macronutrients; 9 calories per gram.
Alcohol
Non-nutrient; provides 7 calories per gram.
Nutrient Dense Foods
Foods high in nutrients relative to calories.
Calorie Dense Foods
Foods high in calories relative to nutrients.
Hunger
Physiological need for food intake.
Appetite
Psychological desire to eat, not always linked to hunger.
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI)
Nutrient recommendations for healthy individuals.
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
Daily nutrient intake level sufficient for most.
Adequate Intake (AI)
Estimated nutrient intake level based on observed data.
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
Maximum daily intake unlikely to cause adverse effects.
USDA Dietary Guidelines
Guidelines published every 5 years for healthy eating.
USDA MyPlate
Visual guide for balanced eating and portion control.
Malnutrition
Imbalance of nutrients; includes undernutrition and overnutrition.
Chronic Diseases
Long-lasting health conditions often linked to diet.
Heart Disease
Leading cause of death; diet plays a significant role.
Cancer
Second leading cause of death; dietary factors involved.
Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Evidence-based recommendations for healthy eating.
Sustainability
Consideration of environmental impact in food choices.
Food Insecurity
Limited access to sufficient, safe, nutritious food.
Empty Calories
Calories from foods with little nutritional value.
USDA Food Patterns
Guidelines for daily food intake amounts.
Recommended Daily Amounts
Caloric intake recommendations for various diets.
Fruits Serving Size
1½ to 2½ cups based on caloric intake.
Vegetables Serving Size
2 to 4 cups based on caloric intake.
Grains Serving Size
5 to 10 ounces based on caloric intake.
Protein Foods Serving Size
5 to 7 ounces based on caloric intake.
Milk Products Serving Size
3 cups consistently across all caloric intakes.
Oils Serving Size
5 to 10 teaspoons based on caloric intake.
MyPlate
An educational tool for healthy eating guidance.

MyPlate Shortcomings
Lacks detail on healthier food choices.
Ingredient Statements
List of food components by weight order.
Nutrition Facts Box
Label detailing nutrient content of food.
Daily Values
Nutrient intake recommendations based on 2000 calorie diet.
Fat Daily Value
Original: 65g, Updated: 78g.
Sodium Daily Value
Original: 2400mg, Updated: 2300mg.
Carbohydrate Daily Value
Original: 300g, Updated: 275g.
Fiber Daily Value
Original: 25g, Updated: 28g.
Vitamin D Daily Value
Original: 10μg, Updated: 20μg.
Calcium Daily Value
Original: 1000mg, Updated: 1300mg.
Potassium Daily Value
Original: 3500mg, Updated: 4700mg.
Chyme
Semiliquid mass formed in the stomach.
Peristalsis
Muscle contractions pushing chyme through intestines.
Segmentation
Muscle contractions mixing chyme with digestive juices.
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva to aid in digestion.
Gastric Juice
Mixes with food to aid protein breakdown.
Pancreatic Juice
Neutralizes gastric acid and digests macronutrients.
Bile
Emulsifies fats for enzymatic breakdown.
Intestinal Juice
Contains enzymes for final nutrient digestion.
Absorption
Process of nutrient uptake in the body.
Small intestine
Primary site for nutrient absorption, 20 feet long.
Villi
Finger-like projections that enhance nutrient absorption.
Microvilli
Tiny projections with enzymes for nutrient processing.
Crypts
Tubular glands secreting intestinal juices.
Goblet cells
Cells that secrete mucus in the intestine.
Tight junctions
Structures that prevent leakage between intestinal cells.
Enterocyte
Absorptive cell in the intestinal lining.
Leptin
Hormone that decreases hunger, produced by fat cells.
Ghrelin
Hormone that increases hunger, affects body weight.
Gastrin
Hormone that stimulates gastric acid release.
Secretin
Hormone that prompts bicarbonate release from pancreas.
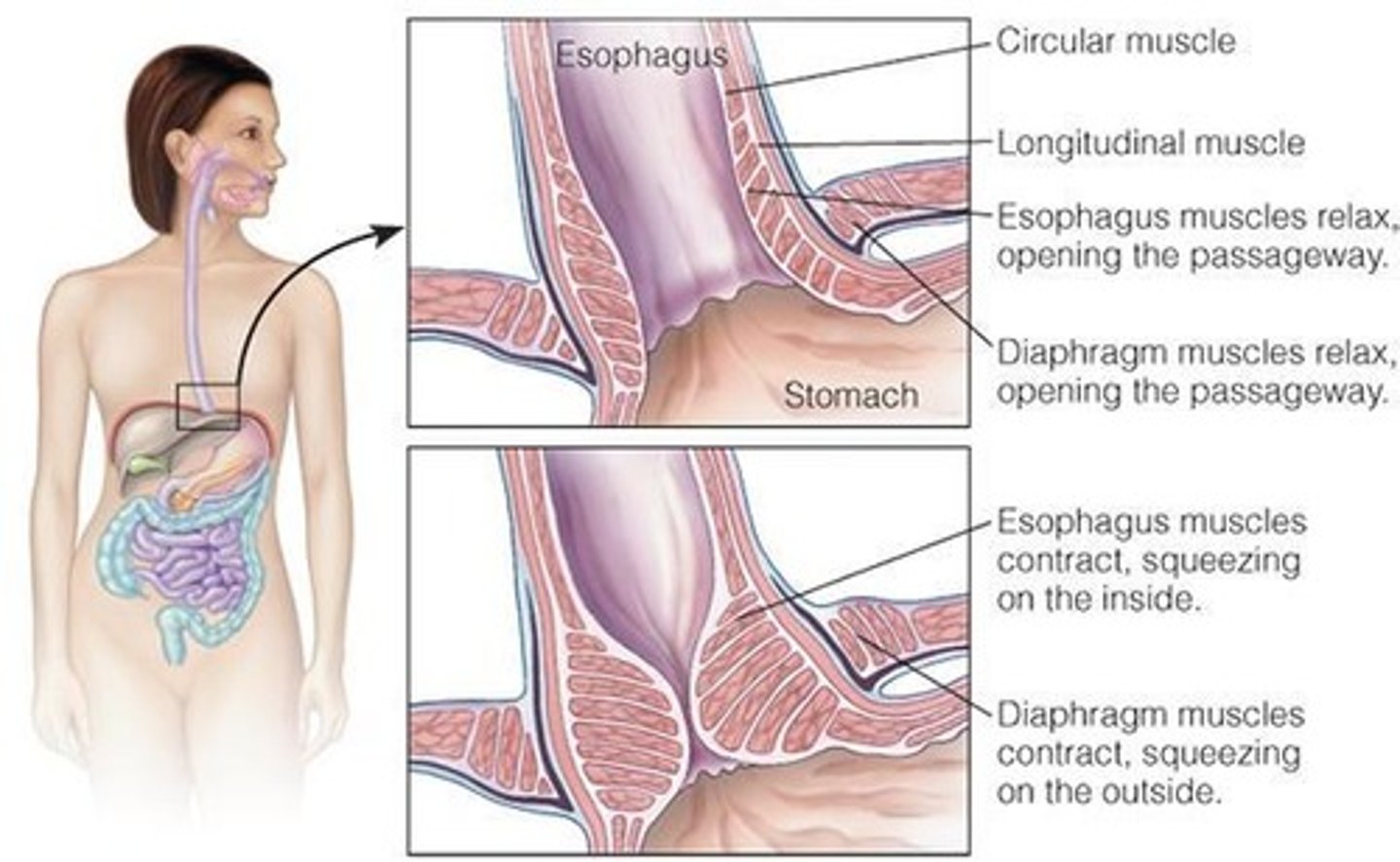
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Hormone that triggers bile release from gallbladder.
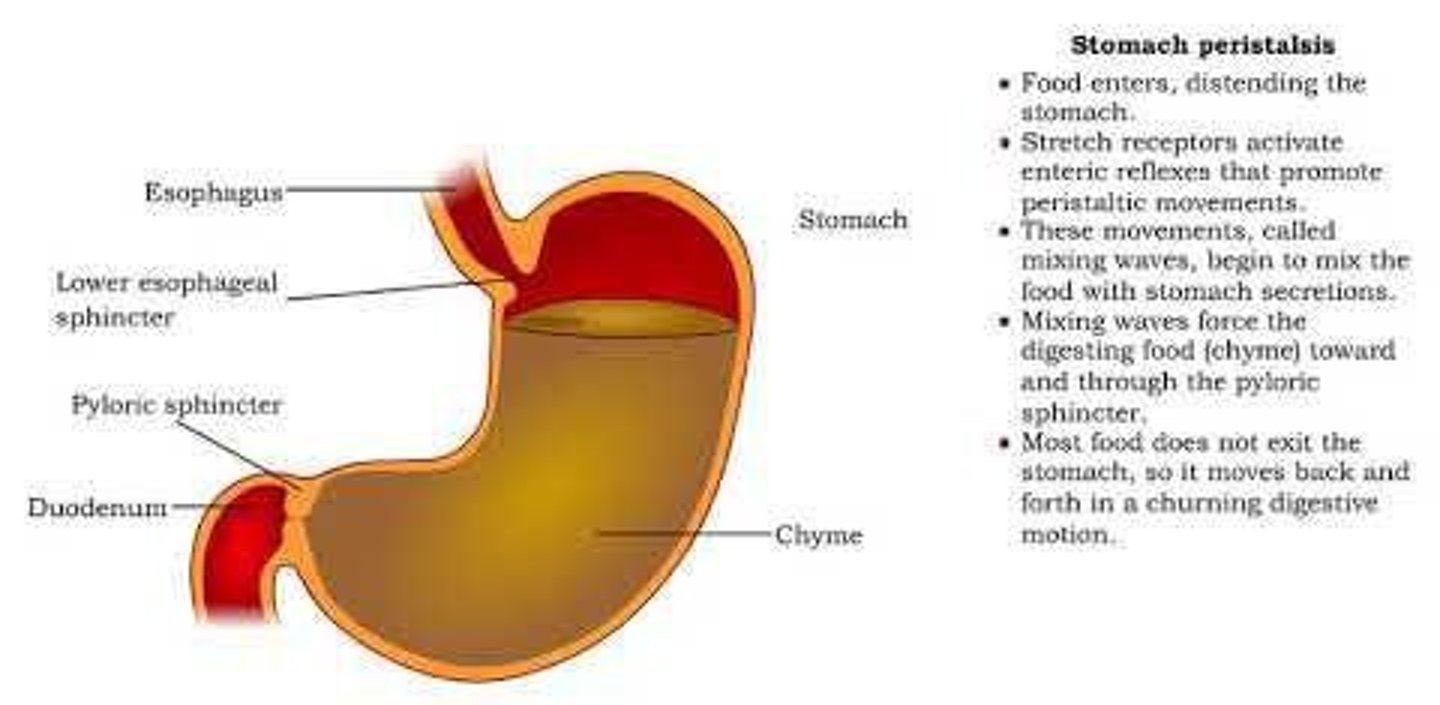
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, basic units of carbohydrates.
Glucose
Primary energy source, blood sugar.
Fructose
Sweetest sugar, found in fruits.
Galactose
Sugar present in dairy products.
Disaccharides
Sugars formed from two monosaccharides.
Maltose
Disaccharide made of two glucose units.
Sucrose
Table sugar, glucose and fructose combination.
Lactose
Milk sugar, composed of galactose and glucose.
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides, like starch.
Glycogen
Energy storage form of glucose in animals.
Starch
Energy storage form of glucose in plants.
Fiber
Indigestible part of plants, recommended 28 g/day.
Soluble fiber
Dissolves in water, aids cholesterol reduction.
Insoluble fiber
Does not dissolve in water, promotes bowel movement.
Dietary fiber sources
Includes fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes.
Fiber health benefits
May lower risks of heart disease and diabetes.
Bile
Substance that helps lower blood cholesterol.
Pectins
Soluble fiber that lowers cholesterol levels.
Psyllium
Soluble fiber that aids in digestion.
Hemicellulose
Type of insoluble fiber found in plant cell walls.
Cellulose
Insoluble fiber that provides bulk to stools.
Lignins
Non-carbohydrate component of dietary fiber.
Resistant Starch
Starch that resists digestion in the small intestine.
Satiety
Feeling of fullness after eating.
Fecal Weight
Mass of waste material in the intestines.
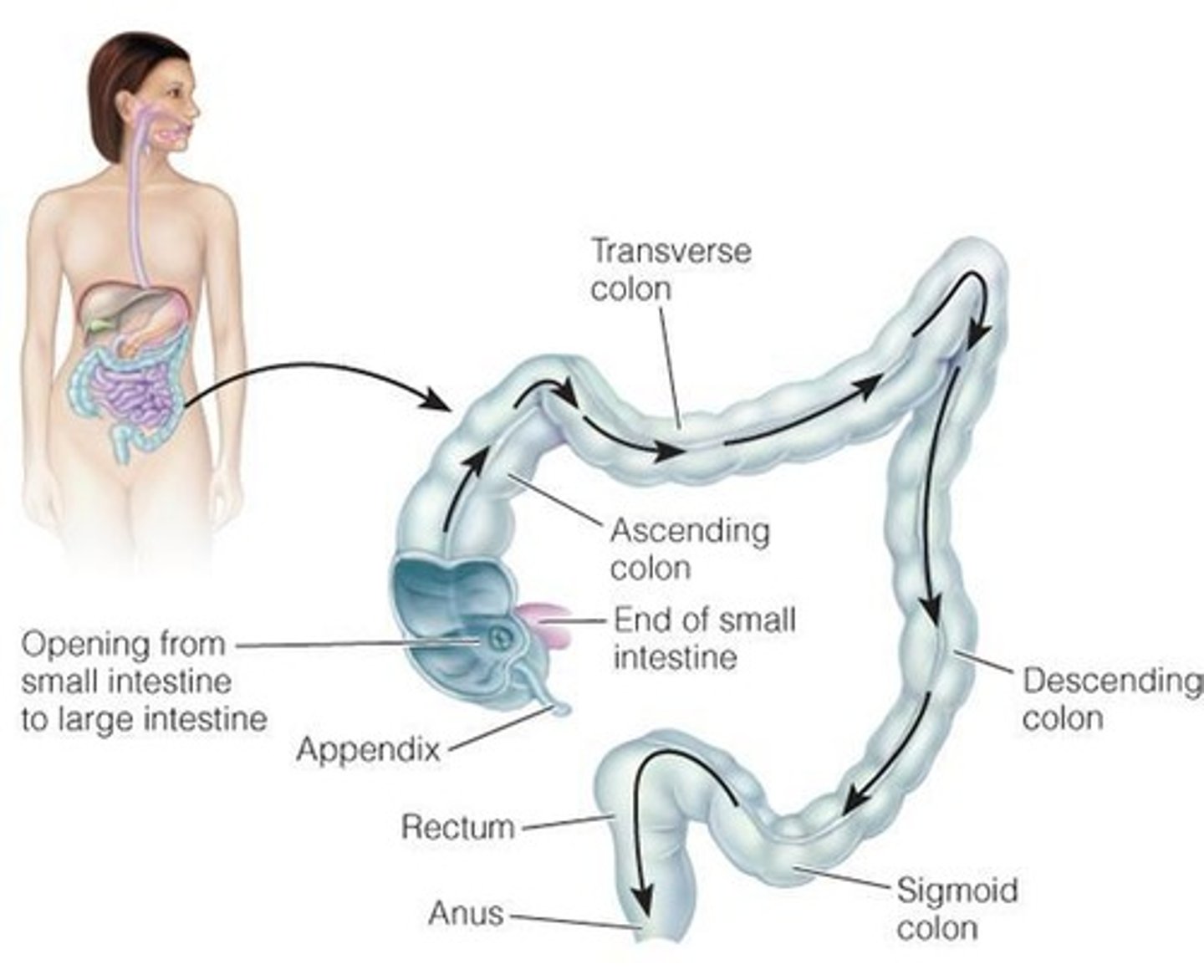
Transit Time
Time taken for food to pass through the GI tract.
Diverticulosis
Condition of having diverticula in the colon.
Hemorrhoids
Swollen veins in the lower rectum.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix.
Whole Grains
Grains that contain all parts of the seed.
Fiber Intake
Amount of dietary fiber consumed.
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars absorbed in the GI tract.
Lactase
Enzyme that breaks down lactose.