Nervous & Hormonal Coordination
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintaining a constant internal environment/Control, maintenance & regulation of the internal conditions & environment of an organism
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions
Autonomic
Don't require conscious thought
Stimulus
Change in internal/external environment
Effectors
Muscles or glands which bring about a response. They restore optimum levels in the body in response to internal stimuli, or react to an external stimuli to prevent harm
Negative feedback
The action taken by the body to return something to a normal/optimum level following a deviation from that level. It is how the body keeps conditions within it constant at the optimum level (homeostasis). It does the opposite what the stimulus causes.
Receptors
Specialised cells which detect stimuli
Coordination centre
Brain, spinal cord, receive & process information from receptors
Osmoregulation
water control
Thermoregulation
ability to control internal body temperature
High temperature/ low or high pH effect on enzymes
Enzymes denature; active site cannot bind with substrate, enzyme cannot catalyse reactions
If temperature too high
Thermoreceptors detect rise in temp.
Thermoreceptors send impulses to hypothalamus
Hypothalamus send impulses to effectors to lower body temp.
Hair lies flat; Hair erector muscles relax, prevents pockets of warm air being trapped in them
Vasodilation; arterioles dilate; increase amount of blood flow to capillaries near skin surface, heat lost by radiation
Sweating; sweat glands excrete sweat, evaporation of sweat lower body temperature
If temperature too low
Thermoreceptors detect drop in temperature
Thermoreceptors send impulses to hypothalamus
Hair erector muscles contract; traps pockets of warm air around skin, insulates body
Vasoconstrictions: reduced blood flow to skin surface, reduced radiation of heat from body
Body shivers; rapid muscle contractions require respiration which produces heat as a byproduct
Effect of low temperature on metabolism
If temperature too low, metabolic reactions become too slow
Nervous & Endocrine system
Two main systems that control the body
Autonomic systems (don't require conscious thought)
Nervous system
Consists of CNS & peripheral nervous system. The network of nerve cells which transmit nerve impulses between parts of the body. Information is sent through the nervous system along neurones as electrical impulses.
Endocrine system
The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream from glands throughout the body. Hormones travel in the blood stream to specific target organs, where they have an effect.
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical messenger that travels in the blood & acts on target cells. They are produced by endocrine glands. In plants, hormones are chemical messengers that affect growth (e.g. auxin)
Glands (7)
Ovary
Thyroid
Testes
Thymus
Pancreas
Adrenal
Pituitary
Hormones (6)
Adrenaline
Testosterone
Estrogen
Progesterone
Insulin
Glucagon
Sensitivity
The ability to detect & respond to changes in the environment
Differences between nervous & endocrine system

Adrenaline
Produced by adrenal gland (found on top of kidney)
Prepares body for fight or flight response
Increases heart rate & breathing rate
Testosterone
Produced in testes
Main sex hormone in males
Development of secondary sexual characteristics in males (hair growth, deeper voice)
Oestrogen
Produced in ovaries
Main sex hormones in females
Development of secondary sexual characteristics in females (breast development) & controls menstrual cycle
Progesterone
Produced in ovaries
Maintains pregnancy
Maintains uterus lining so fertilised egg can implant, & cushions fertilised egg to allow it to develop
Insulin
Produced by pancreas
Lowers blood glucose levels
Converts glucose in blood into glycogen for storage in muscles & liver
Glucagon
Produced by pancreas
Raises blood glucose levels
Converts glycogen into glucose to be released in the bloodstream
Nervous coordination (from stimulus to response)
1. Stimulus causes change in internal/external environment
2. Receptor cells detect the changes
3. Information is sent from receptors to the co-ordination centre
4. Co-ordination centre processes information & generates a response
5. Co-ordination centre sends instructions to effector
6. Effector carries out response
Sensory neurone
Neurone which carries impulses from receptor cells to the CNS
Motor neurone
Neurone which carries impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)
Relay neurone
Neurone which acts as a bridge for the electrical signals between neurones, connects sensory & motor neurones
Neurone
A nerve cell
Synapse
Gap between neurones
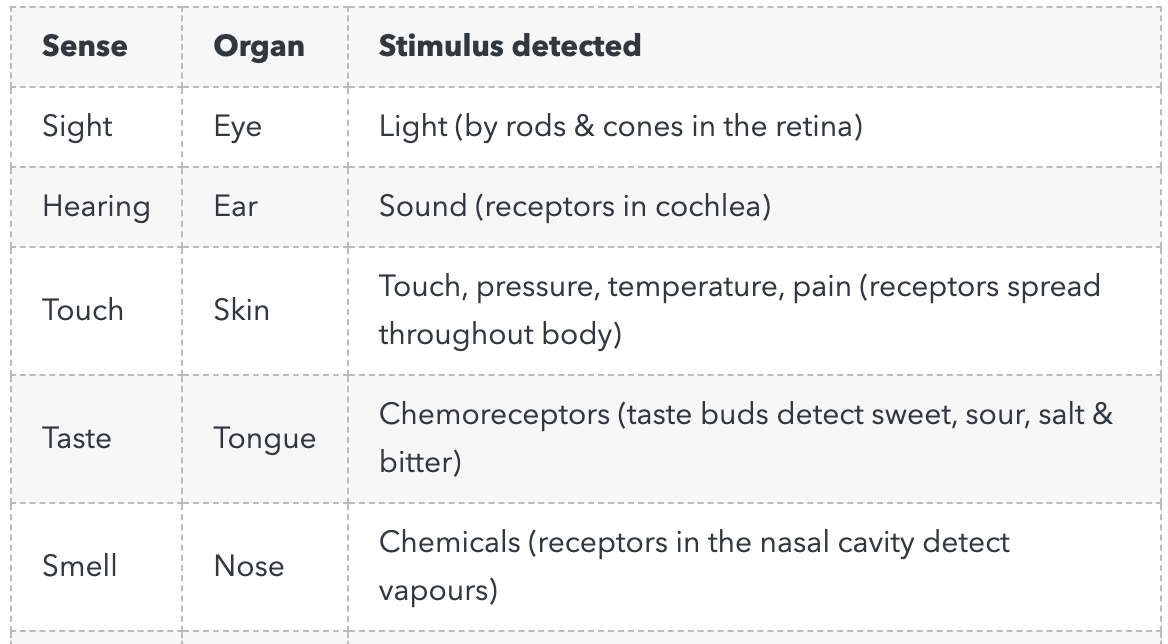
Sense, Organs, Stimulus Detected
Synaptic transmissions
the way information is carried between nerve cells
Vesicles
small bags with neurotransmitters inside in presynaptic neurone, fuse with membrane of postsynaptic neurone & release neurotransmitters
What happens to electrical impulses at synapses?
electrical impulses are converted into chemical messengers called neurotransmitters which diffuse across synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters after use
Neurotransmitters may be taken up by presynaptic neurone and reused, they can be broken down by enzymes within synaptic cleft or recycled in liver
Synaptic transmission process
1. An electrical impulse arrives at the end of one nerve cell (impulse reaches dendrites at end of axon)
2. Neurotransmitters are released into the gap between nerve cells (synaptic cleft)
3. Neurotransmitters diffuse from the first nerve cell (presynaptic neurone) across the gap & bind to receptors on the second nerve cell (postsynaptic neurone)
4. The binding of these neurotransmitters stimulates the second nerve cell (postsynaptic neurone) to generate an impulse.
Reflex Action
Reflex actions are responses that are automatic, unconscious, rapid, & designed to protect the body
Reflex Arc (general)
Stimuli detected by receptor cells
Stimulates sensory neurone to carry impulse to CNS
Relay neurone in CNS passes on response to motor neurone
Motor neurone stimulates an effector to carry out the response