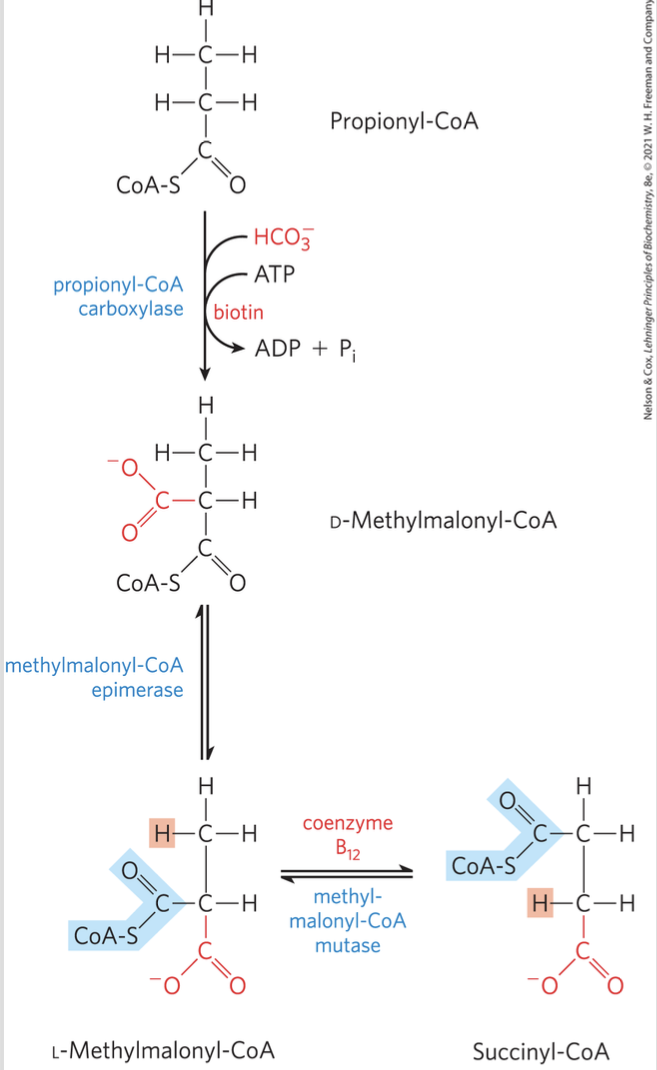
FIGURE 17-12 Oxidation of propionyl-CoA produced by oxidation of odd-number fatty acids
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
1
New cards
Step 1
First, propionyl-CoA carboxylase (with biotin as a cofactor) carboxylates it to D-methylmalonyl-CoA.
2
New cards
Step 2
This is epimerized to the L-isomer by methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase.
3
New cards
Step 3
methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, using coenzyme B12, rearranges it into succinyl-CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle. ATP provides energy for the initial carboxylation.
4
New cards
Image
5
New cards